Abstract
Objectives
To determine the effect of Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccination and its timing on the risk of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children.
Design
Cumulative incidence and relative risk of type 1 diabetes was compared among three birth cohorts of Finnish children: those born during the 24 months before the H influenzae type b vaccination trial, those in the trial cohort who were vaccinated at 3 months of age and later with a booster vaccine, and those in the trial cohort who were vaccinated at 24 months of age only. The probability of type 1 diabetes was estimated using regression analysis assuming that there were no losses to 10 year follow up and no competing risks.
Setting
Finland (total population 5 million and annual birth rate 1.3%).
Subjects
128 936 children born from 1 October 1983 to 1 September 1985, and 116 352 children born from 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987.
Main outcome measures
Probability of type 1 diabetes among children vaccinated with H influenzae type b and non-vaccinated children.
Results
No statistically significant difference was found at any time during the 10 year follow up in the risk of type 1 diabetes between the children born before the vaccination period and those vaccinated at the age of 24 months only (relative risk 1.01). The difference in the risk between the cohort vaccinated first at the age of 3 months and the cohort vaccinated at the age of 24 months only was not statistically significant either (1.06).
Conclusion
It is unlikely that H influenzae type b vaccination or its timing cause type 1 diabetes in children.
Key messages
The gradual increase in vaccination programmes does not permit any particular one to be pinpointed as being responsible for the increase in type 1 diabetes in Finland
There is no difference in the risk of type 1 diabetes between children not vaccinated against H influenzae type b and those vaccinated at the age of 24 months only
The difference in risk between children vaccinated against H influenzae type b at the age of 3 months and those vaccinated at the age of 24 months was not statistically significant
It is very unlikely that H influenzae type b vaccination or its timing causes type 1 diabetes in Finnish children
Introduction
Damage of the pancreatic β cells leading to type 1 diabetes in genetically susceptible individuals is believed to be induced by environmental risk factors. The effect of infection or immunisation on the development of type 1 diabetes has been discussed widely for several decades. Some investigators have suggested that certain vaccines—and particularly the timing of vaccination—might either trigger the development of type 1 diabetes or protect against it.1–5
Most information concerning the effect of vaccines on the pancreatic β cells derives from animal studies. It has been suggested that whole cell pertussis vaccine can have an adjuvant effect leading to an autoimmune process and β cell damage.6 In an animal model, however, induction of type 1 diabetes can be prevented by a single injection of BCG vaccine,7 or complete Freund’s adjuvant.8,9
Epidemiological studies of the association between vaccinations and risk of type 1 diabetes are rare. One Swedish study found a decreased risk of type 1 diabetes among children vaccinated against measles.1 The results of two recently published cohort studies from Sweden show that neither pertussis nor BCG vaccinations have a significant effect on the incidence of type 1 diabetes.10,11 A case-control study of BCG vaccination in Canada also failed to show that the vaccine protected against the development of type 1 diabetes.12 The possibility that the elimination of naturally acquired mumps infection by vaccination may reduce the risk of type 1 diabetes has been also discussed.2
In a large trial in 1985-7, a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine was shown to be 90% effective in protecting against H influenzae type b.13 Since 1988 the vaccine has been available for all Finnish children. Classen and Classen speculated that the start of nationwide vaccination in the 1980s seems to be associated temporally with the accelerated increase in the incidence of type 1 diabetes in young children in Finland.4 Because of the design of the original vaccine trial, we had a unique opportunity to determine the possible effect of H influenzae type b vaccination and its timing on the risk of type 1 diabetes.
Subjects and methods
Efficacy of H influenzae type b vaccine
All children born between 1 October 1985 and 31 August 1987 were eligible to participate in an efficacy trial of H influenzae type b vaccine (H influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide conjugated to diphtheria toxoid13). Children born on odd numbered days were scheduled to receive the conjugate at 3, 4, and 6 months of age followed by a booster dose at 14 to 18 months of age. The control group consisted of children born on even numbered days. They were scheduled to receive H influenzae type b vaccine at 24 months of age only. All the children were also vaccinated according to the routine immunisation programme consisting of BCG vaccine during the first week of life, pertussis, diphtheria, and tetanus vaccine at 3, 4, 5, and 24 months of age, polio vaccine at 6, 12, and 24 months of age, and measles, mumps, and rubella at 14-18 months of age. Of 116 352 children born during 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987, around 114 000 were enrolled in the study: 58 000 in the vaccine group and 56 000 in the control group.
