Abstract
We have analyzed the in vitro chemosensitivity profiles of 115 Kenyan isolates for chloroquine (CQ), piperaquine, lumefantrine (LM), and dihydroartemisinin in association with polymorphisms in pfcrt at codon 76 and pfmdr1 at codon 86, as well as with variations of the copy number of pfmdr1. The median drug concentrations that inhibit 50% of parasite growth (IC50s) were 41 nM (interquartile range [IQR], 18 to 73 nM), 50 nM (IQR, 29 to 96 nM), 32 nM (IQR, 17 to 46 nM), and 2 nM (IQR, 1 to 3 nM) for CQ, LM, piperaquine, and dihydroartemisinin, respectively. The activity of CQ correlated inversely with that of LM (r2 = −0.26; P = 0.02). Interestingly, parasites for which LM IC50s were higher were wild type for pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86. All isolates had one pfmdr1 copy. Thus, the decrease in LM activity is associated with the selection of wild-type pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86 parasites, a feature that accounts for the inverse relationship between CQ and LM. Therefore, the use of LM-artemether is likely to lead to the selection of more CQ-susceptible parasites.
Chemotherapy is still the main approach for the control of malaria, and current strategies for malaria treatment rely on the use of combinations of drugs that include artemisinin compounds. Although this strategy is designed to reduce the chance of resistance emerging, there is considerable concern that this will inevitably occur.
For instance, the combination of lumefantrine (LM) and artemether (ATM), known as Coartem, has become the first-line treatment for malaria in many African countries, including Kenya (19). ATM is converted in vivo to dihydroartemisinin (DHA). Emerging reports indicate that the use of LM (in Coartem) selects for parasites that show increased tolerance to Coartem, and these parasites select for a wild-type pfmdr1 genotype or show increased copy numbers of pfmdr1, a gene associated with chloroquine (CQ) and mefloquine (MFQ) resistance (7, 13, 15, 20, 36, 38). Thus, there is concern that resistance to LM could emerge rapidly. On the other hand, recent reports from Southeast Asia indicate that resistance to artemisinin derivatives is increasing, threatening the concept of artemisinin-based combinations (8).
Another combination, piperaquine (PQ) and DHA, known as Artekin, is undergoing clinical evaluation (17, 39, 42). This drug is efficacious, safe, and affordable and thus is likely to become an alternative to Coartem. PQ is a bisquinoline derivative consisting of two linked CQ molecules. Although reports indicate that PQ retains potency against CQ-resistant parasites (3), there is concern that PQ could become less susceptible against a backdrop of high CQ resistance (17, 22).
In this paper, we sought to analyze the in vitro activities of the antimalarials LM, DHA, and PQ in relation to polymorphisms in pfcrt at codon 76 (pfcrt-76) and in pfmdr1 at codon 86 (pfmdr1-86) and in relation to pfmdr1 copy number variations in Kenyan isolates. We used CQ as a reference drug.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
CQ was purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (Poole, Dorset, United Kingdom). LM, PQ, and DHA were gifts from Steve Ward, Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Liverpool, United Kingdom.
Parasite adaptation.
Plasmodium falciparum parasites were collected from malaria patients as part of several clinical studies that took place between 2005 and 2008 in the Kilifi district of Kenya. From the field, blood samples were collected, placed in “transport medium” (containing RPMI medium and albumin), and taken to the laboratory for long-term culture adaption, and other isolates were cryopreserved in liquid nitrogen before adaption. The detailed description of this long-term parasite adaptation procedure is given elsewhere (32). Provision of informed consent for the original studies was ensured by the Kenya Medical Research Institute, Nairobi.
Chemosensitivity testing.
Routine cultures were carried out in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco BRL, United Kingdom) supplemented with 15% (vol/vol) normal human serum, 25 mM bicarbonate, 2 mM glutamine, 25 mM HEPES buffer, and 3.6 nM para-aminobenzoic acid. The human blood used to culture the parasites was obtained from healthy subjects and was washed three times with RPMI culture medium that was not supplemented with serum. CQ was dissolved in distilled water, and LM and PQ were dissolved in 90% methanol plus 10% HCl; DHA was dissolved in 70% ethanol. The ranges tested (in a threefold dilution) were 7,180 to 0.12 nM for CQ and PQ, 17,505 to 0.3 nM for LM, and 163 to 0.22 nM for DHA. Assays were carried out in 200 μl of culture containing 0.5% parasitemia and 1.5% hematocrit, in 96-well microtiter plates. Cultures were incubated at 37°C in a gas mixture of 90% N2, 5% CO2, and 5% O2 for 66 h. Thereafter, [3H]hypoxanthine was added to the culture for another 18 h. Cells were then lysed by freeze-thawing; radiolabeled DNA was harvested on fiberglass paper (TomTec, Inc., and Perkin-Elmer); and the amount of ionizing radiation was determined using a Wallac 1450 MicroBeta counter.
