Abstract
The principal management of acute cholecystitis is early cholecystectomy. However, percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage (PTGBD) may be preferable for patients with moderate (grade II) or severe (grade III) acute cholecystitis. For patients with moderate (grade II) disease, PTGBD should be applied only when they do not respond to conservative treatment. For patients with severe (grade III) disease, PTGBD is recommended with intensive care. Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration (PTGBA) is a simple alternative drainage method with fewer complications; however, its clinical usefulness has been shown only by case-series studies. To clarify the clinical value of these drainage methods, proper randomized trials should be done. This article describes techniques of drainage for acute cholecystitis.
Key words: Acute cholecystitis, Cholecystostomy, Drainage, Percutaneous, Endoscopy, Acalculous cholecystitis, Guidelines
Introduction
Biliary drainage used to be a surgical procedure consisting of external biliary drainage done under local anesthesia — called “percutaneous cholecystostomy”. With the popularization of ultrasonography, percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage (PTGBD), which is an interventional procedure, has become a standard method. The usefulness of PTGBD as a drainage method for high-risk patients is endorsed by many case-series studies (level 4),1–8 but its superiority over conventional treatment has not been proven by randomized controlled trials (RCTs) based on the highest level of evidence (level 2b).11 Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration (PTGBA), is an alternative biliary drainage method in which the gallbladder contents are puncture-aspirated without placing a drainage catheter. The usefulness of PTGBA has been reported only in case-series studies (level 4).3,9,10
Acalculous cholecystitis is known to occur in elderly or high-risk patients with poor systemic condition, and it can be treated by biliary drainage alone (level 4).1,2,13,14
This article describes the details of drainage procedures used for acute cholecystitis, and indicates the grades of recommendation for the procedures established by the Guidelines.
Procedures for gallbladder drainage
Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage (PTGBD)
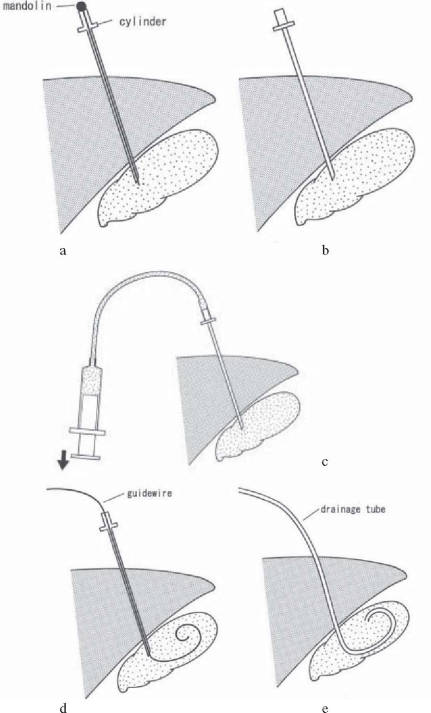
PTGBD is an essential technique for nonoperative gallbladder drainage. After ultrasound-guided transhepatic gallbladder puncture is done with an 18-G needle, a 6- to 10-Fr pigtail catheter is placed in the gallbladder, using a guidewire under fluoroscopy (Seldinger technique; Fig. 1). The advantage of the technique is its simplicity. However, although bile aspiration and lavage are easily performed by this technique, it has disadvantages in that the drainage tube cannot be extracted until a fistula forms around the tube (around 2 weeks) and there is a risk of dislocation of the tube. The superiority of PTGBD over conservative treatment has not be proven by RCTs (level 2b)9 (Table 1).
Fig. 1a–e.
Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder drainage (PTGBD) procedure. a A hollow needle (external cylinder with a mandolin) is inserted into the gallbladder. b Only the mandolin is removed and the external cylinder remains. c Backflow of bile is confirmed. d A guidewire is inserted into the gallbladder. e After removal of the external cylinder, a drainage tube is passed over the guidewire into the gallbladder. The guidewire is then withdrawn, and the tube is fixed to the skin
Table 1.
