Abstract
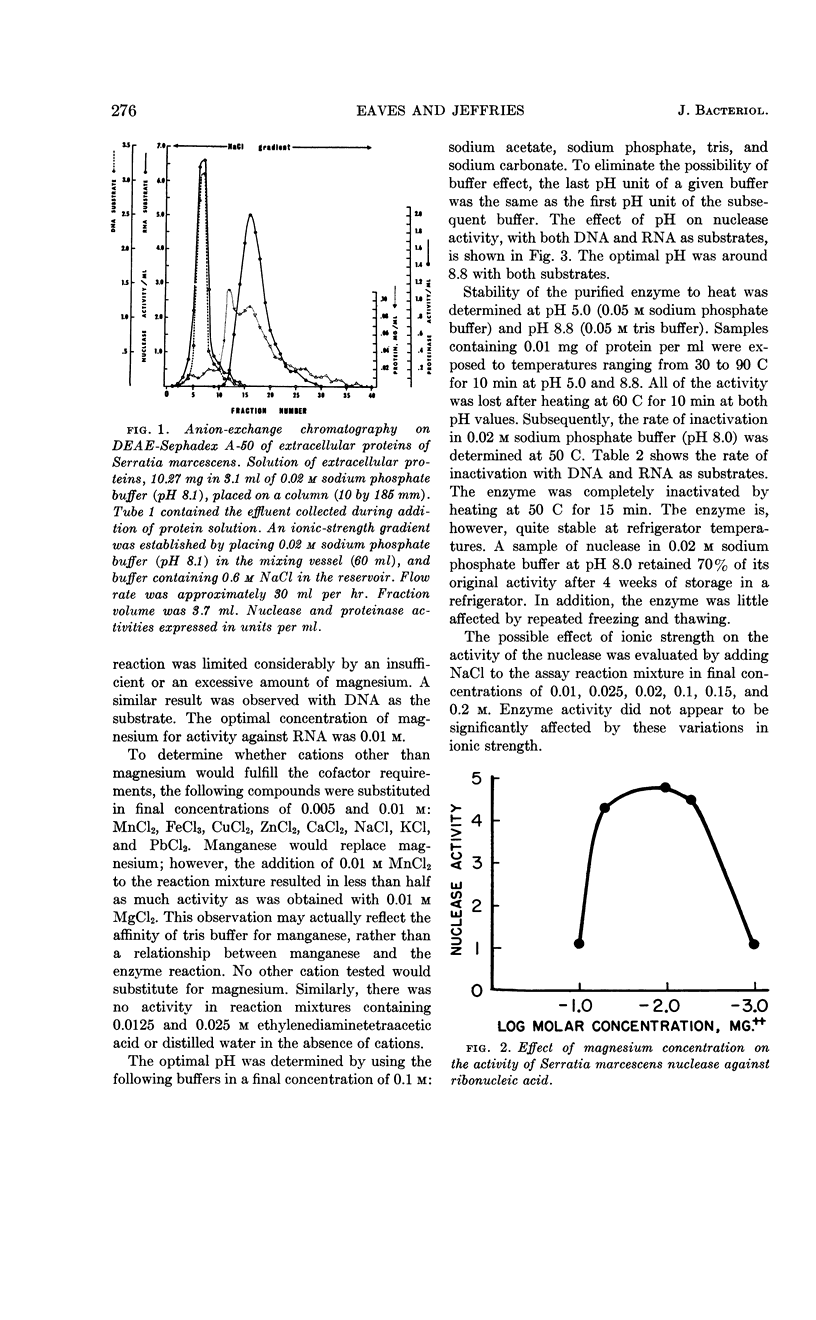
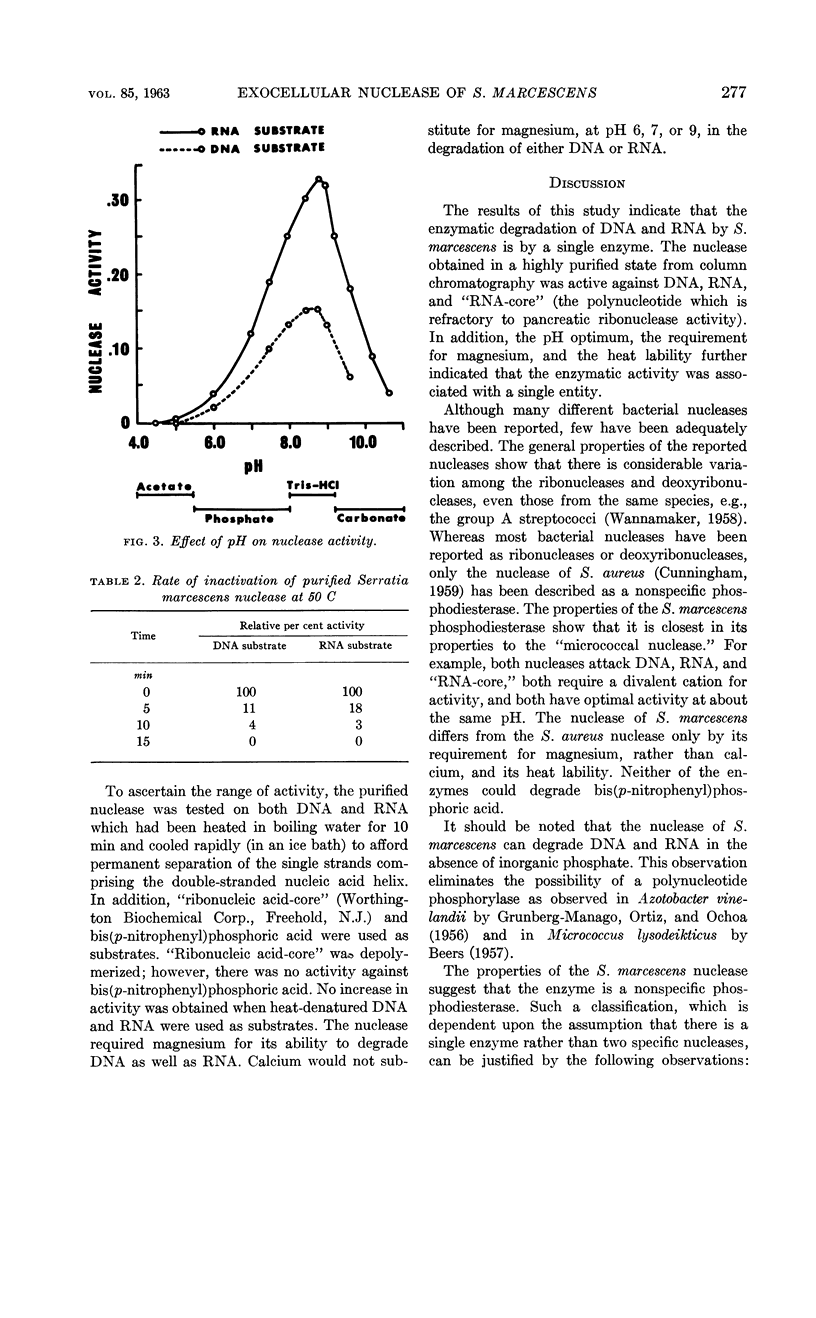
Eaves, George N. (Wayne State University College of Medicine, Detroit, Mich.) and Charles D. Jeffries. Isolation and properties of an exocellular nuclease of Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol. 85:273–278. 1963.—The exocellular nuclease of Serratia marcescens, isolated by anion-exchange chromatography on diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex, depolymerized deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid, and the polynucleotide which is refractory to pancreatic ribonuclease activity. The enzyme was tentatively classified as a nonspecific phosphodiesterase. Magnesium was essential for activity, which was optimal at pH 8.8. The purified enzyme was completely inactivated by heating at 50 C for 15 min.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANFINSEN C. B., REDFIELD R. R., CHOATE W. L., PAGE J., CARROLL W. R. Studies on the gross structure, cross-linkages, and terminal sequences in ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):201–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEERS R. F., Jr Polynucleotides; partial purification and properties of a polynucleotide phosphorylase from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1957 Aug;66(4):686–693. doi: 10.1042/bj0660686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUNNINGHAM L. Micrococcal nuclease and some products of its action. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 4;81:788–791. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb49360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNBERG-MANAGO M., ORTIZ P. J., OCHOA S. Enzymic synthesis of polynucleotides. I. Polynucleotide phosphorylase of azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Apr;20(1):269–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90286-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFRIES C. D., HOLTMAN D. F., GUSE D. G. Rapid method for determining the activity of microorganisms on nucleic acids. J Bacteriol. 1957 Apr;73(4):590–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.4.590-591.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY M. The lysis of group A hemolytic streptococci by extracellular enzymes of Streptomyces albus. I. Production and fractionation of the lytic enzymes. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):555–568. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHIMURA S. Extracellular ribonucleases from Bacillus subtilis. I. Crystallization and specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 4;45:15–27. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSTROWSKI W., WALCZAK Z. Nucleolytic enzymes of Thiobacillus thioparus. Purification and properties of ribonuclease. Acta Biochim Pol. 1961;8:345–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WANNAMAKER L. W. The differentiation of three distinct desoxyrlbonucleases of group A Streptococci. J Exp Med. 1958 Jun 1;107(6):797–812. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



