Abstract
Cdk5 regulates adhesion and migration in a variety of cell types. We previously showed that Cdk5 is strongly activated during stress fiber formation and contraction in spreading cells. Here we determine the mechanism linking Cdk5 to stress fiber contractility and its relevance to cell migration. Immunofluorescence showed that Cdk5 colocalized with phosphorylated myosin regulatory light chain (pMRLC) on contracting stress fibers. Inhibiting Cdk5 activity by various means significantly reduced pMRLC level and cytoskeletal contraction, with loss of central stress fibers. Blocking Cdk5 activity also reduced Rho-Rho kinase (ROCK) signaling, which is the principal pathway of myosin phosphorylation under these conditions. Next, we examined the effect of Cdk5 activity on Src, a known regulator of Rho. Inhibiting Cdk5 activity increased Src activation and phosphorylation of its substrate, p190RhoGAP, an upstream inhibitor of Rho. Inhibiting both Cdk5 and Src activity completely reversed the effect of Cdk5 inhibition on Rho and prevented the loss of central stress fibers, demonstrating that Cdk5 exerts its effects on Rho-ROCK signaling by suppressing Src activity. Moreover, inhibiting either Cdk5 or ROCK activity increased cell migration to an equal extent, while inhibiting both kinases produced no additional effect, demonstrating that Cdk5-dependent regulation of ROCK activity is a physiological determinant of migration rate.
Cell migration is essential for morphogenesis during embryonic development and for epithelial homeostasis and wound healing throughout life. As myosin II is involved in all aspects of cell migration, from cell polarization and adhesion to protrusion and tail retraction (34, 48), the signaling pathways regulating myosin-dependent cytoskeletal contraction are of particular interest. Myosin contraction is regulated by phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain (MRLC) at Thr18/Ser19. Although a number of kinases have been identified which phosphorylate these sites, the principal kinases in most cells are myosin light chain kinase (MLCK), a calcium/calmodulin-regulated enzyme, and Rho kinase (ROCK), a downstream effector of the Rho family GTPase RhoA. To provide the stringent control of cytoskeletal contraction needed for migration, RhoA is subject to both positive regulation by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), such as GEF-H1 (4, 21), and negative regulation by GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), such as the Src-regulated protein p190RhoGAP (1, 3, 10, 13). An additional level of regulation is provided by guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors, which bind to inactive RhoA and other Rho family GTPases, sequestering them in the cytosol (3). Two major downstream effectors of RhoA with regard to the cytoskeleton are the mammalian homologue of diaphanous, involved in actin polymerization (43), and ROCK, which phosphorylates MRLC and myosin phosphatase (20).
Cdk5, a serine/threonine kinase, is an atypical member of the well-known family of cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks). Unlike the other Cdks, it has no known function in cell cycle regulation and is activated by one of two noncyclin proteins, p35 or p39 (16, 41). Phosphorylation of Cdk5 at Y15 increases its activity severalfold (36, 49). Although Cdk5 is most abundant in neuronal cells, where it regulates migration, cytoskeletal dynamics, and membrane trafficking (37, 38, 45), a growing body of evidence indicates that Cdk5 has similar functions in nonneuronal cells (35). In particular, Cdk5 has been shown to strengthen cell-to-matrix adhesion and regulate migration in lens epithelial cells (28), corneal epithelial cells (11, 12, 40), keratinocytes (27), and CHO-K1 cells (15). The effects of Cdk5 on adhesion and migration have been linked, at least in part, to Cdk5-dependent phosphorylation of talin, which strengthens adhesion by slowing the rate of focal adhesion turnover (15). However, we have observed that Cdk5 not only binds to focal adhesions, where talin is located, but also to stress fibers (33). Moreover, in spreading cells, Cdk5 exerts its greatest effect on adhesion 1 to 2 h after plating (28), when stress fiber contraction is pronounced and Cdk5 activity is maximum (33). Therefore, we hypothesized that Cdk5 might regulate the MRLC phosphorylation necessary for stress fiber contraction and stability. To test this possibility, we examined the relationship of Cdk5 activity to MRLC phosphorylation and cytoskeletal contraction in spreading human lens epithelial cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture and transfection.
Human lens epithelial cells (FHL124) were cultured at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 95% air/5% CO2 in medium consisting of one part KGM (Lonza Biologics Inc., Portsmouth, NH) to four parts M199 (Invitrogen-GIBCO, Carlsbad, CA), 50 μg/ml gentamicin (Quality Biological, Inc., Gaithersburg, Maryland), and 10% fetal bovine serum. Where indicated, cells were transiently transfected using Lipofectamine (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions and incubated for 48 h before use. To suppress Cdk5 expression, cells were transfected with 160 nM of the appropriate antisense oligonucleotides (sc-29263; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) or with a scrambled control (sc-37007; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and were harvested after 48 h. To inhibit Cdk5 activity, cells were transfected with dominant negative green fluorescent protein (GFP)-dnCdk5(D144N) or GFP-Cdk5 (as a control) and were harvested after 48 h.
Pharmacological inhibition.
Cells were harvested after 2 h incubation in the presence of the appropriate inhibitor: 15 μM olomoucine (Calbiochem, San Diego, CA) for inhibition of Cdk5, 10 μM PP1 (Biomol International, Plymouth Meeting, PA) for inhibition of Src family kinases, 2.0 μg/ml cell-permeable C3 transferase (Cytoskeleton Inc., Denver, CO) for inhibition of Rho, 10 μM Y-27632 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) for inhibition of ROCK, and 10 μM ML-7 and ML-9 (Biomol, Plymouth Meeting, PA) for inhibition of MLCK.
Cell spreading assay.
The cell spreading assay was performed as previously described (33). For biochemical analysis, cells plated on culture dishes were collected by scraping, pelleted, and lysed with PBSTDS buffer (1× phosphate-buffered saline[PBS], 1% Triton X-100, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS]), containing complete protease inhibitor (Roche Diagnostics Corporation, Indianapolis, IN) and protein tyrosine and serine/threonine phosphatase inhibitors (Chemicon/Upstate USA, Inc., Lake Placid, NY). Cell lysates were used for immunoblotting as previously described (22).
Antibodies and fluorescent probes.
Cdk5 monoclonal (J-3; sc-6247) and phospho-specific Cdk5(pY15) (sc-12918-R) antibodies were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. MRLC (ab11082-100) monoclonal antibody was purchased from Abcam Inc., Cambridge, MA. Phosphorylated MRLC (pMRLC) (sc-12896), polyclonal antibody against Thr18/Ser19 pMRLC (sc-3674S), and polyclonal antibody raised against Ser19 pMRLC (sc-3671S) were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. The specificity of the pMRLC antibody was confirmed by using blocking peptide (see Fig. 2E). Antibodies for active Src (phospho-Tyr416-Src) (2101S) and phosphotyrosine (P-Tyr-100) (9411) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology Inc., Danvers, MA. Rabbit polyclonal antibody against Src (sc-18) was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. p190RhoGAP antibody (05-378) was purchased from Upstate, Lake Placid, NY. Anti-rabbit and anti-mouse IgG horseradish peroxidase-linked secondary antibodies were from Amersham Bioscience, Piscataway, NJ. Alexa 568-goat anti-rabbit IgG, Alexa 488-donkey anti-mouse IgG, Alexa 488-phalloidin, Alexa 568-phalloidin, and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) were from Invitrogen.
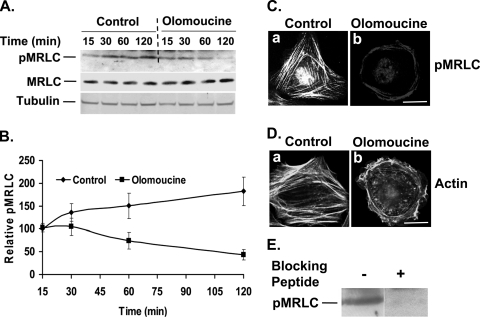
FIG. 2.
