Abstract
AIM
Rituximab has dramatically improved the survival of patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHL), but the dosing regimen currently used should be optimized. However, the concentration–effect relationship of rituximab has never been described by pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK–PD) modelling, precluding the simulation of new dosing regimens. The aim of this study was to develop a PK–PD model of rituximab in relapsed/resistant follicular NHL (FL).
METHODS
A model describing the relationship between rituximab concentrations and progression-free survival (PFS) was developed using data extracted from the pivotal study, which evaluated 151 relapsed/resistant FL patients. The influence of FCGR3A genetic polymorphism on the efficacy of rituximab was quantified using data from 87 relapsed/resistant FL patients. The predictive performance of the model was analysed using two independent datasets: a study that evaluated rituximab combined with chemotherapy [rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, adriamycin and prednisone (R-CHOP)] in 334 relapsed/resistant FL patients and a study that evaluated rituximab monotherapy in 47 asymptomatic FL patients with known FCGR3A genotype.
RESULTS
For R-CHOP, observed and model-predicted PFS (90% confidence interval) at 24 months were 0.50 and 0.48 (0.40, 0.56), respectively, for the observation arm, and 0.62 and 0.59 (0.50, 0.65), respectively, for the rituximab maintenance arm. For rituximab monotherapy, observed and predicted PFS at 24 months were 0.67 and 0.63, respectively, for FCGR3A-V/V patients, and 0.41 and 0.36 (0.25, 0.49), respectively, for FCGR3A-F carriers.
CONCLUSIONS
Our model provides a satisfactory prediction of PFS at 24 months. It can be used to simulate new dosing regimens of rituximab in populations of FL patients and should improve the design of future clinical trials.
Keywords: dose–response relationship, pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modelling, progression-free survival, rituximab
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ABOUT THIS SUBJECT
Serum concentrations of rituximab influence its clinical efficacy in follicular lymphoma (FL), but its concentration–effect relationship has not been described by pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK–PD) modelling.
The genetic polymorphism of FCGR3A influences rituximab efficacy and its in vitro concentration–effect relationship.
Increasing rituximab dose and/or number of infusions may lead to a better clinical response in FL.
WHAT THIS PAPER ADDS
This study is the first to describe the concentration–effect relationship of rituximab in populations of FL patients.
This PK–PD model relates progression-free survival with rituximab concentrations and takes into account the influence of FCGR3A polymorphism.
Clinical trials testing new dosing regimens of rituximab can be designed using this PK–PD model.
Introduction
Rituximab (MabThera®, Rituxan®) is a chimeric monoclonal antibody directed against CD20 antigen expressed by most B cells. It has dramatically improved the survival of patients affected by B-lymphoproliferative disorders and is currently approved for follicular lymphoma (FL), diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, as well as for certain autoimmune diseases (immune cytopenia and rheumatoid arthritis).
In early dose-escalation studies of rituximab as a single agent, no relationship was found between concentration and efficacy or concentration and toxicity [1, 2]. In chronic lymphocytic disease, a dose-escalation trial has tested rituximab doses ranging from 375 to 2250 mg m−2, the highest dose giving the highest response rate. However, these studies included a small number of patients and no convincing rituximab dose-ranging study has been published yet. In FL, the original dosing regimen of rituximab was 375 mg m−2 week−1 for 4 weeks, this dose being based mainly on practical and empirical considerations [3]. Later, several alternative dosing regimens were proposed in relapsed FL, with an increase in the number of rituximab infusions [4–6]. Since both rituximab and chemotherapy [notably cyclophosphamide, vincristine, adriamycin and prednisone (CHOP)] are effective, with complementary mechanisms of action and nonsynergistic toxicities [7], their association was tested. The first randomized trial comparing CHOP with or without rituximab (R-CHOP) in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma showed the superiority of R-CHOP in terms of duration of response. In FL, several randomized trials have shown that the combination of rituximab and chemotherapy dramatically increases both objective response and survival compared with chemotherapy alone [8, 9]. Furthermore, rituximab maintenance after induction with either rituximab alone [10–12] or rituximab combined with chemotherapy [13, 14] increases survival in relapsed FL. Overall, the available data suggest that an increase in rituximab dose and/or number of infusions may lead to better response rate and longer response duration, but they do not provide the quantitative information needed to optimize rituximab dose and/or dosing schedule.
As observed for other therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, a given mg m−2 dose of rituximab leads to a large range of rituximab serum concentrations in patients [2, 15, 16] and a large interindividual variability in clinical response is observed [17, 18]. This variability in therapeutic effect is indeed partly explained by rituximab pharmacokinetic variability [11, 15, 17, 19] because a low exposure to rituximab is associated with progressive disease [15, 17] and a shorter time to progression [19]. Several other factors have been suggested to influence rituximab efficacy, including tumour burden, level of CD20 expression [15, 17], and FCGR3A genetic polymorphism [20–22]. The FCGR3A gene encodes FcγRIIIa, a receptor of the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G (IgG) expressed by both macrophages and natural killer cells. This gene presents a biallelic polymorphism generating a FcγRIIIa-158 V (valine) or FcγRIIIa-158F (phenylalanine) allotype, the affinity for human IgG1 Fc portion being higher for the V allotype than for the F allotype [23, 24]. Cartron et al.[20] have shown that homozygous VV FL patients have a higher probability of response to rituximab than F carriers (Fx), a difference confirmed by others [21, 22]. In addition, Ghielmini et al.[21] showed that VV genotype is associated with a better event-free survival. However, the potential interest of adjusting rituximab dose according to FCGR3A genotype has never been investigated.
Clinical trial simulation may be used to explore the interest of such an individualized dose. This technique requires a relevant description of the concentration–effect relationship of rituximab using pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK–PD) modelling. No such model has been reported and the necessary information is sparse and scattered in the literature. The aim of the present study was to design a PK–PD model, based on data available in the literature and able to simulate the efficacy of rituximab in two common therapeutic settings: R-CHOP treatment, i.e. symptomatic, relapsed or resistant FL, where rituximab is combined with CHOP chemotherapy; and rituximab monotherapy, i.e. asymptomatic and FL with low tumour bulk, where rituximab is administered alone.