Results were expressed as the drug concentration required for 50% inhibition of [3H]hypoxanthine incorporation into parasite nucleic acid (IC50), obtained by nonlinear regression analysis of the dose-response curve. We employed two reference P. falciparum laboratory strains: V1S, a multidrug-resistant strain, and 3D7, a drug-sensitive strain. IC50s were measured two and four times for field isolates and reference strains, respectively.
Genotyping of pfcrt at codon 76 and of pfmdr1 at codon 86.
Blood samples (50 μl) of in vitro-adapted isolates were spotted onto filter paper, air dried, and stored in plastic bags with silica gel at ambient temperature. DNA was extracted by boiling, and single-base changes at pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86 were detected as reported previously (24).
Assessment of the copy number of pfmdr1.
The P. falciparum reference isolates used in the analysis of pfmdr1 copy numbers were DD2 (2 to 3 copies), D10 (1 copy), and 3D7 (1 copy). To estimate the copy numbers of pfmdr1, we used a relative-quantification TaqMan real-time PCR assay published elsewhere (29). In summary, the relative expression of pfmdr1 in each isolate was compared with that of a housekeeping gene (β-tubulin) using specific fluorescently labeled probes (6-carboxyfluorescein and 2,7-dimethoxy-4,5-dichloro-6-caboxy-fluorescein) in a real time PCR assay. Every TaqMan run contained three calibrator DNA reference strains with known copy numbers. All assays were run in triplicate on an Applied Biosystems real-time PCR system, model 7500.
Statistical analysis.
Statistical analyses were carried out using the Stata program, version 9 (Stata, Inc.). We compared differences between groups using the Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test. We measured correlation using pairwise correlation analysis. All pairwise correlations of drug activity were estimated using log-transformed IC50s. The level of significance was set at a P value of <0.05.
RESULTS
Chemosensitivity test.
We first established the IC50s of drugs against reference strains. Against V1S, the IC50s of CQ, PQ, LM, and DHA were 158 ± 75, 42 ± 10, 24 ± 14, and 2 ± 1 nM, respectively; against 3D7, these values were 6.5 ± 2.3, 27 ± 17, 96 ± 12, and 2.0 ± 0.1 nM, respectively.
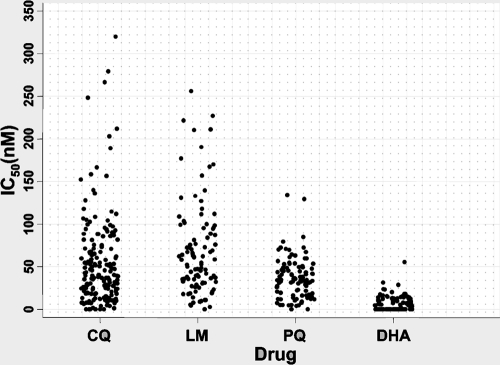
We have adapted 115 isolates for long-term culture and analyzed their drug chemosensitivity profiles. The median IC50s of CQ, PQ, LM, and DHA were 41 nM (interquartile range [IQR], 18 to 73 nM), 32 nM (IQR, 17 to 46 nM), 50 nM (IQR, 29 to 96 nM), and 2 nM (IQR, 1 to 3 nM), respectively (Fig. 1). As expected, DHA was the most active drug, followed by PQ, CQ, and LM. Interestingly, LM IC50s were >100 nM for about 20% of isolates (Fig. 1).
FIG. 1.
In vitro activities of CQ, LM, PQ, and DHA against Plasmodium falciparum isolates.
We have assessed the correlation between the drugs tested. LM activity correlated with DHA activity (r2 = 0.4; P < 0.0001) and with PQ activity (r2 = 0.19; P = 0.05). Interestingly, we observed an inverse relationship between the activities of CQ and LM (r2 = −0.26; P = 0.02), suggesting that selection of LM resistance would be associated with an increase in CQ activity (Table 1).