Cdk5 inhibition decreases the phosphorylation of MRLC. (A) Cells were plated in tissue culture dishes and allowed to spread for 15, 30, 60, and 120 min in the absence or presence of olomoucine. Immunoblotting with specific antibodies detected pMRLC (upper panel) and total MRLC (middle panel). Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower panel). (B) Results of four independent experiments of the type shown in panel A were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of pMRLC to MRLC was plotted to determine relative levels of pMRLC. The values represent means ± SD. (C) Cells were allowed to spread on fibronectin in the absence (panel a) or presence (panel b) of olomoucine for 120 min and were immunostained with pMRLC antibody. A significant reduction in pMRLC immunofluorescence was observed, and pMRLC-stained stress fibers were restricted to the cell periphery. Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Cells were allowed to spread on fibronectin in the absence or presence of olomoucine for 120 min and were stained with phalloidin. Control cells had concave cell boundaries and contained well-formed stress fibers (panel a). Olomoucine-treated cells had no concave boundaries or center stress fibers (panel b). Scale bar, 20 μm. (E) The specificity of the pMRLC antibody used in these studies was confirmed by using a blocking peptide corresponding to the short amino acid sequence containing phosphorylated Thr18 and Ser19 of MRLC of human origin. The blocking peptide concentration used was five times higher than the antibody concentration, as recommended by the supplier. The band of approximately 17 kDa was absent in blocking-peptide-treated membrane, confirming the specificity of the antibody.
Immunofluorescence staining.
Fixed cells were permeabilized with 0.25% Triton X-100 in PBS and then blocked with 5% goat serum in PBS. The cells were incubated with a 1:200 dilution of the indicated primary antibodies in PBS at 4°C overnight. After being thoroughly washed in PBS, the cells were incubated in 1:250 Alexa-conjugated appropriate secondary antibodies for 1 h. To visualize actin or nuclei, cells were incubated with phalloidin (1:50) or DAPI (1:2,500) for 1 h. After being stained, cells were thoroughly washed with PBS and mounted with gel mounting solution (Biomeda Corporation, Foster City, CA).
Fluorescence microscopy.
Fluorescence-labeled cells were viewed using a Zeiss Axioplan II microscope with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm to detect transfected GFP fusion proteins. Confocal fluorescence microscopy was carried out using a Leica laser scanning microscope (Leica TCS SP2; Leica Microsystems, Germany). Fluorescent Alexa probes were viewed with excitation wavelengths of 488 nm (Alexa 488) and 568 nm (Alexa 568), and colocalization was assessed using Leica image analysis software. Images were made using a 40× objective with a 2.5× magnifier to produce a 100× magnification.
ROCK activity assay.
Cells were fixed and harvested in 10% trichloroacetic acid and 10 mM of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane on ice. After centrifugation, pellets were dissolved in 10 μl of 1 M Tris base and then mixed with 100 μl of extraction buffer (8 M urea, 2% SDS, 5% sucrose, and 5% 2-mercaptoethanol). After brief sonication, cell lysates were clarified by centrifugation at 14,000 × g at 4°C for 10 min. A small portion of supernatants (30 μg) was taken for protein determination by Bio-Rad Dc protein assay. Equal amounts of cell extracts were subjected to 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes (Invitrogen). Membranes were incubated with rabbit polyclonal antibody specific for phospho-myosin binding subunit (phospho-Thr853-MBS) or myosin binding subunit (MBS) (MBL International Corporation, Woburn, MA). Bands were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence (Amersham Bioscience). ROCK activity was expressed as the ratio of phospho-MBS to total MBS.
Rho-GTP assay.
Measurement of GTP-bound Rho was assessed by Rhotekin affinity chromatography, using the Rho activation assay kit (Millipore, Lake Placid, NY), according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, cells were lysed in ice-cold lysis buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.2, 1% Triton X-100, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, 500 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2) containing a protease inhibitor mixture (Roche Diagnostics Corporation). Equal amounts (300 μg) of cell lysates were incubated on a rocker platform at 4°C for 45 min with 30 μg of GST-Rhotekin Rho binding domain coupled to glutathione-agarose beads. After incubation, beads were washed three times with the washing buffer (50 mM Tris·HCl, pH 7.2, 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 1% Triton X-100). Bound Rho-GTP was eluted with Laemmli's SDS-sample buffer (Boston Bioproducts; BP-110R) containing dithiothreitol and boiled for 5 min. The samples were subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes (Invitrogen), and detected by immunoblotting, using a specific monoclonal anti-Rho antibody (specific for RhoA, RhoB, RhoC, and clone 55; catalog no. 05-778; Upstate).
Scratch wound experiments.
Multiple scratch wounds were made in confluent cell cultures with a 20.0-μl pipette tip. After suspended cells were washed away, the cultures were refed with medium with or without the indicated inhibitors and incubated for 6 h. Wound closure was photographed immediately after wounding and after 6 h with a microscope equipped with a digital camera (Carl Zeiss, Thornwood, NY). The extent of closure was quantified by ImageProPlus software and defined as the ratio of the wound area remaining at 6 h to the original wound area (0 h) (n = 4).
Analysis of Src activation and phosphorylation of Src substrate p190RhoGAP.
After incubation, cells were lysed in PBSTDS buffer, and 20 μg of total cell extracts was subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane (Invitrogen), and immunoblotted with antibodies to total Src and active Src (specific antibody against phospho-Tyr416-Src). For p190RhoGAP phosphorylation studies, 0.5 mg of cell extracts containing protease inhibitors was used for immunoprecipitation of p190RhoGAP. The resulting immune complexes were divided into two equal aliquots, analyzed in 10% acrylamide gels, and immunoblotted with antibodies against p190RhoGAP and phosphotyrosine. Three independent experiments were performed for Src activation and phosphorylation of the Src substrate p190RhoGAP.
Data analysis.
Immunoblots were quantified by densitometric scanning using ImageQuant (GE Healthcare, Piscataway, NJ) image analysis software. Results are expressed as mean densities ± standard deviations (SD) from three to four independent experiments. The relative density for the protein of interest was normalized to beta-tubulin. For statistical analysis, Student's t test was performed using SigmaPlot (Systat, San Jose, CA) software, and P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Time-dependent rearrangement of actin cytoskeleton in spreading cells.
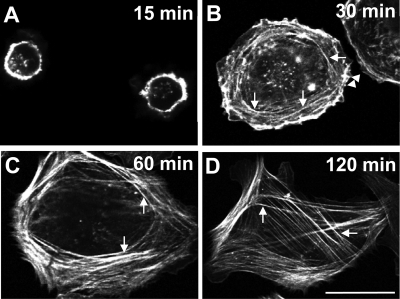
Fluorescence microscopy of phalloidin-stained human lens epithelial cells spreading on fibronectin showed a time-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton similar to that seen in other cell types (6, 30). By 15 min after plating, the cells were small and rounded and contained a prominent band of polymerized actin around the cell periphery (Fig. 1A). By 30 min, the peripheral band of polymerized actin began to reorganize into short radial fibers (arrowheads) and transverse arcs (arrows), which crossed the radial fibers at right angles (Fig. 1B). By 60 min, 96% of the cells (215 counted) contained well-formed stress fibers and a few cells had distinctly concave boundaries, indicative of myosin-dependent contraction (Fig. 1C). By 120 min, 97% of the cells (210 counted) contained stress fibers throughout and showed distinctly concave cell boundaries (Fig. 1D). These changes in actin organization and cell morphology suggest that a marked increase in myosin-dependent contraction occurs 60 to 120 min after plating.
FIG. 1.