Methods
No published study contains all the data necessary to design a PK–PD model of rituximab effect in FL. Data from several studies were therefore combined after verification of their compatibility. However, because data were sparse and heterogeneous within and across studies, several assumptions had to be made to allow model building. Both model building and the validation process are summarized in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
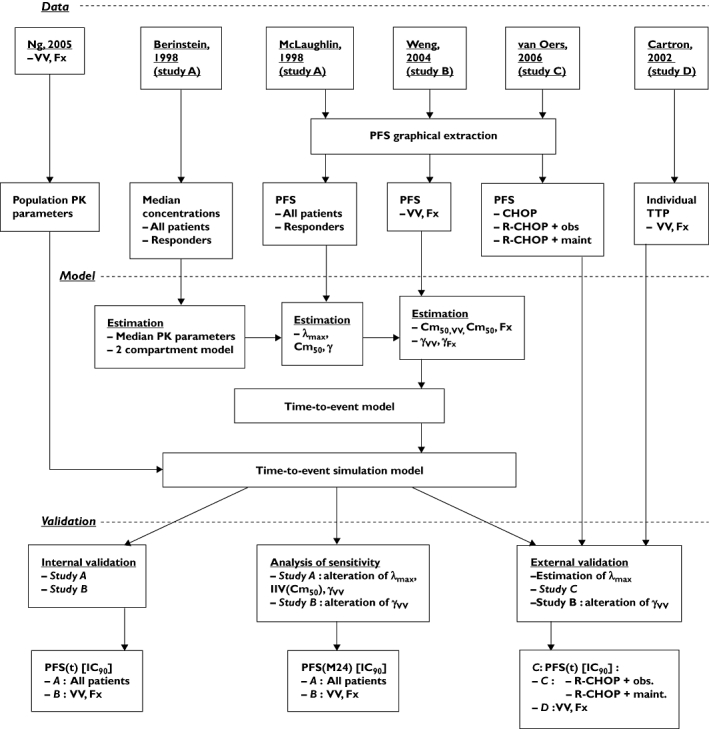
Flow chart of the study. The study consists of three steps: obtaining data, model building and validation steps. Abbreviations are explained within in the text
Data
Rituximab pharmacokinetics has been described in a few publications [16, 25, 26]. Because no biological marker of rituximab efficacy, measurable over time, has been described in FL, its pharmacodynamics can only be based on clinical end-points [8, 10, 12–14, 17, 20, 27, 28], i.e. objective response, progression-free survival (PFS), event-free survival (EFS) or overall survival (OS). EFS takes into account therapeutic failures and deaths of any origin in responders. PFS is an accurate end-point to describe long-term survival because, contrary to OS or EFS, it accounts for all assessable patients, and death related to disease or treatment [29]. In addition, PFS is the end-point most often reported in studies of rituximab in FL. Thus, we designed a PK–PD model linking rituximab serum concentrations with PFS.
The ideal source of data would report both rituximab pharmacokinetics and PFS data, for both R-CHOP and rituximab monotherapy conditions, as well as the influence of FCGR3A genotype on PFS. No such publication is available. Both pharmacokinetic and PFS data of the pivotal study were reported [15, 17] (study A, Table 1), but FCGR3A status was not studied. Thus, to quantify the influence of FCGR3A genotype, we looked for a study in which the population and the treatment by rituximab were similar to those of the pivotal study, and in which PFS was reported. These conditions were fulfilled by the report of Weng et al.[22] (study B, Table 1). To validate our model and to test its predictive performance in R-CHOP and rituximab monotherapy conditions, we used independent datasets. R-CHOP condition was studied by van Oers et al.[14] (study C). In this study, PFS is reported for patients treated by R-CHOP with or without rituximab maintenance (Table 1). Rituximab monotherapy condition was studied by Cartron et al.[20] (study D), where PFS is reported for both VV and Fx patients (Table 1).
Table 1.
Summary of the characteristics of studies used for the simulation
| Study | Clinical situation | Treatment | Dosing regimen of rituximab | Number of assessable subjects | Availability of FCGR3A status | Reported PFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pivotal, 1998 (study A) [15, 17] | Relapsed/resistant FL (80%), CLL (18%), other (2%) | Rituximab | 4 × 375 mg m−2 week−1 | 151 | No | PFS of overall population and responders |
| Weng et al. 2004 (Study B) [22] | Relapsed/resistant FL | Rituximab | 4 × 375 mg m−2 week−1 | 87 | Yes | PFS of VV, VF, FF and F-carrier subgroups |
| van Oers et al. 2006 (Study C) [14] | Relapsed/resistant FL | CHOP or R-CHOP | 8 × 375 mg m−2 every 21 days with or without 375 mg m−2 maintenance at least every 3 months | 465 | No | PFS of CHOP and R-CHOP with or without rituximab maintenance |
| Cartron et al. 2002 (Study D) [20] | First-line FL | Rituximab | 4 × 375 mg m−2 week−1 | 49 | Yes | PFS of VV and F-carrier patients subgroups |
CHOP, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, adriamycin, prednisone; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; F, 158-phenylalanine allele; FL, follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; PFS, progression-free survival; V, 158-valine allele.
To verify that our model was able to describe R-CHOP and rituximab monotherapy conditions, we simulated the results of the ‘R-CHOP without maintenance’ arm of study C and those of study D. To analyse the relevance of our quantification of the influence of FCGR3A genotype, we simulated the results in VV and Fx patients of study D. To analyse the ability of the model to describe rituximab maintenance, we simulated the results of the ‘R-CHOP with maintenance’ arm of study C. Because individual times to progression (TTP) of studies A, B and C were not reported, PFS data of these studies were extracted from the figures of the publications.
Data extraction
The charts displaying PFS were digitalized, and TTP and probabilities of progression were determined using Engauge digitizer (freeware under GNU license). Such an approach has been used previously by other authors [30]. Good precision was required especially for study A, which was used to build the model. PFS curves of other studies were used only for visual check of model accuracy. In study B, since PFS following R-CHOP with or without rituximab maintenance was reported only for initial responders, PFS was recalculated to take into account all treated patients, considering that initial nonresponders were in progression. Individual data of study D were used.
To determine the horizontal (probability), the thickest part of the curve was selected, which led to the maximum error. At this part the coordinates of each edge of the curve were determined, which gave lower and upper values for probability. The interval delimited by lower and upper values was divided by the total range of values (i.e. for probability, the total range is 0–1). This resulted in an error in percentage. The same procedure was applied to determine the error in event occurrence.
Pharmacokinetic model
In the report of the pivotal study [15, 17], median pharmacokinetic profiles of the whole population as well as those of responders and nonresponders are given. These concentrations were described using a two-compartment model with first-order transfer constants, a model previously used to describe rituximab pharmacokinetics [16, 25, 26]. For all patients and responders of study A, central and peripheral volumes of distribution (Vc and Vp, respectively), and systemic and distribution clearances (respectively CLc and CLd) were estimated. Using the pharmacokinetic parameters of rituximab obtained from study A, the pharmacokinetics was computed for overall and responder patients using Winnonlin Professional 4.1 (Pharsight Corp., Mountain View, CA, USA) [31]. The performance of the model was evaluated using standard errors of parameter estimates and by visual inspection of observed and predicted concentrations vs. time.