TABLE 1.
Correlation of in vitro antimalarial activitiesa
| Drug 1 | Drug 2 | Correlation coefficient (r2) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM | CO | −0.26 | 0.02 |
| LM | PQ | 0.19 | 0.05 |
| LM | DHA | 0.40 | <0.0001 |
| PQ | CQ | 0.16 | 0.13 |
| PQ | DHA | 0.04 | 0.69 |
| DHA | CQ | 0.14 | 0.16 |
All pairwise correlations of drug activity were estimated using log-transformed IC50s. Significant associations are shown in boldface.
pfcrt-76.
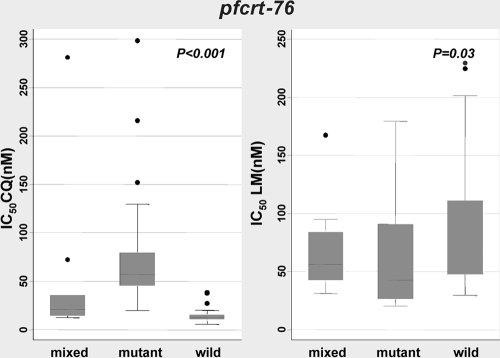
We also analyzed the pfcrt-76 genotype in association with drug activity (Fig. 2). Based on CQ IC50s, isolates can be classified into three distinct groups. For the first group, which has wild-type pfcrt-76 (n = 31), the median IC50 of CQ is 13 nM (IQR, 10 to 15 nM). The second group is composed of mixed-genotype (wild-type and mutant) isolates (n = 11), for which the median CQ IC50 is 21 nM (IQR, 15 to 35 nM). The third group, which forms the majority of isolates (n = 70), consists of pfcrt-76 mutants for which the median CQ IC50 is 57 nM (IQR, 46 to 80 nM). These differences are significant (P < 0.001) (Fig. 2). Based on the pfcrt genotype, more than 60% of isolates are resistant to CQ.
FIG. 2.
Relationship between CQ and LM IC50s and the pfcrt genotype at codon 76.
Median PQ IC50s were very similar for pfcrt-76 mutant (38 nM [IQR, 20 to 58 nM]) (n = 39) and wild-type (35 nM [IQR, 18 to 56 nM]) (n = 23) parasites. However, the median LM IC50 was lowest (43 nM [IQR, 27 to 90 nM]) for the pfcrt-76 mutant group (n = 40), intermediate (56 nM [IQR, 42 to 84 nM]) for the mixed-genotype group (n = 9), and highest (67 nM [IQR, 48 to 111 nM]) for wild-type parasites (n = 23); these differences were statistically significant (P = 0.03) (Fig. 2). Thus, wild-type pfcrt-76 parasites were associated with decreased susceptibility to LM, in line with the inverse relationship with CQ resistance. DHA IC50s did not differ as a function of the pfcrt-76 genotype.
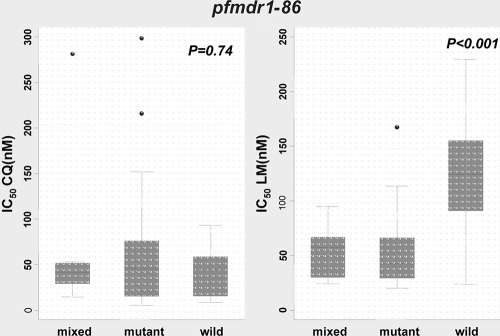
pfmdr1-86.
Median CQ IC50s were similar for wild-type and mutant pfmdr1-86 parasites (Fig. 3). However, the median DHA IC50 was higher (though marginally so) for pfmdr1 wild-type isolates (n = 23) than for mutant isolates (n = 47) (3 nM [IQR, 3 to 4 nM] versus 2 nM [IQR, 1 to 3 nM]; P = 0.04). Interestingly, as in the case of pfcrt-76, the median LM IC50 was highest (124 nM [IQR, 90 to 155 nM]) for pfmdr1-86 wild-type parasites (n = 17), intermediate (57 nM [IQR, 30 to 67 nM]) for mixed genotypes (n = 8), and lowest (43 nM [IQR, 29 to 66 nM]) for mutant isolates (n = 47); these differences were statistically significant (P < 0.001) (Fig. 3). Thus, pfmdr1-86 contributes significantly to reduced susceptibility to LM.
FIG. 3.