The actin cytoskeleton undergoes time-dependent rearrangement during spreading. Human lens epithelial cells (FHL124) were plated on fibronectin; allowed to spread for 15, 30, 60, and 120 min; and stained with phalloidin. (A) Cells attached and spread within 15 min. A prominent band of polymerized actin formed around the cell perimeter. (B) By 30 min, the peripheral band of actin began to reorganize into short radial stress fibers (arrowheads) and actin-containing transverse arcs (arrows), which crossed the radial fibers at right angles. (C) By 60 min, more than 90% of cells contained numerous, well-formed ventral stress fibers (arrows). (D) By 120 min, cell borders became sharply concave as cells appeared to contract and more than 95% of cells retained well-formed stress fibers (arrows), which often spanned the entire cell. Scale bar, 20 μm.
Cdk5 activity regulates phosphorylation of MRLC.
Since recent work from this laboratory demonstrated that Cdk5 activity increases as lens epithelial cells spread on fibronectin (33), we next asked whether Cdk5 activity might affect MRLC phosphorylation necessary for myosin-dependent cytoskeletal organization and contraction. Cells were allowed to spread in the presence or absence of a pharmacological inhibitor of Cdk5 activity, olomoucine, for various time intervals from 15 to 120 min. In the absence of the inhibitor, immunoblotting for pMRLC showed a time-dependent increase in myosin phosphorylation (Fig. 2A), consistent with the changes in cytoskeletal organization and cell morphology. In the presence of olomoucine, this increase in phosphorylation was obliterated (Fig. 2A). At 120 min, the level of pMRLC decreased by 76% (P < 0.05) compared to that in untreated cells, indicating that Cdk5 activity does, indeed, affect phosphorylation of MRLC (Fig. 2B). Similar results were obtained using an antibody from a different source to detect pMRLC (not shown). The reduction in the pMRLC level seen in the presence of olomoucine was associated with a slight increase (18%) in the total MRLC level. By fluorescence microscopy, the untreated cells showed intense staining of pMRLC and actin at 120 min, with well-formed stress fibers and concave boundaries (Fig. 2C, panel a; Fig. 2D, panel a). In contrast, olomoucine-treated cells exhibited a range of morphologies with few, if any, concave cell boundaries. pMRLC-stained stress fibers (Fig. 2C, panel b) and polymerized actin (Fig. 2D, panel b) were seen only in the cell periphery. Approximately 30% of olomoucine-treated cells had no concave cell boundaries at all (Fig. 2C, panel b; Fig. 2D, panel b). These cytoskeletal changes are consistent with an effect of Cdk5 activity on myosin-dependent contraction.
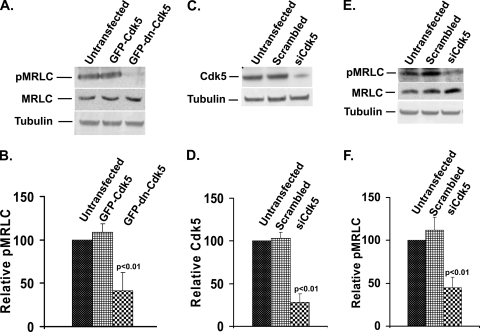
Since pharmacological inhibitors may have off-target effects, we used two additional methods to confirm the involvement of Cdk5 activity in MRLC phosphorylation. First, cells were transfected with GFP-tagged dominant negative Cdk5 [GFP-dnCdk5(D144N)] to depress Cdk5 activity. Transfection efficiency of cells as judged by green fluorescence was 65 to 70%. The pMRLC level was significantly reduced (59%) in GFP-dnCdk5(D144N)-transfected cells compared to that in control (GFP-Cdk5-transfected) cells (Fig. 3A and B). This reduction in pMRLC was associated with a 15% increase in total MRLC level. To further confirm the involvement of Cdk5 in MRLC phosphorylation, we used Cdk5 small interfering RNA (siRNA) oligonucleotides to suppress Cdk5 expression. Cells were transfected with Cdk5 siRNA or scrambled siRNA oligonucleotides. Transfection efficiency as judged by green fluorescence was observed between 65 to 75% each time. Transfected cells were then harvested at various time points and analyzed by immunoblot analysis. The levels of Cdk5 were quantified and compared. By 48 h after transfection, Cdk5 siRNA suppressed Cdk5 expression by 72% (Fig. 3C and D). These cells were replated and allowed to spread for 2 h; pMRLC levels were then analyzed by immunoblotting. Silencing Cdk5 expression by siRNA led to a 55% reduction in the pMRLC level (Fig. 3E and F). This reduction in pMRLC was again associated with a slight increase (20%) in the total MRLC level. These results confirm that Cdk5 regulates phosphorylation of MRLC during spreading of lens epithelial cells. By immunofluorescence, cells transfected with GFP-dnCdk5(D144N) or Cdk5 siRNA lacked stress fibers and appeared less contracted, with only thin, weakly stained stress fibers at the cell periphery. In contrast, control cells transfected with either GFP-Cdk5 or scrambled oligonucleotides showed no defect in stress fiber organization (not shown), thus confirming the olomoucine results and previous findings (33).
FIG. 3.
Dominant negative Cdk5 and Cdk5 siRNA significantly decrease MRLC phosphorylation. (A) Cells were transfected with GFP-tagged constructs of wild-type Cdk5 (GFP-Cdk5) or dominant negative Cdk5(D144N) (GFP-dn-Cdk5). After 48 h incubation for expression of the transfected construct, the cells were replated and allowed to spread for 2 h, and proteins were extracted and immunoblotted with specific antibodies to detect pMRLC (upper panel), total MRLC (middle panel), and tubulin (lower panel). Lane 1, untransfected; lane 2, transfected with GFP-Cdk5; lane 3, transfected with GFP-dnCdk5(D144N). (B) Results of three independent experiments of the type shown in panel A were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of pMRLC to MRLC was plotted to determine the relative levels of pMRLC. The values represent means ± SD. (C) Cells were transiently transfected with Cdk5 siRNA (siCdk5) or scrambled siRNA, replated after 48 h, and allowed to spread for 120 min. Cdk5 was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Cdk5 monoclonal (J-3) antibody (upper panel). Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower panel). Lane 1, untransfected; lane 2, transfected with scrambled siRNA; lane 3, transfected with Cdk5 siRNA. (D) The results of immunoblotting experiments (n = 3) were quantified by densitometry and normalized to tubulin. The values represent means ± SD. Endogenous Cdk5 was significantly lower (P < 0.01) in Cdk5 siRNA-transfected cells than in untransfected cells or cells transfected with scrambled siRNA. (E) Experimental conditions were the same as in panel C. Levels of pMRLC, total MRLC, and tubulin were determined by immunoblotting. Lane 1, untransfected; lane 2, transfected with scrambled siRNA; lane 3, transfected with Cdk5 siRNA. (F) Results of three independent experiments of the type shown in panel E were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of pMRLC to MRLC was plotted to determine relative levels of pMRLC. The values represent means ± SD. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant (P < 0.01) decrease in pMRLC level in Cdk5 siRNA-transfected cells compared to that in untransfected or scrambled siRNA-transfected cells.
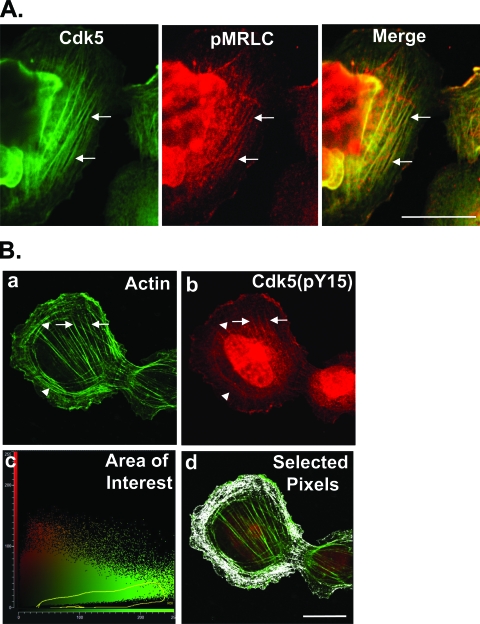
Cdk5 colocalizes with pMRLC on stress fibers.