Time-to-event model
A parametric time-to-event (TTE) model was used to describe PFS. Exponential and Weibull hazard models were tested. Both led to a satisfactory description of PFS data, but the Weibull model led to incoherent results, e.g. a decrease of PFS with time. Therefore, the exponential model was used:
| (1) |
where λ (month−1) is the hazard function and t is time. For a given value of time to progression (TTPX), a hazard value λX can be calculated from (1) by λX = ln(2)/TTPX. Since the literature provides median data only, the model was designed to describe a hazard function. Our initial approach was to relate hazard to rituximab concentration. However, estimated pharmacodynamic parameters were unrealistic. Therefore, concentration was replaced by mean-time concentration, defined as follows:
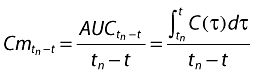 |
(2) |
where tn is the time of the nth rituximab infusion such as t > tn, Cmtn-t is the mean-time concentration between tn and t, and AUCtn-t is the area under the concentration vs. time curve between tn and t. Mean-time concentration increases and decreases with C, but Cm is higher than C when C decreases with time, i.e. except during infusions. Mean-time concentration was calculated over all the follow-up of the studies, using pharmacokinetic parameters estimated from study A. The hazard function was:
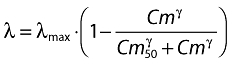 |
(3) |
where λmax is the maximum value of median hazard, i.e. that of patients not in progression in whom rituximab is not given or no more active, Cm50 is the Cm value which leads to 50% decrease of λmax and γ is a shape factor. We assumed that Cm50 and γ were the same for all FL, whereas the value of λmax varied with severity grade or concomitant treatment, and had therefore to be determined from the results of each study.
Parameter determination
Lambda max.Since λmax is expected to vary with severity grade or concomitant treatment, this parameter had to be determined in each therapeutic condition. Because in FL the therapeutic benefit of rituximab and chemotherapy are considered to be additive [7], λmax should be equal to the value of λ for patients treated by chemotherapy alone (λCT), hence λmax = λCT. In study C, median TTP for the ‘chemotherapy alone’ arm was 14 months and therefore λmax = λCT = 0.050 month−1 (Table 2). When rituximab is given alone, λmax had to be determined indirectly. If the effects of rituximab and chemotherapy are independent, the hazard ratio of chemotherapy alone vs. chemotherapy combined with rituximab (HRCT/RTX-CT) should be equal to the hazard ratio of no treatment vs. rituximab alone. Therefore, λmax = λRTX × HRCT/RTX-CT, where λRTX is the value of λmax when rituximab is given alone. The value of HRCT/RTX-CT was determined using the Marcus et al. study, in which the efficacy of cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone (CVP) was compared with that of CVP + rituximab in relapsed FL [28]. In this study, median TTP were 15 and 32 months for chemotherapy alone and for chemotherapy + rituximab, respectively. Corresponding hazards were therefore λCT = 0.046 month−1 and λRTX-CT = 0.022 month−1, giving a value of HRCT/RTX-CT equal to 0.046/0.022 = 2.1. In study A, median TTP of the overall population was 9.0 months, λRTX = 0.077 month−1 and λmax = 0.077 × 2.1 = 0.16 months−1 (Table 2). The value of λmax could not be calculated from study B, because results were not given of the overall group. However, because the patients of this study were relapsed/resistant FL, we selected the same value of λmax (0.16 month−1) as in study A. In study D, the analysis of individual data gave median TTP = 22 months, λRTX = 0.032 month−1 and λmax = 0.067 month−1 (Table 2).
Table 2.
Parameters of the relationship between rituximab mean-concentration and progression-free survival
| Value in study: | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Significance | Method | Pivotal [15, 17] (A) | Weng [22] (B) | van Oers [14] (C) | Cartron [20] (D) |
| λmax (month−1) | λ in absence of RTX or CT | Fixed for each study | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.050 | 0.067 |
| Cm50,O (mg l−1) | Cm50 in overall population | Estimated in A, reported in studies B, C and D | 35.1 (2.2)* | – | – | – |
| Cm50,R (mg l−1) | Cm50 in responders | 18.0 (0.87)* | – | – | – | |
| Cm50,VV (mg l−1) | Cm50 in VV patients | Calculated from study B (HRFx/VV) and Cm50,O | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| Cm50,Fx (mg l−1) | Cm50 in Fx patients | 78.9 | 78.9 | 78.9 | 78.9 | |
| γO | γ in overall population | Estimated in A, reported in studies B, C and D | 0.48 (0.052)* | – | – | – |
| γR | γ in responders | 1.5 (0.11)* | – | – | – | |
| γVV | γ in VV patients | Fixed | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| γFx | γ in Fx patients | 0.48 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
In study A, for estimated parameters, results are presented as: estimation (standard deviation). CT, chemotherapy; Cm50, mean-time concentrations leading to 50% of the maximum hazard; γ, shape factor; λ, hazard; RTX, rituximab.
Cm50 and γ
Once the value of λmax was determined, Cm50 and γ were estimated for the overall group (Cm50,O and γO, respectively) and for responders (Cm50,R and γR, respectively), using the data of study A (Table 2), with the help of Winnonlin professional 4.1. The performance of the model was evaluated using standard errors of parameter estimates and by visual inspection of observed and predicted concentrations vs. time.
Influence of FCGR3A genotype
Because insufficient information was available to estimate the value of γ for VV and Fx patients (γVV and γFx, respectively), these parameters were fixed as follows. In study A, estimated γR was thrice the value of γO, suggesting an increase of γ with response (Table 2). The proportion of VV and Fx patients in the pivotal study is unknown, but the proportion of VV patients should be higher in responders than in the whole group of patients. Therefore, γVV should be > γFx because FCGR3A polymorphism leads to differences in rituximab efficacy [20–22]. Because F carriers nevertheless respond to rituximab, the proportion of VV in responders of the pivotal study should be <100%, γVV should be >γR (i.e. γVV > 1.5, Table 2). This unknown (but >1.5) value was fixed to 2.0 (Table 2). Since around 85% of individuals are Fx [32], we considered that γFx .5 γO = 0.5 (Table 2).
Because FCGR3A is not a prognostic factor in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHL) [33], λmax should not be influenced by FCGR3A genotype. The influence of FCGR3A genotype on rituximab efficacy was quantified by different values of Cm50 and γ in VV (Cm50,VV and γVV, respectively) and Fx patients (Cm50,Fx and γFx, respectively).