Relationship between CQ and LM IC50s and the pfmdr1 genotype at codon 86.
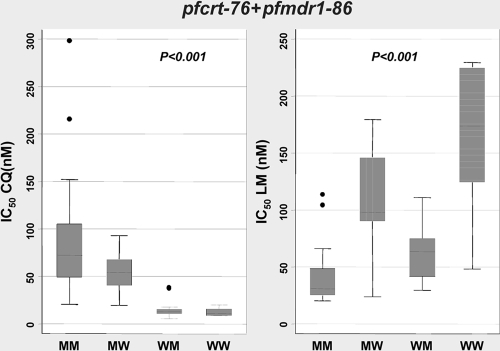
pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86.
We also investigated the effects of both pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86 mutations in relation to drug activity. To do so, we excluded parasites with mixed genotypes (at pfcrt-76 or pfmdr1-86). Parasites were classified as pfcrt-76 mutant and pfmdr1-86 mutant (M-M), pfcrt-76 mutant and pfmdr1-86 wild type (M-W), pfcrt-76 wild type and pfmdr1-86 mutant (W-M), or wild type at both genes (W-W). The median CQ IC50 for parasites with the M-M genotype (n = 45) was significantly higher (72 nM [IQR, 49 to 105 nM]) than those for all others; the next highest median CQ IC50 (54 nM [IQR, 41 to 68 nM]) was that for M-W parasites (n = 15), and, as expected, the lowest CQ IC50s (13 nM [IQR, 11 to 15 nM] and 11 nM [IQR, 9 to 15 nM]) were observed for W-M (n = 21) and W-W (n = 6) parasites, respectively (Fig. 4). Likewise, the median LM IC50 for M-M parasites (n = 25) was significantly lower (31 nM [IQR, 25 to 48 nM]) than those for M-W (99 nM [IQR, 90 to 146 nM]) (n = 11) and W-M (63 nM [IQR, 41 to 75 nM]) (n = 17) parasites. The highest median LM IC50, 173 nM (IQR, 124 to 224 nM), was observed for W-W parasites (n = 6). These observations were statistically significant (P < 0.001) (Fig. 4). Thus, as expected, the presence of mutant genotypes in pfcrt76 and pfmdr186 is strongly associated with CQ resistance but also with increased susceptibility to LM.
FIG. 4.
Relationship between CQ and LM IC50s and the pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86 genotypes at codons 76 and 86, respectively. MM, mutant pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86; MW, mutant pfcrt-76 and wild-type pfmdr1-86; WM, wild-type pfcrt-76 and mutant pfmdr1-86; WW, wild-type pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86.
Analysis of pfmdr1 copy number.
To gain more insight into the mechanism of decreased susceptibility to LM, we analyzed pfmdr1 copy number variations in association with drug chemosensitivity profiles. We used the reference strain Dd2, which has 3 pfmdr1 copies, though 2 copies have also been reported (5, 41), and the single-copy-number strains D10 and 3D7. Since we did not know the exact copy number for our Dd2 clone, we classified our data as isolates with 1 copy versus those with more than 1 copy. We eliminated data where threshold cycle (CT) values were >35 and ΔΔCT values were >1.5.
All 78 isolates analyzed for pfmdr1 amplification were estimated to have one single copy of pfmdr1. Thus, no association could be established between pfmdr1 amplification and drug activities.
DISCUSSION
Coartem has been adopted in many parts of Africa, including Kenya, as the first-line treatment against malaria. We have generated baseline information on the in vitro susceptibilities of P. falciparum isolates in Kilifi, an area of endemicity on the Kenyan coast, to LM and DHA. LM IC50s are around 50 nM for most of the isolates; however, it is noteworthy that IC50s for more than 20% of the isolates are >100 nM. The in vitro activity of LM against field isolates from several areas where malaria is endemic has been investigated using the WHO microtest. In all these studies, LM activity was high, with IC50s of <30 nM for more than 95% of isolates (1, 4, 16, 21, 25, 26). In our study, we observed a higher LM IC50 range, and IC50s of >200 nM for some isolates, findings similar to those of a report from Senegal (27).