Overall, 98% of children were vaccinated.13 The median age of the children when vaccinated with H influenzae type b was 3.1 months for the first dose, 4.2 months for the second dose, 6.4 months for the third dose, and 17.3 months for the booster dose. The median age of the control group when vaccinated was 24.6 months.13
Population
The data on births were obtained from the Finnish medical birth registry, which is updated continuously by the National Research and Development Centre for Welfare and Health.
We compared the risk and the cumulative incidence of type 1 diabetes among three birth cohorts of children. Cohort 1 comprised 128 936 children born from 1 October 1983 to 1 September 1985, 24 months before the H influenzae type b vaccination period.
The birth cohort from 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987 comprised 116 352 children eligible for enrolment in the efficacy trial. This cohort was divided into two further cohorts. Cohort 2 comprised children born on odd numbered days—that is, children vaccinated with H influenzae type b at 3, 4, 6, and 14-18 months of age. Cohort 3 comprised children born on even numbered days—that is, children vaccinated at 24 months of age only.
New cases of type 1 diabetes diagnosed in these cohorts were ascertained during the period from 1 October 1983 to 31 December 1986 through the nationwide hospital discharge registry and, after the beginning of 1987, through the nationwide prospective childhood diabetes registry. Both of these data sources have been found to have complete coverage, and thus all cases of type 1 diabetes diagnosed in these cohorts up to December 1997 were identified.
Analysis of the birth cohort data
We used regression analysis to estimate the probability of type 1 diabetes. We assumed that all children in cohorts 2 and 3 received vaccine as scheduled and that there were no losses to follow up and no competing risks. Each child was followed up for 10 years. Data were analysed as counts of cases with denominators being the number of children at risk. The binomial model was obtained assuming that the probability of becoming diabetic was the same for each child and that outcomes were independent. The differences in the risk of type 1 diabetes between cohorts were estimated by calculating (a) the risk ratio between cohort 1 and cohort 2 by comparing the risk in children born before the vaccination study period with the risk in children who received the H influenzae type b vaccine at 24 months of age, and (b) the risk ratio between cohort 2 and cohort 3 by comparing the risk in children in the two arms of the vaccination study—that is, by comparing those children who received the H influenzae type b vaccine in early infancy with those who received it at 24 months of age.
Results
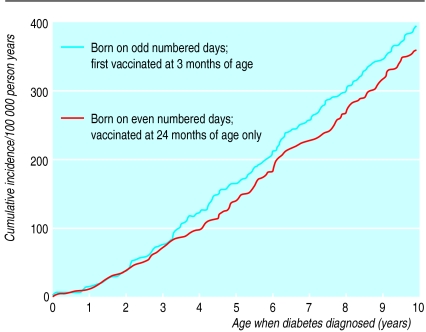
By December 1996, a total of 537, 235, and 214 cases of type 1 diabetes were diagnosed in the three cohorts: the birth cohort from 1 October 1983 to 31 September 1985 before the H influenzae type b vaccination period (cohort 1), and the birth cohort from 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987 divided into two: those vaccinated first at the age of 3 months (cohort 2) and those vaccinated at the age of 24 months only (cohort 3) (table 1). Figure 1 shows the cumulative incidence of type 1 diabetes in cohorts 2 and 3. When the children were aged 10 years, the cumulative incidence of type 1 diabetes was 397 per 100 000 person years in children vaccinated first at the age of 3 months (cohort 2), and 375 per 100,000 person years in the cohort of children vaccinated at the age of 24 months only (cohort 3).
Table 1.
