Abstract
Organometallic pyridocarbazole scaffolds are investigated as protein kinase inhibitors. Whereas our previous designs employed solely a maleimide pharmacophore for achieving the two crucial canonical hydrogen bonds to the hinge region of the ATP binding site, we have now extended our investigations to include the related lactam metallo-pyridocarbazoles. The synthetic access of the two regioisomeric lactam pyridocarbazoles is described and the distinct biological properties of the two lactam scaffolds are revealed by employing a ruthenium half sandwich complex as a model system, resulting in organometallic lead structures for the inhibition of the protein kinases TrkA and CLK2. These new lactam metallo-pyridocarbazoles expand our existing molecular toolbox and assist towards the generation of metal complex scaffolds as lead structures for the design of selective inhibitors for numerous kinases of the human kinome.
Introduction
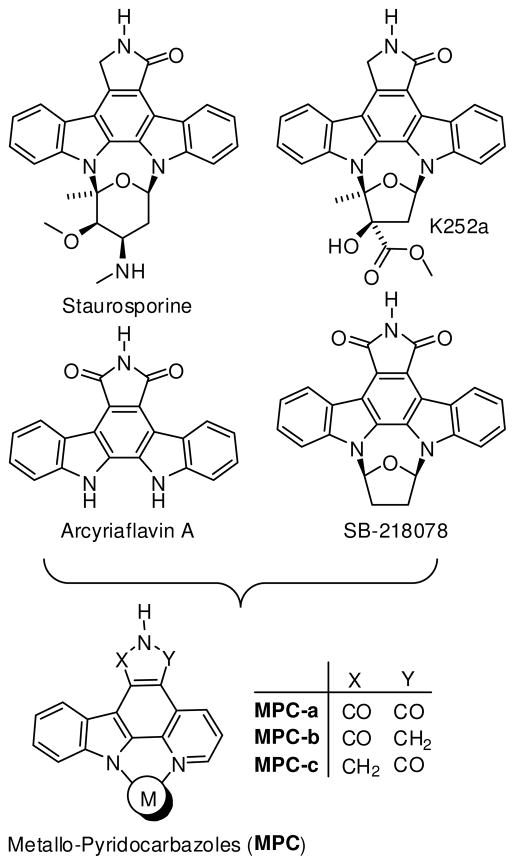
Recently, our group has initiated a research program that aims at exploring the versatility of organometallic complexes as structural scaffolds for the design of enzyme inhibitors. Unlike traditional applications for metals in medicine, we envisioned that substitutionally inert transition metals could act as a scaffold to organize organic ligands in three-dimensional space. As a proof-of-principle, we chose kinases as our main targets and started by morphing the indolocarbazole natural product class and synthetic derivatives thereof into chemically inert metallo-pyridocarbazoles (MPC, Figure 1).1 Based on this scaffold, we have reported over the last 5 years organometallic inhibitors for the kinases GSK32–7, Pim14,6,8, MSK14, PAK19, and PI3K10. Multiple co-crystal structures of metal complexes bound to the ATP binding sites of kinases are deposited in the Protein Databank (e.g. 2BZH, 2BZI, 2OI4, 2BZJ, 2IWI, 3CST, 3BWF, 3FXZ), all of them confirming that the metal exerts a purely structural role and is not in direct contact with any residue in the active site.7–11 Some of the published inhibitors belong to the most potent and selective compounds known for their respective kinases and we hypothesize that this is caused at least in parts by the combination of globular shape and rigidity of these scaffolds.
FIGURE 1.
Indolocarbazole natural products and derivatives as an inspiration for metallo-pyridocarbazoles as protein kinase inhibitors.