Since the above results suggested that Cdk5 regulates myosin phosphorylation and stress fiber contraction, we tested whether Cdk5 associates with contracting stress fibers by immunostaining with anti-Cdk5 and anti-pMRLC antibodies. Immunofluorescence showed distinct colocalization of Cdk5 with pMRLC on stress fibers (Fig. 4A), consistent with a functional role for Cdk5 in regulating stress fiber contraction. At earlier times, when some cells still contained peripheral transverse arcs, fluorescence staining of the actin cytoskeleton showed that the highly active, phosphorylated form of Cdk5, Cdk5(pY15), colocalized primarily with the central stress fibers, with little or none on the transverse arcs, suggesting that Cdk5 may preferentially regulate contraction of central stress fibers (Fig. 4B). Other immunostaining results demonstrated that Cdk5(pY15) and the Cdk5 activator, p35, also colocalize with pMRLC (not shown) and the actin cytoskeleton (33).
FIG. 4.
Cdk5 and Cdk5(pY15) localize on contracting stress fibers in spreading cells. (A) Cells were allowed to spread on fibronectin for 120 min and immunostained for Cdk5 and pMRLC. The colocalization of Cdk5 and pMRLC shown in the merged image implies that Cdk5 is preferentially associated with contracting stress fibers. Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Cells were allowed to spread on fibronectin for 60 min and immunostained with antibody to Cdk5(pY15) and phalloidin. At this time, a minority of cells still contained both central stress fibers and peripheral transverse arcs. (a) Phalloidin staining of such a cell shows well-formed central stress fibers (arrow) and a distal array of transverse arcs (arrowhead). (b) Immunostaining shows Cdk5(pY15) on central stress fibers (arrow), with little or none on transverse arcs (arrowhead). (c) The cytofluorogram of the confocal image shows the distribution of red and green pixels. Each pixel in the images shown in panels a and b is represented by a single point in the cytofluorogram plotted by the Leica confocal software. The coordinates of the point are determined by the intensity of the red signal (y axis) and green signal (x axis) of that pixel in images shown in panels a and b. We designated an area of interest (outlined in yellow) corresponding to pixels with a strong green signal (rich in actin), but little or no red signal [relatively poor in Cdk5(pY15)]. (d) The pixels [rich in actin, but poor in Cdk5(pY15)] corresponding to the outlined area of interest from the cytofluorogram were highlighted in white using the Leica confocal software. These pixels are primarily associated with peripheral actin fibrils composing transverse arcs, indicating that these structures are relatively poor in Cdk5(pY15) compared to the central stress fibers, which are relatively rich. Scale bar, 20 μm.
Rho-ROCK signaling is a major pathway for MRLC phosphorylation in spreading lens cells.
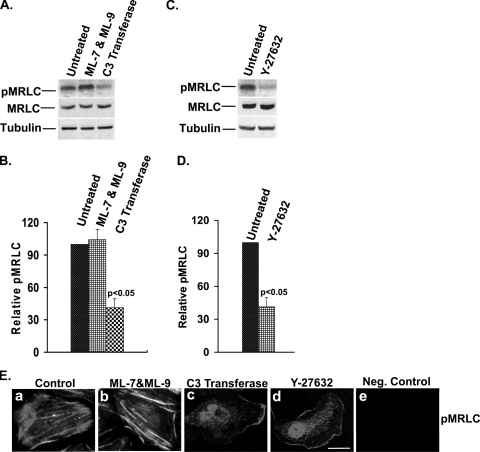
Although these findings indicate that Cdk5 regulates MRLC phosphorylation, MRLC itself cannot be a substrate for Cdk5, as it does not contain a (Ser/Thr)Pro site, which is required for phosphorylation by proline-directed Ser/Thr kinases, such as Cdk5. Therefore, we asked whether Cdk5 activity might affect the upstream signaling pathways responsible for myosin phosphorylation in spreading cells. To address this question, we first determined which signaling pathways regulate MRLC phosphorylation under these conditions. Inhibition of MLCK with the specific inhibitors ML-7 and ML-9 did not show any significant change in the level of pMRLC (Fig. 5A and B), stress fiber formation, or cytoskeletal contraction (Fig. 5E, panel b). In contrast, the Rho inhibitor, C3 transferase, reduced pMRLC levels by about 60% (P < 0.05) (Fig. 5A and B). Moreover, cells treated with C3 transferase showed significantly less pMRLC immunofluorescence and no visible stress fibers (Fig. 5E, panel c), indicating that MRLC was phosphorylated primarily by the Rho signaling pathway in spreading lens epithelial cells. Since ROCK is a major downstream effector of Rho known to phosphorylate MRLC, cells were treated with ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 and the levels of pMRLC were again quantified and compared. The ROCK inhibitor produced almost identical reductions in pMRLC level (59%; P < 0.05) (Fig. 5C and D), pMRLC immunofluorescence, and stress fiber organization (Fig. 5E, panel d), confirming the importance of the Rho-ROCK pathway for myosin phosphorylation in spreading lens epithelial cells. Interestingly, total MRLC levels were also slightly increased (12 to 16%) when either Rho or ROCK was inhibited (Fig. 5A and C).
FIG. 5.
Inhibition of Rho-ROCK but not of MLCK significantly affects myosin phosphorylation, stress fiber organization, and cytoskeletal contraction in spreading cells. Cells were allowed to spread in the absence or presence of inhibitors of MLCK (ML-7 & ML-9, 10 μM), Rho (C3 transferase, 2.0 μg/ml) or ROCK (Y-27632, 10 μM) for 120 min. (A) Levels of pMRLC (upper panel) and total MRLC (middle panel) were determined by immunoblotting. Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower panel). Lane 1, untreated; lane 2, treated with MLCK inhibitor (ML-7 plus ML-9); lane 3, treated with Rho inhibitor (C3 transferase). (B) The results of three independent experiments of the type shown in panel A were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of pMRLC to MRLC was plotted to determine the relative levels of pMRLC. The values represent means ± SD. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant (P < 0.05) decrease in pMRLC level in C3 transferase-treated cells compared to that in untreated cells. (C) Levels of pMRLC (upper panel) and total MRLC (middle panel) were determined by immunoblotting. Tubulin was used as a loading control (lower panel). Lane 1, untreated; Lane 2, treated with ROCK inhibitor (Y-27632). (D) Results of three independent experiments of the type shown in panel C were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of pMRLC to MRLC was plotted to determine relative levels of pMRLC. The values represent means ± SD. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant (P < 0.05) decrease in pMRLC level in Y-27632-treated cells compared to untreated cells. (E) Cells were allowed to spread on fibronectin for 120 min in the absence or presence of inhibitors, as indicated in Materials and Methods, and were immunostained with pMRLC antibody. By immunofluorescence, control cells (panel a) and ML-7- and ML-9-treated cells (panel b) showed intense staining of pMRLC, with well-formed stress fibers throughout the entire cell. More than 95% of cells had concave cell boundaries and appeared contracted in both control and ML-7- and ML-9-treated cells. In contrast, cells treated with Rho inhibitor C3 transferase (panel c) and ROCK inhibitor Y-27632 (panel d) showed significantly less pMRLC immunofluorescence, fewer stress fibers, and few if any concave boundaries, consistent with reduced contraction. The negative control (panel e) has no primary (pMRLC) antibody. Scale bar, 20 μm.
Cdk5 inhibition decreases Rho activation and ROCK activity.
