Abstract
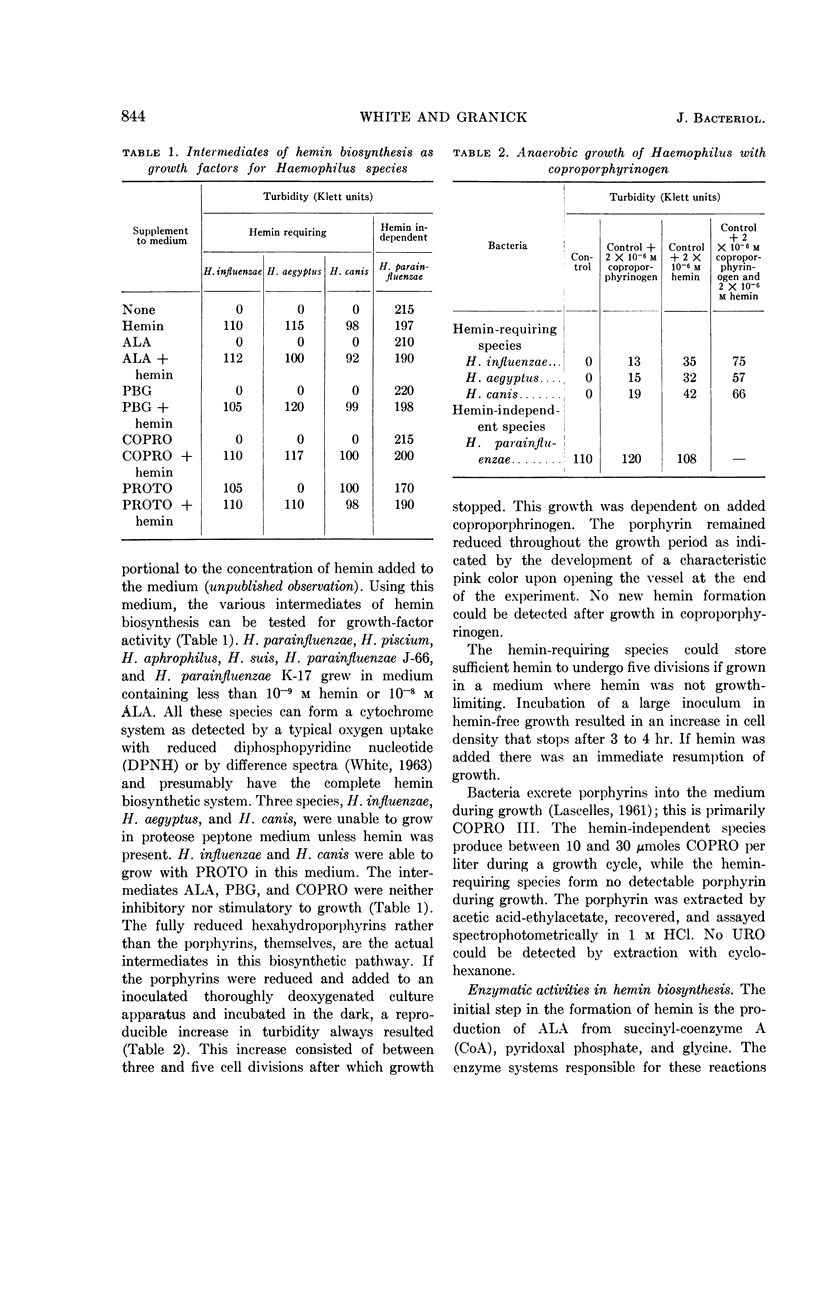
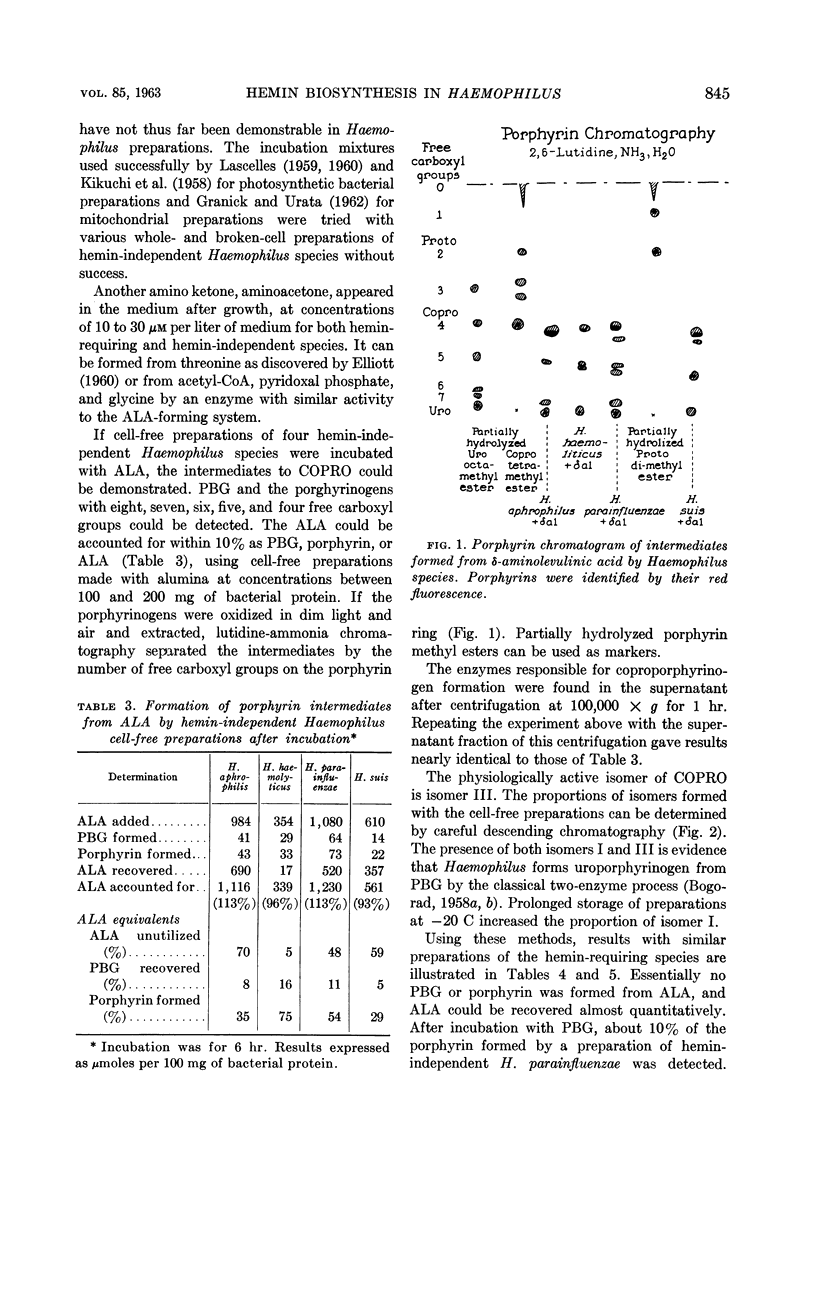
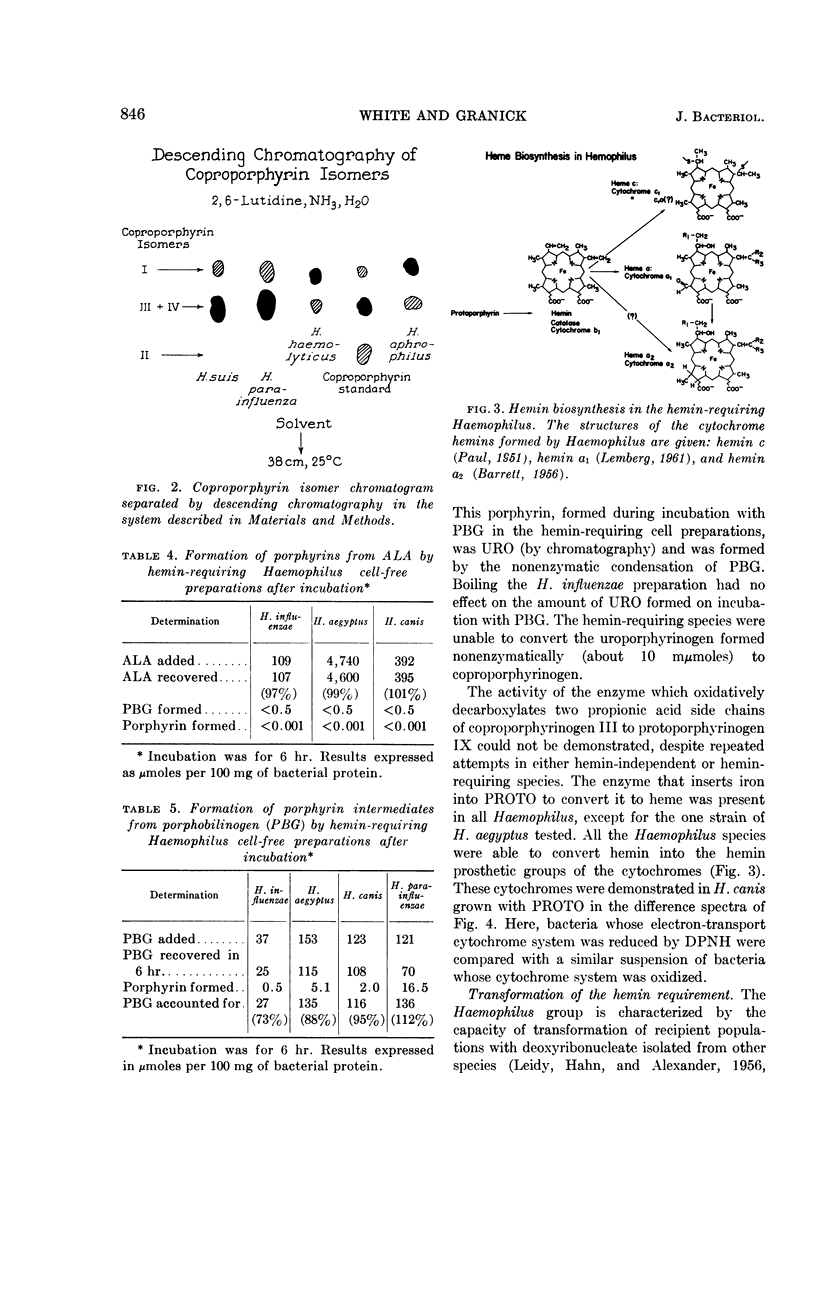
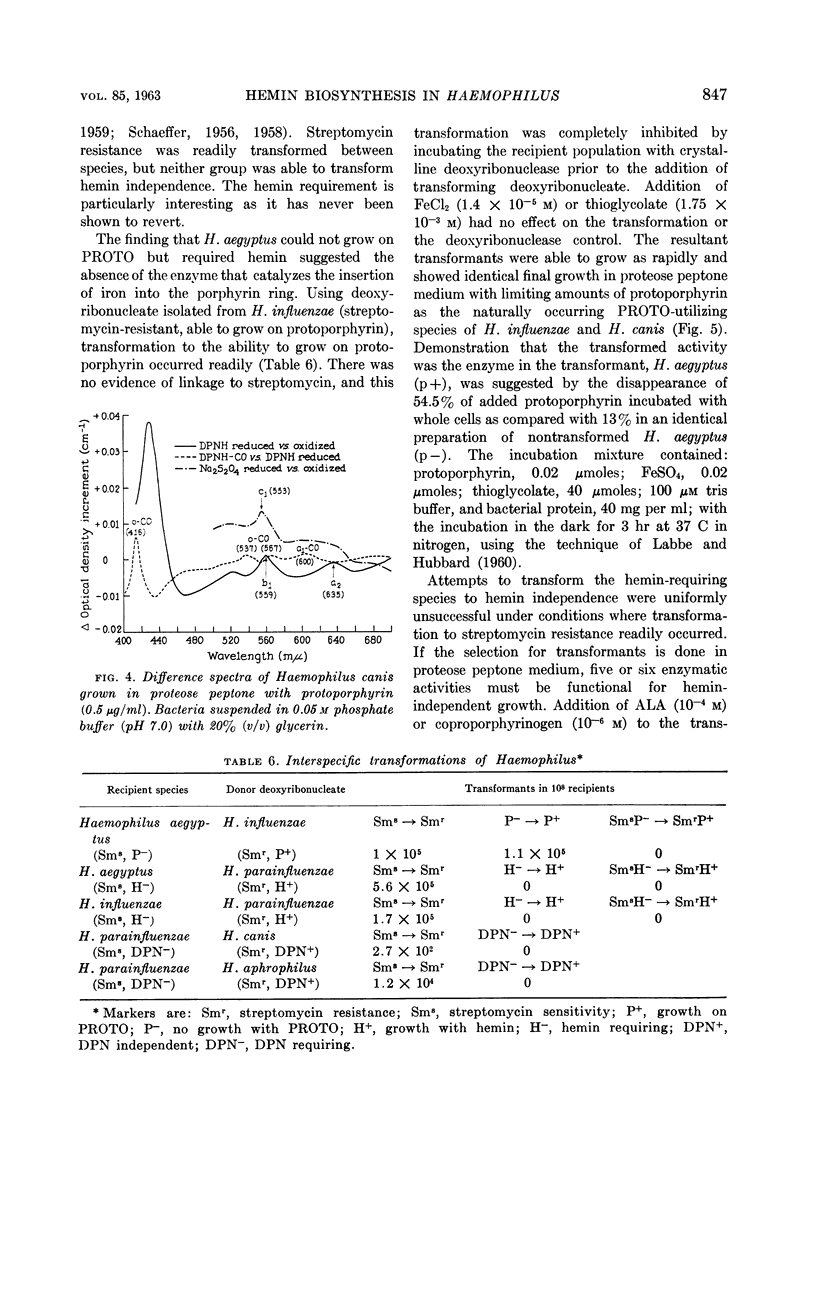
White, David C. (The Rockefeller Institute, New York, N.Y.) and S. Granick. Hemin biosynthesis in Haemophilus. J. Bacteriol. 85:842–850. 1963.—Hemin-independent Haemophilus species have been shown to form hemin by the classical hemin biosynthetic pathway. Three distinct species of Haemophilus [H. influenzae, H. aegyptius, and H. canis (H. haemoglobinophilus)] all lost the enzymatic capacities to convert δ-aminolevulinic acid to protoporphyrin, which accounts for their dependence on hemin for growth. The strain of H. aegyptus tested cannot form hemin from protoporphyrin, can be transformed with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from H. influenzae, and the resultant progeny have the enzymatic activity to convert protoporphyrin to hemin. Attempts to transform these species to hemin independence with DNA from hemin-independent H. parainfluenzae are unsuccessful under conditions where streptomycin resistance is readily transformed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER H. E., HAHN E., LEIDY G. On the specificity of the desoxyribonucleic acid which induces streptomycin resistance in Hemophilus. J Exp Med. 1956 Sep 1;104(3):305–320. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.3.