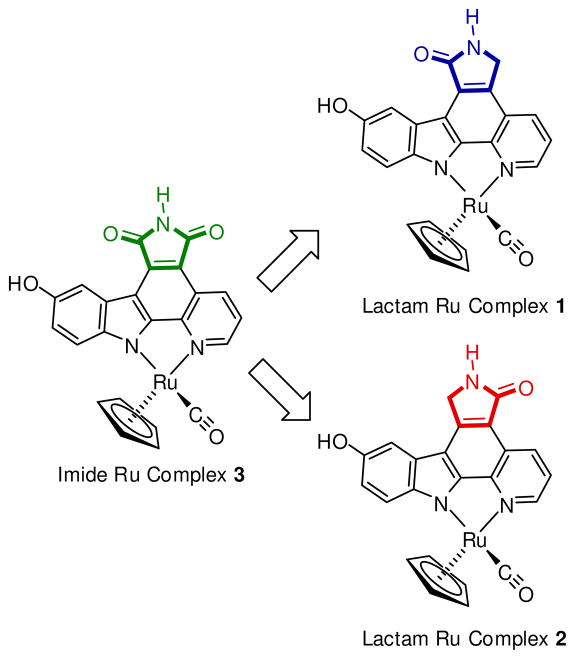
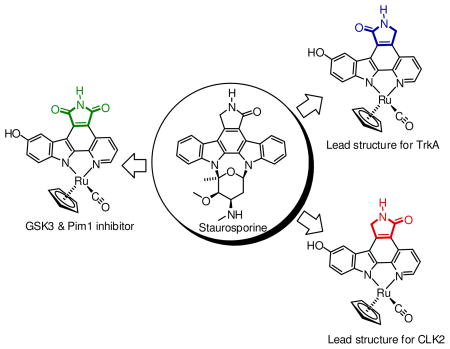
To date, all published MPC complexes contain the maleimide pharmacophore MPC-a, whereas the indolocarbazole alkaloids staurosporine and K252a, among others, possess a lactam moiety instead (Figure 1).12 The lactam or imide is essential for the binding to most kinases as they both can undergo two key hydrogen-bonds with the hinge region of the ATP binding site. However, at the same time it is known that certain kinases prefer the one pharmacophore over the other. Thus, in order to expand the versatility and generality of our MPC scaffold for the design of selective kinase inhibitors, we were seeking synthetic access of the two regioisomeric lactam pyridocarbazole complexes MPC-b and MPC-c (Figure 1). We here now report our progress into this direction and disclose the synthesis of lactam ruthenium complexes 1 and 2 (Figure 2). In fact, it turns out that lactam complexes 1 and 2 and the previously reported maleimide complex 3 differ significantly in their kinase selectivity profiles. For example, whereas maleimide 3 is a promising lead structure for developing selective inhibitors for GSK3 and Pim-1,3,5–8 lactam 1 constitutes a lead structure for TrkA, and lactam 2 is a potential starting point for CLK2 inhibitor design.
FIGURE 2.
Ruthenium half sandwich complexes as a model system to compare the protein kinase inhibition properties of imide and lactam metallo-pyridocarbazoles. Compounds 1–3 are racemic but only one enantiomer is shown for clarity.
Results and Discussion
Synthesis
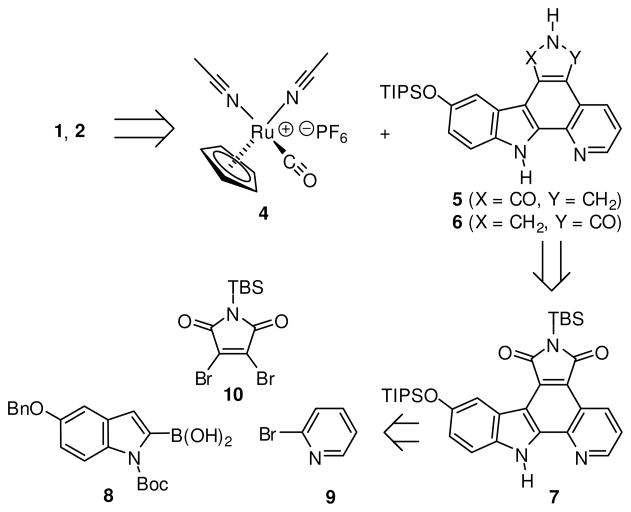
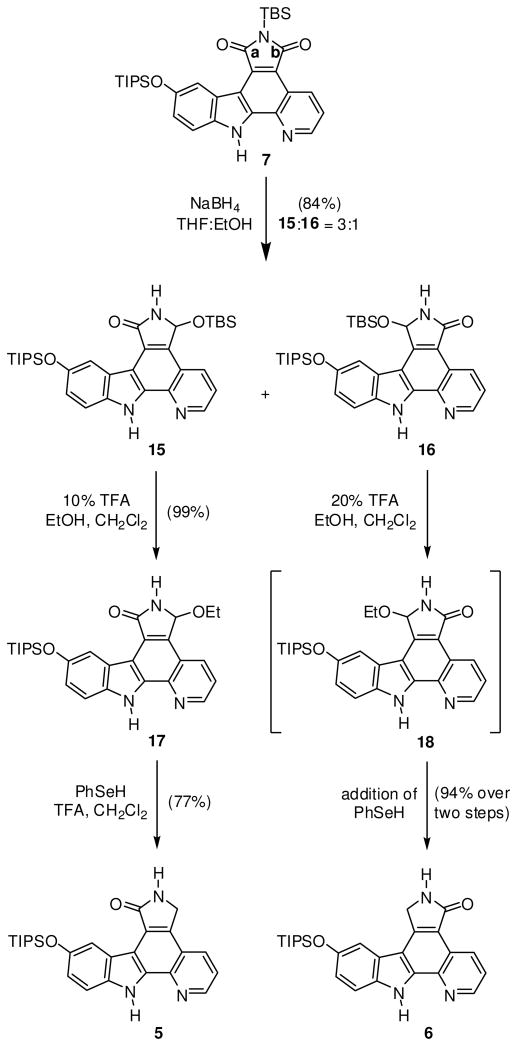
A retrosynthetic analysis of the ruthenium complexes 1 and 2 is shown in Scheme 1. The complexes 1 and 2 are accessed from the ruthenium half sandwich complex 4 and the triisopropylsilyl (TIPS)-protected lactam pyridocarbazoles 5 and 6, respectively. Both lactams 5 and 6 can be synthesized in two consecutive reduction steps starting with the imide pyridocarbazole 7. Heterocycle 7 itself can be assembled from three easily accessible building blocks (8–10) in a series of six linear steps which include three C-C bond formation reactions.13,14
SCHEME 1.