RCT comparing PTGBD and conservative treatment for high-risk acute cholecystitis (PTGBD)
| n | (ICUa) | Symptom improvement | Mortality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTGBD group | 63 | (6) | 86% | 17.5% |
| Conservative treatment | 60 | (2) | 87% | 13% NS |
a No. of patients in ICU (intensive care unit) (Adapted from reference 9)
Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration (PTGBA)
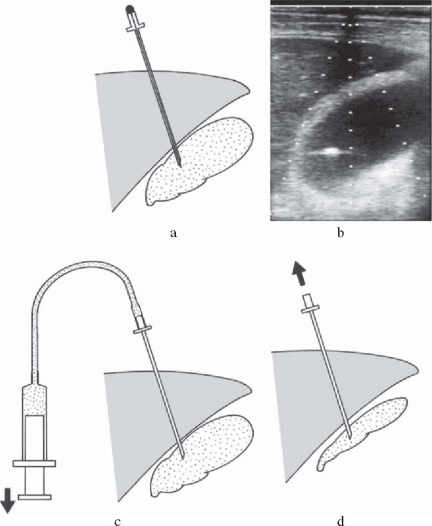
PTGBA is a method to aspirate bile via the gallbladder with a small-gauge needle under ultra sonographic guidance (Fig. 2); it is an easy low-cost bedside-applicable procedure, without X-ray guidance. It has various advantages as compared with PTGBD, such as the absence of complications, including those caused by tube displacement, as it requires no drainage tube management3 and less restriction of the patient’s activity of daily living (ADL), but an RCT (level 2b)12 has indicated that the drainage is less effective (Table 2). However, as it is known that the effect of drainage is enhanced when PTGBA is performed two times or more (level 4),10,11 an RCT should be performed to confirm the effect of PTGBA by comparing it with PTGBD not only in terms of drainage but also in terms of other outcomes, including complications and the effects on patients’ ADL.
Fig. 2a–d.
Percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration (PTGBA) procedure. a Under ultrasound guidance, the gallbladder is punctured transhepatically by a needle with a mandolin. The mandolin is then removed. b Real-time ultrasound image: the needle tip is confirmed as a high-echoic spot in the gallbladder, revealing successful puncture under real-time ultrasound guidance. c The mandolin is removed, and bile is aspirated. d After sufficient aspiration of bile, the needle is withdrawn
Table 2.
Comparisons of results for PTGBA and PTGBD
| Authors | Number of patients | Technical success | Clinical responses | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ito (2004)12 | PTGBA, 28 | 82% | 61% | 0.4% |
| PTGBD, 30 | 100% | 90%* | 0.3% | |
| Kutsumi (2004)10 | PTGBA, 94 | 100% | 83% (91%a) | 1.1% |
| PTGBD, 13 | 100% | – | 23.1% | |
| Chopra (2001)3 | PTGBA, 31 | 97% | 74% | 0 |
| PTGBD, 22 | 97% | 86% | 12%* | |
| Mizumoto (1992)11 | PTGBA, 58 | 98% | 81% (94%a) | 2.5% |
| – |
* P < 0.05
a PTGBA was performed twice or more
For PTGBA, considering the potential for bile leakage into the peritoneal cavity, a transhepatic puncture route is chosen, and the gallbladder contents should be completely aspirated until the gallbladder collapses, as shown by ultrasound-guided checking of the needle tip (Fig. 2).
The use of a large-gauge (18-G) needle is convenient for aspirating highly viscous bile containing inflammatory products and biliary sludge, but we should be careful to prevent bile leakage after removing the needle. While a small-gauge (21-G) needle has a lower risk of leakage after removal, aspiration of highly viscous bile is difficult with such needles and should be conducted while washing with saline containing antibiotics. Many stadies (level 2b, 4)10–12 report the use of 21-G needles.
Endoscopic nasogallbladder drainage (ENGBD)
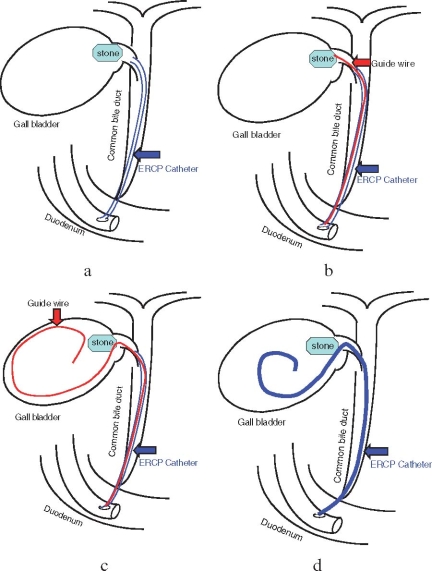
ENGBD is an external drainage procedure done by placing a 5- to 7-Fr tube, using a guide-wire technique, after selective cannulation into the gallbladder (Fig. 3). ENGBD can be used for patients with severe comorbid conditions, especially those with end-stage liver disease, in whom the percutaneous approach is difficult to perform. However, because it requires a difficult endoscopic technique, and relevant case-series studies have been conducted only at a limited number of institutions (level 4),15–19 ENGBD has not been established as a standard method.