Number of Finnish children in birth cohorts with type 1 diabetes by age at which disease was diagnosed. Values are number (cumulative incidence per 1000 children)
| Age at diagnosis (years) | Cohort 1* (n=128 936) | Cohort 2† (n=59 238) | Cohort 3‡ (n=57 114) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-1.9 | 33 (0.3) | 21 (0.4) | 21 (0.4) |
| 2-4.9 | 147 (1.1) | 77 (1.3) | 62 (1.1) |
| 5.0-10 | 257 (2.0) | 137 (2.3) | 131 (2.3) |
| All | 437 (3.4) | 235 (4.0) | 214 (3.7) |
Born from 1 October 1983 to 1 September 1985.
Born on odd numbered days from 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987; vaccinated first at 3 months of age.
Born on even numbered days from 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987; vaccinated at 24 months of age only.
Figure 1.
Cumulative incidence of type 1 diabetes per 100 000 person years in Finnish children aged 10 years or under
There was no statistically significant difference in the risk of type 1 diabetes between the children born before the vaccination period (cohort 1) and the children vaccinated at the age of 24 months only (cohort 3) at any point during the 10 years’ follow up (relative risk 1.01). This comparison showed that when the potential effect of H influenzae type b vaccination at a very early age was ruled out, the risk of type 1 diabetes was equal in the vaccinated and non-vaccinated children. The risk did not differ significantly between the cohort of children vaccinated in infancy (cohort 2) and the cohort of children vaccinated at the age of 24 months only (cohort 3) either (relative risk 1.06, table 2). Thus the probability of becoming diabetic was the same for each child and was not influenced by H influenzae type b vaccination or its timing.
Table 2.
Relative risk of type 1 diabetes in Finnish children up to 10 years after Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccination
| Age (years) | Cohort 3* v cohort 1†
|
Cohort 2‡v cohort 3*
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative risk | P value | Relative risk | P value | ||
| 0-1.9 | 1.04 | 0.194 | 0.96 | 0.960 | |
| 2-4.9 | 1.00 | 0.748 | 1.20 | 0.291 | |
| 0-10 | 1.01 | 0.228 | 1.06 | 0.545 | |
Born on even numbered days from 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987; vaccinated at 24 months of age only.
Born from 1 October 1983 to 31 September 1985.
Born on odd numbered days from 1 October 1985 to 31 August 1987; vaccinated first at 3 months of age.
Discussion
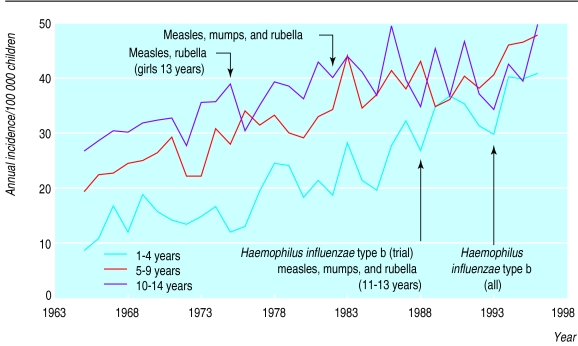
In Finland, the incidence of type 1 diabetes in children aged 14 years or under is the highest in the world, and its incidence has been increasing by 2-3% per year since the mid-1960s.14–19 Our previous studies have confirmed that this increase is real, and not due to changes in diagnostic patterns.17–19 The incidence exceeded 40 per 100 000 people per year in 1994, and in 1996 it was the highest recorded at 45 per 100 000 people per year.19 Actually, the long term increase in incidence has been virtually linear since 196518,19 or even since 1953 when the incidence in Finland nationwide was estimated for the first time.20 Our previous analysis of birth cohort effects, of children born from 1965 to 1984, showed that the increase in incidence was mainly related to the time period and that all childhood age groups were similarly affected.17 Since the mid-1980s, however, the increase in incidence of type 1 diabetes has been significantly greater in children aged 4 years or under than in older children.19 A more detailed analysis of the change in incidence shows that the relative increase within the 1-4 year old age group has been 4.5%, 6.3%, and 4.8% per year during the three periods 1965 to 1974, 1975 to 1984, and 1985 to 1996 respectively. Thus, the difference in incidence trends between age groups seems to be mainly due to a lesser increase among the oldest children rather than an accelerated increase among the youngest ones.