Retrosynthetic analysis of lactam pyridocarbazole complexes 1 and 2.
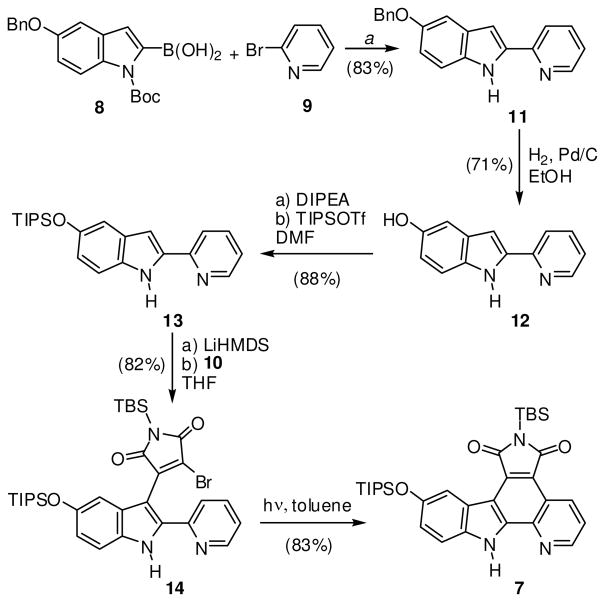
The synthesis of imide pyridocarbazole 7 is outlined in Scheme 2. Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling of boronic acid 8 with α-halogenated pyridine 9 furnished the desired 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole with the Boc-protection group partially removed. Unable to completely separate the two compounds, the purified mixture was adsorbed onto silica gel and heated under high vacuum to completely remove the Boc group to afford the 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 11 in 83% over two steps. Alternatively, the potassium trifluoroborate analog of indole 8 could also be used for this transformation.13,15,16 Before conducting the next two C-C bond formation reactions, the benzyl-protection group was first exchanged for a TIPS group in order to render the scaffold more soluble in organic solvents. This was accomplished by hydogenolysis with H2, Pd/C furnishing the phenol derivative 12 (71%), followed by treatment with TIPS triflate in the presence of the base di(isopropyl)ethylamine to afford the TIPS-protected pyridoindole 13 (88%). 2-Pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 13 was deprotonated with LiHMDS and reacted with dibromomaleimide 10 to afford monobromide 14 in 82% yield. The final C-C bond could then be installed by a photocyclization of 14 in toluene with a medium pressure Hg lamp using an uranium filter (50% transmission at 350 nm) to provide pyridocarbozole 7 (83%). In summary, the bis-silyl protected ligand 7 was prepared in a total of six steps in an overall yield of 35%.
SCHEME 2.
Synthesis of maleimide pyridocarbazole 7. a Reaction conditions: First, 1.1 equiv of 8, 1.0 equiv 9, 0.1 equiv of Pd(0) catalyst, 2.75 equiv Na2CO3, DME/H2O, reflux, overnight, then 10:1 mass ratio silica gel:indole, high vacuum, 80 °C, overnight.
The first of two reduction steps conducted on the imide pyridocarbazole 7 is shown in Scheme 3. Two equivalents of NaBH4 were added at 0 °C each hour for a total of eight hours, followed by warming to room temperature to furnish regioisomeric products 15 and 16 in a ratio of 3:1 in a combined yield of 84%. Slow addition of the reducing agent at low temperature is critical, preventing the loss of the tert-butyldimethylsilyl (TBS) protection group. Migration of the TBS group to the newly formed sp3 oxygen atom retains the TBS group required for the solubility of the compounds in organic solvents and the successful separation of the two regioisomers using column chromatography.
SCHEME 3.
Synthesis of lactam pyridocarbazoles 5 and 6 from maleimide 7.