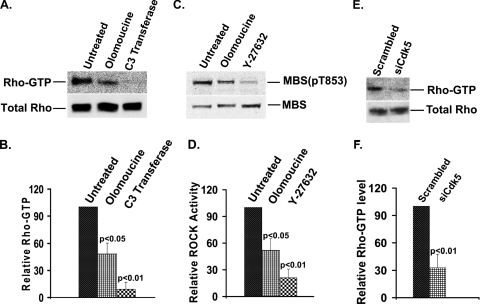
To test whether Cdk5 activity affects signaling through Rho and ROCK, we treated cells with the Cdk5 inhibitor olomoucine and measured Rho-GTP level and ROCK activity. Olomoucine treatment decreased Rho-GTP level by 52% (P < 0.05) (Fig. 6A and B) and suppressed ROCK activity by 48% (P < 0.05) (Fig. 6C and D), indicating that Cdk5 activity regulates Rho-GTP formation and ROCK activity. To confirm this finding by an independent method, cells were transfected with Cdk5 siRNA or with a scrambled siRNA oligonucleotide. Western blot analysis demonstrated that expression of Cdk5 was efficiently suppressed (as shown in Fig. 3C and D). Suppression of Cdk5 was accompanied by a 67% (P < 0.01) reduction in the Rho-GTP level (Fig. 6E and F), confirming that Cdk5 regulates the Rho-ROCK signaling pathway upstream of myosin phosphorylation.
FIG. 6.
Cdk5 inhibition significantly decreases the Rho-GTP level and ROCK activity in spreading cells. (A) Cells were allowed to spread in the absence or presence of the Cdk5 inhibitor (olomoucine, 15 μM) or Rho inhibitor (C3 transferase, 2.0 μg/ml). Rho-GTP was isolated by affinity chromatography on Rhotekin beads and immunoblotted using a monoclonal anti-Rho antibody (upper panel). Total Rho level is shown in the lower panel. Lane 1, untreated; lane 2, treated with olomoucine; lane 3, treated with C3 transferase. (B) The results were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of Rho-GTP to total Rho for each treatment was normalized to the untreated control. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant decrease (P < 0.05) in Rho-GTP/total Rho in olomoucine-treated cells compared to that in untreated cells. C3 transferase was used as a positive control for inhibition of Rho. The values represent means ± SD (n = 3). (C) Cells were allowed to spread in the absence or presence of the Cdk5 inhibitor (olomoucine, 15 μM) or ROCK inhibitor (Y-27632, 10 μM) for 120 min. ROCK activity was assayed by in vitro kinase assay, using MBS of myosin phosphatase as a substrate. MBS(pT853) and total MBS were identified by immunoblotting using specific antibodies. Lane 1, untreated; lane 2, treated with olomoucine; lane 3, treated with Y-27632. (D) ROCK activity was expressed as the ratio of phospho-MBS [MBS(pT853)] to total MBS, normalized to untreated controls. The graph represents the average ratio of MBS(pT853)/MBS ± SD (n = 3). (E) Cells were transiently transfected with Cdk5 siRNA (siCdk5), replated after 48 h, and allowed to spread for 120 min. Rho-GTP was isolated by affinity chromatography on Rhotekin beads and detected by Western blotting using anti-Rho antibody (upper panel). Total Rho level is shown in lower panel. Lane 1, transfected with scrambled siRNA; lane 2, transfected with Cdk5 siRNA. (F) The results of immunoblotting experiments were quantified by densitometry. The values represent means ± SD (n = 3). Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant decrease (P < 0.01) in the Rho-GTP level in Cdk5 siRNA-transfected cells compared to that in scrambled siRNA-transfected cells.
Cdk5 regulates Rho activity and cytoskeletal contraction by suppressing Src-p190RhoGAP signaling.
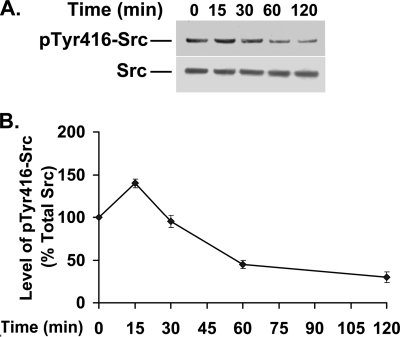
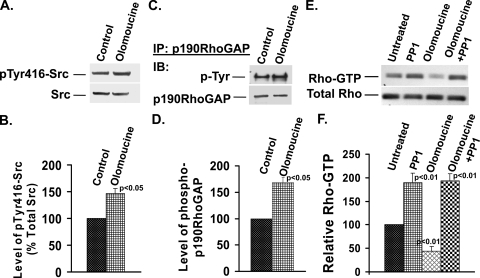
Previous work with migrating corneal epithelial cells has shown that Cdk5 downregulates Src activity (12). Moreover, the elevated Cdk5 activity seen 1 to 2 h after plating lens epithelial cells (33) is temporally correlated with a decrease in Src activity (Fig. 7A and B). Since Src is known to downregulate Rho activity by phosphorylating—and thus activating—p190RhoGAP (1), we examined whether Cdk5 regulates Rho activity by affecting the Src-p190RhoGAP signaling pathway. Src activity as measured by the level of phosphorylated Tyr416-Src increased by 47% compared to that of controls when Cdk5 activity was inhibited with olomoucine (Fig. 8A and B). To determine whether this Cdk5-dependent increase in Src activity affects p190RhoGAP phosphorylation, we inhibited Cdk5 activity with olomoucine, immunoprecipitated p190RhoGAP, and immunoblotted for phosphotyrosine. Cells treated with olomoucine showed a significant increase (68%) in tyrosine-phosphorylated p190RhoGAP levels compared with those of controls (Fig. 8C and D), which paralleled the increase in Src activity. Thus, the Cdk5-dependent regulation of Src activity in spreading cells significantly affects Src's ability to activate p190RhoGAP.
FIG. 7.
Src activity decreases at later times in spreading cells. Cells were plated and allowed to spread for 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min. (A) Cell lysates were immunoblotted to detect phosphorylated Tyr416-Src (upper panel) and total Src (lower panel). (B) The results of three experiments of the type shown in panel A were quantified by densitometry, and the ratio of phosphorylated to total Src was plotted as a percentage of the initial value (t = 0). The values represent means ± SD. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant decrease (P < 0.01) in Tyr416-Src phosphorylation after 60 min of spreading compared to the result at t = 0.
FIG. 8.
Cdk5 inhibition significantly increases Src activation and phosphorylation of p190RhoGAP in spreading cells. Cells were allowed to spread for 120 min in the presence or absence of olomoucine. (A) Cell extracts were immunoblotted for pTyr416-Src (upper panel) and total Src (lower panel). (B) Experiments of the type shown in panel A were quantified by densitometry and normalized to determine the relative levels of pTyr416-Src to total Src. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant increase (P < 0.05) in pTyr416-Src/Total Src in olomoucine-treated cells compared to untreated cells. The values represent means ± SD (n = 3). (C) Cells were replated and incubated in the absence or presence of olomoucine for 120 min. p190RhoGAP was immunoprecipitated (IP) from cell lysates, divided into two aliquots, and immunoblotted (IB) for phosphotyrosine (P-Tyr) or p190RhoGAP. (D) Experiments of the type shown in panel C were quantified by densitometry and normalized to determine the relative levels of pTyr-p190RhoGAP. Statistical analysis demonstrated a significant increase (P < 0.05) in pTyr-p190RhoGAP in olomoucine-treated cells compared to that in untreated cells. The values represent means ± SD (n = 3). (E) Cells were allowed to spread for 60 min and then incubated for 120 min in the absence or presence of PP1, olomoucine, or both. Rho-GTP level was isolated by affinity chromotography on Rhotekin beads and immunoblotted using an anti-Rho antibody (upper panel). Total Rho level is shown in the lower panel. Lane 1, untreated; lane 2, treated with PP1; lane 3, treated with olomoucine; lane 4, treated with both PP1 and olomoucine. (F) The results of three independent experiments as shown in panel E were quantified by densitometry. The values represent means ± SD. PP1-treated cells showed a significant increase (P < 0.01) in Rho-GTP level compared to untreated controls, whereas olomoucine-treated cells showed a significant reduction (P < 0.01). Rho-GTP in the presence of both inhibitors was significantly greater than that of untreated controls or in the presence of olomoucine alone (P < 0.01) but not significantly different from that in the presence of PP1 alone.
