Abstract
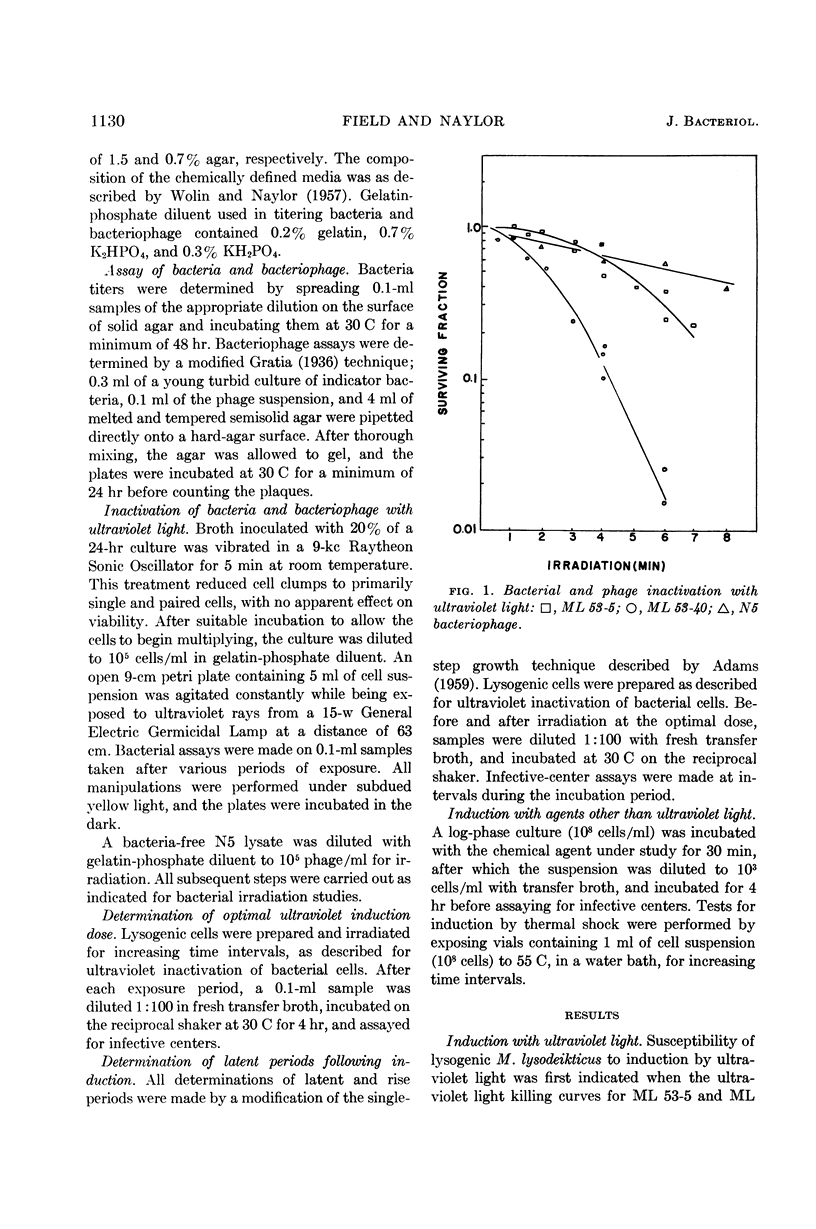
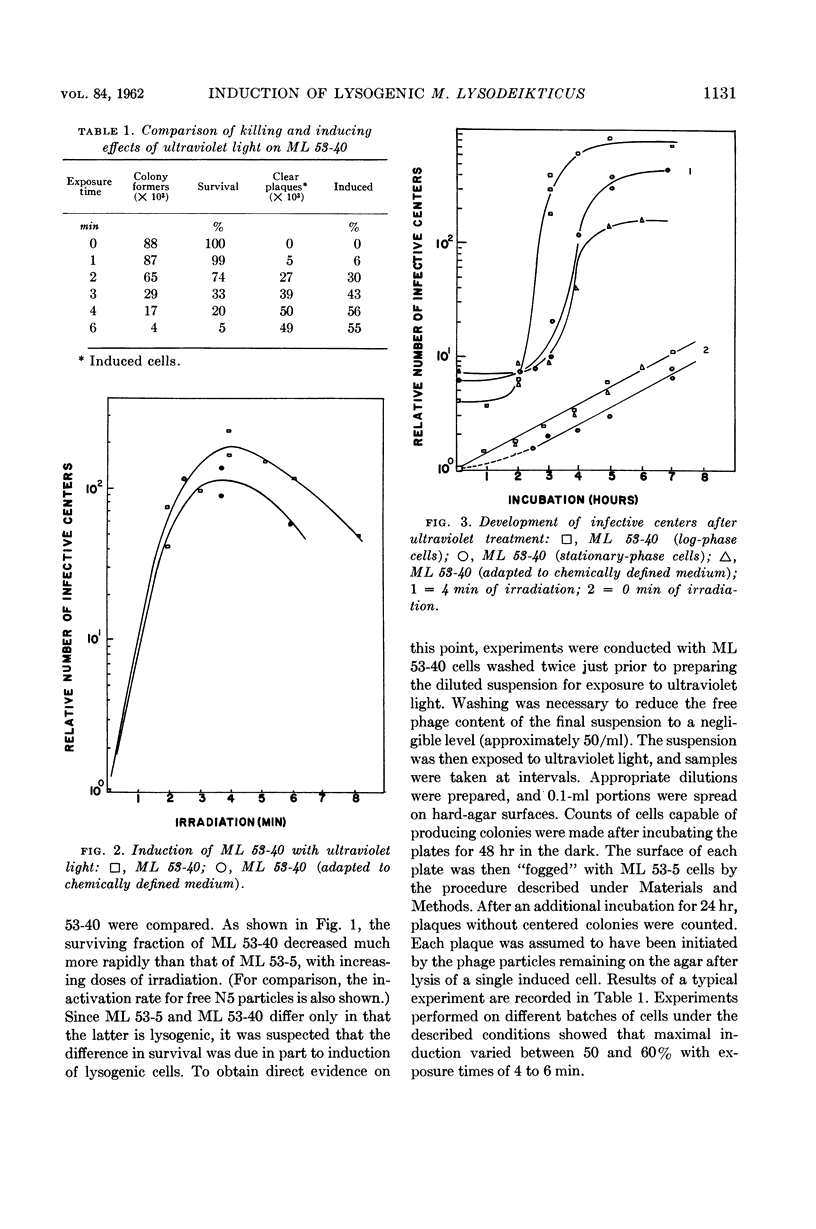
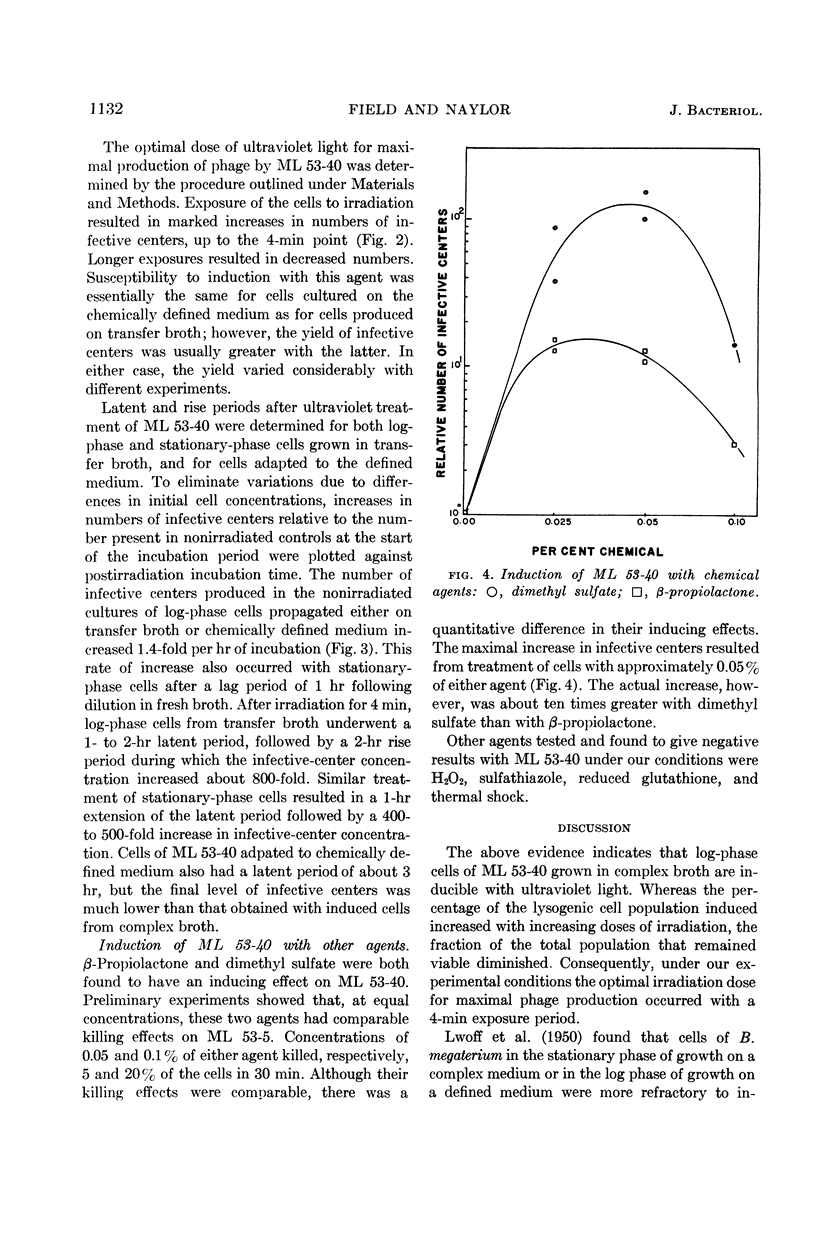
Field, A. K. (Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y.) and H. B. Naylor. Induction of lysogenic Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J. Bacteriol. 84:1129–1133. 1962.—Between 50 and 60% of log-phase cells of Micrococcus lysodeikticus strain ML 53-40, lysogenic for N5 bacteriophage, were induced by an optimal dose of ultraviolet light. Induction of dilute cell suspensions caused a subsequent 200- to 800-fold increase in infective-center concentration. Cells in the stationary growth phase and cells adapted to a chemically defined medium were also induced by ultraviolet irradiation. Dimethyl sulfate induced the lysogenic culture to about the same extent as did ultraviolet light, whereas β-propiolactone was less effective.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GOTS J. S., BIRD T. J., MUDD S. L-Az-aserine as an inducing agent for the development of phage in the lysogenic Escherichia coli, K-12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Jul;17(3):449–450. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROMAN N. B., EATON M., BOOHER Z. K. Studies of mono- and polylysogenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.320-325.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL-ASHESHOV E., ASHESHOV I. N. The induction of the lytic cycle in lysogenic bacteria by phagolessin A 58. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):174–187. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F. Effets de la carence gluciaique sur l'induction d'un Pseudomonas pyocyanea lysogène. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Apr;82(4):433–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., WOLLMAN E. L. Induction of phage development in lysogenic bacteria. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1953;18:101–121. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1953.018.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LWOFF A., SIMINOVITCH L., KJELDGAARD N. Induction de la production de bacteriophages chez une bactérie lysogène. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1950 Dec;79(6):815–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUJI N., SEKIGUCHI M., IIJIMA T., TAKAGI Y. Induction of phage formation in the lysogenic Escherichia coli K-12 by mitomycin C. Nature. 1959 Oct 3;184(Suppl 14):1079–1080. doi: 10.1038/1841079b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. H., SRB A. M. Induction of mutations with beta-propiolactone. Science. 1951 Nov 9;114(2967):490–492. doi: 10.1126/science.114.2967.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE J. J., DELBRUCK M. Mutual exclusion between an infecting phage and a carried phage. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):301–318. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.301-318.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN H. L., NAYLOR H. B. Basic nutritional requirements of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):163–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.163-167.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



