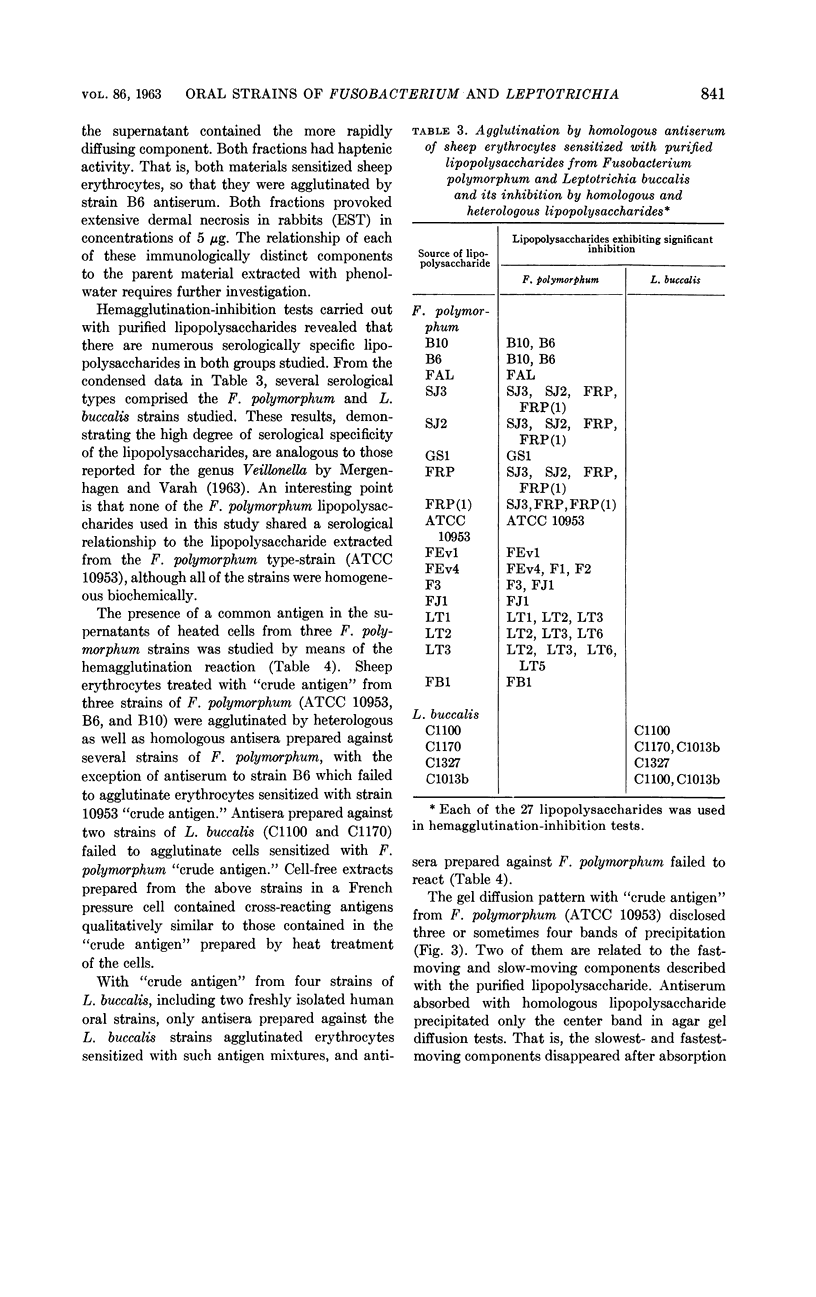
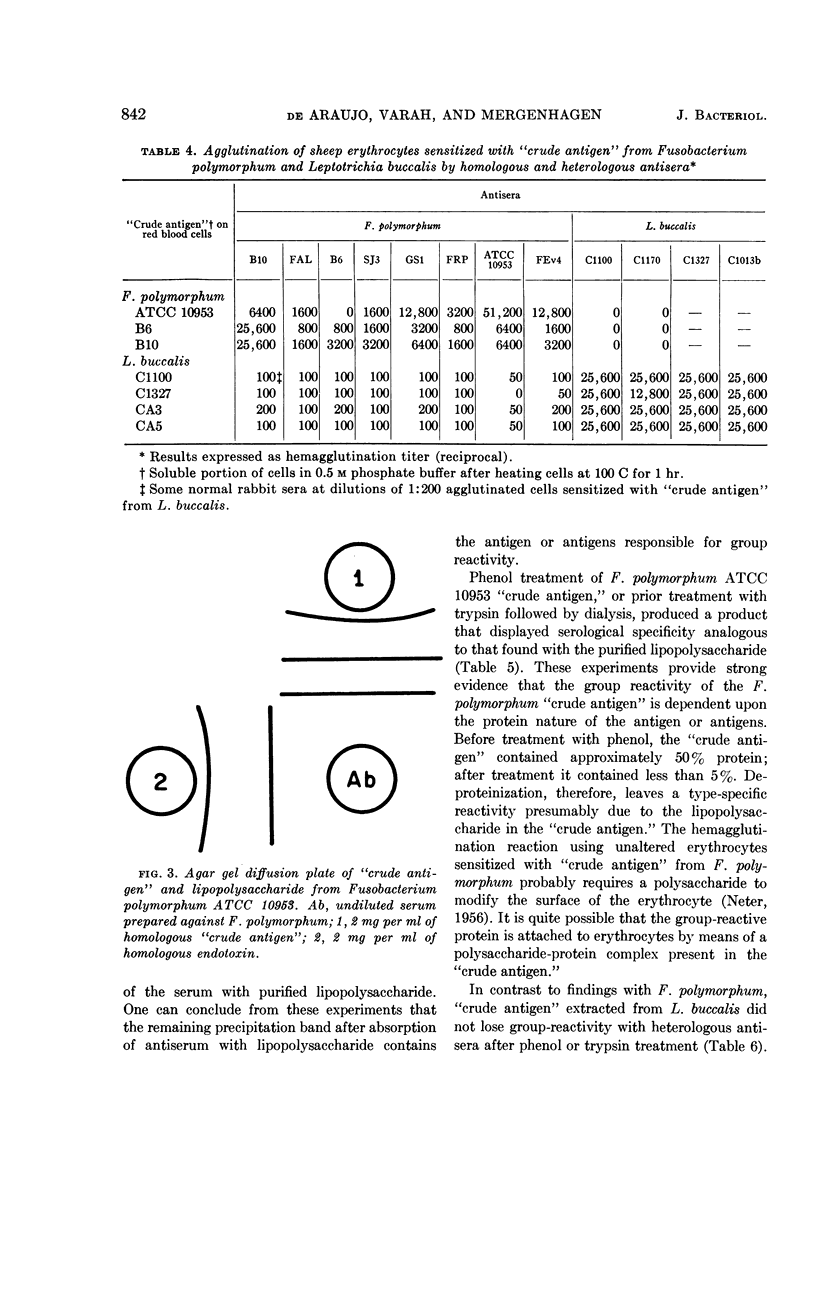
Abstract
de Araujo, Wilson C. (National Institute of Dental Research, Bethesda, Md.), Eileen Varah, and Stephan E. Mergenhagen. Immunochemical analysis of human oral strains of Fusobacterium and Leptotrichia. J. Bacteriol. 86:837–844. 1963.—Lipopolysaccharides, isolated by phenol-water extraction of 27 strains of oral gram-negative bacteria conforming either to Fusobacterium polymorphum or Leptotrichia buccalis, were shown to be endotoxic by their ability to alter dermal reactivity to epinephrine and to be serologically specific by hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition tests. Numerous serotypes of these organisms were detected by hemagglutination tests with purified lipopolysaccharides. A F. polymorphum lipopolysaccharide produced two visible precipitin bands in agar gel with antiserum prepared against the homologous organism. Each of the immunologically distinct components of the endotoxin, isolated by differential centrifugation, altered dermal reactivity to epinephrine and acted as a hapten in hemagglutination tests. Crude antigens from F. polymorphum strains, released in supernatant fluids of heat-killed bacterial suspensions, showed broad serological cross-reactivity with antiserum prepared against homologous and heterologous strains of F. polymorphum but not with antiserum prepared against L. buccalis strains. Broad serological cross-reactivity of these crude F. polymorphum antigens could be eliminated by prior treatment with phenol or trypsin, indicating that the common antigen or antigens in these organisms are protein. Double-diffusion tests in agar identified and differentiated type-specific lipopolysaccharide from other antigens extracted by heat from these organisms. Similarly prepared crude antigens from L. buccalis had broad serological activity with antiserum prepared against various strains of L. buccalis but not with F. polymorphum. In contrast to the crude antigens from F. polymorphum, this serological cross-reactivity could not be eliminated by treatment with phenol or trypsin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. Isolation of Leptotrichia buccalis and Fusobacterium species from oral material. Nature. 