To determine whether Src activity is required for Cdk5-dependent regulation of Rho, we tested whether the Src inhibitor PP1 was able to reverse the effects of Cdk5 inhibition (Fig. 8E and F). To avoid blocking Src activity during the early phase of cell spreading, when Src is required for focal adhesion formation and cell attachment, we allowed cells to spread for 60 min before adding PP1. At this time, 97% of cells contained well-formed stress fibers but had not acquired the distinct, concave boundaries associated with contraction (Fig. 1C). Cells were then incubated for an additional 120 min in the absence or presence of the Src inhibitor, PP1; the Cdk5 inhibitor, olomoucine; or both inhibitors in combination. Treatment with PP1 alone increased Rho-GTP levels almost twofold, indicating that Src-dependent suppression of Rho-GTP formation is a major determinant of Rho activity in spreading cells, even at late times, when Src activity is relatively low. Treatment with olomoucine alone under these experimental conditions reduced Rho-GTP levels to 44% of the control level (P < 0.05), which is comparable to the effect of olomoucine added immediately after plating (compare Fig. 6A and B and Fig. 8E and F). The effect of olomoucine on MRLC phosphorylation under these conditions also mimicked its effect when added immediately after plating (not shown). Next, we tested the effect of olomoucine and PP1 together. The effect of olomoucine on Rho-GTP was completely reversed in the presence of PP1, demonstrating that Cdk5 regulates the Rho signaling pathway via Src-p190RhoGAP.
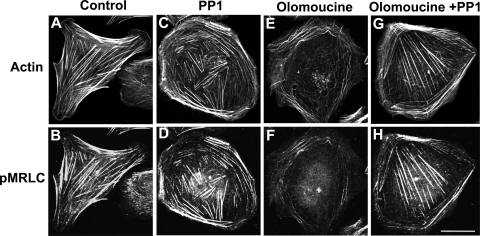
Finally, we tested the ability of PP1 to reverse the effects of olomoucine on stress fiber architecture and contraction. Cells were again allowed to spread for 60 min before inhibitors were added. After an additional 120-min incubation, cells were fixed and stained to detect actin (Fig. 9A, C, E, and G) and pMRLC (Fig. 9B, D, F, and H). Control cells had concave cell boundaries and numerous, well-formed stress fibers that were intensely immunostained for pMRLC (Fig. 9A and B). PP1, which increased Rho activity, did not diminish the number of stress fibers or pMRLC immunofluorescence (Fig. 9C and D). In contrast, olomoucine alone caused stress fibers to dissociate and depressed pMRLC immunostaining to very low levels. All central stress fibers disappeared (Fig. 9E and F). However, when both PP1 and olomoucine were present, the effects of olomoucine on stress fiber stability and contraction were reversed and central stress fibers were protected (Fig. 9G and H), indicating that Cdk5 exerts its effects on stress fibers by signaling through Src.
FIG. 9.
Inhibition of Src kinase reverses the effect of Cdk5 inhibition on stress fiber stability and contraction. Cells were allowed to spread on fibronectin for 60 min; then incubated for 120 min in the absence or presence of PP1, olomoucine, or both; and double stained with phalloidin (panels A, C, E, and G) and pMRLC antibody (panels B, D, F, and H). (A) Control cells had concave boundaries and well-formed stress fibers. (B) Immunostaining of the same cell with pMRLC showed prominent immunofluorescence on stress fibers. (C) PP1 treatment did not change stress fiber organization. (D) PP1 also had no significant effect on pMRLC immunofluorescence. (E) Olomoucine-treated cells showed a significant loss of central stress fibers. (F) Olomoucine greatly reduced pMRLC immunofluorescence. (G) PP1 blocked the effect of olomoucine on stress fibers. Central stress fibers, which were lost with olomoucine treatment, were preserved. (H) PP1 blocked the effect of olomoucine on pMRLC immunofluorescence. Immunostaining of pMRLC on central stress fibers was especially prominent. Scale bar, 20 μm.
Cdk5-dependent regulation of Rho-ROCK signaling affects cell migration rate.
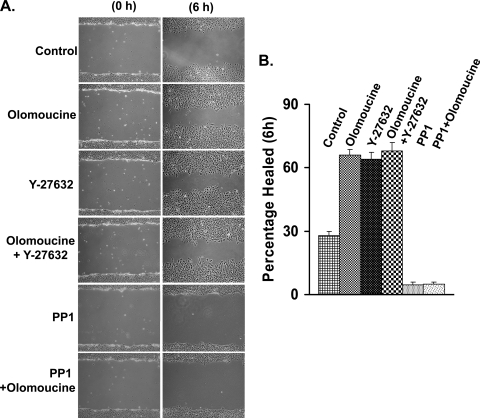
Since myosin-dependent cytoskeletal contraction plays an important role in cell migration (34), regulation of myosin phosphorylation and cytoskeletal organization by Cdk5 may contribute to previously observed effects of Cdk5 on cell migration (11, 12, 40). To test this possibility, we compared the effect of Cdk5 inhibition and ROCK inhibition on scratch wound closure (Fig. 10A and B). In untreated lens epithelial cells, 28% of the scratch wound area was healed after 6 h. Olomoucine alone significantly increased scratch wound healing to 66% at 6 h, as previously seen in corneal epithelial cells (11, 12, 40). The ROCK inhibitor, Y-27632, showed an almost identical effect (64% healed) on epithelial scratch wound closure. Moreover, the addition of both inhibitors together did not yield any significant additional effect (68% healed) on scratch wound closure, indicating that Cdk5 may exert its effect through ROCK. In contrast, inhibition of Src with PP1 almost completely arrested cell migration and blocked the effect of olomoucine. Since both Src (17) and Cdk5 (15) phosphorylate multiple substrates involved in cell migration, the effects of these inhibitors on migration are complex and not due solely to Src-p190RhoGAP-Rho signaling. Nonetheless, since ROCK inhibition closely mimics the effect of Cdk5 inhibition on cell migration, while inhibiting both enzymes has no significant additional effect, the regulation of Rho-ROCK signaling by Cdk5 clearly plays a considerable role in determining the rate of cell migration.
FIG. 10.
Cdk5-dependent regulation of ROCK affects cell migration. (A) Multiple scratch wounds were made in confluent cell cultures with a 20-μl pipette tip and allowed to heal in unsupplemented medium (control) or in medium containing Cdk5 inhibitor (olomoucine, 15 μM), ROCK inhibitor (Y-27632, 10 μM), Src kinase inhibitor (PP1, 10 μM), or the indicated combinations of these inhibitors. The wound area was photographed immediately after wounding (0 h) or 6 h postwounding. (B) The graph shows the percentage of the wound area healed, and values are means ± SD (n = 4). All treatment groups were statistically different (P < 0.01) from the control, but there was no significant difference among treatments with olomoucine, Y-27632, or olomoucine plus Y-27632.