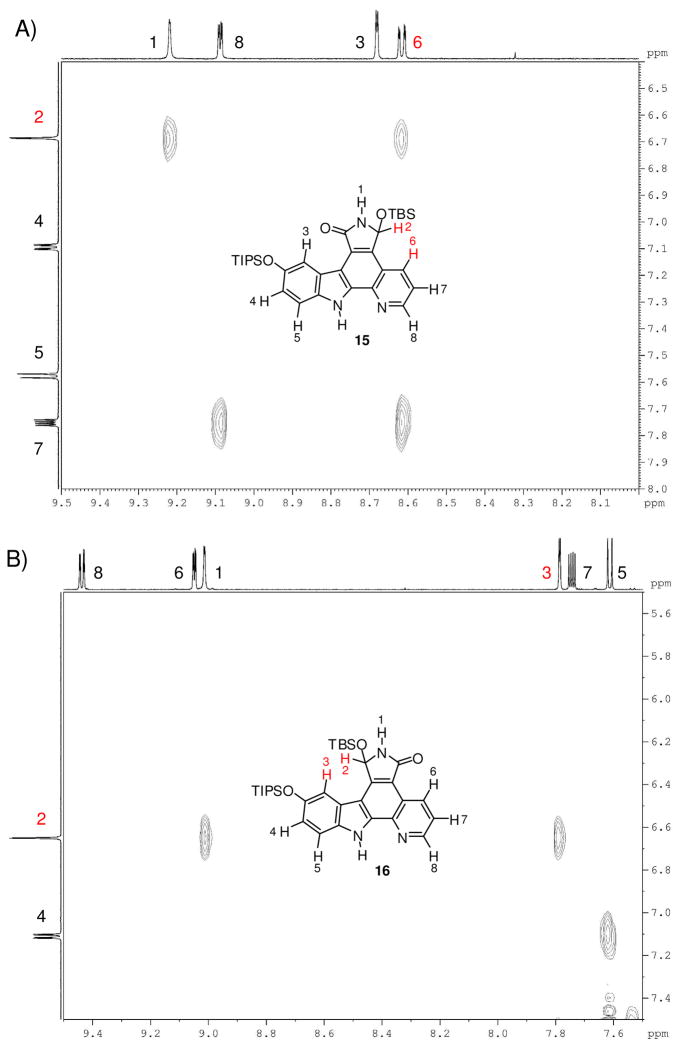
The constitutions of the two regioisomeric lactams 15 and 16 were assigned by rotational frame nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (ROESY) analysis of both regioisomers 15 and 16 (Figure 3). We were initially surprised by the observed regioselectivity because we expected the reaction to occur primarily at the more electrophilic carbonyl group a of heterocycle 7 (Scheme 3).17,18 This carbonyl group is directly conjugated to the electron poor pyridine, unlike the carbonyl b, which is directly conjugated to the electron rich indole. Additionally, we suspected that nucleophilic attack of carbon center b would be more hindered as a result of the hydride approaching from the same side as the bulky TIPS group.19–21 However, a likely explanation for this observed result could be the difference in the transition state energies, with migration of the TBS group preferring the more electron rich oxygen atom conjugated to the indole.
FIGURE 3.
1H-1H-ROESY spectra (DMSO-d6, 600 MHz) of compounds 15 and 16. A) Compound 15: Through-space correlation between H2 and H6. B) Compound 16: Through-space correlation between H2 and H3.
Transformation of heterocycles 15 and 16 to their corresponding lactams is outlined in Scheme 3. First, the TBS group of 15 was replaced by an ethyl group through treatment with 0.1% ethanol in the presence of 10% TFA to afford heterocycle 17 in near quantitative yield. This ether derivative could then smoothly be reduced to lactam 5 in 77% yield using phenylselenol and a slight excess of TFA in refluxing methylene chloride.22,23 It is noteworthy, that initial attempts to directly convert TBS-protected ligand 15 to lactam 5 failed and we attributed this to the size of the TBS ether, precluding the necessary nucleophilic attack of phenylselenol. In analogy, treatment of TBS-protected ligand 16 with 0.1% ethanol in now 20% TFA afforded intermediate 18, which due to its poor solubility, was immediately reacted with phenylselenol in refluxing methylene chloride to furnish lactam 6 in excellent yield (94%) over two steps.
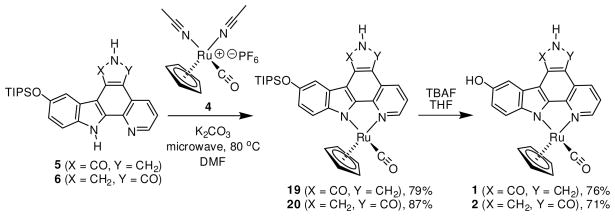
Introduction of the ruthenium half sandwich fragment using both lactam ligands 5 and 6 is shown in Scheme 4. Unable to optimize the coordination step using regular heating with an oil bath, we were pleased to discover that the complexation proceeds very smoothly under microwave irradiation. Lactams 5 and 6 were each reacted with ruthenium precursor 4 in the presence of K2CO3 in anhydrous DMF at 80 °C. After only 10 minutes, both reactions were complete as judged by thin layer chromatography. After column chromatography, TIPS-protected ruthenium complexes 19 and 20 were isolated in high yields of 79% and 87%, respectively. Lactam inhibitor complexes 1 and 2 were then prepared by careful treatment with tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) (76% and 71%, respectively). It should be noted that lactam ruthenium complexes 20 and 2, in contrast to 19 and 1, are slightly air sensitive, slowly oxidizing to their corresponding imide analogs if left in solution for long periods of time. Also, this process is accelerated in the presence of base. Therefore, it is critical to thoroughly purge both reactions 6→20 and 20→2 with inert gas. Furthermore, as a precaution, DMSO stock solutions of ruthenium complex 2 were purged with nitrogen and stored frozen at −20 °C until assayed for activity.
