Abstract
The family Asfarviridae contains only a single virus species, African swine fever virus (ASFV). ASFV is a viral agent with significant economic impact due to its devastating effects on populations of domesticated pigs during outbreaks but has not been reported to infect humans. We report here the discovery of novel viral sequences in human serum and sewage which are clearly related to the asfarvirus family but highly divergent from ASFV. Detection of these sequences suggests that greater genetic diversity may exist among asfarviruses than previously thought and raises the possibility that human infection by asfarviruses may occur.
The family Asfarviridae contains a single double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) virus called African swine fever virus (ASFV), which is thought to have evolved from an ancestral virus common to the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses including poxviruses, iridoviruses, and phycodnaviruses (10, 11). ASFV infects ticks and swine but has not been reported to infect humans. ASFV infection of wild swine typically causes persistent infection with few symptoms (9, 17, 24, 25), but domesticated pigs can develop severe disease including acute hemorrhagic fever with nearly 100% mortality. As there is no vaccine and disease is contained by animal quarantine and slaughter, ASFV outbreaks can decimate pig populations and have significant economic impact. A 2007 outbreak in the former Soviet republic of Georgia resulted in the death and slaughter of over 80,000 pigs (20).
ASFV is endemic in sub-Saharan Africa but has also been introduced to countries in Europe, South America, and the Caribbean (26). Characterization of various ASFV isolates has led to the identification of 22 genotypes based on sequence variation in the portion of the B646L gene encoding the C terminus of the major capsid protein (2, 4, 14). Within this segment of B646L, approximately 14% of the nucleotide sites are variable among the ASFV isolates studied (2, 4). The ASFV genome has been completely sequenced for the Vero cell-adapted BA71V strain (29) and several wild isolates (5). Like many other large dsDNA viruses, ASFV contains open reading frames with homology to cellular genes involved in DNA replication, transcription, repair, and protein modification (29). ASFV also has an array of open reading frames with potential function in modulating host cell function or immune response (7).
We report here the discovery of novel viral sequences in human serum from the Middle East and in sewage from Spain that have clear similarity to ASFV genes. Of the 36 sequences identified, 29 did not have significant overlap or nucleotide identity with any of the other sequences. These 29 sequences are similar to 18 different ASFV genes, with some sequences matching to different regions within the same ASFV genes. Sequence and phylogenetic analyses indicate that the novel viral sequences are most closely related to the asfarvirus family but are highly divergent from known ASFV strains. We therefore hypothesize that these viral sequences are derived from at least one novel virus in the Asfarviridae family, which we refer to herein as ASFV-like virus (ASFLV).
Discovery of novel asfarvirus-related viral sequences.
We analyzed total nucleic acid extracted from human serum samples by 454 sequencing as an approach to identifying potential novel human pathogens. Serum samples were collected from patients with acute febrile illness (AFI) and from healthy volunteers (normal serum [NS]) in the Middle East between 2002 and 2005 and stripped of identifying information before analysis to protect patient confidentiality. Total nucleic acid was extracted from 199 AFI and 200 NS samples and reverse transcribed to enable detection of both RNA and DNA viruses. Each sample was then amplified by sequence-independent PCR using a primer that incorporates a 6-nucleotide barcode unique to that sample. Amplicons from multiple samples were pooled and subjected to 454 pyrosequencing. Additional details on serum sample processing and sequence data analysis are provided in the “Supplemental methods” section of the supplemental material. From one AFI sample and three NS samples, we identified six novel viral sequences with no significant nucleotide similarity to known viruses but whose translated sequences had detectable sequence identity to several ASFV proteins (Table 1), as determined using tBLASTx (1).
TABLE 1.
