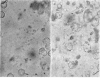
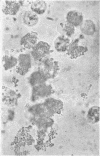
Abstract
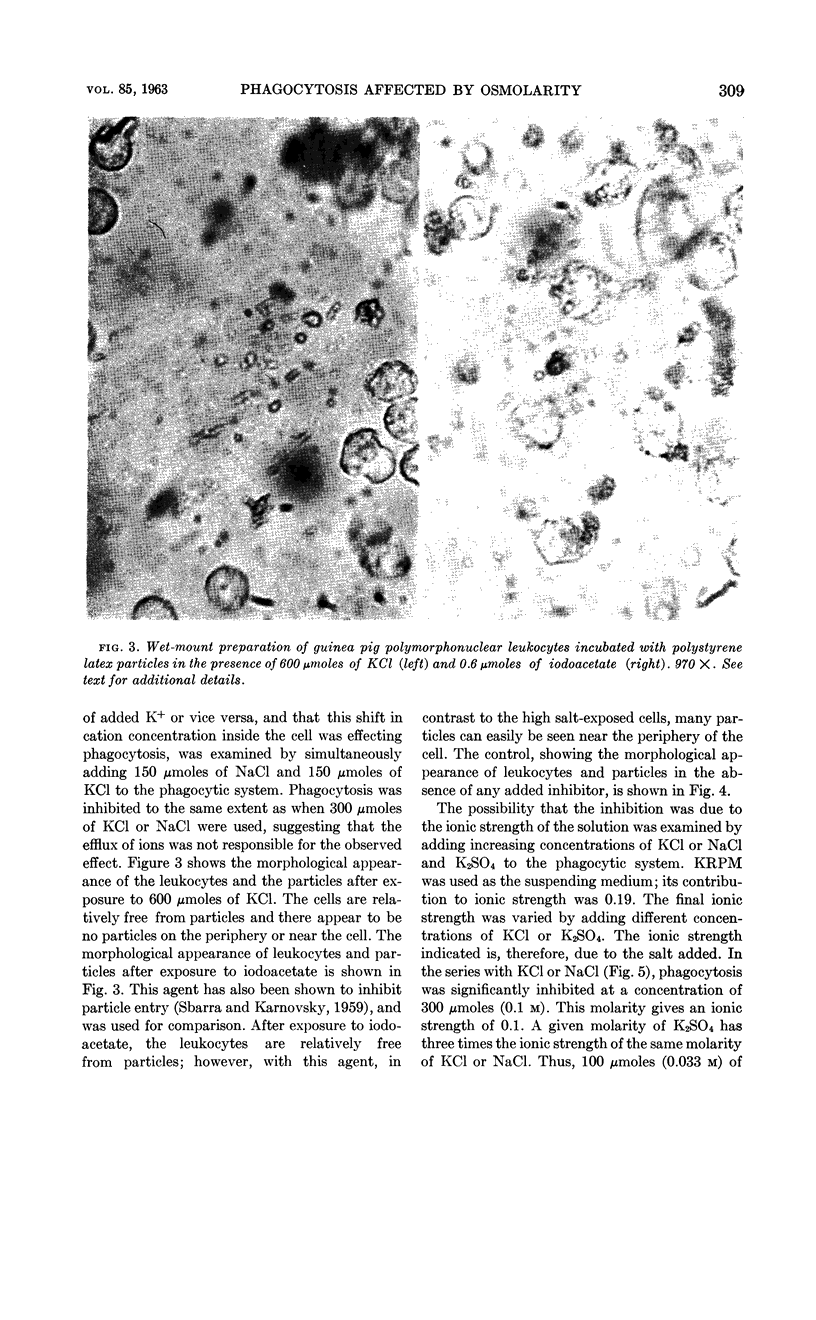
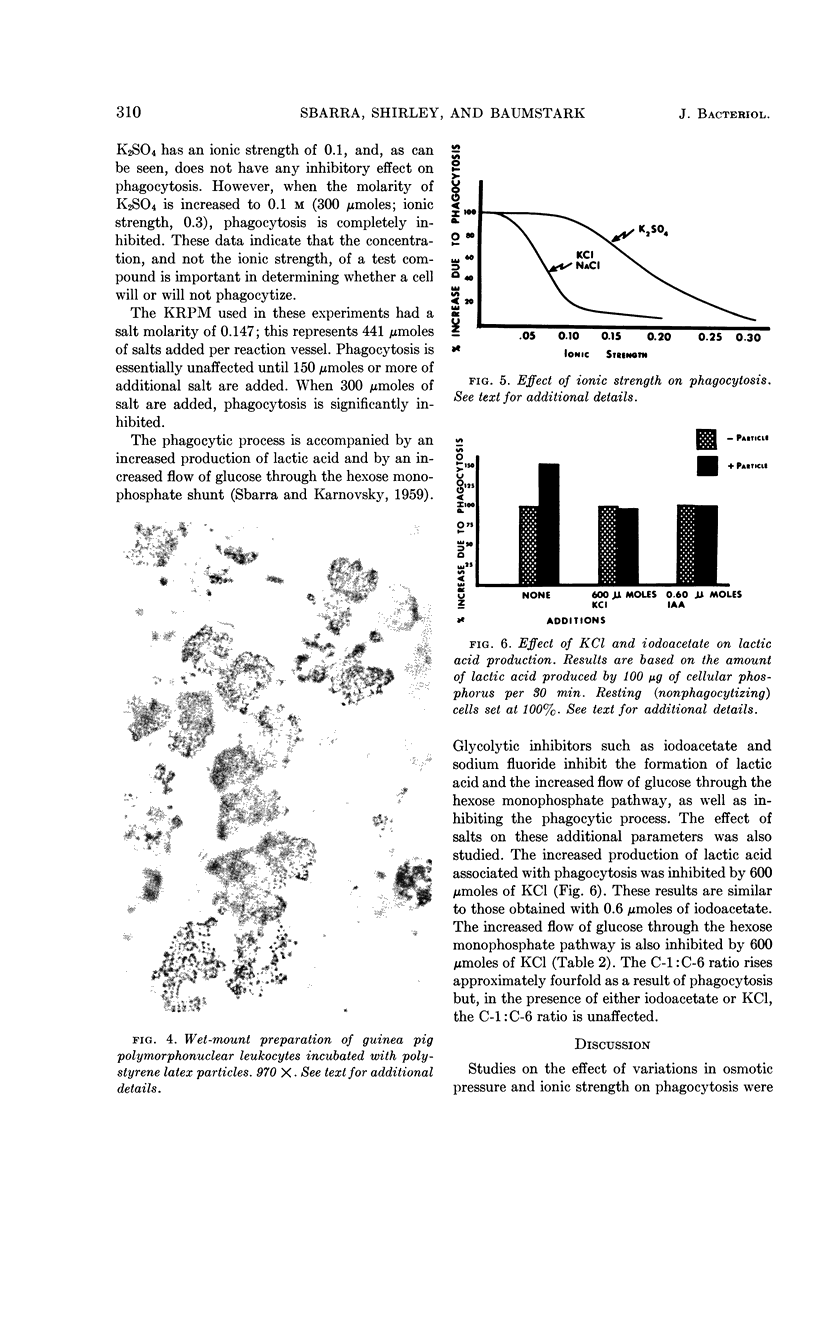
Sbarra, Anthony J. (St. Margaret's Hospital, Boston, Mass.), William Shirley, and John S. Baumstark. Effect of osmolarity on phagocytosis. J. Bacteriol. 85:306–313. 1963.—The effect of a number of different compounds on phagocytosis was studied. Phagocytosis was monitored by morphological and biochemical means. It was found that the addition of compounds such as KCl, NaCl, sodium or potassium malonate, and K2SO4 to the phagocytic system inhibited phagocytosis. The increased salt concentration specifically inhibited the respiratory activity associated with phagocytosis. The endogenous respiration of the leukocytes was unaffected. Glycolysis and the increased flow of glucose through the hexose monophosphate pathway were also inhibited by the elevated concentration of salts. In addition, cells exposed to high salt concentrations appeared to be reduced in size as compared with normal cells. The inhibition can be reversed by lowering the salt concentration. It was suggested that the increased osmotic pressure of the system was responsible for the inhibition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHN Z. A., MORSE S. I. Functional and metabolic properties of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. I. Observations on the requirements and consequences of particle ingestion. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:667–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELSBACH P., SCHWARTZ I. L. Studies on the sodium and potassium transport in rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1959 May 20;42(5):883–898. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King E. J. The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1932;26(2):292–297. doi: 10.1042/bj0260292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKINNEY G. R., MARTIN S. P., RUNDLES R. W., GREEN R. Respiratory and glycolytic activities of human leukocytes in vitro. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Jan;5(7):335–340. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.5.7.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., SHIRLEY W., BARDAWIL W. A. 'Piggy-back' phagocytosis. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:255–256. doi: 10.1038/194255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]