Childhood immunisation has a long history in Finland (table 3). BCG vaccination was started at the beginning of the 1940s, and the immunisation programme has been expanded during the past 40 years. At present, 96%-99% of Finnish children have been vaccinated against nine bacterial or viral infections before the age of 2 years.21 The incidence of type 1 diabetes has been increasing linearly, particularly among young children, since the early 1950s in Finland; thus it is very likely that the incidence was already increasing in Finland before the first nationwide childhood immunisation programme, with BCG vaccine, was started in 1941.17–19 The steady increase in incidence of type 1 diabetes concomitantly with the gradual expansion of the immunisation programme does not permit any particular vaccination scheme to be pinpointed as being responsible for the increase, nor enable it to be ascertained whether some vaccines may decrease the risk of type 1 diabetes (fig 2).
Table 3.
History of vaccination in Finland
| Vaccine (year) | Target population |
|---|---|
| BCG (1941) | At birth, all neonates |
| Diphtheria: | |
| 1943 | Children in connection with epidemics |
| 1953 | Military conscripts |
| 1957 | Most children, all children visiting child health centres |
| Pertussis (1952) | All children visiting child health centres |
| Tetanus: | |
| 1956 | Military conscripts |
| 1957 | All children aged 7 years or under |
| Polio (1957) | All people aged 17 years or under |
| Pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus, and polio (1957) | All children visiting child health centres |
| Mumps (1960) | Military conscripts |
| Measles (1975) | All children visiting child health centres |
| Rubella (1975) | Girls aged 13 years, mothers after delivery |
| Measles, mumps, and rubella: | |
| 1982 | All children visiting child health centres |
| 1988 | Children aged 11-13 years |
| Haemophilus influenzae type b: | |
| 1986-8 | Field trial |
| 1988 | Available to all |
| 1993 | All children visiting child health centres |
Figure 2.
Age specific annual incidence of type 1 diabetes per 100 000 Finnish children aged 14 years or under from 1965 to 1996 and at start of nationwide vaccination programmes
It is very difficult to evaluate possible long term unwanted consequences of immunisation and their timing using a controlled setting.22 The efficacy in preventing the target infection disease and short term safety can be obtained through studies of a relatively short duration. Once the efficacy has been confirmed it is therefore neither justified nor ethical to keep control groups of children non-vaccinated for 10 years or longer just as reference for the potential unknown long term consequences of vaccinations to become apparent in vaccinated children. Historical controls—that is, birth cohorts born before the start of a vaccination programme—can be used, but they are less than ideal as many other and often unknown factors may influence secular trends between birth cohorts. Nevertheless, it is important to attempt to collect long term safety data on vaccination whenever possible. The results of this study based both on a randomised design and on the use of historical controls show that it is very unlikely that H influenzae type b vaccination or its timing causes type 1 diabetes in Finnish children.
Acknowledgments
We thank the researchers of the Haemophilus influenzae type b project, especially Professor Juhani Eskola and Dr Helena Käyhty for their collaborative support and for helpful criticism and comments on the paper. We also thank Dr B Classen for his suggestions for this analysis.
Editorial by Elliman
Footnotes
Funding: National Institutes of Health grant DK-37957.
Competing interests: None declared.
