Full text
PDF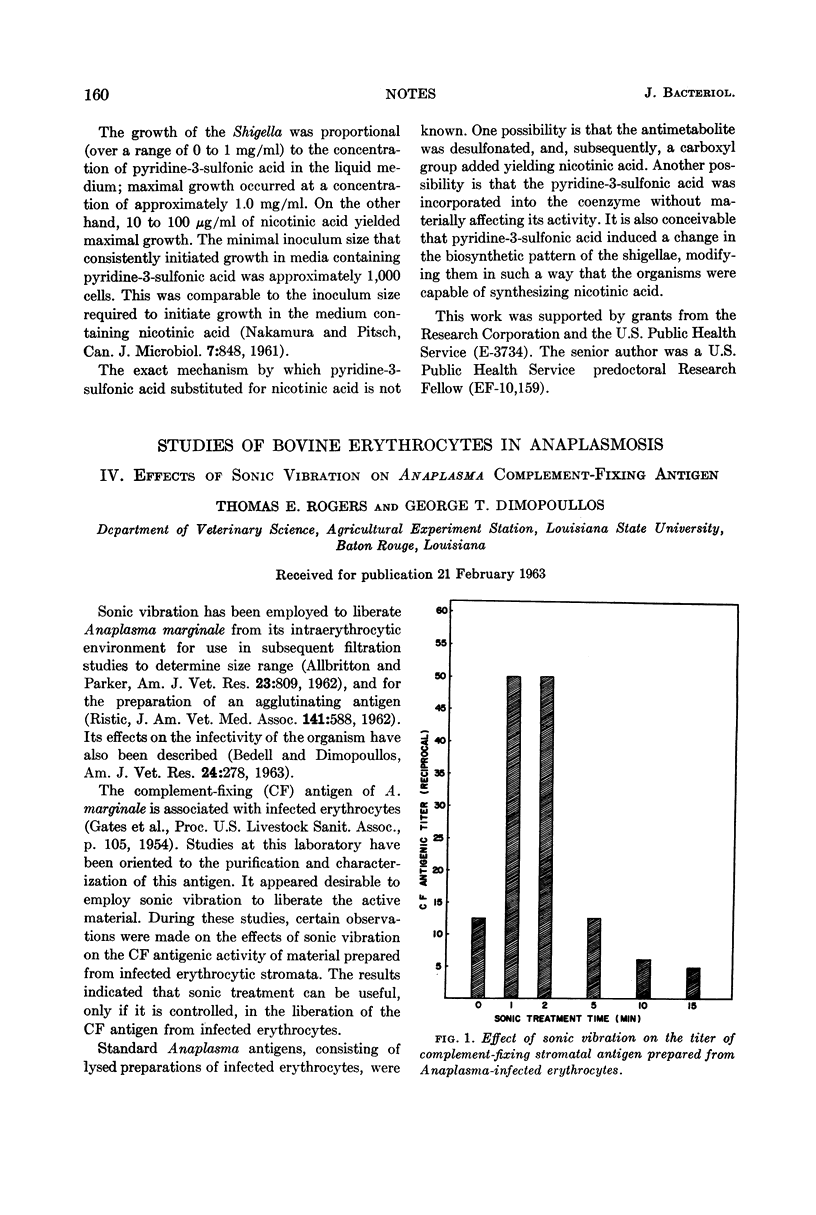

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEDELL D. M., DIMOPOULLOS G. T. Biologic properties and characteristics of Anaplasma marginale. II. The effects of sonic energy on the infectivity of whole blood preparations. Am J Vet Res. 1963 Mar;24:278–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLISON S. A., ERLANGER B. F., ALLEN P. The chemical reversal of ultraviolet effects on bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1955 May;69(5):536–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.5.536-540.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARVIE E. I. The growth of Escherichia coli in buffer substrate and distilled water. J Bacteriol. 1955 Apr;69(4):393–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.4.393-398.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINMETS F., LEHMAN J. J. Preliminary studies on the restoration of viability of ultraviolet-inactivated bacteria by metabolites and cofactors. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Dec;59(2):313–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90497-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L., BLATTBERG B. A test of the validity of reactivation of bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):743–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.743-746.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAMURA M., PITSCH B. L. Effect of size of inocula on the growth of Shigella sonnei in a chemically defined medium. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Oct;7:848–849. doi: 10.1139/m61-106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RISTIC M. A capillary tube-agglutination test for anaplasmosis--a preliminary report. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1962 Sep 1;141:588–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


