Abstract
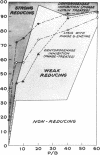
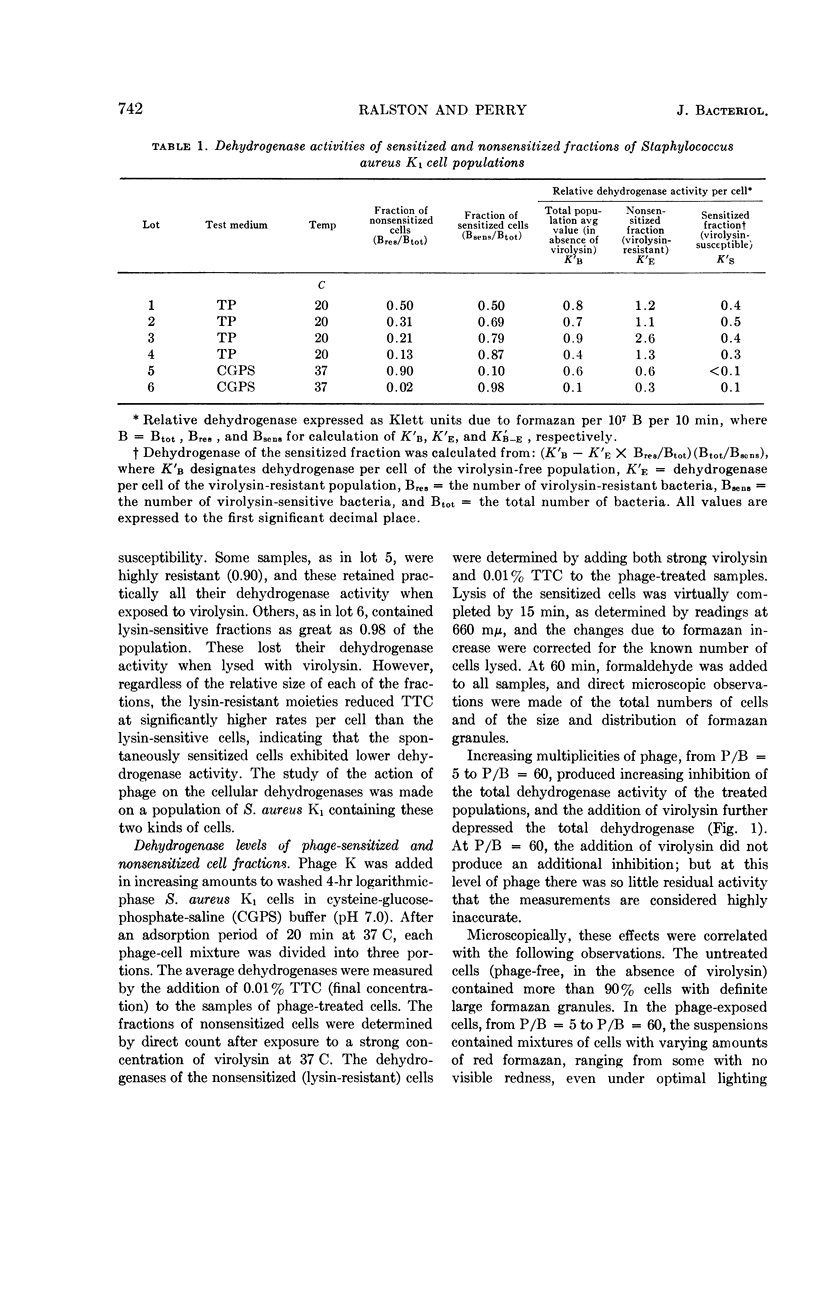
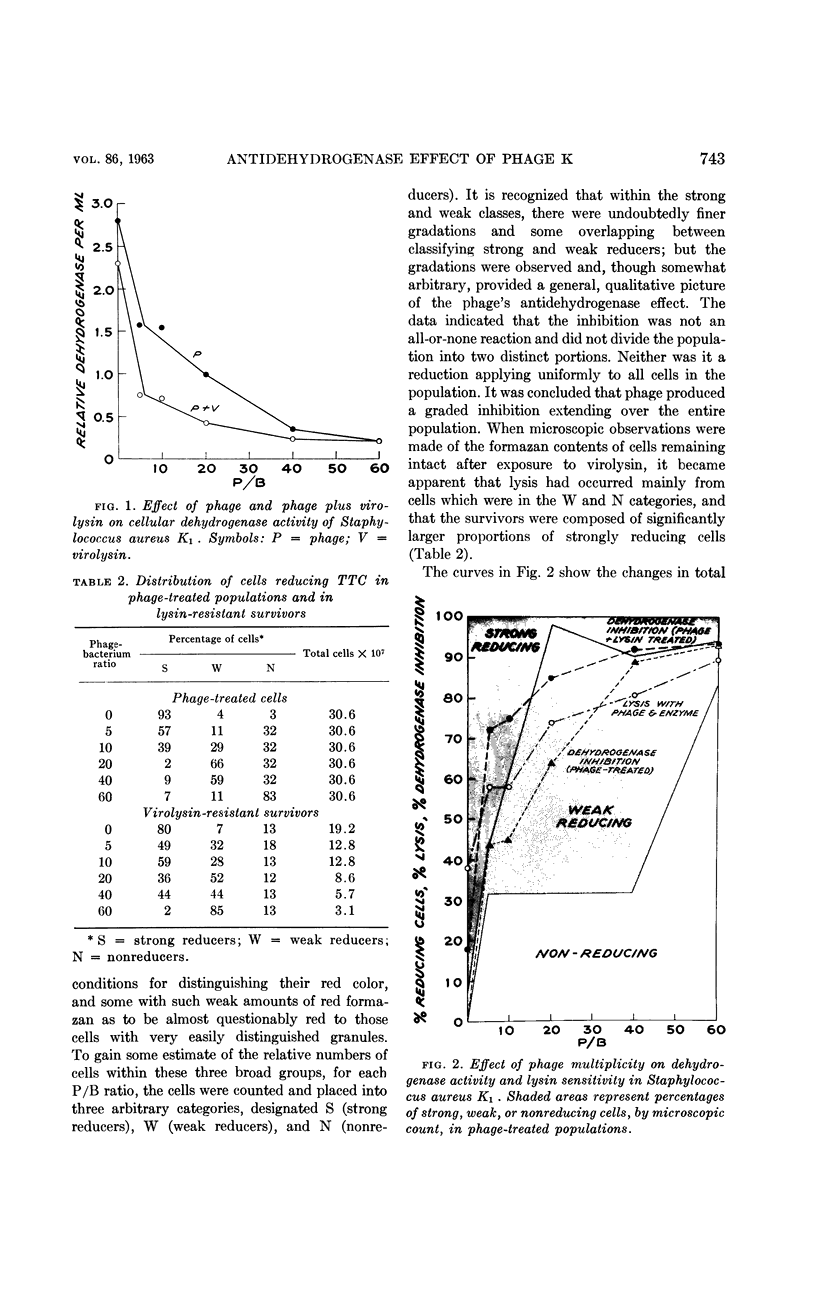
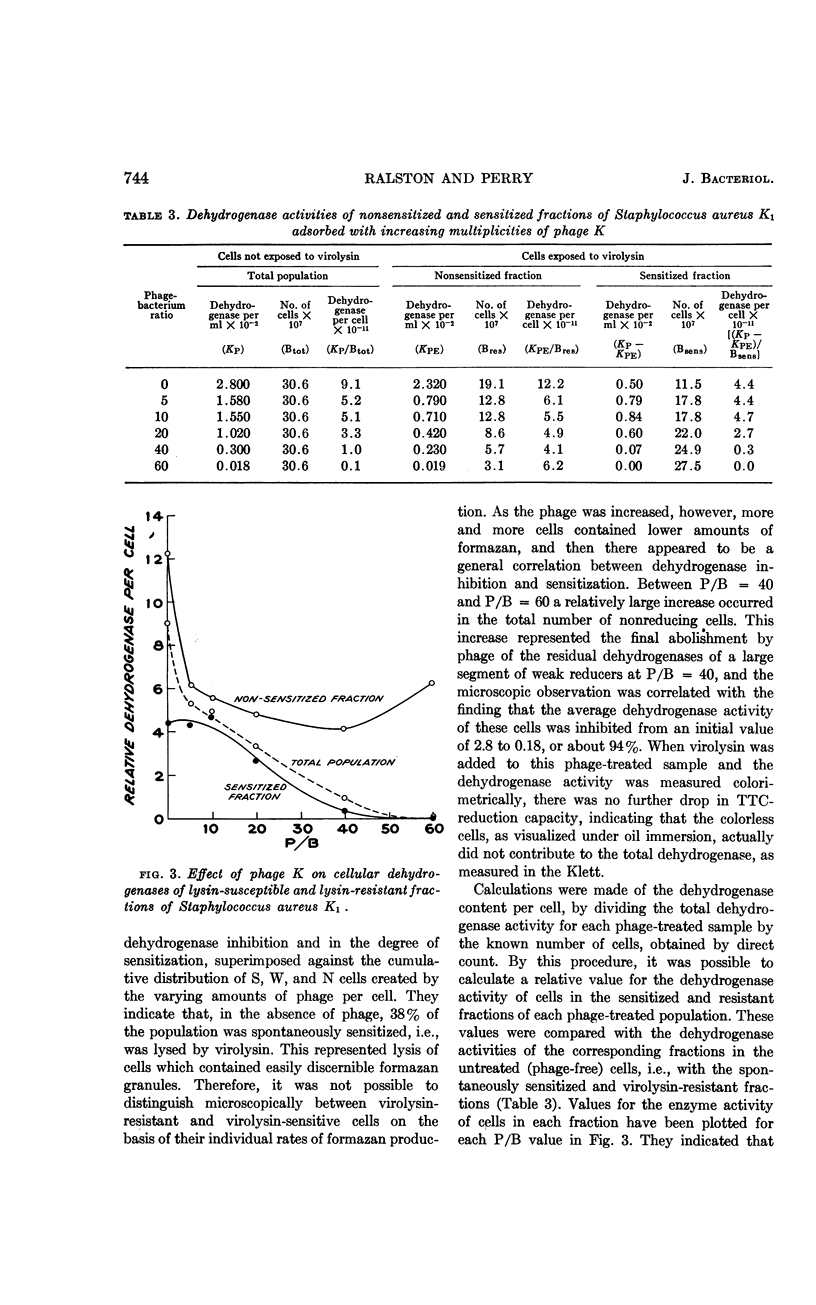
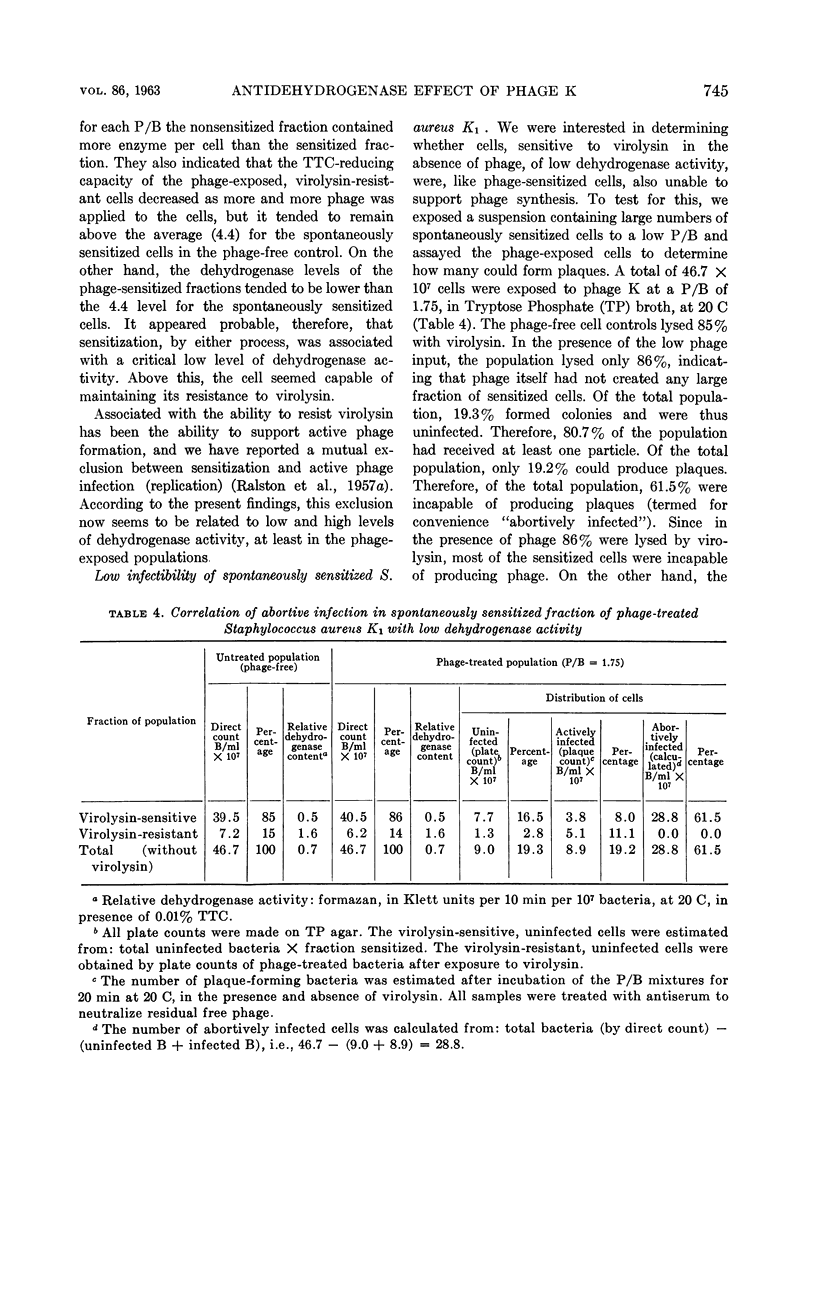
Ralston, D. J. (University of California, Berkeley) and M. D. Perry. Inhibitory action of phage K on staphylococcal dehydrogenases. II. Its possible relationship to sensitization and cell lysis. J. Bacteriol. 86:740–748. 1963.—By measuring the reduction of the dye triphenyl tetrazolium chloride to the insoluble red formazan, an analysis was made of the inhibition by phage K of the dehydrogenase capacity of populations of Staphylococcus aureus K1, to determine to what extent this might be associated with the ability of phage K to sensitize the cells—a reaction characterized by the conversion of the cell wall to susceptibility to lysis by the staphylococcal enzyme, virolysin. Increasing multiplicities of phage progressively increased the fractions of sensitized cells and also caused increasing inhibition of the dehydrogenase activity of the populations. The dehydrogenase activities of the sensitized fractions were compared with those of the nonsensitized fractions. Over a wide range of phage-bacterium ratios, the dehydrogenase activities of the sensitized fractions were found to be lower than those of the nonsensitized fractions. Microscopically, this was reflected by the appearance of large numbers of cells with a reduced amount of visible formazan granules. When lysin was added to the phage-treated cells, lysis occurred mainly from cell fractions which possessed little or no tetrazolium-reducing capacity. The data indicated that