Novel viral sequences with similarity to ASFV
| Sample | Sequencea | Total readsb | ASFV genec | E valued | % Identitye | Protein description (reference[s]) | Accession no.f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human AFI and NS | AFI-1 | 23,224 | G1211R | 1e−10 | 64 | DNA polymerase (15, 19) | FJ957903 |
| NS-1.1 | 83,028 | B354L | 3e−11 | 42 | ATPase (10) | FJ957904 | |
| NS-1.2 | 14,737 | NP1450L | 2e−13 | 45 | RNA polymerase, largest subunit (27) | FJ957905 | |
| NS-2.1 | 42,635 | M1249L | 2e−10 | 36 | Unknown | FJ957906 | |
| NS-2.2 | 3,870 | P1192R | 5e−12 | 37 | Topoisomerase II (3, 8) | FJ957907 | |
| NS-3 | 2,602 | C962R | 7e−12 | 38 | Primase or ATPase (10, 12) | FJ957908 | |
| Sewage fractions | SF-3g† | 78,573 | G1211R | 2e−26 | 51 | DNA polymerase (15, 19) | FJ957909 |
| SF-6g† | 6,633 | G1211R | 1e−25 | 51 | DNA polymerase (15, 19) | FJ957910 | |
| SF-8.1# | 33,028 | D250R | 4e−14 | 60 | NTPh pyrophosphohydrolase (10) | FJ957911 | |
| SF-8.2 | 33,028 | EP1242L | 1e−19 | 45 | RNA polymerase, subunit 2 (27) | FJ957912 | |
| SF-8.3 | 33,028 | EP364R | 5e−9 | 39 | Nuclease (11) | FJ957913 | |
| SF-8.4§ | 33,028 | EP424R | 5e−9 | 58 | RNA methyltransferase (11) | FJ957914 | |
| SF-8.5 | 33,028 | F1055L | 3e−18 | 32 | Helicase (23) | FJ957915 | |
| SF-8.6g | 33,028 | F1055L | 6e−8 | 50 | Helicase (23) | FJ957916 | |
| SF-8.7† | 33,028 | G1211R | 5e−23 | 49 | DNA polymerase (15, 19) | FJ957917 | |
| SF-8.8 | 33,028 | G1340L | 1e−8 | 27 | Unknown | FJ957918 | |
| SF-8.9¶ | 33,028 | H339R | 5e−13 | 44 | Unknown | FJ957919 | |
| SF-9.1* | 13,968 | C962R | 4e−10 | 40 | Primase or ATPase (10, 12) | FJ957920 | |
| SF-9.2 | 13,968 | CP2475L | 5e−10 | 41 | 220-kDa polyprotein (21) | FJ957921 | |
| SF-9.3§ | 78,307 | EP424R | 2e−11 | 44 | RNA methyltransferase (11) | FJ957922 | |
| SF-10 | 16,843 | C475L | 9e−14 | 46 | Polyadenylate polymerase (6) | FJ957923 | |
| Unassigned | UA.1g | NA | B646L | 1e−11 | 44 | Major capsid protein (13) | FJ957924 |
| UA.2g | NA | B962L | 7e−37 | 50 | Helicase (28) | FJ957925 | |
| UA.3 | NA | C475L | 1e−10 | 31 | Polyadenylate polymerase (6) | FJ957926 | |
| UA.4 | NA | C475L | 8e−9 | 37 | Polyadenylate polymerase (6) | FJ957927 | |
| UA.5 | NA | C962R | 6e−38 | 38 | Primase or ATPase (10, 12) | FJ957928 | |
| UA.6* | NA | C962R | 1e−17 | 32 | Primase or ATPase (10, 12) | FJ957929 | |
| UA.7g | NA | CP2475L | 2e−15 | 30 | 220-kDa polyprotein (21) | FJ957930 | |
| UA.8# | NA | D250R | 5e−14 | 60 | NTP pyrophosphohydrolase (10) | FJ957931 | |
| UA.9g | NA | EP1242L | 1e−20 | 44 | RNA polymerase, subunit 2 (27) | FJ957932 | |
| UA.10g† | NA | G1211R | 2e−26 | 51 | DNA polymerase (15, 19) | FJ957933 | |
| UA.11 | NA | G1211R | 1e−15 | 41 | DNA polymerase (15, 19) | FJ957934 | |
| UA.12 | NA | G1340L | 6e−15 | 32 | Unknown | FJ957935 | |
| UA.13 | NA | G1340L | 1e−28 | 50 | Unknown | FJ957936 | |
| UA.14¶ | NA | H339R | 8e−12 | 35 | Unknown | FJ957937 | |
| UA.15 | NA | M448R | 2e−9 | 34 | Unknown | FJ957938 |
Sets of sequences whose members were similar to the same regions of the ASFV genome and had significant overlap and nucleotide sequence identity with each other are indicated by the same symbols (†, #, §, *, or ¶).