SCHEME 4.
Synthesis of lactam complexes 1 and 2, which are formed as racemates but only one enantiomer is shown for clarity.
Kinase inhibition
In order to identify similarities and differences between the new lactam half sandwich complexes 1 and 2 compared to the imide compound 3, racemic mixtures of complexes 1–3 were screened at one concentration against a panel of 253 human kinases (Millipore KinaseProfiler).24 As expected, the racemic mixture of maleimide 3 displayed high potencies for GSK3 (α-isoform: 0% activity at 30 nM, 10 μM ATP), and Pim1 and Pim2 (1% and -1% activity at 30 nM, respectively, 10 μM ATP), whereas most other protein kinases were not inhibited to a significant degree (see Supporting Information). In contrast, lactams 1 and 2 displayed only very moderate inhibition of GSK3 with activities above 40% at concentrations of 100 nM (10 μM ATP). Furthermore, under the conditions of the screening (100 nM compound, 10 μM ATP), lactam 1 demonstrated a surprising selectivity for just very few kinases (Flt3(D835Y), MLCK, Pim1, and TrkA), whereas lactam 2 showed highest inhibitory activity against the protein kinases CLK2, PKG1β, and Pim1 (1%, 2%, and 2% remaining activities at 100 nM of 2, 10 μM ATP, respectively; see Supporting Information).
To investigate the inhibition of TrkA and CLK2 in more detail, the racemic half sandwich complexes 1–3 were first resolved into their individual enantiomers. The chiral separation of imide 3 has been reported recently,8 and the chiral separation of lactam ruthenium complexes 1 and 2 was accomplished by resolving the individual enantiomers of their TIPS-protected half sandwich analogs 19 and 20, with the TIPS group serving as a handle to increase solubility in organic solvents. The resolution of 10 mg of each enantiomer of TIPS-protected complexes 19 and 20 was achieved using an analytical HPLC chiral column, and subsequently all four stereoisomers were treated separately with TBAF and purified over column chromatography. Assignment of the absolute configuration for each enantiomer for both complexes was achieved by comparing individual CD spectra with known reference compounds (see Supporting Information).
Table 1 displays the IC50 values of the individual enantiomers of 1–3 against Pim1, GSK3β, TrkA, and CLK2. The data demonstrate that by simply removing one carbonyl group of imide 3 a profound influence on the potency and selectivity of the half sandwich scaffold is achieved. As reported recently, (RRu)-3 and some derivatives show a high selectivity for GSK3 and Pim1, whereas the enantiomer (SRu)-3 is a very selective inhibitor of Pim1.5–8 However, replacing one carbonyl group by a methylene group of the Pim1 inhibitor lead structure (SRu)-3 (IC50 = 0.2 nM) reduces the binding affinities for Pim1 by the factors of 200 and 30 for the lactam complexes (SRu)-1 and (SRu)-2, respectively. Even more pronounced, replacing the imide group for a lactam in the GSK3 inhibitor lead structure (RRu)-3 (IC50 = 1.0 nM) reduces the binding affinities for GSK3β by the factors of 330 and 1000, for the complexes (RRu)-1 and (RRu)-2, respectively.
TABLE 1.
IC50 values of imide and lactam half-sandwich complexes 1–3 and (RRu)-21 against Pim1, GSK3β, TrkA, and CLK2.a
| Pim1 | GSK3β | TrkA | CLK2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (RRu)-3 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 65 | b |
| (SRu)-3 | 0.2 | 15 | 40 | b |
| (RRu)-1 | 80 | 330 | 20 | c |
| (SRu)-1 | 40 | 1000 | 50 | c |
| (RRu)-2 | 25 | 1000 | 75 | 30 |
| (SRu)-2 | 6 | 370 | 15 | 5 |
| (RRu)-21 | 390 | 1200 | 6 | d |
IC50 data were obtained by phosphorylation of substrate peptides with [γ-32P]ATP or [γ-33P]ATP and 100 μM ATP in the presence different concentrations of organometallic kinase inhibitors. Each IC50 value was determined from at least two independent measurements and the average was taken. See experimental section for more details.
Racemic 3: IC50 = 35 nM at 100 μM ATP.
Racemic 1: 26% CLK2 activity at 100 nM 1 and 10 μM ATP.
50% CLK2 activity at 100 nM of (RRu)-21 at 10 μM ATP.
