Abstract
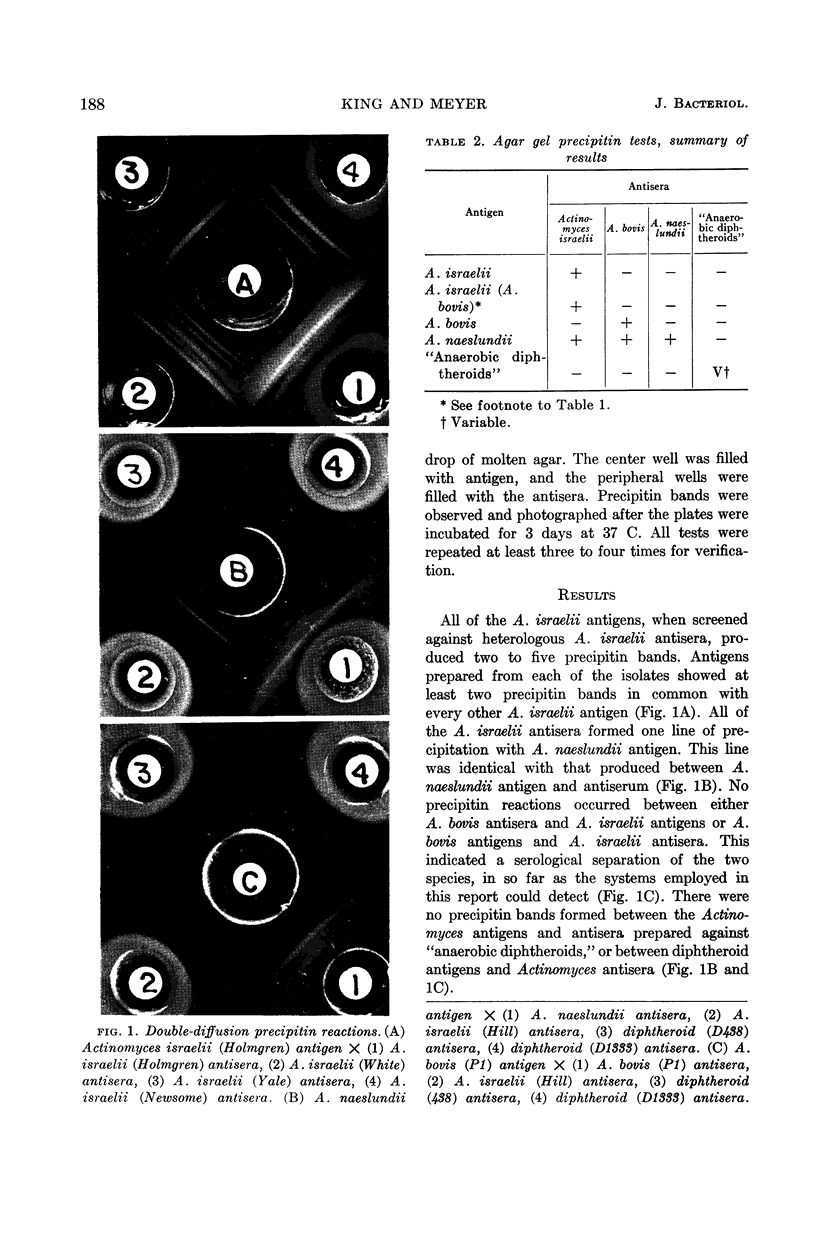
King, Sylvia (Hektoen Institute, Chicago, Ill.) and Esther Meyer. Gel diffusion technique in antigen-antibody reactions of Actinomyces species and “anaerobic diphtheroids.” J. Bacteriol. 85:186–190. 1963.—The Ouchterlony agar gel diffusion test was used to establish antigenic patterns produced by Actinomyces israelii, A. bovis, and A. naeslundii, as compared with those of “anaerobic diphtheroids.” The organisms studied included Actinomyces species isolated from cases of human and bovine actinomycosis, and from the normal oral cavity of human volunteers. The “anaerobic diphtheroids” were obtained from a variety of clinical conditions. A. israelii was serologically distinct from A. bovis, and A. naeslundii shared a minor component with the other two Actinomyces species. There were no cross reactions between the “anaerobic diphtheroids” and any of the Actinomyces species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CUMMINS C. S. Chemical composition and antigenic structure of cell walls of Corynebacterium, Mycobacterium, Nocardia, Actinomyces and Arthrobacter. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:35–50. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. Studies on the cell-wall composition and taxonomy of Actinomycetales and related groups. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Feb;18(1):173–189. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. The chemical composition of the cell wall in some gram-positive bacteria and its possible value as a taxonomic character. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):583–600. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINER D. C. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis using precipitin reactions in agargel. Pediatrics. 1958 Oct;22(4 Pt 1):616–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWELL A., Jr, MURPHY W. C., 3rd, PAUL F., STEPHAN R. M. Oral strains of Actinomyces. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):82–95. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.82-95.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KADEN R. Präzipitation von Sporotrichon-Antiserum im Agarmedium. Z Haut Geschlechtskr. 1956 Aug 15;21(4):87–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING S., MEYER E. Metabolic and serologic differentiation of Actinomyces bovis and anaerobic diphtheroids. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):234–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.234-238.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KROEGER A. V., SIBAL L. R. Biochemical and serological reactions of an oral filamentous organism. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:581–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.581-585.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KWAPINSKI J. B. Researches on the antigenic structure of Actinomycetales. IV. Chemical and antigenic structure of Actinomyces israeli. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1960;23:158–172. doi: 10.1159/000160928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KWAPINSKI J. B., SNYDER M. L. Antigenic structure and serological relationships of Mycobacterium, Actinomyces, Streptococcus, and Diplococcus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Nov;82:632–639. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.5.632-639.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUBERT J. H., LYNCH H. J., Jr, AJELLO L. Evaluation of the agar-plate precipitin test for histoplasmosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:845–849. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEELIGER H. A serologic study of Hyphomycetes causing mycetoma in man. J Invest Dermatol. 1956 Jan;26(1):81–93. doi: 10.1038/jid.1956.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLACK J. M., SPEARS R. G., SNODGRASS W. G., KUCHLER R. J. Studies with microaerophilic actinomycetes. II. Serological groups as determined by the reciprocal agglutinin adsorption technique. J Bacteriol. 1955 Oct;70(4):400–404. doi: 10.1128/jb.70.4.400-404.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTER L. S. Evaluation of criteria used in the identification of actinomyces bovis with particular reference to the catalase reaction. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1956 Dec 1;7(3-4):220–228. doi: 10.1007/BF02249072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. M., Winger A., Moore D. W. SEROLOGICAL GROUPING OF ACTINOMYCES BY MEANS OF FLUORESCENT ANTIBODIES. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82(1):54–65. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.54-65.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON L., LOVESTEDT S. A. An Actinomyces-like organism obtained from the human mouth. Proc Staff Meet Mayo Clin. 1951 May 9;26(10):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]