DISCUSSION
The present study demonstrates that Cdk5 is a key regulator of Rho-dependent myosin contraction in spreading lens epithelial cells and indicates that this effect is mediated by Cdk5-dependent suppression of Src activity. Although Src activity declines during the later stages of cell spreading (Fig. 7A and B), our findings indicate that it continues to be a major regulator of Rho activity. The increase in Src activity produced by Cdk5 inhibition increases Src-dependent phosphorylation of p190RhoGAP, thus decreasing Rho activity, Rho-dependent myosin phosphorylation by the Rho effector, ROCK, and cytoskeletal contraction.
The demonstration that Cdk5 activity regulates Rho activation and Rho-dependent myosin contraction, together with the finding that Cdk5 colocalizes with contracting stress fibers, is consistent with a model in which Rho is activated locally, in the vicinity of the contracting stress fibers. This view is consistent with recent studies using fluorescent biosensors, which have shown that Rho activation is highly localized and under strict temporal control (2, 8, 31). For example, Rho is specifically activated in the posterior region of migrating cells during tail retraction and in discrete regions of the advancing cell front (31). Similarly, during cytokinesis, active Rho is seen only in the cleavage furrow (2). The present data provide additional support for local activation of Rho and suggest that Rho-GEFs, GAPs, and other regulatory factors may also be regulated locally, on and around contracting stress fibers.
The results of this study indicate that ROCK plays a major role in regulating myosin phosphorylation and cytoskeletal contraction during cell spreading and migration and are consistent with recently published findings involving other cell types (9, 47). We also consistently observed a small increase in total MRLC levels when Rho-ROCK signaling was inhibited, suggesting that ROCK may regulate MRLC synthesis or stability, as well. Despite the importance of ROCK, specific inhibitors of Rho and ROCK did not completely eliminate MRLC phosphorylation in spreading lens epithelial cells, particularly along the cell periphery, indicating that other signaling pathways are also likely to be involved. Such pathways may be particularly important for contraction of peripheral actin fibrils, which our data indicate were not greatly affected by inhibition of Cdk5. Since we observed no effect of MLCK inhibitors on myosin phosphorylation, this kinase does not appear to be involved in spreading cells, although it may play an important role in other circumstances (25). Other kinases that may contribute to MRLC phosphorylation in spreading cells include integrin-linked kinase (7, 44), Zipper-interacting protein kinase (26, 24), p21-activated kinase (5), and myotonic dystrophy-related Cdc42-binding kinase (23).
Cell migration is a complex, stepwise process, requiring stringent control of cytoskeletal structure and cell-to-matrix adhesion. The relationship between adhesive strength and migration rate is described by a bell-shaped curve (14). Thus, the rate of migration increases as adhesion between the cell and the extracellular matrix increases until an optimal rate is achieved; thereafter, increasing adhesion decreases the migration rate. For many cell types in culture, tail retraction is the rate-determining step in migration (29); thus, a slight decrease in adhesive strength increases the migration rate. However, each cell type is unique, and adhesive strength depends on the matrix composition as well as the cell type. Cdk5 has been shown to increase adhesive strength in a variety of cell types (11, 12, 15, 28). The recent finding that Cdk5 phosphorylates the focal adhesion protein, talin, provides a partial explanation of the effect of Cdk5 on adhesive strength (15). In the cell type used to investigate this effect (CHO-K1), the decrease in adhesion produced by mutating talin at the site phosphorylated by Cdk5 decreased—rather than increased—the migration rate. The present study demonstrates that Cdk5 also strengthens adhesion by regulating the stability and contractility of stress fibers, particularly central stress fibers. Our data link Cdk5-dependent stabilization of central stress fibers to Cdk5-mediated regulation of Src-p190RhoGAP, the Rho-ROCK signaling pathway, and myosin phosphorylation. Central stress fibers are responsible for tight attachment of the cell to the extracellular matrix through focal adhesions (19, 32, 46) and are regulated primarily by the Rho-ROCK pathway (18, 39). Accordingly, this pathway is particularly prominent in stationary cells, which require strong attachment to the substratum (39). The loss of central stress fibers due to suppression of myosin IIA increases the migration rate in fibroblasts (9, 42). Similarly, the loss of central stress fibers due to inhibition of either Cdk5 or ROCK reduces adhesive strength and—in lens epithelial cells—increases the migration rate. Moreover, we found that inhibiting both ROCK and Cdk5 does not produce any further effect on the migration rate, suggesting that regulation of ROCK by Cdk5 contributes significantly to the effect of Cdk5 on migration. These findings are consistent with previous reports indicating that corneal epithelial cell migration is enhanced by inhibiting either Cdk5 (12, 40) or ROCK (47). Thus, the present results linking Cdk5 to Rho-ROCK signaling via Src and p190RhoGAP implicate Cdk5 in the regulation of a major pathway controlling myosin-dependent contraction, cell attachment, and cell migration.
Acknowledgments
We thank John Reddan, Oakland University, for providing the human lens epithelial cells (FHL124) and the NEI Imaging Core Facility for confocal microscopy.
This work was supported by the National Eye Institute Intramural Research Program Z01-EY000238-20.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 12 October 2009.
REFERENCES
- 1.Arthur, W. T., and K. Burridge. 2001. RhoA inactivation by p190RhoGAP regulates cell spreading and migration by promoting membrane protrusion and polarity. Mol. Biol. Cell 12:2711-2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Birkenfeld, J., P. Nalbant, B. P. Bohl, O. Pertz, K. M. Hahn, and G. M. Bokoch. 2007. GEF-H1 modulates localized RhoA activation during cytokinesis under the control of mitotic kinases. Dev. Cell 12:699-712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Buchsbaum, R. J. 2007. Rho activation at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 120:1149-1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chang, Y. C., P. Nalbant, J. Birkenfeld, Z. F. Chang, and G. M. Bokoch. 2008. GEF-H1 couples nocodazole-induced microtubule disassembly to cell contractility via RhoA. Mol. Biol. Cell 19:2147-2153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chew, T. L., R. A. Masaracchia, Z. M. Goeckeler, and R. B. Wysolmerski. 1998. Phosphorylation of non-muscle myosin II regulatory light chain by p21-activated kinase (gamma-PAK). J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 19:839-854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Defilippi, P., C. Olivo, M. Venturino, L. Dolce, L. Silengo, and G. Tarone. 1999. Actin cytoskeleton organization in response to integrin-mediated adhesion. Microsc. Res. Tech. 47:67-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Deng, J. T., J. E. Van Lierop, C. Sutherland, and M. P. Walsh. 2001. Ca2+-independent smooth muscle contraction. A novel function for integrin-linked kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 276:16365-16373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.El-Sibai, M., O. Pertz, H. Pang, S. C. Yip, M. Lorenz, M. Symons, J. S. Condeelis, K. M. Hahn, and J. M. Backer. 2008. RhoA/ROCK-mediated switching between Cdc42- and Rac1-dependent protrusion in MTLn3 carcinoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 314:1540-1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Even-Ram, S., A. D. Doyle, M. A. Conti, K. Matsumoto, R. S. Adelstein, and K. M. Yamada. 2007. Myosin IIA regulates cell motility and actomyosin-microtubule crosstalk. Nat. Cell Biol. 9:299-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Frame, M. C., V. J. Fincham, N. O. Carragher, and J. A. Wyke. 2002. v-Src's hold over actin and cell adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3:233-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gao, C., S. Negash, H. T. Guo, D. Ledee, H. S. Wang, and P. Zelenka. 2002. CDK5 regulates cell adhesion and migration in corneal epithelial cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 1:12-24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gao, C. Y., M. A. Stepp, R. Fariss, and P. Zelenka. 2004. Cdk5 regulates activation and localization of Src during corneal epithelial wound closure. J. Cell Sci. 117:4089-4098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Heasman, S. J., and A. J. Ridley. 2008. Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9:690-701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Holly, S. P., M. K. Larson, and L. V. Parise. 