Fig. 3a–d.
Endoscopic nasogallbladder drainage (ENGBD) procedure.19a An endoscopic retrograde cholanglopancreatography (ERCP) catheter was inserted in the cystic duct, but the gallbladder was not visualized because of a stone impacted in the neck of the gallbladder. b Through the ERCP catheter, a hydrophilic guidewire was passed beyond the obstruction. c A radiofocus guidewire was inserted into the gallbladder. d An ENGBD catheter was inserted into the gallbladder for drainage
The Guidelines established the following grades of recommendation for gallbladder drainage, based on the currently available evidence.
Q1. What procedure should be chosen when gallbladder drainage is required in acute cholecystitis?
PTGBD: Recommendation
PTGBA: Recommendation
ENGBD: Recommendation
Discussion at the Tokyo International Consensus Meeting
PTGBD versus conservative treatment
Henry Pitt (USA): This area is an area that is obviously controversial and would be a great opportunity to do a randomized trial, a proper randomized trial of preoperative drainage followed by surgery versus surgery alone, and that is the trial that needs to be done.
Horst Neuhaus (Germany): Yes, I agree, if you consider the comment from Doctor Strasberg this morning (present state of laparoscopic cholecystectomy in America), you mentioned that in severe acute cholecystitis the incidence of complications is higher in early cholecystectomy, and therefore I also think it would be worthwhile to set up a randomized trial in these selected groups of severe acute cholecystitis.
Steven Strasberg (USA): I think an important point is when the percutaneous drainage is done. So if a patient has moderate cholecystitis and they are not going to be operated on with the most reasonable approach, we do not have the data, the most reasonable approach is to treat a patient conservatively, without percutaneous drainage, but to perform percutaneous drainage when the conservative treatment is failing. And the question is what are the criteria for failure. And they would be, local and general signs of inflammation are getting worse or they are not getting better over a period of time. So I mean, it is going to be very difficult to define those criteria at this meeting, but that is going to be the general direction of what we are going to do.
ENGBD
H. Neuhaus: So, concerning the technique I have two remarks.
The first remark is [regarding] the percutaneous route. I think we should aim at doing it via the transhepatic and not the transperitoneal route because of a high risk of complications due to drain dislocation. The second remark is [regarding] the endoscopic route (ENGBD), which was shown and reviewed by Dr. Tsuyuguchi today. Although I like endoscopy very much, I do not believe that the success rate of transcystic cannulation of the gallbladder is nearly 90% in the published literature. Because, before the era of laparoscopic cholecystostomy, we tried to insert naso-cystic catheters for dissolution of stones, and I know how difficult it is. I’m afraid that these data are from small series and are not based on an intention-to-treat analysis.
Acknowledgment
We would like to express our deep gratitude to the Japanese Society for Abdominal Emergency Medicine, the Japan Biliary Association, and the Japanese Society of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, who provided us with great support and guidance in the preparation of the Guidelines. This process was conducted as part of the Project on the Preparation and Diffusion of Guidelines for the Management of Acute Cholangitis (H-15-Medicine-30), with a research subsidy for fiscal 2003 and 2004 (Integrated Research Project for Assessing Medical Technology) sponsored by the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare.
We also truly appreciate the panelists who co operated with and contributed significantly to the International Consensus Meeting, held in Tokyo on April 1 and 2, 2006.
