Abstract
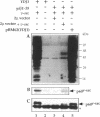
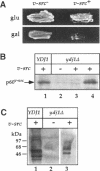
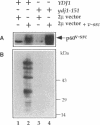
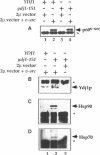
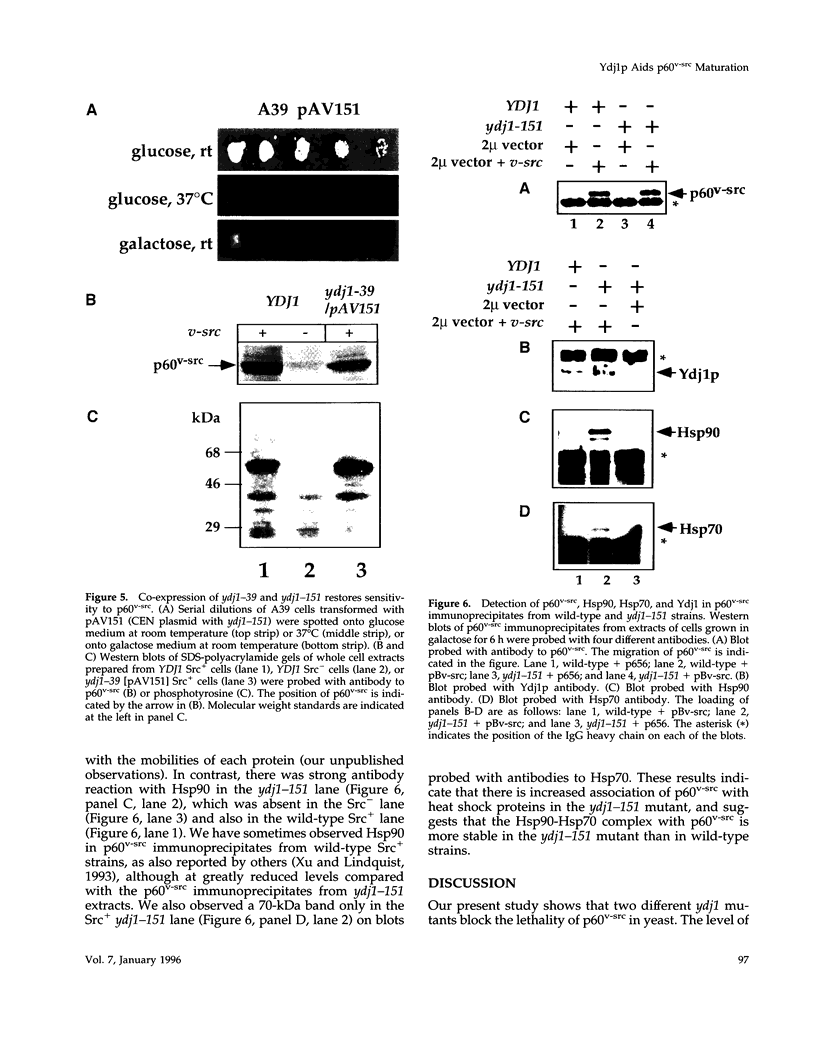
Molecular chaperones have been implicated in the formation of active p60v-src tyrosine kinase. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, expression of p60v-src causes cell death, a phenomenon that requires functional Hsp90. We show here that mutations in a member of a second class of chaperones, the yeast dnaJ homologue YDJ1, suppress the lethality caused by p60v-src. One p60v-src-resistant ydj1 mutant, ydj1-39, which has two point mutations in the highly conserved "J" domain, has reduced levels of v-src mRNA and protein. However, a ydj1 null mutant produces normal quantities of active p60v-src, indicating that Ydj1p facilitates, but is not essential for, the formation of active p60v-src. We also report p60v-src-resistance in a previously identified temperature-sensitive ydj1 mutant, ydj1-151. In this mutant, the level of p60v-src remains unaltered, but the protein is much less active in vivo. In addition, p60v-src immunoprecipitates from the ydj1-151 strain contained Hsp90 and Hsp70 in greater amounts than in wild-type strains. Ydj1 protein was also detected in p60v-src immunoprecipitates from both wild-type and ydj1-151 strains. These results indicate that Ydj1p participates in the formation of active p60v-src via molecular chaperone complexes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aligue R., Akhavan-Niak H., Russell P. A role for Hsp90 in cell cycle control: Wee1 tyrosine kinase activity requires interaction with Hsp90. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 15;13(24):6099–6106. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atencio D. P., Yaffe M. P. MAS5, a yeast homolog of DnaJ involved in mitochondrial protein import. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):283–291. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D. One and two codon insertion mutants of bacteriophage f1. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(3):288–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00425599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohen S. P., Yamamoto K. R. Isolation of Hsp90 mutants by screening for decreased steroid receptor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11424–11428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschelli F., Uptain S. M., Lightbody J. J. The lethality of p60v-src in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the activation of p34CDC28 kinase are dependent on the integrity of the SH2 domain. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105(Pt 2):519–528. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The specific interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60src, with two cellular proteins. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S. Interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus protein pp60src with the cellular proteins pp50 and pp90. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;123:1–22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70810-7_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Jarosik G., Andersen J., Queral-Lustig A., Fedor-Chaiken M., Broach J. R. Expression of Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein pp60v-src in Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2180–2187. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J., Yonemoto W., Darrow D. Interaction between the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein and two cellular phosphoproteins: analysis of the turnover and distribution of this complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):9–19. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. J., Cyr D. M., Douglas M. G. Eukaryotic homologues of Escherichia coli dnaJ: a diverse protein family that functions with hsp70 stress proteins. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jun;4(6):555–563. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.6.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. J., Cyr D. M., Douglas M. G. YDJ1p facilitates polypeptide translocation across different intracellular membranes by a conserved mechanism. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1143–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80063-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. J., Douglas M. G. Characterization of YDJ1: a yeast homologue of the bacterial dnaJ protein. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):609–621. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. J., Langley E., Wilson E. M., Vidal J. Hormone-dependent transactivation by the human androgen receptor is regulated by a dnaJ protein. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 10;270(10):5251–5257. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.10.5251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. J., Tsai J., Casey P. J., Douglas M. G. Farnesylation of YDJ1p is required for function at elevated growth temperatures in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18890–18895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Lindquist S. Conservation of Hsp90 macromolecular complexes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24983–24988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellaiah A., Davis A., Mohanakumar T. Cloning of a unique human homologue of the Escherichia coli DNAJ heat shock protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 18;1174(1):111–113. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90103-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Transit of pp60v-src to the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7117–7121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutforth T., Rubin G. M. Mutations in Hsp83 and cdc37 impair signaling by the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase in Drosophila. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1027–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr D. M., Douglas M. G. Differential regulation of Hsp70 subfamilies by the eukaryotic DnaJ homologue YDJ1. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9798–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyr D. M., Langer T., Douglas M. G. DnaJ-like proteins: molecular chaperones and specific regulators of Hsp70. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Apr;19(4):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldheim D., Rothblatt J., Schekman R. Topology and functional domains of Sec63p, an endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein required for secretory protein translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3288–3296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio M., Wilson L. K., Trager J. B., Thorner J., Martin G. S. Aberrant protein phosphorylation at tyrosine is responsible for the growth-inhibitory action of pp60v-src expressed in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Biol Cell. 1994 Mar;5(3):283–296. doi: 10.1091/mbc.5.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydman J., Nimmesgern E., Ohtsuka K., Hartl F. U. Folding of nascent polypeptide chains in a high molecular mass assembly with molecular chaperones. Nature. 1994 Jul 14;370(6485):111–117. doi: 10.1038/370111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. A., Brott B. K., De Leon J. H., Perdew G. H., Jove R., Pratt W. B. Reconstitution of the multiprotein complex of pp60src, hsp90, and p50 in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):2902–2908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Garber E. A., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Biochemical properties of p60v-src mutants that induce different cell transformation parameters. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):849–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.849-857.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura Y., Yahara I., Lindquist S. Role of the protein chaperone YDJ1 in establishing Hsp90-mediated signal transduction pathways. Science. 1995 Jun 2;268(5215):1362–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.7761857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Jove R., Hanafusa H. Characterization of avian and viral p60src proteins expressed in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4455–4459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E. J., McCarty J., Bukau B., Chirico W. J. Conserved ATPase and luciferase refolding activities between bacteria and yeast Hsp70 chaperones and modulators. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 24;368(3):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00704-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luke M. M., Sutton A., Arndt K. T. Characterization of SIS1, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae homologue of bacterial dnaJ proteins. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):623–638. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyata Y., Yahara I. The 90-kDa heat shock protein, HSP90, binds and protects casein kinase II from self-aggregation and enhances its kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7042–7047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. F., Lindquist S. Mutational analysis of Hsp90 function: interactions with a steroid receptor and a protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3917–3925. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.7.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S., Iwahori A., Kato S. Human cDNA encoding DnaJ protein homologue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 18;1174(1):114–116. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90104-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Khursheed B., Garabedian M. J., Fortin M. G., Lindquist S., Yamamoto K. R. Reduced levels of hsp90 compromise steroid receptor action in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):166–168. doi: 10.1038/348166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B. The role of heat shock proteins in regulating the function, folding, and trafficking of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21455–21458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. Targeting, disruption, replacement, and allele rescue: integrative DNA transformation in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:281–301. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94022-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. A., Way J. C. Eukaryotic DnaJ homologs and the specificity of Hsp70 activity. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90287-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stancato L. F., Chow Y. H., Hutchison K. A., Perdew G. H., Jove R., Pratt W. B. Raf exists in a native heterocomplex with hsp90 and p50 that can be reconstituted in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21711–21716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall D., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The NH2-terminal 108 amino acids of the Escherichia coli DnaJ protein stimulate the ATPase activity of DnaK and are sufficient for lambda replication. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 18;269(7):5446–5451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendler P. A., Boschelli F. Src homology 2 domain deletion mutants of p60v-src do not phosphorylate cellular proteins of 120-150 kDa. Oncogene. 1989 Feb;4(2):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Lindquist S. Heat-shock protein hsp90 governs the activity of pp60v-src kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7074–7078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong T., Arndt K. T. The yeast SIS1 protein, a DnaJ homolog, is required for the initiation of translation. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1175–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90646-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]