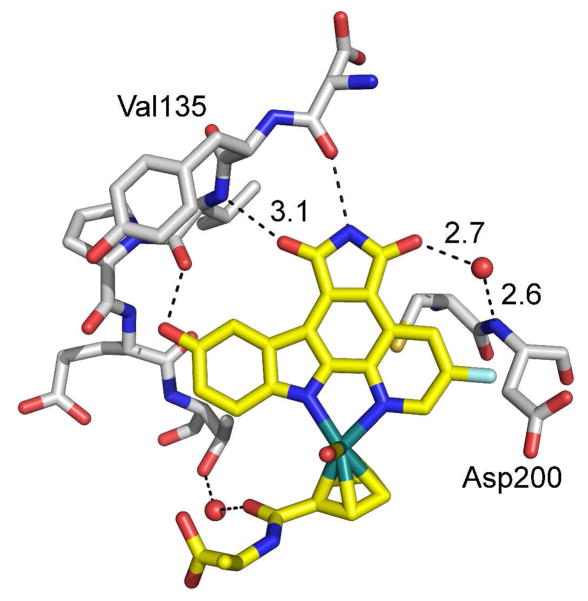
This dramatic loss in binding affinities of (RRu)-3 for GSK3 by removing a single carbonyl group can be rationalized with the help of a recently solved crystal structure of a related ruthenium half sandwich complex with GSK3β.7 Figure 4 shows the hydrogen bond interactions of the maleimide pyridocarbazole in the ATP binding site of GSK3β and reveals that both carbonyl groups are involved in hydrogen bonds, one with the hinge residue valine 135 and a second water-mediated contact with aspartate 200. This explains the preference of GSK3 for the maleimide over the lactam, which can provide only one of the two hydrogen bonding contacts.25
FIGURE 4.
Crystal structure of a maleimide-containing ruthenium pyridocarbazole half sandwich complex with GSK3β (PDB code 2JLD) showing the hydrogen bonding interactions of the maleimide carbonyl groups in the ATP binding site of GSK3β.
Thus, having eliminated the intrinsic preference of the half sandwich scaffold for GSK3 and Pim1 by transforming the imide group of 3 into lactam moieties, the individual enantiomers of complexes 1 and 2 can now be used as lead structures for other kinases. In fact, Table 1 demonstrates that the enantiomer (RRu)-1 displays a significant selectivity for TrkA over Pim1 (4-fold) and GSK3β (16.5-fold) and is therefore a promising lead structure for the development of further improved inhibitors of protein kinase TrkA, whereas (SRu)-2 displays an IC50 of just 5 nM (100 μM ATP) against CLK2, thus serving as a lead structure for the development of CLK2 inhibitors.
Improved inhibitor for protein kinase TrkA
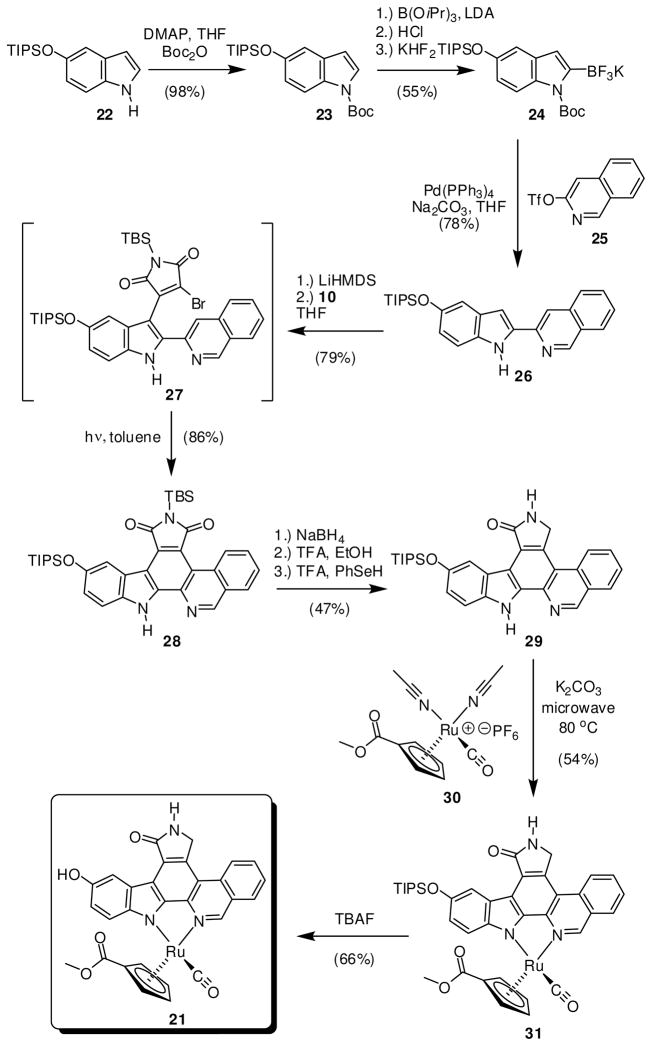
In order to verify that the obtained lactam complexes are indeed promising lead structures for the design of organometallic complexes as inhibitors for protein kinases different from Pim1 or GSK3, we decided to use (RRu)-1 as a starting point for the proof-of-principle design of a more potent and selective inhibitor for TrkA. From previous structure activity relationships with organoruthenium half sandwich complexes5,13,14 we envisioned that the complex (RRu)-21, differing from complex (RRu)-1 by a fused benzene ring at the pyridine moiety and a methylester at the cyclopentadienyl ring, might be an improved inhibitor for TrkA with a diminished affinity for Pim1. The synthesis of racemic 21 is summarized in Scheme 5. Starting with 5-(triisopropylsilyloxy)indole 22, Boc-protection afforded 23 (98%), which was subsequently converted to the stable trifluoroborate 24 (55%). Suzuki-Miyaura cross coupling of 24 with triflate 25 in refluxing anhydrous THF furnished 2-isoquinolin-3-yl-1H-indole 26 (77%) with complete loss of the Boc group. Next, isoquinolinyl-indole 26 was deprotonated with LiHMDS and condensed with dibromomaleimide 10 to afford the rather unstable monobromide 27 (79%). The final C-C bond could then be installed by a photocyclization in toluene with a medium pressure Hg lamp using an uranium filter to provide heterocycle 28 in a yield of 86%. Next, 28 was converted to the lactam 29 in a yield of 47% by