References
- 1.Kiviniemi H, Makela JT, Autio R, Tikkakoski T, Leinonen S, Siniluoto T, et al. Percutaneous cholecystostomy in acute cholecystitis in high-risk patients: an analysis of 69 patients. Int Surg. 1998;83:299–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sugiyama M, Tokuhara M, Atomi Y. Is percutaneous cholecystostomy the optimal treatment for acute cholecystitis in the very elderly? World J Surg. 1998;22:459–63. doi: 10.1007/s002689900416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chopra S, Dodd GD, 3rd, Mumbower AL, Chintapalli KN, Schwesinger WH, Sirinek KR, et al. Treatment of acute cholecystitis in non-critically ill patients at high surgical risk: comparison of clinical outcomes after gallbladder aspiration and after percutaneous cholecystostomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;176:1025–31. doi: 10.2214/ajr.176.4.1761025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Akhan O, Akinci D, Ozmen MN. Percutaneous cholecystostomy. Eur J Radiol. 2002;43:229–36. doi: 10.1016/S0720-048X(02)00158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Donald JJ, Cheslyn-Curtis S, Gillams AR, Russell RC, Lees WR. Percutaneous cholecystolithotomy: is gall stone recurrence inevitable? Gut. 1994;35:692–5. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.5.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hultman CS, Herbst CA, McCall JM, Mauro MA. The efficacy of percutaneous cholecystostomy in critically ill patients. Am Surg. 1996;62:263–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Melin MM, Sarr MG, Bender CE, van Heerden JA. Percutaneous cholecystostomy: a valuable technique in high-risk patients with presumed acute cholecystitis. Br J Surg. 1995;82:1274–7. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800820939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Davis CA, Landercasper J, Gundersen LH, Lambert PJ. Effective use of percutaneous cholecystostomy in high-risk surgical patients: techniques, tube management, and results. Arch Surg. 1999;134:727–31. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.134.7.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hatzidakis AA, Prassopoulos P, Petinarakis I, Sanidas E, Chrysos E, Chalkiadakis G, et al. Acute cholecystitis in high-risk patients: percutaneous cholecystostomy vs conservative treatment. Eur Radiol. 2002;12:1778–84. doi: 10.1007/s00330-001-1247-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kutsumi H, Nobutani K, Ikezawa S, Nishida S, Shiomi H, Fukiya E, et al. Effectiveness of ultrasound-guided percutaneous transhepatic gallbladder aspiration (PTGBA) for acute calculous cholecystitis (in Japanese with English abstract) J Jpn Biliary Assoc. 2004;18:132–27. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mizumoto H, Takahara K, Suzuki Y, Matsutani S, Tsuchiya Y, Ohto M. Treatment of acute cholecystitis by direct-puncture bile aspiration with ultrasound image control (in Japanese with English abstract) Nippon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi (Jpn J Gastroenterol) 1992;89:61–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ito K, Fujita N, Noda Y, Kobayashi G, Kimura K, Sugawara T, et al. Percutaneous cholecystostomy versus gallbladder aspiration for acute cholecystitis: a prospective randomized controlled trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183:193–6. doi: 10.2214/ajr.183.1.1830193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Babb RR. Acute acalculous cholecystitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992;15:238–41. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199210000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lillemoe KD. Surgical treatment of biliary tract infections. Am Surgeon. 2000;66:138–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tamada K, Seki H, Sato K, Kano T, Sugiyama S, Ichiyama M, et al. Efficacy of endoscopic retrograde cholecystoendoprosthesis (ERCCE) for cholecystitis. Endoscopy. 1991;23:2–3. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Johlin FC, Jr, Neil GA. Drainage of the gallbladder in patients with acute acalculous cholecystitis by transpapillary endoscopic cholecystotomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993;39:645–51. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5107(93)70216-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nakatsu T, Okada H, Saito K, Uchida N, Minami A, Ezaki T, et al. Endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage (ETGBD) for the treatment of acute cholecystitis. J Hepato biliary Pancreat Surg. 1997;4:31–5. doi: 10.1007/BF01211341. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shrestha R, Trouillot TE, Everson GT. Endoscopic stenting of the gallbladder for symptomatic gallbladder disease in patients with end-stage liver disease awaiting orthotopic liver transplantation. Liver Transpl Surg. 1999;5:275–81. doi: 10.1002/lt.500050402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Toyota N, Takada T, Amano H, Yoshida M, Miura F, Wada K. Endoscopic naso-gallbladder drainage in the treatment of acute cholecystitis: alleviates inflammation and fixes operator’s aim during early laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006;13:80–5. doi: 10.1007/s00534-005-1062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]