Previous reports have indicated that the use of Coartem is associated with the selection of parasites with wild-type pfmdr1-86, which are tolerant of low LM concentrations (7, 15, 36-38). Our data clearly indicate that the presence of wild-type pfmdr1-86 is associated with an increase in the LM IC50 (reduced susceptibility) and that this increase is more pronounced for parasites harboring a wild-type genotype at pfcrt-76, in line with a recent report (37). Since this genotype is associated with CQ susceptibility, it is not surprising that an inverse relationship exists between CQ and LM activity, a feature that has been reported in other areas where malaria is endemic (27, 30).
We also investigated variation in the copy number of pfmdr1. There was no evidence of pfmdr1 amplification in our isolates. This is consistent with previous data showing that pfmdr1 amplification is a relatively rare event in African isolates compared with those in Southeast Asia (14, 36, 37, 40, 41); the high rate of parasites with more than 1 pfmdr1 copy in Southeast Asia is likely due to the use of MFQ (23, 28, 29, 33). In Africa, MFQ is not used routinely for malaria treatment. Thus, under these conditions, one would expect parasites with multiple pfmdr1 copies to be rare in Africa. In Southeast Asia, reduced LM susceptibility has been associated with an increase in the pfmdr1 copy number (30); thus, it is possible that the continuous use of Coartem would select for parasites with increased pfmdr1 copy numbers.
The significant decrease in LM susceptibility in vitro for parasites with wild-type pfmdr1 and pfcrt genotypes that we report here is in line with previous work showing the emergence of LM-tolerant parasites after a single use of Coartem (7, 13, 15, 20, 36-38). However, it should be borne in mind that Coartem is effective at treating malaria, with high success rates (>90 to 95%), in many areas where malaria is endemic, including Kenya (11, 12, 18, 42). Thus, the mechanisms of Coartem resistance in vivo will likely involve other genes. Nevertheless, we propose that an increase in the frequency of parasites that are wild type for both pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86 (and probably in the pfmdr1 copy number) in the population would be the first step in the selection of resistance to LM and that these parasites will form the backdrop for LM resistance and thus for Coartem resistance.
Artekin is now undergoing clinical evaluation and is likely to become an alternative to Coartem (17, 39, 42). PQ is active against Kilifi isolates, with IC50s falling between 2 and 132 nM, and IC50s of >100 nM were found for only two of the isolates tested. Similar results were obtained for isolates from other areas of malaria endemicity (2, 3, 6). We also demonstrate that polymorphism in pfcrt-76 and pfmdr1-86 is not associated with decreased susceptibility to PQ. However, a recent study using transgenic parasite lines has indicated that the presence of the pfcrt mutant decreases susceptibility to PQ in vitro (22), and in vivo, Artekin efficacy may be reduced in an area of high CQ resistance in Southeast Asia (17). In Africa, however, this drug remains effective, probably due to the lower level of CQ resistance in Africa than in Southeast Asia (17, 39, 42).
We have also generated data on the activity of DHA. As expected, this drug is very active against P. falciparum; most IC50s are <25 nM. Our data indicate that wild-type pfmdr1-86 parasites are less susceptible to DHA than mutant parasites (although this difference is marginal), in line with previous reports (9, 10, 31, 34). Likewise, previous investigations have indicated that an increase in the pfmdr1 copy number and the presence of wild-type pfcrt genotypes are associated with reduced artemisinin susceptibility (20, 29, 33, 35). If this feature is translated in vivo, the emergence of LM resistance could be associated with a decrease in DHA efficacy. However, it remains to be seen whether the same would happen in vivo.
In conclusion, using laboratory-adapted African isolates, we have provided data showing that parasites that are less susceptible to LM in vitro are predominantly pfmdr1 and pfcrt wild type. We propose that such parasites would form a backdrop on which LM resistance may thrive. Since Coartem has been rolled out in Africa, it is therefore critical to monitor LM and DHA activity in vitro and polymorphism in pfcrt and pfmdr1.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Director of the Kenya Medical Research Institute for permission to publish these data.
This study was supported by the European Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership (EDCTP), The Wellcome Trust (WT077092 and WT084538), and The Global Health Research Award (GHRA-06-03) from the Health Research Board (Ireland) to Angus Bell and A.N. L.M. is an EDCPT Ph.D.-funded student. S.B. is funded through a Junior Group grant (SFB544, A7) by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG).
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 21 September 2009.