The values of Cm50 for VV and Fx patients (Cm50,VV and Cm50,Fx, respectively) were calculated from the value of Cm50,O and the results of study B as follows. In this study, the PFS of VV and Fx subjects at 24 months (M24) were 0.45 and 0.14, respectively. The corresponding hazards were 0.082 month−1 and 0.033 month−1, Fx/VV hazard ratio (HRFx/VV) being therefore 2.5. In study A, the estimated hazard at M24 (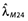 ) was 0.08. The M24 hazards for Fx and VV patients in this study were deduced from
) was 0.08. The M24 hazards for Fx and VV patients in this study were deduced from 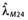 and HRFx/VV as follows:
and HRFx/VV as follows:
| (4) |
| (5) |
where λFx,M24 and λVV,M24 are the hazard values at M24 of Fx and VV patients, respectively, and 0.85 and 0.15 are proportions of Fx and VV subjects in the general population, respectively [32]. The values of Cm50,Fx and Cm50,VV were calculated by transferring γFc, γVV, λFx,M24 and λVV,M24 values in Equation 3.
Simulation process
The population of simulated patients was built using distributions of body surface area (BSA), sex and FCGR3A genotype as follows. BSA was assumed to be normally distributed with a mean of 1.7 m2 and a standard deviation of 0.2, values that characterize a standard population. The sex ratio, which is variable among trials of rituximab in FL, was fixed to 1. Genotype proportions of 15% and 85% were used for VV and Fx [32], respectively.
We used the population pharmacokinetic parameters reported by Ng et al.[16]: a two-compartment model with first-order constants and a log-normal distribution for central volume of distribution and systemic clearance (VC and CLC, respectively) with an influence of BSA and sex on both VC and CLC. A mixed (additive and proportional) distribution was used as residual error model.
PFS was described by a TTP model based on Equation 1 with a hazard function defined by Equation 3. The interindividual variability of Cm50 being unknown, its random effects (η) were assumed to be log-normally distributed with mean = 0 and standard deviation ωCm50 = 50%.
Simulations were carried out using Trial Simulator II 2.1 (Pharsight Corp.) [34].
Internal validation
Evaluation of the simulation process
The results of studies A and B (Table 1) were simulated. For a given trial with n assessable patients, n patients were generated and 500 complete trials were stochastically simulated. The TTE model was validated using visual predictive checks (VPC) [35, 36], which consisted in predicting the PFS profiles in 500 simulated replications of each study. The observed probabilities of progression were compared with the 90% confidence interval (CI), delimited by the 5–95% interpercentile range of simulated probabilities computed from the 500 simulated replicates of the dataset. The aim of these VPC was to evaluate the ability of the model to describe PFS in studies A and B.
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis was performed for parameters given fixed values, i.e. ωCm50, λmax and γVV. For each of them a low and a high value were chosen, and for each analysis 500 simulations of the n assessable patients were made. The lowest tested value of λmax was 0.077 month−1, which is the value of hazard corresponding to a PFS = 0.5 in study A; the highest tested value was 0.30 month−1, which is twice the λmax in study A. The lowest tested value of ωCm50 was 10% and the highest tested value was 150%. The lowest tested value of γVV was the estimated value, i.e. γVV = 0.48 (Table 2) and the highest tested value was 8.0. Sensitivity analysis for λmax and Cm50 was performed by simulating study A and sensitivity analysis for γVV was performed by simulating studies A and C. The observed PFS at 20 and 24 months in studies A and B, respectively, were compared with estimated 90% CI.
External validation
The predictive performance of the TTE model were tested using independent datasets, i.e. studies C and D, in which PFS was reported. The model was tested as described, by simulating these two studies C and D (Table 1).
Results
Precision of data extraction
The precision of PFS data extraction was accurate for study A (error <0.5%). The intervals were larger in studies B and C (0.5% < error < 1.5%). This is due to the fact that the graphs of these publications are small and with a longer duration of follow-up.
Model fitting results
The median pharmacokinetic data reported by Berinstein et al.[15] were satisfactorily described by the two-compartment model (Figure 2A). For the whole group of patients, estimated median parameters were Vc = 2.4 l, CLc = 0.0083 l h−1, Vp = 3.7 l and CLd = 0.022 l h−1, and for responders, estimated median parameters were Vc = 2.3 l, CLc = 0.0073 l h−1, Vp = 3.6 l and CLd = 0.023 l h−1.
Figure 2.
Results of model building for median rituximab concentrations (A) and progression-free survival (PFS) (B). For all patients, observations are displayed as closed and open circles for all patients and responders, respectively. Predictions are displayed as solid and dashed lines for all patients and responders, respectively. (C) Reduction of λmaxvs. mean-time concentration. VV and Fx patients are displayed as solid and dashed lines, respectively
The Weibull model was better than the exponential model in terms of Akaike's information criterion (respectively −171.2 vs.−151.7) and in terms of residual sum of squares (respectively 0.024 vs. 0.025). However, the estimated Weibull factor was <1. This may be interpreted as a decrease in risk with time, which is not relevant for FL. Therefore we rejected the Weibull model, not because this is the wrong model, but because it may be a non-identifiable model. The PFS of all patients and responders from study A were satisfactorily described by the TTE model (Figure 2B, Table 2). The values of Cm50,Fx and Cm50,VV were 7.8 and 78.9 mg l−1, respectively (Figure 2C, Table 2).
Internal validation of the model
Evaluation of the simulation process
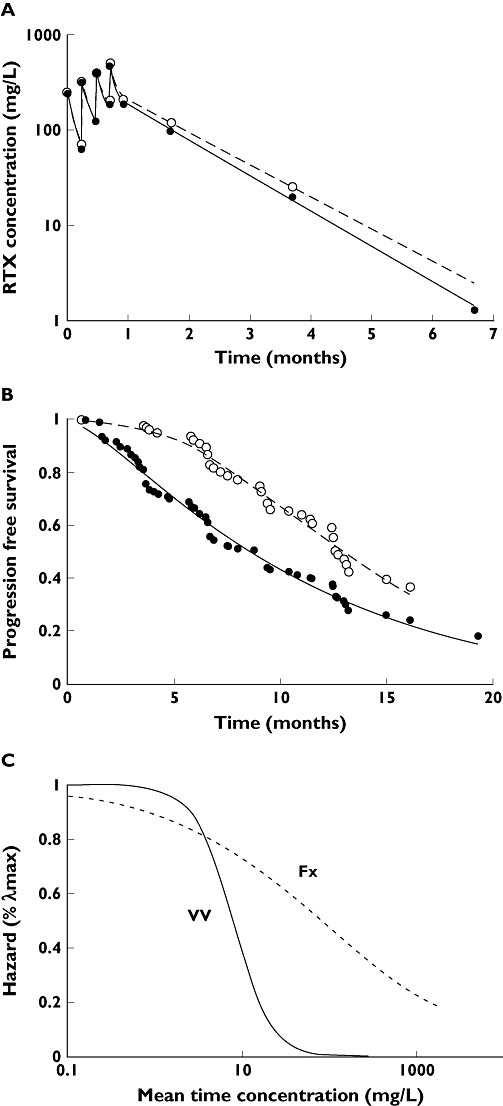
The simulation TTE model described PFS of study A satisfactorily (Figure 3A, Tables 2 and 3). In study B, the PFS was slightly overestimated, probably because the value of λmax could not be devised from the data of this study.