The total number of reads generated from each sample is given for each sequence whose parent sample is known. For samples that were sequenced in more than one sequencing run, the total number of reads for the run in which the indicated novel sequence was identified is given. NA, not applicable.
ASFV genes to which the novel viral sequences have sequence similarity, as determined using tBLASTx (1). ASFV genes are listed using nomenclature for the BA71V strain (29).
E value for tBLASTx comparison of the novel viral sequences to the ASFV BA71V complete genome (29).
Amino acid identity between the novel viral sequences and corresponding sequences in the ASFV BA71V strain within the region of similarity identified using tBLASTx.
GenBank accession numbers.
Sequence was assembled from two or more overlapping reads.
NTP, nucleoside triphosphate.
ASFV-related sequences were also found in sewage collected from an urban wastewater treatment plant in Barcelona, Spain. Briefly, viral particles from the sewage samples were concentrated and separated into fractions by cesium chloride equilibrium gradient centrifugation. Fractions with high concentrations of virus, as determined by quantitative PCR for human adenovirus, were treated first with DNase I to degrade nonviral DNA not protected by a viral capsid and then with a lysis buffer to disrupt viral capsids and release viral nucleic acids. Total nucleic acid was extracted from these fractions and was reverse transcribed and PCR amplified prior to 454 sequencing as described above. Additional details on the processing of sewage samples are provided in the “Supplemental methods” section of the supplemental material. Fifteen ASFV-related sequences were identified in five sewage fractions (SF).
We also identified an additional 15 ASFV-related sequences from our sequencing runs which could not be assigned to specific samples due to lack of a perfect sequence match with the barcode sequence. All of these unassignable sequences were identified in sequencing runs containing multiple samples including the sewage fractions which were found to contain ASFV-related sequences. We did not detect ASFV-related sequences in the other samples in these sequencing runs and therefore speculate that these unassignable sequences are derived from the sewage samples within these runs that contained ASFV-like sequences. However, as we cannot verify the specific sample source of these unassignable sequences, they are reported here as unassigned (UA) sequences.
A total of 36 novel ASFV-related sequences were identified, all of whose best-scoring tBLASTx matches were to the respective ASFV genes from various ASFV isolates (not shown). These sequences are listed in Table 1 and were positionally mapped to the complete genome for the ASFV BA71V strain (Fig. 1) (29). These novel viral sequences were similar not only to ASFV genes such as the DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase genes, which are also conserved in other large dsDNA virus families (10), but also to multiple ASFV genes including EP364R and M448R, which do not have significant similarity to genes in other viral families and are therefore, to date, specific to ASFV.
FIG. 1.
Novel viral sequences with similarity to ASFV genes. Novel viral sequences were positionally mapped to the complete genome of the ASFV BA71V strain (29) based on the similarity of the associated amino acid sequences to ASFV proteins. Each novel viral sequence is represented by a black bar, and the ASFV genomic nucleotide position to which it is similar is indicated below the bar.
Novel asfarvirus-related sequences are highly divergent from ASFV.
The low amino acid identity between the novel viral sequences and the corresponding ASFV proteins (Table 1) suggested that these sequences may belong to a genetically distinct virus rather than to a new isolate of ASFV. We therefore performed multiple sequence alignments to compare the DNA polymerase-like sequences from our samples to the corresponding sequences from ASFV isolates. Sequences SF-3, SF-6, SF-8.7, and UA.10 all mapped to the same region of ASFV DNA polymerase (Fig. 1) and were nearly identical in nucleotide sequence where they overlapped (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). These sequences formed a 575-nucleotide consensus sequence, whose translated sequence had 51% amino acid identity with ASFV DNA polymerase when compared by tBLASTx (E value of 2e−26). Alignment of the regions of similarity between our novel DNA polymerase sequence and the corresponding ASFV sequences showed that the ASFV sequences were highly conserved with each other, but the sequence from our samples was divergent except for small blocks of amino acids which were conserved with ASFV sequences (Fig. 2A). The same result was obtained using the NS-1.2 and NS-2.2 sequences, which are similar to ASFV RNA polymerase and topoisomerase II, respectively (see Fig. S2A and B in the supplemental material). We also performed phylogenetic analysis using sequence SF-8.3, with similarity to the EP364R gene, which appears to be ASFV specific. Sequences from ASFV isolates were again found to be highly conserved with each other, whereas the novel viral sequence was divergent (Fig. 2B). The same result was obtained using the UA.15 sequence, with similarity to another ASFV-specific gene, M448R (see Fig. S2C in the supplemental material).
