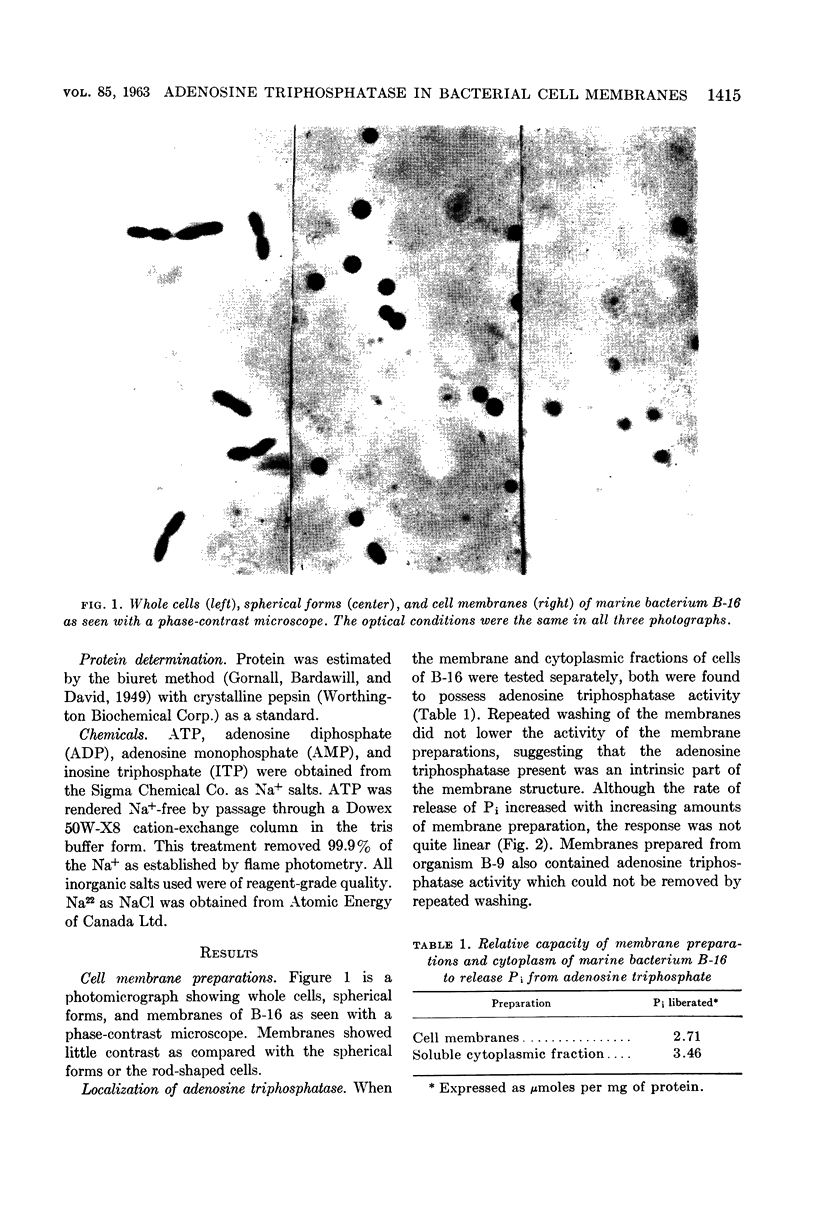
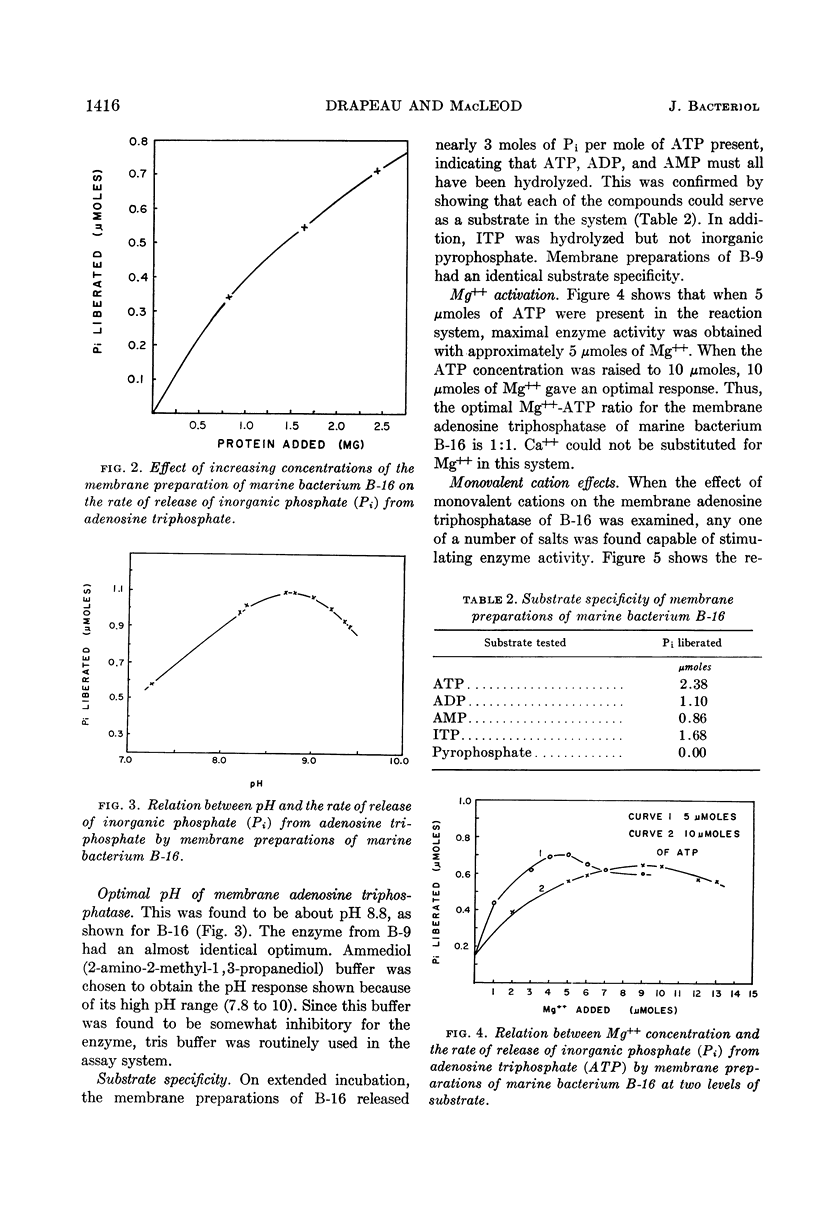
Abstract
Drapeau, Gabriel R., (Macdonald College of McGill University, Quebec, Canada) and Robert A. MacLeod. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XII. Ion activation of adenosine triphosphatase in membranes of marine bacterial cells. J. Bacteriol. 85:1413–1419. 1963.—Isolated membranes of two species of marine bacteria, a Pseudomonas and a Cytophaga, have been shown to possess adenosine triphosphatase activity. The optimal pH for enzyme action of both organisms was 8.8. The enzyme system was found to be capable of splitting inorganic o-phosphate from adenosine triphosphate (ATP), adenosine diphosphate, adenosine monophosphate, and inosine triphosphate but not from inorganic pyrophosphate. Mg++ was required for enzyme activity; with the Pseudomonas species, the optimal Mg++ to ATP ratio was 1:1. Ca++ could not replace Mg++. In the presence of the optimal concentration of Mg++, the enzyme system was further stimulated, nonspecifically, by a number of different salts. Maximal activation was achieved at an ionic strength of 0.3 to 0.4. No evidence of an adenosine triphosphatase specifically activated by a combination of Na+ and K+ was obtained with either organism. No effect of ouabain on either the membrane adenosine triphosphatase activity or Na+ transport by whole cells could be detected. The results suggest that the mechanism of ion regulation in marine bacterial cells is different from that in animal cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMS A., McNAMARA P., JOHNSON F. B. Adenosine triphosphatase in isolated bacterial cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1960 Dec;235:3649–3662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., SIMON K. A., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNHAM E. T., GLYNN I. M. Adenosinetriphosphatase activity and the active movements of alkali metal ions. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:274–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL T. J., SOLOMON A. K. Effect of ouabain on sodium flux in human red cells. Nature. 1959 Apr 18;183(4668):1127–1128. doi: 10.1038/1831127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., CLARIDGE C. A., HORI A., MURRAY J. F. Observations on the function of sodium in the metabolism of a marine bacterium. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jun;232(2):829–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A., ONOFREY E. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. III. The relation of sodium and potassium to growth. J Cell Physiol. 1957 Dec;50(3):389–401. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030500305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAYNE W. J. Effects of sodium and potassium ions on growth and substrate penetration of a marine pseudomonad. J Bacteriol. 1960 Nov;80:696–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.5.696-700.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRATT D., HAPPOLD F. C. Requirements for indole production by cells and extracts of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:232–236. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.232-236.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C., GREENWALT J. W., LOW H. The hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate by cell fractions of Bacillus megaterium. I. Localization and general characteristics of the enzymic activities. J Biol Chem. 1962 Mar;237:847–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]