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRETT J. The prosthetic group of cytochrome a2. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):626–639. doi: 10.1042/bj0640626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOGORAD L. The enzymatic synthesis of porphyrins from porphobilinogen. I. Uroporphyrin I. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):501–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOGORAD L. The enzymatic synthesis of porphyrins from porphobilinogen. II. Uroporphyrin III. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUMFITT W. Some growth requirements of Haemophilus influenzas and Haemophilus pertussis. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jan;77(1):95–100. doi: 10.1002/path.1700770109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT W. H. Aminoacetone formation by Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem J. 1960 Mar;74:478–485. doi: 10.1042/bj0740478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIKUCHI G., KUMAR A., TALMAGE P., SHEMIN D. The enzymatic synthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1214–1219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABBE R. F., HUBBARD N. Preparation and properties of the iron-protoporphyrin chelating enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jul 1;41:185–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. Adaptation to form bacteriochlorophyll in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides: changes in activity of enzymes concerned in pyrrole synthesis. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:508–518. doi: 10.1042/bj0720508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. Synthesis of tetrapyrroles by microorganisms. Physiol Rev. 1961 Apr;41:417–441. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1961.41.2.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASCELLES J. The synthesis of enzymes concerned in bacteriochlorophyll formation in growing cultures of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:487–498. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIDY G., HAHN E., ALEXANDER H. E. Interspecific transformation in Hemophilus: a possible index of relationship between H. influenzae and H. aegyptius. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:86–88. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEIDY G., JAFFEE I., ALEXANDER H. E. Emergence of competence (for transformation) of three Hemophilus species in a chemically defined environment. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Dec;111:725–731. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSES V. Tricarboxylic acid cycle reactions in the fungus Zygorrhynchus moelleri. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Oct;13(2):235–251. doi: 10.1099/00221287-13-2-235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLAS R. E. H., RIMINGTON C. Paper chromatography of porphyrins; some hitherto unrecognized porphyrins and further notes on the method. Biochem J. 1951 Mar;48(3):306–309. doi: 10.1042/bj0480306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANO S., GRANICK S. Mitochondrial coproporphyrinogen oxidase and protoporphyrin formation. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1173–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFFER P. Interspecific reactions in bacterial transformation. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1958;12:60–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEFFER P. Transformation interspécifique chez des bactéries du genre Hemophilus. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Aug;91(2):192–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. Cytochrome and catalase patterns during growth of Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1962 Apr;83:851–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.4.851-859.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C. Respiratory systems in the hemin-requiring Haemophilus species. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jan;85:84–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.1.84-96.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., SMITH L. Hematin enzymes of Hemophilus parainfluenzae. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1332–1336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