2000. Multiple roles of integrins in cell motility. Exp. Cell Res. 261:69-74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Huang, C., Z. Rajfur, N. Yousefi, Z. Chen, K. Jacobson, and M. H. Ginsberg. 2009. Talin phosphorylation by Cdk5 regulates Smurf1-mediated talin head ubiquitylation and cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 11:624-630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Humbert, S., R. Dhavan, and L. Tsai. 2000. p39 activates cdk5 in neurons, and is associated with the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 113:975-983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huveneers, S., and E. H. Danen. 2009. Adhesion signaling—crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J. Cell Sci. 122:1059-1069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Katoh, K., Y. Kano, M. Amano, K. Kaibuchi, and K. Fujiwara. 2001. Stress fiber organization regulated by MLCK and Rho-kinase in cultured human fibroblasts. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 280:C1669-C1679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Katoh, K., Y. Kano, and S. Ookawara. 2007. Rho-kinase dependent organization of stress fibers and focal adhesions in cultured fibroblasts. Genes Cells 12:623-638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kimura, K., M. Ito, M. Amano, K. Chihara, Y. Fukata, M. Nakafuku, B. Yamamori, J. Feng, T. Nakano, K. Okawa, A. Iwamatsu, and K. Kaibuchi. 1996. Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). Science 273:245-248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Krendel, M., F. T. Zenke, and G. M. Bokoch. 2002. Nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1 mediates cross-talk between microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:294-301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ledee, D. R., C. Y. Gao, R. Seth, R. N. Fariss, B. K. Tripathi, and P. S. Zelenka. 2005. A specific interaction between muskelin and the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator p39 promotes peripheral localization of muskelin. J. Biol. Chem. 280:21376-21383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Leung, T., X. Q. Chen, I. Tan, E. Manser, and L. Lim. 1998. Myotonic dystrophy kinase-related Cdc42-binding kinase acts as a Cdc42 effector in promoting cytoskeletal reorganization. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18:130-140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.MacDonald, J. A., M. A. Borman, A. Muranyi, A. V. Somlyo, D. J. Hartshorne, and T. A. Haystead. 2001. Identification of the endogenous smooth muscle myosin phosphatase-associated kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:2419-2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Maddala, R., N. Skiba, and P. Vasantha Rao. 2007. Lens fiber cell elongation and differentiation is associated with a robust increase in myosin light chain phosphorylation in the developing mouse. Differentiation 75:713-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Murata-Hori, M., F. Suizu, T. Iwasaki, A. Kikuchi, and H. Hosoya. 1999. ZIP kinase identified as a novel myosin regulatory light chain kinase in HeLa cells. FEBS Lett. 451:81-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Nakano, N., A. Nakao, K. Ishidoh, R. Tsuboi, E. Kominami, K. Okumura, and H. Ogawa. 2005. CDK5 regulates cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion in human keratinocytes. Br. J. Dermatol. 153:37-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Negash, S., H. S. Wang, C. Gao, D. Ledee, and P. Zelenka. 2002. Cdk5 regulates cell-matrix and cell-cell adhesion in lens epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 115:2109-2117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Palecek, S. P., C. E. Schmidt, D. A. Lauffenburger, and A. F. Horwitz. 1996. Integrin dynamics on the tail region of migrating fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 109(Pt 5):941-952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Partridge, M. A., and E. E. Marcantonio. 2006. Initiation of attachment and generation of mature focal adhesions by integrin-containing filopodia in cell spreading. Mol. Biol. Cell 17:4237-4248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pertz, O., L. Hodgson, R. L. Klemke, and K. M. Hahn. 2006. Spatiotemporal dynamics of RhoA activity in migrating cells. Nature 440:1069-1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Prahalad, P., I. Calvo, H. Waechter, J. B. Matthews, A. Zuk, and K. S. Matlin. 2004. Regulation of MDCK cell-substratum adhesion by RhoA and myosin light chain kinase after ATP depletion. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 286:C693-707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Qiao, F., C. Y. Gao, B. K. Tripathi, and P. S. Zelenka. 2008. Distinct functions of Cdk5(Y15) phosphorylation and Cdk5 activity in stress fiber formation and organization. Exp. Cell Res. 314:3542-3550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ridley, A. J., M. A. Schwartz, K. Burridge, R. A. Firtel, M. H. Ginsberg, G. Borisy, J. T. Parsons, and A. R. Horwitz. 2003. Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302:1704-1709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rosales, J. L., and K. Y. Lee. 2006. Extraneuronal roles of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Bioessays 28:1023-1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sasaki, Y., C. Cheng, Y. Uchida, O. Nakajima, T. Ohshima, T. Yagi, M. Taniguchi, T. Nakayama, R. Kishida, Y. Kudo, S. Ohno, F. Nakamura, and Y. Goshima. 2002. Fyn and Cdk5 mediate semaphorin-3A signaling, which is involved in regulation of dendrite orientation in cerebral cortex. Neuron 35:907-920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Smith, D. S., P. L. Greer, and L. H. Tsai. 2001. Cdk5 on the brain. Cell Growth Differ. 12:277-283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Smith, D. S., and L. H. Tsai. 2002. Cdk5 behind the wheel: a role in trafficking and transport? Trends Cell Biol. 12:28-36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Totsukawa, G., Y. Wu, Y. Sasaki, D. J. Hartshorne, Y. Yamakita, S. Yamashiro, and F. Matsumura. 2004. Distinct roles of MLCK and ROCK in the regulation of membrane protrusions and focal adhesion dynamics during cell migration of fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 164:427-439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tripathi, B. K., M. A. Stepp, C. Y. Gao, and P. S. Zelenka. 2008. The Cdk5 inhibitor olomoucine promotes corneal debridement wound closure in vivo. Mol. Vis. 14:542-549. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tsai, L. H., I. Delalle, V. S. Caviness, Jr., T. Chae, and E. Harlow. 1994. p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371:419-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Vicente-Manzanares, M., J. Zareno, L. Whitmore, C. K. Choi, and A. F. Horwitz. 2007. Regulation of protrusion, adhesion dynamics, and polarity by myosins IIA and IIB in migrating cells. J. Cell Biol. 176:573-580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Watanabe, N., P. Madaule, T. Reid, T. Ishizaki, G. Watanabe, A. Kakizuka, Y. Saito, K. Nakao, B. M. Jockusch, and S. Narumiya. 1997. p140mDia, a mammalian homolog of Drosophila diaphanous, is a target protein for Rho small GTPase and is a ligand for profilin. EMBO J. 16:3044-3056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wilson, D. P., C. Sutherland, M. A. Borman, J. T. Deng, J. A. Macdonald, and M. P. Walsh. 2005. Integrin-linked kinase is responsible for Ca2+-independent myosin diphosphorylation and contraction of vascular smooth muscle. Biochem. J. 392:641-648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Xie, Z., K. Sanada, B. A. Samuels, H. Shih, and L. H. Tsai. 2003. Serine 732 phosphorylation of FAK by Cdk5 is important for microtubule organization, nuclear movement, and neuronal migration. Cell 114:469-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yee, H. F., Jr., A. C. Melton, and B. N. Tran. 2001. RhoA/rho-associated kinase mediates fibroblast contractile force generation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 280:1340-1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yin, J., and F. S. Yu. 2008. Rho kinases regulate corneal epithelial wound healing. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 295:C378-C387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zelenka, P. S., and P. Arpitha. 2008. Coordinating cell proliferation and migration in the lens and cornea. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 19:113-124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zukerberg, L. R., G. N. Patrick, M. Nikolic, S. Humbert, C. L. Wu, L. M. Lanier, F. B. Gertler, M. Vidal, R. A. Van Etten, and L. H. Tsai. 2000. Cables links Cdk5 and c-Abl and facilitates Cdk5 tyrosine phosphorylation, kinase upregulation, and neurite outgrowth. Neuron 26:633-646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]