REFERENCES
- 1.Anderson, T. J., S. Nair, H. Qin, S. Singlam, A. Brockman, L. Paiphun, and F. Nosten. 2005. Are transporter genes other than the chloroquine resistance locus (pfcrt) and multidrug resistance gene (pfmdr) associated with antimalarial drug resistance? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49:2180-2188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barends, M., A. Jaidee, N. Khaohirun, P. Singhasivanon, and F. Nosten. 2007. In vitro activity of ferroquine (SSR 97193) against Plasmodium falciparum isolates from the Thai-Burmese border. Malar. J. 6:81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Basco, L. K., and P. Ringwald. 2003. In vitro activities of piperaquine and other 4-aminoquinolines against clinical isolates of Plasmodium falciparum in Cameroon. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47:1391-1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Basco, L. K., and P. Ringwald. 2007. Molecular epidemiology of malaria in Cameroon. XXIV. Trends of in vitro antimalarial drug responses in Yaounde, Cameroon. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 76:20-26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chinbuah, A. M., J. O. Gyapong, F. Pagnoni, E. K. Wellington, and M. Gyapong. 2006. Feasibility and acceptability of the use of artemether-lumefantrine in the home management of uncomplicated malaria in children 6-59 months old in Ghana. Trop. Med. Int. Health 11:1003-1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Deloron, P., J. Le Bras, J. A. Ramanamirija, and P. Coulanges. 1985. Plasmodium falciparum in Madagascar: in vivo and in vitro sensitivity to seven drugs. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 79:357-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dokomajilar, C., S. L. Nsobya, B. Greenhouse, P. J. Rosenthal, and G. Dorsey. 2006. Selection of Plasmodium falciparum pfmdr1 alleles following therapy with artemether-lumefantrine in an area of Uganda where malaria is highly endemic. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:1893-1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dondorp, A. M., F. Nosten, P. Yi, D. Das, A. P. Phyo, J. Tarning, K. M. Lwin, F. Ariey, W. Hanpithakpong, S. J. Lee, P. Ringwald, K. Silamut, M. Imwong, K. Chotivanich, P. Lim, T. Herdman, S. S. An, S. Yeung, P. Singhasivanon, N. P. Day, N. Lindegardh, D. Socheat, and N. J. White. 2009. Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 361:455-467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Duraisingh, M. T., P. Jones, I. Sambou, L. von Seidlein, M. Pinder, and D. C. Warhurst. 2000. The tyrosine-86 allele of the pfmdr1 gene of Plasmodium falciparum is associated with increased sensitivity to the anti-malarials mefloquine and artemisinin. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 108:13-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Duraisingh, M. T., C. Roper, D. Walliker, and D. C. Warhurst. 2000. Increased sensitivity to the antimalarials mefloquine and artemisinin is conferred by mutations in the pfmdr1 gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Microbiol. 36:955-961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Falade, C. O., A. O. Ogundele, B. O. Yusuf, O. G. Ademowo, and S. M. Ladipo. 2008. High efficacy of two artemisinin-based combinations (artemether-lumefantrine and artesunate plus amodiaquine) for acute uncomplicated malaria in Ibadan, Nigeria. Trop. Med. Int. Health 13:635-643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Falade, C. O., O. O. Ogunkunle, H. O. Dada-Adegbola, A. G. Falade, P. Ibarra de Palacios, P. Hunt, M. Virtanen, A. M. Oduola, and L. A. Salako. 2008. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of artemether-lumefantrine in the treatment of acute uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Nigerian infants and children. Malar. J. 7:246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Happi, C. T., G. O. Gbotosho, O. A. Folarin, A. Sowunmi, T. Hudson, M. O'Neil, W. Milhous, D. F. Wirth, and A. M. Oduola. 2009. Selection of Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance gene 1 alleles in asexual stages and gametocytes by artemether-lumefantrine in Nigerian children with uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53:888-895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Holmgren, G., A. Bjorkman, and J. P. Gil. 2006. Amodiaquine resistance is not related to rare findings of pfmdr1 gene amplifications in Kenya. Trop. Med. Int. Health 11:1808-1812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Humphreys, G. S., I. Merinopoulos, J. Ahmed, C. J. Whitty, T. K. Mutabingwa, C. J. Sutherland, and R. L. Hallett. 