FIG. 2.
Novel viral sequences are divergent from ASFV. (A) The translated sequence from the novel DNA polymerase consensus sequence was aligned to corresponding sequences from various ASFV isolates using AlignX (VectorNTI suite; Invitrogen). Residues which are highly conserved are shaded in gray, and those which are divergent are in black. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of the translated SF-8.3 sequence and corresponding sequences from the EP364R genes of various ASFV isolates was performed using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Bootstrap values over 65% are shown. Sequences were aligned using ClustalX (2.0), and phylogenetic trees were visualized using TreeView (16). GenBank accession numbers for ASFV sequences are provided in the supplemental material. Abbreviations: Benin, Benin 97/1 (5); Kenya, Kenya 1950; Malawi, Malawi Lil-20/1 1983; Mkuzi, Mkuzi 1979; OURT, OURT 88/3 (5); Pretorisuskop, Pretorisuskop/96/4; Tengani, Tengani 62.
Novel viral sequences are most closely related to the asfarvirus family.
As viruses in multiple dsDNA viral families encode homologs of DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase, and topoisomerase II, we compared those sequences from our samples to corresponding ones from ASFV isolates as well as other dsDNA viruses from families including Poxviridae, Iridoviridae, Phycodnaviridae, Herpesviridae, and Ascoviridae. We also included in our analyses several sequences that had the most significant E values aside from those for ASFV strains when the novel DNA and RNA polymerase sequences were queried against the nucleotide database by tBLASTx. The novel topoisomerase II sequence did not have any hits with significant E values other than those for ASFV strains.
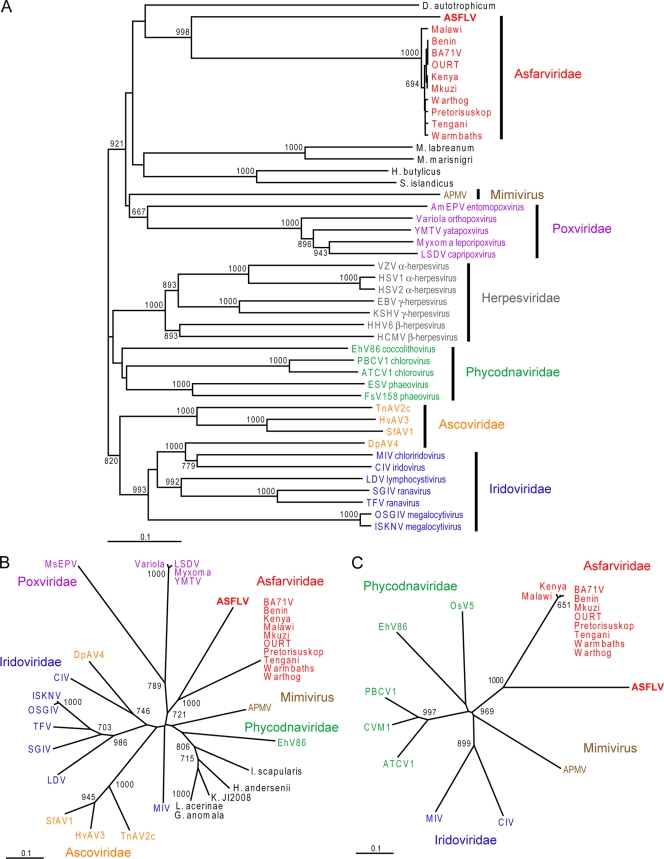
We found that our translated DNA polymerase consensus sequence formed a separate branch which was most closely related to the cluster containing the ASFV isolates (Fig. 3A). The same result was observed for the RNA polymerase (Fig. 3B) (NS-1.2) and topoisomerase II (Fig. 3C) (NS-2.2) sequences. For all three proteins, grouping of the various dsDNA viruses was consistent with their classifications and with previously published studies using other sets of conserved genes (10, 18, 22).