Figure 3.
Visual predictive checks of studies A, B, C and D. Visual predictive checks of study A (A), study B (B), study C which compared rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, adriamycin and prednisone (R-CHOP) without maintenance (C1) and R-CHOP with maintenance (C2), and study D (D). The solid lines are observed progression-free survival (PFS) and the dashed lines are 5th, 50th and 95th percentiles of predicted PFS. The 5th and 95th percentiles determine the 90% confidence interval (CI). In study B and D, the PFS of Fx and VV patients are displayed as black and grey lines, respectively. The value of PFS at 24 months (vertical dashed lines) is given in Table 3. In Figure 3D, the confidence interval for VV patients is too large to be represented
Table 3.
Comparison of observed and predicted TTP and PFS at 24 months
| Study | Condition | Observed median TTP (months)* | Predicted median TTP (months)† | Observed PFS at 24 months* | Predicted PFS at 24 months† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pivotal [15, 17] (A) | All patients | 9.0 | 8.6 (7.1, 10.1) | – | – |
| Weng [22] (B) | Fx | 5.6 | 7.6 (5.7, 10.4) | 0.17 | 0.081 (0.024, 0.17) |
| VV | 17.8 | 19.2 (11.7, 30.0) | 0.45 | 0.40 (0.20, 0.61) | |
| Van Oers [14] (C) | R-CHOP + observation | 21.6 | 21.1 (18.9, 27.7) | 0.50 | 0.48 (0.40, 0.56) |
| R-CHOP + maintenance | 58.3 | 31.7 (25.4, 39.1) | 0.61 | 0.59 (0.50, 0.65) | |
| Cartron [20] (D) | Fx | 16.4 | 17.1 (12.1, 23.3) | 0.41 | 0.36 (0.25, 0.49) |
| VV‡ | >37.5 (not reached) | 37.1 | 0.67 | 0.63 |
Data are presented as
median and
median (90% CI).
For VV patients, median TTP was not reached at the end of the follow-up.
Because of a small number of subjects, 90% CI was too large to be displayed. TTP, times to progression; PFS, progression-free survival; R-CHOP, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, adriamycin and prednisone.
Sensitivity analysis
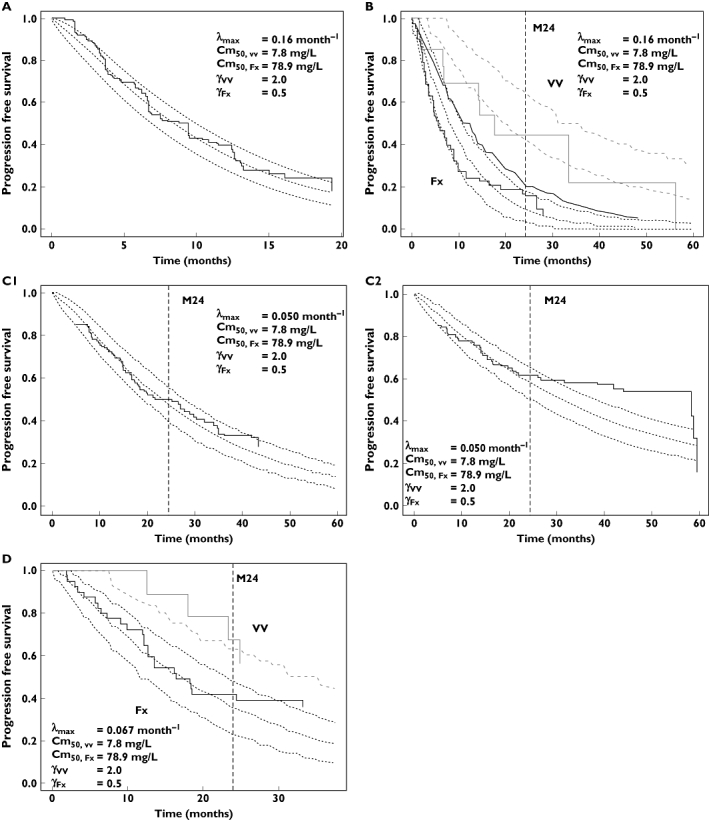
A high value of ωCm50 led to overestimation of PFS (Figure 4A). PFS was very sensitive to λmax value, but the result of this analysis suggests that the selected values of λmax are correct. PFS was not sensitive to γVV value. However, the result of the sensitivity analysis using study C suggests that the hypothesis of γVV > γR in study A, i.e. γVV = 2.0, was correct (Figure 4B).
Figure 4.
Sensitivity analysis for fixed parameters. Sensitivity analysis of fixed parameters ωCm50 (%), λmax (month−1) and γVV in study A (A) and B (B). The meaning of these parameters is described in the text. This analysis was made with data of study A for ωCm50 and λmax and with data of study A and B for γVV. For each parameter, 500 simulations were made for each value of parameters. The 5th, 50th and 95th percentiles of progression-free survival (PFS) predictions are displayed at 20 months for study A and at 24 months for study B. The observed value at this time is displayed as dashed lines
External validation
The performance of the model in predicting the PFS for R-CHOP and rituximab monotherapy was satisfactory up to 30 months (Figure 3C1,C2,D). After this point, the PFS was underpredicted by the model. This suggests that the model is valid up to 30 months. To be conservative, the model was considered to be valid up to 24 months.
Discussion
Recent attempts at improving the efficacy of rituximab [4–6, 10–14] emphasize the need for better knowledge of its concentration–effect relationship before testing new dosing regimens. The present work aimed at developing a PK–PD model of rituximab in FL. This model was built using median pharmacokinetic profiles from the pivotal study [15, 17], a population pharmacokinetic model [16], and graphically extracted data from several studies. The inaccuracy of data extraction was small (<1.5%) and for study A, which was used to design the model and to estimate the PD parameters, it was even smaller (<0.5%) for both TTP and PFS.
The pharmacokinetic model was built according to current knowledge on rituximab pharmacokinetics. To simulate rituximab concentrations, we used the parameters reported by Ng et al. in rheumatoid arthritis patients [16]. This is acceptable because the parameters that we have estimated using the results of the pivotal study are similar to typical values reported by Ng et al. (data not shown). Even if rituximab clearance was shown to be influenced by the tumour bulk in mice [37], this influence has never been established in patients [26, 38] and therefore could not be accounted for in our model. The use of mean-time concentration (Cm) instead of concentration in the PK–PD model gave satisfactory results. This is an empirical independent variable that allows one to take into account the persistence of the effect of anterior doses, and the reversibility of this effect with time. We also tested the addition of an effect-compartment model to predict the results of the pivotal study, but rate constant of the effect-compartment could not be estimated in the other studies.