1957 Nov 16;180(4594):1056–1057. doi: 10.1038/1801056b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUCCINO R., LINGLEY J., ISRAEL J. Evaluation of the epinephrine skin test as a biological assay for endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:724–726. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISRAELY M. N., OMATA R. R. A selective medium for oral fusobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):677–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.677-680.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLNER P. D., BOHAN C. D. Serology of the soluble antigens of Clostridium perfringens types A-F by agar-gel diffusion. J Bacteriol. 1962 Feb;83:284–296. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.2.284-296.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILMOUR M. N., HOWELL A., Jr, BIBBY B. G. The classification of organisms termed Leptotrichia (Leptothrix) buccalis. I. Review of the literature and proposed separation into Leptotrichia buccalis Trevisan, 1879 and Bacterionema gen. nov., B. matruchotti (Mendel, 1919) comb. nov. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Jun;25:131–141. doi: 10.1128/br.25.2.131-141.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUSTAFSON R. L., KROEGER A. V. Antigenic characteristics of Leptotrichia buccalis (Fusobacterium fusiforme). J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84:1313–1320. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1313-1320.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON R. D., ZAHLER S. A. A study of Leptotrichia buccalis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Mar;73(3):386–393. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.3.386-393.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C., RIBI E. Biological properties of parent endotoxins and lipoid fractions, with a kinetic study of acid-hydrolyzed endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:665–684. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKINS H. C., BARKER H. A. Fermentative processes of the fusiform bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1951 Feb;61(2):101–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.2.101-114.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERGENHAGEN S. E., MARTIN G. R., SCHIFFMANN E. Studies on an endotoxin of a group C Neisseria meningitidis. J Immunol. 1963 Feb;90:312–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERGENHAGEN S. E., VARAH E. Serologically specific lipopolysaccharides from oral veillonella. Arch Oral Biol. 1963 Jan-Feb;8:31–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(63)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERGENHAGEN S. E., ZIPKIN I., VARAH E. Immunological and chemical studies on an oral Veillonella endotoxin. J Immunol. 1962 Apr;88:482–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E. Bacterial hemagglutination and hemolysis. Bacteriol Rev. 1956 Sep;20(3):166–188. doi: 10.1128/br.20.3.166-188.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OMATA R. R., BRAUNBERG R. C. Oral Fusobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1960 Dec;80:737–740. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.6.737-740.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIBI E., HASKINS W. T., MILNER K. C., ANACKER R. L., RITTER D. B., GOODE G., TRAPANI R. J., LANDY M. Physicochemical changes in endotoxin associated with loss of biological potency. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:803–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.803-814.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding E. H., Rettger L. F. The Fusobacterium Genus: I. Biochemical and Serological Classification. J Bacteriol. 1937 Nov;34(5):535–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.34.5.535-548.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varney P. L. THE SEROLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF FUSIFORM BACILLI. J Bacteriol. 1927 Apr;13(4):275–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.13.4.275-314.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]