FIG. 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of novel viral sequences. Translated novel viral sequences similar to ASFV (A) DNA polymerase, (B) RNA polymerase, and (C) topoisomerase II were compared to corresponding sequences from dsDNA viruses and high-scoring nonviral BLAST matches as described in the legend to Fig. 2. Sequences are shown in color as follows: asfarviruses, red; mimivirus, brown; poxviruses, purple; herpesviruses, gray; phycodnaviruses, green; ascoviruses, orange; iridoviruses, blue; nonviral BLAST matches, black. Bootstrap values over 65% are shown. In panel A, virus intrafamily subclassifications are also shown where applicable. For panels B and C, virus families for which the corresponding RNA polymerase and topoisomerase II sequences could not be identified by BLAST were omitted from the analyses. GenBank accession numbers for the sequences analyzed are provided in the “Supplemental methods” section of the supplemental material. Abbreviations: AmEPV, Amsacta moorei entomopoxvirus; APMV, Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus; ATCV1, Acanthocystis turfacea chlorella virus 1; CIV, Chilo iridescent virus; CVM1, chlorella virus Marburg 1; D. autotrophicum, Desulfobacterium autotrophicum; DpAV4, Diadromus pulchellus ascovirus 4; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; EhV86, Emiliania huxleyi virus isolate 86; ESV, Ectocarpus siliculosus virus; FsV158, Feldmannia species virus isolate 158; G. anomala, Glugea anomala; H. andersenii, Hemiselmis andersenii; H. butylicus, Hyperthermus butylicus; HCMV, human cytomegalovirus; HHV6, human herpesvirus 6; HSV1, herpes simplex virus type 1; HSV2, herpes simplex virus type 2; HvAV3, Heliothis virescens ascovirus 3; I. scapularis, Ixodes scapularis; ISKNV, infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus; K. JI2008, Kabatana sp. strain JI2008; KSHV, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus; L. acerinae, Loma acerinae; LDV, lymphocystis disease virus; LSDV, lumpy skin disease virus; M. labreanum, Methanocorpusculum labreanum; M. marisnigri, Methanoculleus marisnigri; MIV, mosquito (Aedes taeniorhynchus) iridescent virus; MsEPV, Melanoplus sanguinipes entomopoxvirus; OSGIV, orange-spotted grouper iridovirus; OsV5, Ostreococcus virus 5; PBCV1, Paramecium bursaria chlorella virus 1; S. islandicus, “Sulfolobus islandicus”; SfAV1, Spodoptera frugiperda ascovirus 1; SGIV, Singapore grouper iridovirus; TFV, tiger frog virus; TnAV2c, Trichoplusia ni ascovirus 2c; VZV, varicella-zoster virus; YMTV, Yaba monkey tumor virus. Other abbreviations are as defined for Fig. 2.
As several additional novel sequences from our samples are similar to other ASFV genes that have also been reported to have homologs in other dsDNA virus families (10, 11), we performed similar phylogenetic analyses on these sequences. We found that 10 of the 11 sequences with similarity to ASFV gene B354L, C962R, D250R, EP1242L, B646L, or B962L were most closely related to, but distinct from, ASFV sequences (not shown), consistent with our results for the DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase, and topoisomerase II sequences. The exception was sequence SF-9.1, which is similar to ASFV C962R but did not group with sequences from any of the dsDNA families in the phylogenetic analysis. SF-9.1 is 99% identical in nucleotide sequence over a 238-nucleotide overlap with sequence UA.6 (not shown), which is also similar to C962R. Two of the three nucleotide changes in SF-9.1 are insertions or deletions resulting in frameshifts that significantly altered portions of the SF-9.1 translated sequence relative to that of UA.6. It is therefore likely that the results of phylogenetic analysis for SF-9.1 differed from those for UA.6 because the frameshifts decreased the overall similarity of the SF-9.1 translated sequence to ASFV.
Discussion.