Our model was validated in relapsed/resistant FL patients treated by rituximab alone and provided a satisfactory prediction of PFS. The influence of FCGR3A polymorphism was well accounted for by using the data of studies A and B. Some patients of these studies were affected by other B-cell malignancies (Table 1) but they constituted a small proportion of the patients (<20%).
The satisfactory description of studies C and D showed that our model is able to predict the PFS accurately up to 24 months, both for R-CHOP (symptomatic, relapsed or resistant FL treated by rituximab combined with chemotherapy), and for rituximab monotherapy as first line (i.e. asymptomatic FL with low tumour bulk). For studies C and D, PFS was underestimated after a certain time of follow-up. This may be due to the fact that the effect of maintenance treatment is probably stronger in initial responders than in the overall patients (Figure 1C2), and/or to the existence of long-lasting remissions, a phenomenon that our model is unable to account for (Figure 1C2,D).
Our PK–PD model was based on several assumptions, and therefore has limitations. The value of λmax was influenced by the severity of the disease and concomitant treatment (i.e. anticancer chemotherapy). This parameter was determined for each of the four studies, under the assumption of an independence of rituximab and chemotherapy effects. Despite the sensitivity of estimated PFS to the value of λmax, our results suggest that λmax values were relevant. Therefore, our model is applicable in situations similar to those of studies A, B, C (R-CHOP treatment) and D (rituximab monotherapy).
Mean value and distribution of Cm50 were supposed to be independent of pathophysiological condition and concomitant treatment. This hypothesis is based on the facts that all studied diseases have the same histological origin (i.e. follicular) and that studied patients had never been treated by rituximab before inclusion. In addition, ωCm50 was fixed to 50%. This value was hardly predictable, since interindividual variability in rituximab pharmacodynamics is high, the known factors of variability explaining only part of it. The sensitivity analysis confirmed that this value was relevant.
The quantitative influence of FCGR3A polymorphism was assessed indirectly, because it does not influence λmax[33]. Our approach was shown to be relevant in studies B and D, but no data were available to test its relevance during the association of rituximab and chemotherapy or in rituximab maintenance. However, simulation of the effect of rituximab maintenance in asymptomatic FL led to PFS profiles similar to EFS profiles displayed in Figure 2 of the publication of Ghielmini et al.[21]. The sensitivity analysis showed that the influence of γVV on PFS was limited.
Data were sparse, and heterogeneous within and between studies. First, relapsed and resistant NHL were taken together because no data on each type separately were available. Second, some factors could not be taken into account in the model, e.g. tumour bulk, stage of disease, previous anticancer treatments or other prognostic factors, such as the Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index [39]. However, even if these factors were shown to influence the rituximab dose–concentration effect relationship in early studies [15, 17], their real influence would remain controversial [40]. Therefore, our model should be applied only in situations for its building and its validation, i.e. in asymptomatic FL with low tumour bulk treated by rituximab alone, and in relapsed/resistant FL treated by R-CHOP. The variability in disease stages or tumour bulk should at least be partly described by the interindividual variability of Cm50.
Since no data were available to validate the model for higher doses than 375 mg m−2, the results of this model for higher doses should be considered with caution. Particularly, no maximum inhibition of λmax could be estimated. Our model implies that λ becomes null when Cm tends to infinity and therefore that it could lead to PFS overestimation.
Despite these limitations, our model is the first to describe the concentration–effect relationship of rituximab in FL. It allows testing dosage alterations while taking into account the FCGR3A genotype in populations of patients similar to those studied here.
Our model is the first to be developed and validated using data from the literature. Our approach (Figure 1) may be adapted for other drugs when no PK–PD model has been described, provided that published data are sufficient. Particularly, our model may be an interesting approach to describe the efficacy of other anticancer monoclonal antibodies or of other anticancer drugs, when pharmacokinetic and survival data are available.
Our model has shown its ability to simulate PFS of VV and Fx patients treated by rituximab up to 24 months in asymptomatic and symptomatic, relapsed or resistant FL. This may allow the simulation of different dosing regimens of rituximab, the comparison of their results, and the design of new clinical trials in populations of FL patients similar to those studied by Cartron and van Oers. As an example, Figure 5 shows the result of the simulation of different dosing regimens of rituximab in asymptomatic FL with low tumour bulk. Predicted PFS at 24 months is higher for larger doses of rituximab, when a maintenance treatment is given, and for VV patients. We are currently simulating the results of other rituximab dosing regimens in both FCGR3A genotypes as a basis for the design of clinical trials aimed at improving rituximab efficacy.
Figure 5.
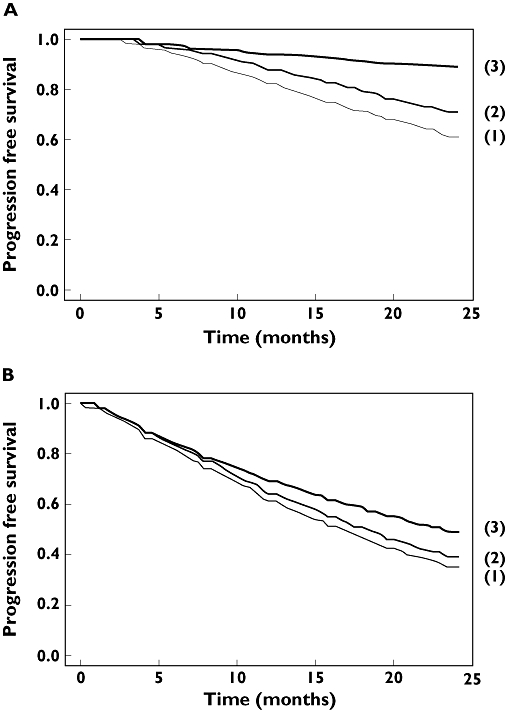
Simulated progression-free survival (PFS) up to 24 months for different dosing regimens and in two FCGR3A genotypes. Three dosing regimens were simulated in asymptomatic follicular lymphoma (FL) treated by rituximab alone: (1) 4 weekly 375 mg m−2 doses, (2) 4 weekly 750 mg m−2 doses and (3) 4 weekly 375 mg m−2 doses followed by a maintenance of 375 mg m−2 every 2 months, in FcγRIIIa-158 VV (a) and F carrier patients (b)
Acknowledgments
D.T. was funded by the association CANCEN, Tours, France. P.G. is funded by INSERM, Paris, France.