first treatment with NaBH4, followed by EtOH with 0.1% TFA, and subsequently PhSeH in the presence of 2 equivalents of TFA. The lactam ligand 29 was reacted with ruthenium half sandwich complex 30 in the presence of K2CO3 in anhydrous DMF at 80 °C under microwave irradiation. After 10 minutes and column chromatography, TIPS-protected ruthenium complex 31 was isolated in a yield of 54%. Finally, treatment of 31 with TBAF at 0 °C afforded the ruthenium complex 21 (66%) and the racemic mixture of 21 was resolved into its enantiomers at this final stage using an analytical chiral HPLC column. The absolute configuration for both enantiomers was assigned by comparison of CD spectra with known reference compounds (see Supporting Information).
SCHEME 5.
Synthesis of lactam complex 21. The half sandwich complexes were formed as racemates but only the (RRu)-enantiomer is shown for clarity.
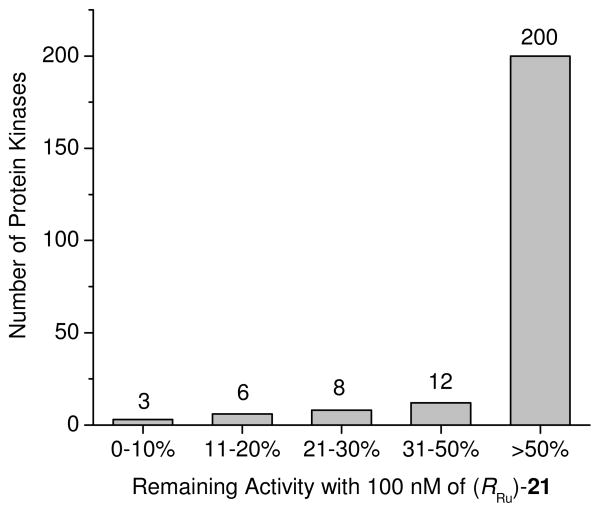
IC50 values of (RRu)-21 at 100 μM ATP against TrkA, GSK3β, and Pim1 are presented in Table 1. Gratifyingly, (RRu)-21 shows a significantly improved potency and selectivity compared to the initial lead structure (RRu)-1. With an IC50 value of 6 nM for TrkA, (RRu)-21 prefers binding to TrkA over Pim1 by a factor of 65 (IC50 = 390 nM) and even a factor of 200 over GSK3β (IC50 = 1200 nM). Thus, (RRu)-21 displays high selectivity over Pim1 and GSK3 and probably most other protein kinases. In fact, a screening of complex (RRu)-21 against a panel of human wild-type protein kinases demonstrates the excellent selectivity profile of (RRu)-21 (Figure 5). From 229 tested protein kinases, 200 remained more than 50% active at a concentration of 100 nM of (RRu)-21 (10 μM ATP) and only 3 kinases, including TrkA and TrkB, displayed activities below 10% under these conditions. Thus, it can be concluded that (RRu)-21 constitutes a highly selective molecular probe for the protein kinase TrkA.
FIGURE 5.
Selectivity profile of (RRu)-21 tested against a panel of 229 human wild-type protein kinases at a single concentration of 100 nM and an ATP concentration of 10 μM. Duplicate measurements were performed and the average was taken.
Conclusions
We have here reported synthetic access to the class of lactam metallo-pyridocarbazoles MPC-b and MPC-c, thus complementing the previously developed imide metallo-pyridocarbazole scaffold MPC-a and therefore expanding our toolbox of using metallo-pyridocarbazoles as general scaffolds for the design of selective kinase inhibitors. The distinct properties of the lactam scaffolds have been demonstrated by using the half sandwich complex 3 as a model system. By replacing the imide pharmacophore of 3 for the lactam moieties in 1 and 2, we have changed the selectivity profile from GSK3/Pim1 selectivity of (RRu)-3 and Pim1 selectivity of (SRu)-3, to TrkA selectivity of (RRu)-1 and CLK2 selectivity of (SRu)-2. These lactam metallo-pyridocarbazoles will serve as scaffolds for the design of protein kinase inhibitors with new selectivity profiles as has been demonstrated with the TrkA- selective organoruthenium complex (RRu)-21.