The detection in this study of multiple viral sequences that are clearly related to, but phylogenetically distinct from, ASFV suggests that at least one additional member of the family Asfarviridae exists. The facts that these sequences were identified in multiple 454 sequencing runs over a period of approximately 7 months and that the first sequences identified, NS-1.2 and NS-2.2, were not detected in subsequent sequencing runs of different samples strongly argue against the possibility that the detection of ASFV-like sequences in these samples is due to cross-contamination.
Since the ASFV-like sequence fragments were identified from two types of samples from different geographic regions, it is possible that these sequences are derived from more than one virus in this family. In support of this possibility, the translated SF-10, UA.3, and UA.4 sequences aligned to the same region in C475L of ASFV but were significantly different from each other in nucleotide sequence. An alignment of the translated SF-10, UA.3, and UA.4 sequences with the corresponding segment of ASFV C475L showed only 28% identity between UA.3 and SF-10 and 71% identity between UA.3 and UA.4 in their respective regions of overlap (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). This suggests the possibility that our samples contained more than one asfarvirus-related virus, although this cannot be conclusively determined since the regions of overlap between these sequences are short.
Although ASFV is not known to infect humans even where the virus is endemic, identification of ASFV-like sequences in serum from multiple human patients suggests that human infection may occur. Further studies are under way to prospectively screen patient samples by PCR for the presence of ASFV-like sequences using primers to the sequences reported here in order to assess prevalence and geographic distribution. These studies, in combination with serological analyses, will be required to determine whether the ASFV-like virus is, in fact, a human virus and whether it is associated with human disease.
The finding of ASFV-like sequences in sewage from Spain indicates that they are not geographically limited to the Middle East, where the human patient specimens were obtained. Although it is unclear whether the source of the ASFV-like sequences in sewage is human or animal, this also suggests the virus may be fecally shed and that screening of stool in addition to serum may be informative. Identification of additional samples containing ASFV-like sequences will be important for the key future goals of obtaining more sequence from the viral genome, determining if the virus can be cultured, and establishing a small-animal model of infection.
Nucleotide sequence accession numbers.
The sequences obtained in this study have been assigned GenBank accession numbers FJ957903 to FJ957938.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Guillermo Pimentel and Erica Dueger for supplying critical reagents, contributing to discussions of this work, and providing feedback on the manuscript.
This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grant U54 AI057160 to the Midwest Regional Center of Excellence for Biodefense and Emerging Infectious Diseases Research.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 7 October 2009.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://jvi.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1.Altschul, S. F., T. L. Madden, A. A. Schaffer, J. Zhang, Z. Zhang, W. Miller, and D. J. Lipman. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3389-3402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bastos, A. D., M. L. Penrith, C. Cruciere, J. L. Edrich, G. Hutchings, F. Roger, E. Couacy-Hymann, and R. Thomson. 2003. Genotyping field strains of African swine fever virus by partial p72 gene characterisation. Arch. Virol. 148:693-706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baylis, S. A., L. K. Dixon, S. Vydelingum, and G. L. Smith. 1992. African swine fever virus encodes a gene with extensive homology to type II DNA topoisomerases. J. Mol. Biol. 228:1003-1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Boshoff, C. I., A. D. Bastos, L. J. Gerber, and W. Vosloo. 2007. Genetic characterisation of African swine fever viruses from outbreaks in southern Africa (1973-1999). Vet. Microbiol. 121:45-55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chapman, D. A., V. Tcherepanov, C. Upton, and L. K. Dixon. 2008. Comparison of the genome sequences of non-pathogenic and pathogenic African swine fever virus isolates. J. Gen. Virol. 89:397-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Claverie, J. M., C. Abergel, and H. Ogata. 2009. Mimivirus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 328:89-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dixon, L. K., C. C. Abrams, G. Bowick, L. C. Goatley, P. C. Kay-Jackson, D. Chapman, E. Liverani, R. Nix, R. Silk, and F. Zhang. 2004. African swine fever virus proteins involved in evading host defence systems. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 100:117-134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Garcia-Beato, R., J. M. Freije, C. Lopez-Otin, R. Blasco, E. Vinuela, and M. L. Salas. 