Competing interests
G.C. has been reimbursed by Roche, which markets rituximab elsewhere than the USA, Johnson & Johnson and Bayer, for attending conferences, and has been paid by Roche for consulting. G.P. received financial support from Roche, Schering Plough, Wyeth and LFB, for attending conferences, expert reports and advisory services. P.G., D.T., E.H. and M.T. have nothing to declare.
REFERENCES
- 1.Coiffier B, Haioun C, Ketterer N, Engert A, Tilly H, Ma D, Johnson P, Lister A, Feuring-Buske M, Radford JA, Capdeville R, Diehl V, Reyes F. Rituximab anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of patients with relapsing or refractory aggressive lymphoma: a multicenter phase II study. Blood. 1998;92:1927–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Maloney DG, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, Bodkin D, Schilder RJ, Neidhart JA, Janakiraman N, Foon KA, Liles TM, Dallaire BK, Wey K, Royston I, Davis T, Levy R. IDEC-C2B8 (Rituximab) anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in patients with relapsed low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood. 1997;90:2188–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cartron G, Blasco H, Paintaud G, Watier H, Le Guellec C. Pharmacokinetics of rituximab and its clinical use: thought for the best use? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2007;62:43–52. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2006.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aviles A, Leon MI, Diaz-Maqueo JC, Garcia EL, Cleto S, Neri N. Rituximab in the treatment of refractory follicular lymphoma – six doses are better than four. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2001;10:313–6. doi: 10.1089/15258160151135088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bremer K. Semi-extended, six weekly rituximab infusions in pre-treated advanced low-grade B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a phase II study. Anticancer Drugs. 2003;14:809–15. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200311000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Piro LD, White CA, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Janakiraman N, Saven A, Beck TM, Varns C, Shuey S, Czuczman M, Lynch JW, Kolitz JE, Jain V. Extended Rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) therapy for relapsed or refractory low-grade or follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 1999;10:655–61. doi: 10.1023/a:1008389119525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Czuczman MS, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, Saleh M, Gordon L, LoBuglio AF, Jonas C, Klippenstein D, Dallaire B, Varns C. Treatment of patients with low-grade B-cell lymphoma with the combination of chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and CHOP chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:268–76. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1999.17.1.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hiddemann W, Kneba M, Dreyling M, Schmitz N, Lengfelder E, Schmits R, Reiser M, Metzner B, Harder H, Hegewisch-Becker S, Fischer T, Kropff M, Reis HE, Freund M, Wormann B, Fuchs R, Planker M, Schimke J, Eimermacher H, Trumper L, Aldaoud A, Parwaresch R, Unterhalt M. Frontline therapy with rituximab added to the combination of cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP) significantly improves the outcome for patients with advanced-stage follicular lymphoma compared with therapy with CHOP alone: results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low-Grade Lymphoma Study Group. Blood. 2005;106:3725–32. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Marcus R, Imrie K, Solal-Celigny P, Catalano JV, Dmoszynska A, Raposo JC, Offner FC, Gomez-Codina J, Belch A, Cunningham D, Wassner-Fritsch E, Stein G. Phase III study of R-CVP compared with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone alone in patients with previously untreated advanced follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4537–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.5376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ghielmini M, Schmitz SF, Cogliatti SB, Pichert G, Hummerjohann J, Waltzer U, Fey MF, Betticher DC, Martinelli G, Peccatori F, Hess U, Zucca E, Stupp R, Kovacsovics T, Helg C, Lohri A, Bargetzi M, Vorobiof D, Cerny T. Prolonged treatment with rituximab in patients with follicular lymphoma significantly increases event-free survival and response duration compared with the standard weekly ×4 schedule. Blood. 2004;103:4416–23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-10-3411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gordan LN, Grow WB, Pusateri A, Douglas V, Mendenhall NP, Lynch JW. Phase II trial of individualized rituximab dosing for patients with CD20-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1096–102. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.12.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hainsworth JD, Litchy S, Shaffer DW, Lackey VL, Grimaldi M, Greco FA. Maximizing therapeutic benefit of rituximab: maintenance therapy versus re-treatment at progression in patients with indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphoma – a randomized phase II trial of the Minnie Pearl Cancer Research Network. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1088–95. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.12.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Forstpointner R, Unterhalt M, Dreyling M, Bock HP, Repp R, Wandt H, Pott C, Seymour JF, Metzner B, Hanel A, Lehmann T, Hartmann F, Einsele H, Hiddemann W. Maintenance therapy with rituximab leads to a significant prolongation of response duration after salvage therapy with a combination of rituximab, fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and mitoxantrone (R-FCM) in patients with recurring and refractory follicular and mantle cell lymphomas: results of a prospective randomized study of the German Low Grade Lymphoma Study Group (GLSG) Blood. 2006;108:4003–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-016725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.van Oers MH, Klasa R, Marcus RE, Wolf M, Kimby E, Gascoyne RD, Jack A, Van't Veer M, Vranovsky A, Holte H, van Glabbeke M, Teodorovic I, Rozewicz C, Hagenbeek A. Rituximab maintenance improves clinical outcome of relapsed/resistant follicular non-Hodgkin lymphoma in patients both with and without rituximab during induction: results of a prospective randomized phase 3 intergroup trial. Blood. 2006;108:3295–301. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-021113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Berinstein NL, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, Bence-Bruckler I, Maloney D, Czuczman M, Green D, Rosenberg J, McLaughlin P, Shen D. Association of serum Rituximab (IDEC-C2B8) concentration and anti-tumor response in the treatment of recurrent low-grade or follicular non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Oncol. 1998;9:995–1001. doi: 10.1023/A:1008416911099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ng CM, Bruno R, Combs D, Davies B. Population pharmacokinetics of rituximab (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) in rheumatoid arthritis patients during a phase II clinical trial. J Clin Pharmacol. 2005;45:792–801. doi: 10.1177/0091270005277075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.McLaughlin P, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Link BK, Levy R, Czuczman MS, Williams ME, Heyman MR, Bence-Bruckler I, White CA, Cabanillas F, Jain V, Ho AD, Lister J, Wey K, Shen D, Dallaire BK. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy for relapsed indolent lymphoma: half of patients respond to a four-dose treatment program. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2825–33. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1998.16.8.2825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Watier H. Variability factors in the clinical response to recombinant antibodies and IgG Fc-containing fusion proteins. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005;5(Suppl. 