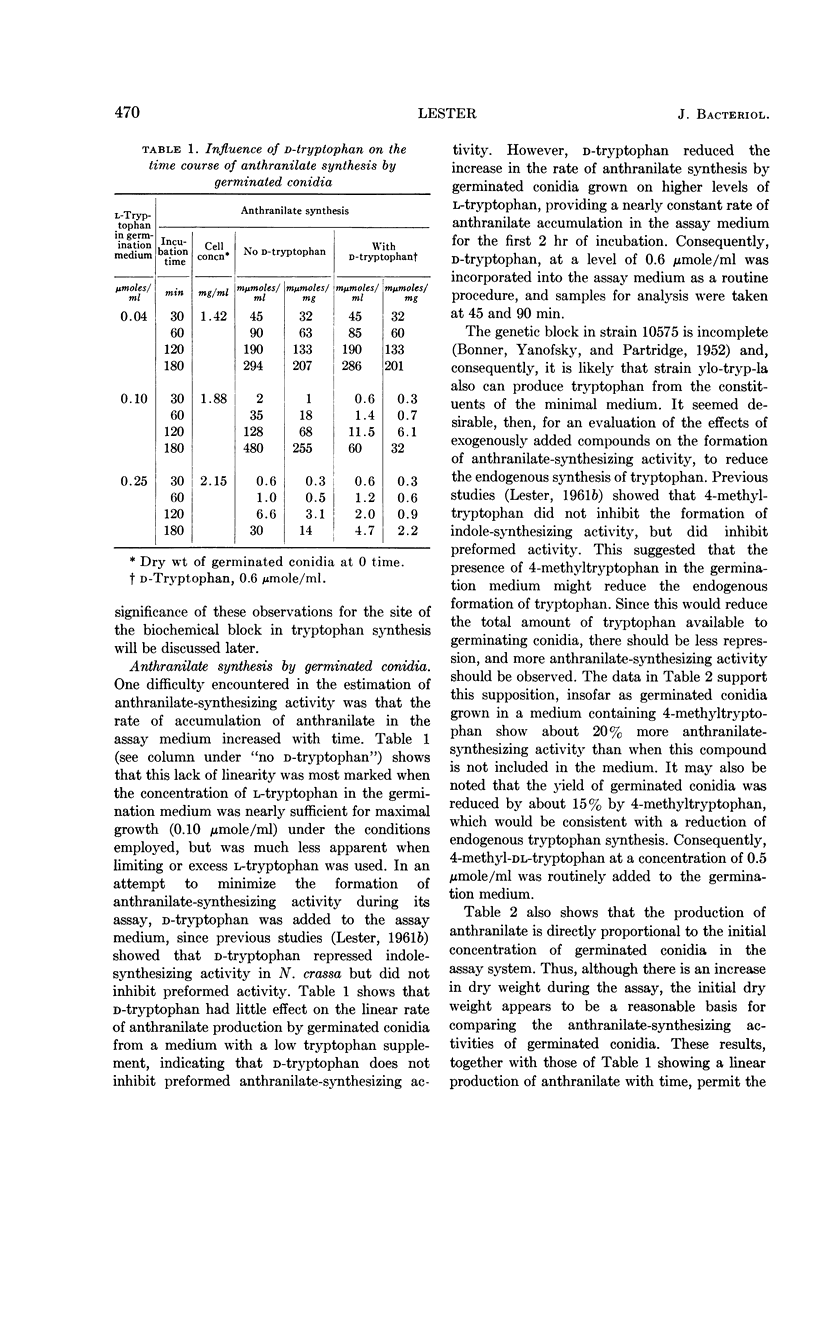
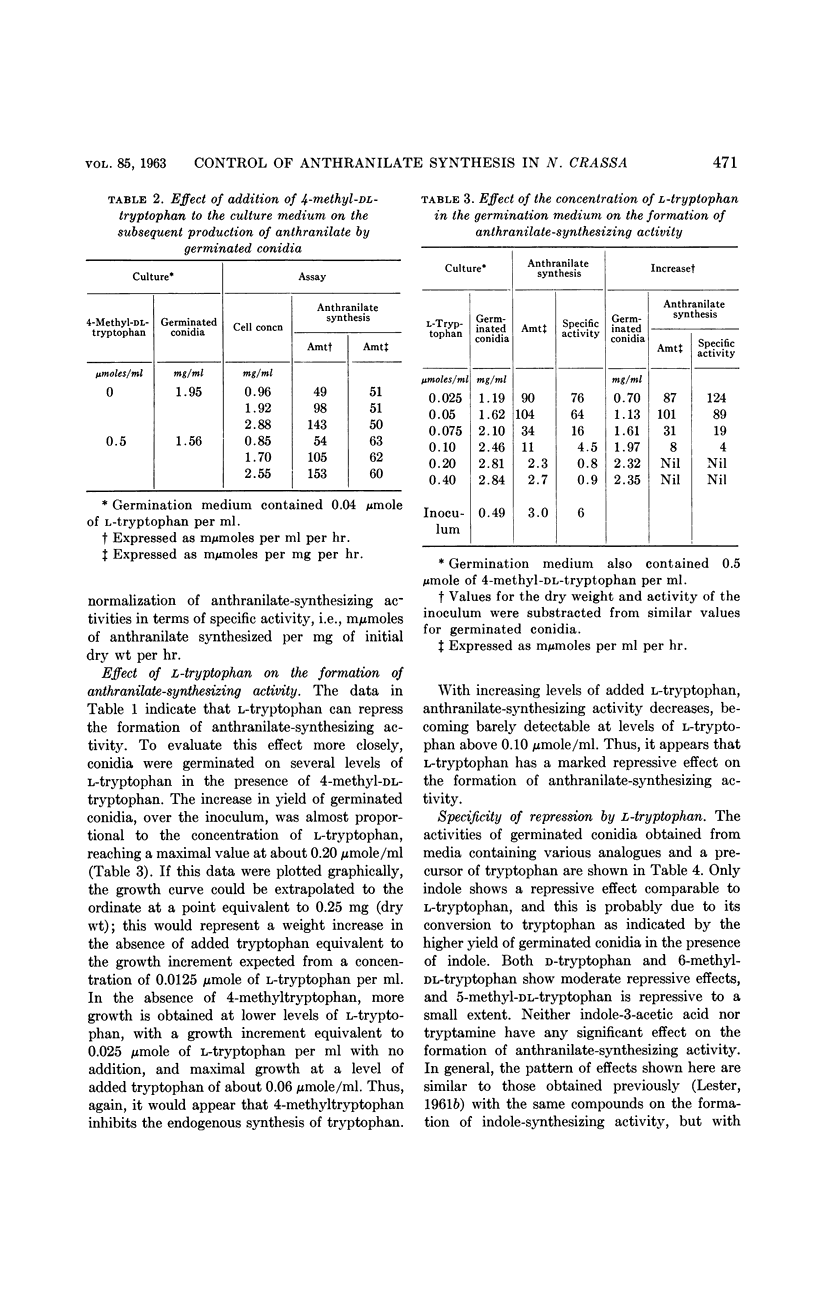
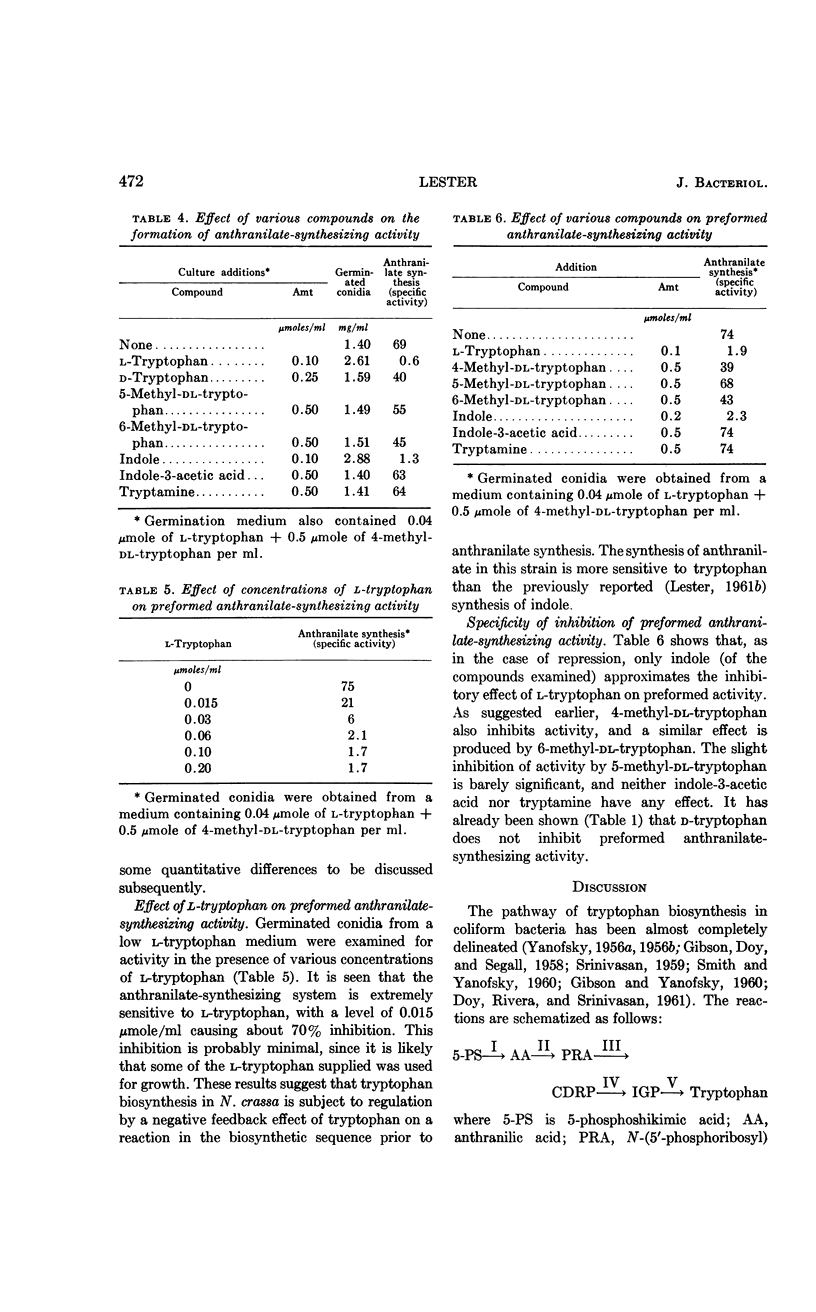
Abstract
Lester, Gabriel (Reed College, Portland, Ore.). Regulation of early reactions in the biosynthesis of tryptophan in Neurospora crassa. J. Bacteriol. 85:468–475. 1963.—The regulation of the biosynthesis of tryptophan was examined in Neurospora crassa, strain ylo-tryp-la, which accumulates anthranil compounds. The block in this strain appeared to be in the conversion of 1-(o-carboxyphenylamino)-1-deoxyribulose-5-phosphate to indole-3-glycerol phosphate, since the dephosphorylated form of the former compound, the anthranilic ribonucleoside, and the anthranilic acid were found. Cells cultured on levels of l-tryptophan greater than 0.1 μmole per ml were almost devoid of anthranilate-synthesizing activity, whereas cells cultured on low levels of tryptophan (e.g., 0.025 μmole/ml) could produce anthranilate at a rate of 125 mμmoles per mg (dry wt) per hr. A repressive effect was also caused by d-, 5-methyl-dl-, and 6-methyl-dl-tryptophan, but none of these compounds was as effective a repressor as l-tryptophan. Neither 4-methyl-dl-tryptophan, tryptamine, nor indole-3-acetic acid repressed the formation of anthranilate-synthesizing activity. Preformed activity was strongly inhibited by l-tryptophan, and to a lesser extent by 4-, 5-, and 6-methyl-dl-tryptophan; d-tryptophan, tryptamine, or indole-3-acetic acid did not inhibit preformed anthranilate-synthesizing activity. These results are indicative of the operation of repression and feedback-inhibition mechanisms early in the biosynthetic sequence leading to tryptophan. The relation of these results to those concerned with other aspects of tryptophan biosynthesis is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORENFREUND E., DISCHE Z. A new spray for spotting of sugars on paper chromatograms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):239–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner D. M., Yanofsky C., Partridge C. W. Incomplete Genetic Blocks in Biochemical Mutants of Neurospora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Jan;38(1):25–34. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G., JACOB F. Sur la répression de la synthèse des enzymes intervenant dans la formation du tryptophane chez Escherichia coll. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Jun 15;248(24):3490–3492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOY C. H., GIBSON F. 1-(o-Carboxyphenylamino)-1-deoxyribulose. A compound formed by mutant strains of Aerobacter aerogenes and Escherichia coli blocked in the biosynthesis of tryptophan. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:586–597. doi: 10.1042/bj0720586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOY C. H., RIVERA A., Jr, SRINIVASAN P. R. Evidence for the enzymatic synthesis of N-(5'-phosphoribosyl) anthranilic acid, a new intermediate in tryptophan biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1961 Jan 25;4:83–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(61)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON F. W., DOY C. H., SEGALL S. B. A possible intermediate in the biosynthesis of tryptophan: 1-deoxy-1-N-o-carboxyphenyl-ribulose. Nature. 1958 Feb 22;181(4608):549–550. doi: 10.1038/181549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON F., YANOFSKY C. The partial purification and properties of indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthetase from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Oct 7;43:489–500. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90471-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER G. Repression and inhibition of indole-synthesizing activity in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1961 Aug;82:215–223. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.2.215-223.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER G. Some aspects of tryptophan synthetase formation in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:964–973. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.964-973.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESTER G., YANOFSKY C. Influence of 3-methylanthranilic and anthranilic acids on the formation of tryptophan synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jan;81:81–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.1.81-90.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATCHETT W. H., DEMOSS J. A. Factors affecting increased production of tryptophan synthetase by a TD mutant of Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1294–1300. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1294-1300.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., COHEN-BAZIRE G. L'effet d'inhibition spécifique dans la biosynthèse de la tryptophane-desmase chez Aerobacter aerogenes. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1953 Feb 2;236(5):530–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH O. H., YANOFSKY C. 1-(o-Carboxyphenylamino)-1-deoxyribulose 5-phosphate, a new intermediate in the biosynthesis of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2051–2057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANOFSKY C. Indole-3-glycerol phosphate, an intermediate in the biosynthesis of indole. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 May;20(2):438–439. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANOFSKY C., RACHMELER M. The exclusion of free indole as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of tryptophan in Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Jun;28(3):640–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YANOFSKY C. The enzymatic conversion of anthranilic acid to indole. J Biol Chem. 1956 Nov;223(1):171–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