1992. A gene homologous to topoisomerase II in African swine fever virus. Virology 188:938-947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Heuschele, W. P., and L. Coggins. 1969. Epizootiology of African swine fever virus in warthogs. Bull. Epizoot. Dis. Afr. 17:179-183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Iyer, L. M., L. Aravind, and E. V. Koonin. 2001. Common origin of four diverse families of large eukaryotic DNA viruses. J. Virol. 75:11720-11734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Iyer, L. M., S. Balaji, E. V. Koonin, and L. Aravind. 2006. Evolutionary genomics of nucleo-cytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Virus Res. 117:156-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Iyer, L. M., E. V. Koonin, D. D. Leipe, and L. Aravind. 2005. Origin and evolution of the archaeo-eukaryotic primase superfamily and related palm-domain proteins: structural insights and new members. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:3875-3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lopez-Otin, C., J. M. Freije, F. Parra, E. Mendez, and E. Vinuela. 1990. Mapping and sequence of the gene coding for protein p72, the major capsid protein of African swine fever virus. Virology 175:477-484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lubisi, B. A., A. D. Bastos, R. M. Dwarka, and W. Vosloo. 2005. Molecular epidemiology of African swine fever in East Africa. Arch. Virol. 150:2439-2452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martins, A., G. Ribeiro, M. I. Marques, and J. V. Costa. 1994. Genetic identification and nucleotide sequence of the DNA polymerase gene of African swine fever virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:208-213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Page, R. D. 2002. Visualizing phylogenetic trees using TreeView. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics, chapter 6, unit 6.2. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Parker, J., W. Plowright, and M. A. Pierce. 1969. The epizootiology of African swine fever in Africa. Vet. Rec. 85:668-674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Raoult, D., S. Audic, C. Robert, C. Abergel, P. Renesto, H. Ogata, S. B. La, M. Suzan, and J. M. Claverie. 2004. The 1.2-megabase genome sequence of Mimivirus. Science 306:1344-1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Rodriguez, J. M., R. J. Yanez, J. F. Rodriguez, E. Vinuela, and M. L. Salas. 1993. The DNA polymerase-encoding gene of African swine fever virus: sequence and transcriptional analysis. Gene 136:103-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rowlands, R. J., V. Michaud, L. Heath, G. Hutchings, C. Oura, W. Vosloo, R. Dwarka, T. Onashvili, E. Albina, and L. K. Dixon. 2008. African swine fever virus isolate, Georgia, 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 14:1870-1874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Simon-Mateo, C., G. Andres, and E. Vinuela. 1993. Polyprotein processing in African swine fever virus: a novel gene expression strategy for a DNA virus. EMBO J. 12:2977-2987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Stasiak, K., S. Renault, M. V. Demattei, Y. Bigot, and B. A. Federici. 2003. Evidence for the evolution of ascoviruses from iridoviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 84:2999-3009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sussman, M. D., Z. Lu, G. F. Kutish, C. A. Afonso, and D. L. Rock. 1993. The identification of an African swine fever gene with conserved helicase motifs and a striking homology to herpes virus origin binding protein, UL9. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Thomson, G. R. 1985. The epidemiology of African swine fever: the role of free-living hosts in Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 52:201-209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thomson, G. R., M. D. Gainaru, and A. F. Van Dellen. 1980. Experimental infection of warthogs (Phacochoerus aethiopicus) with African swine fever virus. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 47:19-22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vinuela, E. 1985. African swine fever virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 116:151-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yanez, R. J., M. Boursnell, M. L. Nogal, L. Yuste, and E. Vinuela. 1993. African swine fever virus encodes two genes which share significant homology with the two largest subunits of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:2423-2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yanez, R. J., J. M. Rodriguez, M. Boursnell, J. F. Rodriguez, and E. Vinuela. 1993. Two putative African swine fever virus helicases similar to yeast ‘DEAH’ pre-mRNA processing proteins and vaccinia virus ATPases D11L and D6R. Gene 134:161-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yanez, R. J., J. M. Rodriguez, M. L. Nogal, L. Yuste, C. Enriquez, J. F. Rodriguez, and E. Vinuela. 1995. Analysis of the complete nucleotide sequence of African swine fever virus. Virology 208:249-278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.