References
- 1.Blom L, Nyström L, Dahlquist G. The Swedish childhood diabetes study: vaccinations and infections as risk determinants for diabetes in childhood. Diabetologia. 1991;34:176–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00418272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hyöty H, Hiltunen M, Reunanen A, Leinikki P, Vesikari T, Lounamaa R, et al. Decline of mumps antibodies in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children and a plateau in the rising incidence of type 1 diabetes after introduction of the mumps-measles-rubella vaccine in Finland. Diabetologia. 1993;36:1303–1308. doi: 10.1007/BF00400810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Classen JB, Classen DC. Vaccines modulate IDDM. Diabetologia. 1996;39:500–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00400684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Classen DC, Classen JB. The timing of pediatric immunization and the risk of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Infect Dis Clin Prac. 1997;6:449–454. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Classen JB, Classen DC. Public should be told that vaccines may have long term adverse effects. BMJ. 1998;318:193. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7177.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Furman BL, Wardlaw AC, Stevenso LQ. Bortadella pertussis-induced hyperinsulinaemia without marked hypoglycaemia: a paradox explained. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981;62:504–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Harada M, Kishimoto Y, Makino S. Prevention of overt diabetes and insulitis in NOD mice by a single BCG vaccination. Diabetes Rec Clin Prac. 1990;8:85–89. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(90)90017-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shehadeh N, Calcinaro F, Bradley BJ, Bruchlim I, Vardi P, Lafferty KJ. Effect of adjuvant therapy on development of diabetes in mouse and man. Lancet. 1994;343:706–707. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91583-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hui-Yu Q, Sadelain MWJ, Hitchon C, Lauzon J, Singh B. Complete Freund’s adjuvant induced T cells prevent the development and adoptive transfer of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1993;150:2072–2080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dahlquist G, Gothefors L. The cumulative incidence of childhood diabetes mellitus in Sweden unaffected by BCG-vaccination. [Letter.] Diabetologia. 1995;38:873–874. doi: 10.1007/BF03035306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Heijbel H, Chen RT, Dahlquist G. Cumulative incidence of childhood-onset IDDM is unaffected by pertussis immunization. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:173–175. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Parent M-E, Fritschi L, Siemiatycki J, Fritschi L, Colle E. Bacille Calmette-Guérin vaccination and incidence of IDDM in Montreal, Canada. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:767–772. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eskola J, Käyhty H, Takala AK, Peltola H, Rönnberg P-R, Kela E, et al. A randomized prospective field trial of a conjugate vaccine in the protection of infants and young children against invasive Haemophilus influenzae type b disease. N Engl J Med. 1990;323:1381–1387. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199011153232004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Diabetes Epidemiology Research International Group. Geographic patterns of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1988;37:1113–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rewers M, LaPorte RE, King H, Tuomilehto J.for the Diabetes Epidemiology Research International Study Group-DERI. Trends in the prevalence and incidence of diabetes: insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in childhood World Health Stat Q 198841179–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Karvonen M, Tuomilehto J, Libman I, LaPorte R.for the WHO Diabetes Mondiale Project Group. A review of the recent epidemiological data on the worldwide incidence of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus Diabetologia 199336883–892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tuomilehto J, Rewers M, Reunanen A, Lounamaa P, Lounamaa R, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, et al. Increasing trend in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in childhood in Finland. Analysis of age, calendar time and birth cohort effect during 1965 to 1984. Diabetologia. 1991;34:282–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00405089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tuomilehto J, Virtala E, Karvonen M, Lounamaa R, Pitkäniemi J, Reunanen A, et al. and the DiMe Study Group. Increase in incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus among children in Finland Int J Epidemiol 199524984–992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tuomilehto J, Karvonen M, Pitkäniemi J, Virtala E, Kohtamäki K, Toivanen L, et al and the Finnish Childhood Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Registry Group. Record-high incidence of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) in Finnish children. Diabetologia. 1999;42 (in press). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Somersalo O, Hiekkala H, Rantakallio P, Tuuteri L. Studies in childhood diabetes. Review of 359 cases. I: onset and physical development. Ann Paediatr Fenn. 1960;6:253–274. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Takala AK, Koskenniemi E, Myllymäki A, Eskola J. Neuvolarokotusten toteutuminen. Duodecim 110:1783-8. [In Finnish.] [PubMed]
- 22.Jefferson T. Vaccination and its adverse effects: real or perceived. BMJ. 1998;317:159–160. doi: 10.1136/bmj.317.7152.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]