1):S29–36. doi: 10.1517/14712598.5.1.s29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Igarashi T, Kobayashi Y, Ogura M, Kinoshita T, Ohtsu T, Sasaki Y, Morishima Y, Murate T, Kasai M, Uike N, Taniwaki M, Kano Y, Ohnishi K, Matsuno Y, Nakamura S, Mori S, Ohashi Y, Tobinai K. Factors affecting toxicity, response and progression-free survival in relapsed patients with indolent B-cell lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma treated with rituximab: a Japanese phase II study. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:928–43. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdf155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cartron G, Dacheux L, Salles G, Solal-Celigny P, Bardos P, Colombat P, Watier H. Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood. 2002;99:754–8. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.3.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ghielmini M, Rufibach K, Salles G, Leoncini-Franscini L, Leger-Falandry C, Cogliatti S, Fey M, Martinelli G, Stahel R, Lohri A, Ketterer N, Wernli M, Cerny T, Schmitz SF. Single agent rituximab in patients with follicular or mantle cell lymphoma: clinical and biological factors that are predictive of response and event-free survival as well as the effect of rituximab on the immune system: a study of the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research (SAKK) Ann Oncol. 2005;16:1675–82. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdi320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Weng WK, Levy R. Two immunoglobulin G fragment C receptor polymorphisms independently predict response to rituximab in patients with follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3940–7. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dall'Ozzo S, Tartas S, Paintaud G, Cartron G, Colombat P, Bardos P, Watier H, Thibault G. Rituximab-dependent cytotoxicity by natural killer cells: influence of FCGR3A polymorphism on the concentration–effect relationship. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4664–9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Koene HR, Kleijer M, Algra J, Roos D, von dem Borne AE, de Haas M. Fc gammaRIIIa-158V/F polymorphism influences the binding of IgG by natural killer cell Fc gammaRIIIa, independently of the Fc gammaRIIIa-48L/R/H phenotype. Blood. 1997;90:1109–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Iacona I, Lazzarino M, Avanzini MA, Rupolo M, Arcaini L, Astori C, Lunghi F, Orlandi E, Morra E, Zagonel V, Regazzi MB. Rituximab IDEC-C2B8: validation of a sensitive enzyme-linked immunoassay applied to a clinical pharmacokinetic study. Ther Drug Monit. 2000;22:295–301. doi: 10.1097/00007691-200006000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Regazzi MB, Iacona I, Avanzini MA, Arcaini L, Merlini G, Perfetti V, Zaja F, Montagna M, Morra E, Lazzarino M. Pharmacokinetic behavior of rituximab: a study of different schedules of administration for heterogeneous clinical settings. Ther Drug Monit. 2005;27:785–92. doi: 10.1097/01.ftd.0000184162.60197.c1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Herold M, Haas A, Srock S, Neser S, Al-Ali KH, Neubauer A, Dolken G, Naumann R, Knauf W, Freund M, Rohrberg R, Hoffken K, Franke A, Ittel T, Kettner E, Haak U, Mey U, Klinkenstein C, Assmann M, von Grunhagen U. Rituximab added to first-line mitoxantrone, chlorambucil, and prednisolone chemotherapy followed by interferon maintenance prolongs survival in patients with advanced follicular lymphoma: an East German Study Group Hematology and Oncology Study. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:1986–92. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.4618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Marcus R, Imrie K, Belch A, Cunningham D, Flores E, Catalano J, Solal-Celigny P, Offner F, Walewski J, Raposo J, Jack A, Smith P. CVP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CVP as first-line treatment for advanced follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2005;105:1417–23. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-08-3175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cheson BD, Horning SJ, Coiffier B, Shipp MA, Fisher RI, Connors JM, Lister TA, Vose J, Grillo-Lopez A, Hagenbeek A, Cabanillas F, Klippensten D, Hiddemann W, Castellino R, Harris NL, Armitage JO, Carter W, Hoppe R, Canellos GP. Report of an international workshop to standardize response criteria for non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. NCI Sponsored International Working Group. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1244. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1999.17.4.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jusko WJ, Ko HC. Physiologic indirect response models characterize diverse types of pharmacodynamic effects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1994;56:406–19. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1994.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Winnonlin Professional 4.1 User's Guide. Mountain View, CA: Pharsight Corp; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lejeune J, Thibault G, Ternant D, Cartron G, Watier H, Ohresser M. Evidence for linkage disequilibrium between Fcgamma RIIIa-V158F and Fcgamma RIIa-H131R polymorphisms in white patients, and for an Fcgamma RIIIa-restricted influence on the response to therapeutic antibodies. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5489–91. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.19.4118. author reply 91–2. Epub 2008 October 27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pennell NM, Bhanji T, Zhang L, Seth A, Sawka CA, Berinstein NL. Lack of prognostic value of FCGR3A-V158F polymorphism in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Haematologica. 2008;93:1265–7. doi: 10.3324/haematol.12638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Trial Simulator 2.2 User's Guide. Mountain View, CA: Pharsight Corp; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brendel K, Dartois C, Comets E, Lemenuel-Diot A, Laveille C, Tranchand B, Girard P, Laffont CM, Mentre F. Are population pharmacokinetic and/or pharmacodynamic models adequately evaluated? A survey of the literature from 2002 to 2004. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2007;46:221–34. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200746030-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yano Y, Beal SL, Sheiner LB. Evaluating pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models using the posterior predictive check. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2001;28:171–92. doi: 10.1023/a:1011555016423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dayde D, Ternant D, Ohresser M, Lerondel S, Pesnel S, Watier H, Le Pape A, Bardos P, Paintaud G, Cartron G. Tumor burden influences exposure and response to rituximab: pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modelling using a syngeneic bioluminescent murine model expressing human CD20. Blood. 2008;24:24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-08-175125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mangel J, Buckstein R, Imrie K, Spaner D, Franssen E, Pavlin P, Boudreau A, Pennell N, Combs D, Berinstein NL. Pharmacokinetic study of patients with follicular or mantle cell lymphoma treated with rituximab as ‘in vivo purge’ and consolidative immunotherapy following autologous stem cell transplantation. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:758–65. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdg201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Solal-Celigny P, Roy P, Colombat P, White J, Armitage JO, Arranz-Saez R, Au WY, Bellei M, Brice P, Caballero D, Coiffier B, Conde-Garcia E, Doyen C, Federico M, Fisher RI, Garcia-Conde JF, Guglielmi C, Hagenbeek A, Haioun C, LeBlanc M, Lister AT, Lopez-Guillermo A, McLaughlin P, Milpied N, Morel P, Mounier N, Proctor SJ, Rohatiner A, Smith P, Soubeyran P, Tilly H, Vitolo U, Zinzani PL, Zucca E, Montserrat E. Follicular lymphoma international prognostic index. Blood. 2004;104:1258–65. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-12-4434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Czuczman MS, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Alkuzweny B, Weaver R, Larocca A, McLaughlin P. Prognostic factors for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients treated with chemotherapy may not predict outcome in patients treated with rituximab. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006;47:1830–40. doi: 10.1080/10428190600709523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


