Abstract
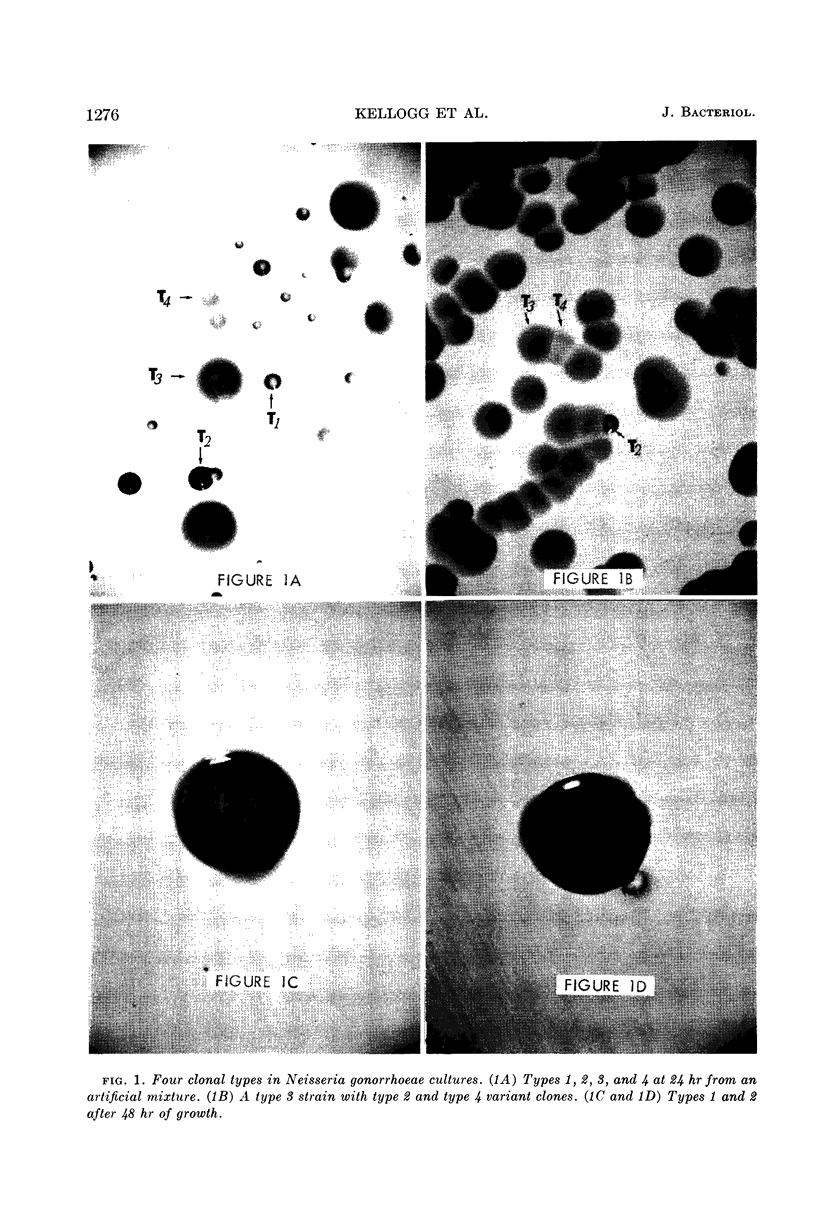
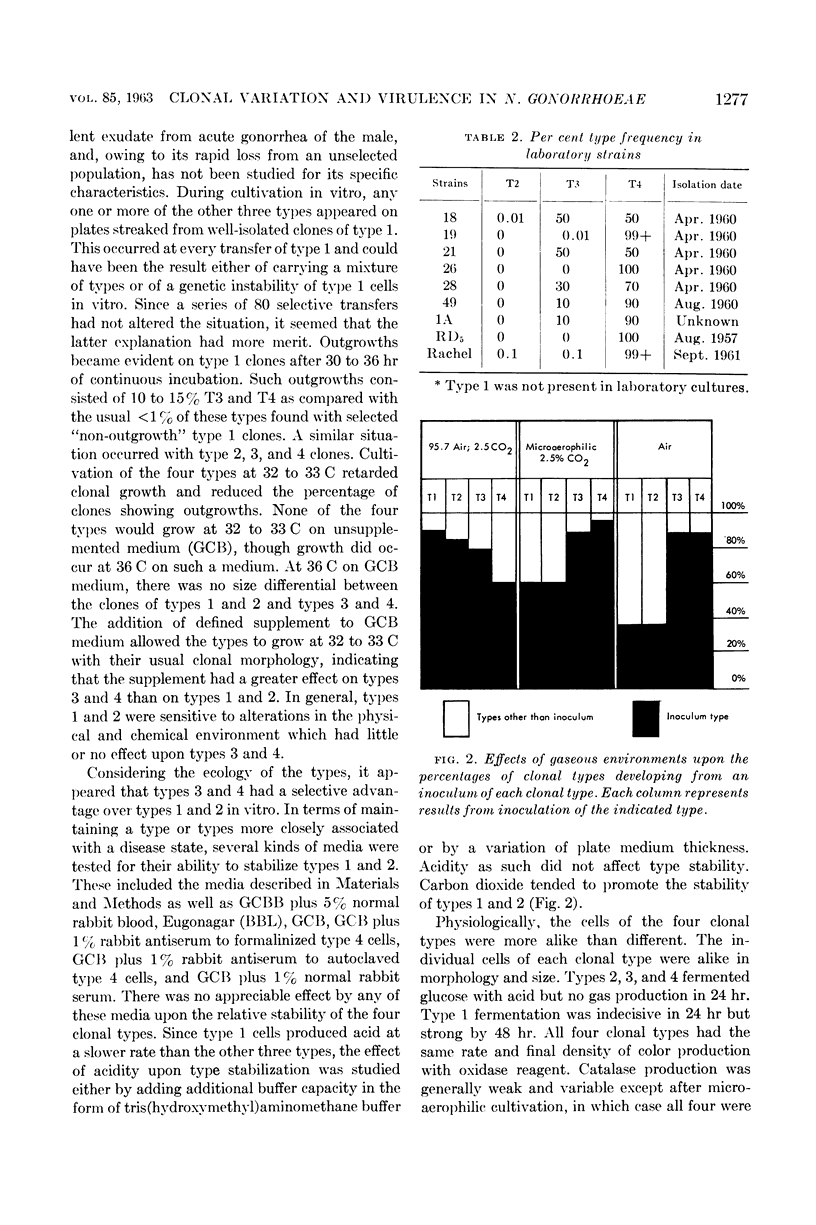
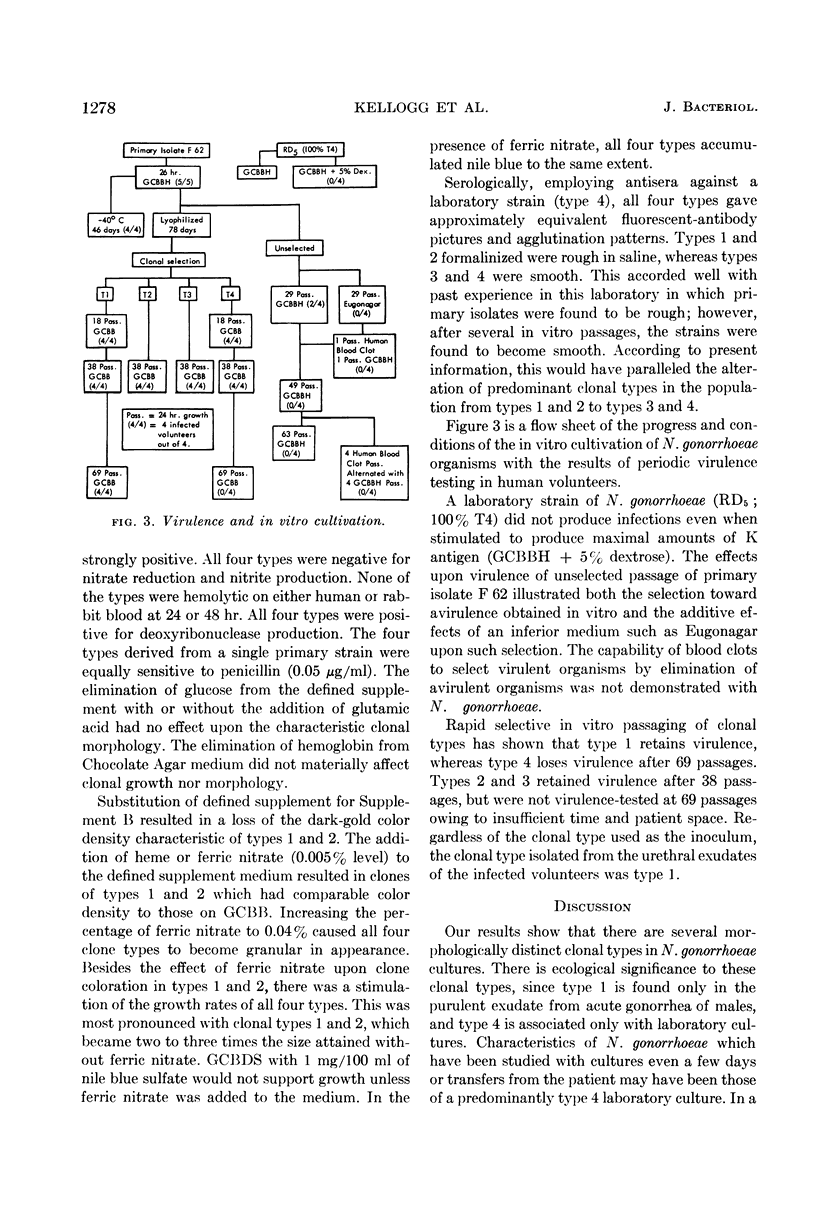
Kellogg, Douglas S., Jr. (Communicable Disease Center, Atlanta, Ga.), William L. Peacock, Jr., W. E. Deacon, L. Brown, and Carl I. Pirkle. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Virulence genetically linked to clonal variation. J. Bacteriol. 85:1274–1279. 1963.—One type, obtained from the purulent exudate of acute gonorrhea was maintained by 69 selective in vitro passages, at which point the organisms produced infections in human volunteers. A predominance of clonal types found in laboratory strains and a lack of ability to infect human volunteers resulted from 69 nonselective in vitro passages. Physiological and serological characteristics of the clonal types are compared. We are now in a position to study Neisseria gonorrhoeae organisms in their virulent form.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DEACON W. E., PEACOCK W. L., Jr, FREEMAN E. M., HARRIS A. Identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by means of fluorescent antibodies. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jun;101(2):322–325. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton H. E., Shoemaker J. The Identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by Means of Bacterial Variation and the Detection of Small Colony Forms in Clinical Material. J Bacteriol. 1945 Nov;50(5):585–587. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHERP H. W. Neisseria and neisserial infections. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1955;9:319–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.09.100155.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]