sensitization by phage was accompanied by a marked decrease in cellular dehydrogenase activity but was not associated with a complete inhibition of these enzymes. A comparison was made between the dehydrogenases of phage-sensitized cells and cells found to be “spontaneously” sensitive to virolysin, i.e., lysed by the enzyme without any prior exposure to phage. Like phage-sensitized cells, the spontaneously sensitized staphylococci possessed low dehydrogenase activity and lacked the capacity to support phage synthesis. In tests of a given cell preparation, the dehydrogenase levels of the phage-sensitized fractions were found to be close to, or even lower than, the level of the spontaneously sensitized fraction, suggesting that in S. aureus K1 the sensitized state is associated in some manner with a reduction of the dehydrogenase activity to a critical level. There is as yet no evidence for any direct causal relationship between sensitization and dehydrogenase inhibition.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEER M. Disposition of membranes in Alcaligenes faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1960 Nov;80:659–664. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.5.659-664.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN D. D., KOZLOFF L. M. Morphological localization of the bacteriophage tail enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S. GROWTH REQUIREMENTS OF BACTERIAL VIRUSES. Bacteriol Rev. 1949 Mar;13(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/br.13.1.1-24.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORBES M., SEVAG M. G. Action of amino acids on bacterial dehydrogenases and glycolysis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Jul;77(3):565–569. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH R. C., SIMINOVITCH L. The action of T2 bacteriophage ghosts on Escherichia coli B. Can J Microbiol. 1955 Dec;1(9):757–774. doi: 10.1139/m55-090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEAGY F. C. The effect of 2,4-dinitrophenol and phage T2 on Escherichia coli B. J Bacteriol. 1950 Mar;59(3):367–373. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.3.367-373.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The effect of phage infection on the metabolic activity of the host cell. Br J Exp Pathol. 1952 Aug;33(4):368–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH G., DRYER W. J. Characterization of an enzyme of phage T2 as a lysozyme. Virology. 1958 Aug;6(1):291–293. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHMAN I. R., HERRIOTT R. M. The protein coats or ghosts or coliphage T2. III. Metabolic studies of Escherichia coli B infected with T2 bacteriophage ghosts. J Gen Physiol. 1958 May 20;41(5):1067–1082. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS M. M., SISTROM W. R. Intracellular location of carotenoid pigments and some respiratory enzymes in Sarcina lutea. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78:778–787. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.778-787.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY J. S. A phage-associated enzyme of Bacillus megaterium which destroys the bacterial cell wall. Virology. 1957 Dec;4(3):563–581. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S. INHIBITORY ACTION OF PHAGE K ON STAPHYLOCOCCAL DEHYDROGENASES. I. EFFECT ON VARIOUS STRAINS OF STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS, INCLUDING MEMBERS OF THE PHAGE-TYPING SERIES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:666–672. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.4.666-672.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B. S., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Lysis from without of S. aureus K1 by the combined action of phage and virolysin. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Nov 20;41(2):343–358. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., BAER B., LIEBERMAN M., KRUEGER A. P. Virolysin, a virus-induced lysin: its appearance and function in phage-infected staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Mar;24:313–325. doi: 10.1099/00221287-24-3-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALSTON D. J., LIEBERMAN M., BAER B., KRUEGER A. P. Staphylococcal virolysin, a phage-induced lysin; its differentiation from the autolysis of normal cells. J Gen Physiol. 1957 May 20;40(5):791–807. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPIZIZEN J. The effect of virus infection of pyruvate metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):333–341. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STORCK R., WACHSMAN J. T. Enzyme localization in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.784-790.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. Characterization of the protoplasmic constituents of bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):696–702. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.696-702.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]