2007. Amodiaquine and artemether-lumefantrine select distinct alleles of the Plasmodium falciparum mdr1 gene in Tanzanian children treated for uncomplicated malaria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51:991-997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kaddouri, H., A. Djimde, S. Dama, A. Kodio, M. Tekete, V. Hubert, A. Kone, H. Maiga, O. Yattara, B. Fofana, B. Sidibe, C. P. Sangare, O. Doumbo, and J. Le Bras. 2008. Baseline in vitro efficacy of ACT component drugs on Plasmodium falciparum clinical isolates from Mali. Int. J. Parasitol. 38:791-798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Karunajeewa, H. A., I. Mueller, M. Senn, E. Lin, I. Law, P. S. Gomorrai, O. Oa, S. Griffin, K. Kotab, P. Suano, N. Tarongka, A. Ura, D. Lautu, M. Page-Sharp, R. Wong, S. Salman, P. Siba, K. F. Ilett, and T. M. Davis. 2008. A trial of combination antimalarial therapies in children from Papua New Guinea. N. Engl. J. Med. 359:2545-2557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kobbe, R., P. Klein, S. Adjei, S. Amemasor, W. N. Thompson, H. Heidemann, M. V. Nielsen, J. Vohwinkel, B. Hogan, B. Kreuels, M. Buhrlen, W. Loag, D. Ansong, and J. May. 2008. A randomized trial on effectiveness of artemether-lumefantrine versus artesunate plus amodiaquine for unsupervised treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Ghanaian children. Malar. J. 7:261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kokwaro, G., L. Mwai, and A. Nzila. 2007. Artemether/lumefantrine in the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 8:75-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lim, P., A. P. Alker, N. Khim, N. K. Shah, S. Incardona, S. Doung, P. Yi, D. M. Bouth, C. Bouchier, O. M. Puijalon, S. R. Meshnick, C. Wongsrichanalai, T. Fandeur, J. Le Bras, P. Ringwald, and F. Ariey. 2009. Pfmdr1 copy number and arteminisin derivatives combination therapy failure in falciparum malaria in Cambodia. Malar. J. 8:11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mayxay, M., M. Barends, A. Brockman, A. Jaidee, S. Nair, D. Sudimack, T. Pongvongsa, S. Phompida, R. Phetsouvanh, T. Anderson, N. J. White, and P. N. Newton. 2007. In vitro antimalarial drug susceptibility and pfcrt mutation among fresh Plasmodium falciparum isolates from the Lao PDR (Laos). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 76:245-250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Muangnoicharoen, S., D. J. Johnson, S. Looareesuwan, S. Krudsood, and S. A. Ward. 2009. Role of known molecular markers of resistance in the antimalarial potency of piperaquine and dihydroartemisinin in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 53:1362-1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nelson, A. L., A. Purfield, P. McDaniel, N. Uthaimongkol, N. Buathong, S. Sriwichai, R. S. Miller, C. Wongsrichanalai, and S. R. Meshnick. 2005. pfmdr1 genotyping and in vivo mefloquine resistance on the Thai-Myanmar border. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 72:586-592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ochong, E. O., I. V. van den Broek, K. Keus, and A. Nzila. 2003. Association between chloroquine and amodiaquine resistance and allelic variation in the Plasmodium falciparum multiple drug resistance 1 gene and the chloroquine resistance transporter gene in isolates from the upper Nile in southern Sudan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 69:184-187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Parola, P., B. Pradines, F. Simon, M. P. Carlotti, P. Minodier, M. P. Ranjeva, S. Badiaga, L. Bertaux, J. Delmont, M. Morillon, R. Silai, P. Brouqui, and D. Parzy. 2007. Antimalarial drug susceptibility and point mutations associated with drug resistance in 248 Plasmodium falciparum isolates imported from Comoros to Marseille, France in 2004-2006. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 77:431-437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pradines, B., P. Hovette, T. Fusai, H. L. Atanda, E. Baret, P. Cheval, J. Mosnier, A. Callec, J. Cren, R. Amalvict, J. P. Gardair, and C. Rogier. 2006. Prevalence of in vitro resistance to eleven standard or new antimalarial drugs among Plasmodium falciparum isolates from Pointe-Noire, Republic of the Congo. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:2404-2408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pradines, B., A. Tall, T. Fusai, A. Spiegel, R. Hienne, C. Rogier, J. F. Trape, J. Le Bras, and D. Parzy. 1999. In vitro activities of benflumetol against 158 Senegalese isolates of Plasmodium falciparum in comparison with those of standard antimalarial drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:418-420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Price, R. N., C. Cassar, A. Brockman, M. Duraisingh, M. van Vugt, N. J. White, F. Nosten, and S. Krishna. 1999. The pfmdr1 gene is associated with a multidrug-resistant phenotype in Plasmodium falciparum from the western border of Thailand. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:2943-2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Price, R. N., A. C. Uhlemann, A. Brockman, R. McGready, E. Ashley, L. Phaipun, R. Patel, K. Laing, S. Looareesuwan, N. J. White, F. Nosten, and S. Krishna. 2004. Mefloquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum and increased pfmdr1 gene copy number. Lancet 364:438-447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Price, R. N., A. C. Uhlemann, M. van Vugt, A. Brockman, R. Hutagalung, S. Nair, D. Nash, P. Singhasivanon, T. J. Anderson, S. Krishna, N. J. White, and F. Nosten. 2006. Molecular and pharmacological determinants of the therapeutic response to artemether-lumefantrine in multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Clin. Infect. Dis. 42:1570-1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reed, M. B., K. J. Saliba, S. R. Caruana, K. Kirk, and A. F. Cowman. 2000. Pgh1 modulates sensitivity and resistance to multiple antimalarials in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature 403:906-909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sasi, P., A. Abdirahman, L. Mwai, S. Muriithi, J. Straimer, L. Schieck, A. Rippert, M. Bashraheil, A. Salim, J. Peshu, K. Awuondo, B. Lowe, M. Pirmohamed, P. Winstanley, S. Ward, A. Nzila, and S. Borrmann. 2009. In vivo and in vitro efficacy of amodiaquine against Plasmodium falciparum in an area of continued use of 4-aminoquinolines in East Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 199:1575-1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sidhu, A. B., A. C. Uhlemann, S. G. Valderramos, J. C. Valderramos, S. Krishna, and D. A. Fidock. 2006. Decreasing pfmdr1 copy number in Plasmodium falciparum malaria heightens susceptibility to mefloquine, lumefantrine, halofantrine, quinine, and artemisinin. J. Infect. Dis. 194:528-535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sidhu, A. B., S. G. Valderramos, and D. A. Fidock. 2005. pfmdr1 mutations contribute to quinine resistance and enhance mefloquine and artemisinin sensitivity in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Microbiol. 57:913-926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sidhu, A. B., D. Verdier-Pinard, and D. A. Fidock. 2002. Chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites conferred by pfcrt mutations. Science 298:210-213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sisowath, C., P. E. Ferreira, L. Y. Bustamante, S. Dahlstrom, A. Martensson, A. Bjorkman, S. Krishna, and J. P. Gil. 2007. The role of pfmdr1 in Plasmodium falciparum tolerance to artemether-lumefantrine in Africa. Trop. Med. Int. Health 12:736-742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sisowath, C., I. Petersen, M. I. Veiga, A. Martensson, Z. Premji, A. Bjorkman, D. A. Fidock, and J. P. Gil. 2009. In vivo selection of Plasmodium falciparum parasites carrying the chloroquine-susceptible pfcrt K76 allele after treatment with artemether-lumefantrine in Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 199:750-757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sisowath, C., J. Stromberg, A. Martensson, M. Msellem, C. Obondo, A. Bjorkman, and J. P. Gil. 2005. In vivo selection of Plasmodium falciparum pfmdr1 86N coding alleles by artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem). J. Infect. Dis. 191:1014-1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Thanh, N. X., T. N. Trung, N. C. Phong, N. X. Thien, B. Dai, G. D. Shanks, M. Chavchich, and M. D. Edstein. 2009. Open label randomized comparison of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine and artesunate-amodiaquine for the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria in central Vietnam. Trop. Med. Int. Health 14:504-511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Uhlemann, A. C., M. Ramharter, B. Lell, P. G. Kremsner, and S. Krishna. 2005. Amplification of Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance gene 1 in isolates from Gabon. J. Infect. Dis. 192:1830-1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ursing, J., P. E. Kofoed, L. Rombo, and J. P. Gil. 2006. No pfmdr1 amplifications in samples from Guinea-Bissau and Liberia collected between 1981 and 2004. J. Infect. Dis. 194:716-718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Yeka, A., G. Dorsey, M. R. Kamya, A. Talisuna, M. Lugemwa, J. B. Rwakimari, S. G. Staedke, P. J. Rosenthal, F. Wabwire-Mangen, and H. Bukirwa. 2008. Artemether-lumefantrine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treating uncomplicated malaria: a randomized trial to guide policy in Uganda. PLoS One 3:e2390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]