Experimental Part
All reactions were carried out using oven-dried glassware and conducted under a positive pressure of nitrogen unless otherwise specified. NMR spectra were recorded on an Avance 300 (300 MHz), DRX-400 (400 MHz), or DRX-500 (500 MHz) spectrometer. ROESY experiments were recorded on a Bruker Avance 600 MHz spectrometer. Infrared spectra were recorded on either a Bruker Alpha FTIR or Nicolet 510 FTIR spectrometer. High resolution mass spectra were obtained with a Finnigan LTQ-FT instrument using either APCI or ESI. Reagents and solvents were used as received from standard suppliers unless otherwise specified. CD spectra were recorded on a JASCO J-810 spectropolarimeter. Ruthenium complexes 4 and 30 were prepared as previously reported.5,26
Compound 11
A biphasic suspension of pyridine 9 (0.87 mL, 9.1 mmol), indole 8 (3.67 g, 10.0 mmol), tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) (1.05 g, 0.91 mmol) and Na2CO3 (2.65 g, 25.0 mmol) in 1,2-dimethoxyethane (39 mL) and water (11 mL) was purged with nitrogen for 15 minutes and then refluxed overnight. The resulting orange reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with water and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and chromatographed using hexanes:EtOAc (8:1 to 1:1). The combined product eluents were isolated as a mixture of a Boc-protected 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole and compound 11. The resulting orange solid (2.82 g) was dissolved into EtOAc and adsorbed onto silica gel (28.2 g) using rotary evaporation. The powder was heated to 80 °C overnight under high vacuum. The silica gel was cooled to room temperature, filtered through cotton with CH2Cl2:MeOH (15:1) and the filtrate dried in vacuo to provide 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 11 (2.27 g, 83% over 2 steps) as a yellow solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 9.54 (s, 1H), 8.57 (ddd, J = 4.9, 1.7, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.79–7.67 (m, 2H), 7.51–7.48 (m, 2H), 7.43–7.29 (m, 4H), 7.18–7.14 (m, 2H), 6.98 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (dd, J = 2.1, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 5.12 (s, 2H). 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 153.9, 150.6, 149.4, 137.9, 137.6, 136.8, 132.2, 129.7, 128.7, 128.0, 127.8, 122.1, 119.9, 114.8, 112.3, 104.3, 100.5, 71.1. IR v (cm−1) 3192, 1622, 1594, 1562, 1543, 1469, 1443, 1299, 1257, 1214, 1150, 1119, 785, 775, 741. HRMS calcd for C20H16N2ONa (M+Na)+ 323.1155, found (M+Na)+ 323.1152.
Compound 12
A suspension of 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 11 (2.14 g, 7.13 mmol) in ethanol (98 mL) was purged with nitrogen for 15 minutes. Following thorough nitrogen purge, palladium (10 wt% on activated carbon, dry) (2.14 g) was added and the reaction mixture was carefully purged with hydrogen gas for approximately 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was then stirred at room temperature under an atmosphere of hydrogen, monitoring by thin layer chromatography. After 2 hours, the resulting dark reaction mixture was filtered through celite with CH2Cl2:MeOH (10:1) and the filtrate concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (1:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide the 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 12 (1.07 g, 71%) as an off-white solid. 1H-NMR consistent with literature reported spectrum.3
Compound 13
A solution of 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 12 (1.07 g, 5.10 mmol) in DMF (18.3 mL) was cooled to 0 °C and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (4.50 mL, 25.5 mmol) was added dropwise. After stirring for 10 minutes at 0 °C, triisopropylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (1.44 mL, 5.36 mmol) was added dropwise over 15 minutes and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for an additional hour. The resulting yellow solution was cooled to 0 °C and excess 1 M NH4OAc was carefully added. The mixture was then further diluted with water and extracted with CH2Cl2. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with CH2Cl2:MeOH (100:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide the 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 13 (1.65 g, 88%) as a white solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 10.30 (s, 1H), 8.59 (ddd, J = 4.9, 1.7, 1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.80 (td, J = 8.0, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.70 (ddd, J = 8.0, 7.4, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.17-7.13 (m, 3H), 6.95 (dd, J = 2.1, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 1.39-1.27 (m, 3H), 1.17 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 150.7, 150.1, 149.1, 137.5, 136.7, 132.5, 129.8, 121.9, 119.9, 117.8, 111.8, 109.9, 100.4, 18.1, 12.8. IR v (cm−1) 3150, 2940, 2861, 1595, 1545, 1442, 1292, 1280, 1222, 1150, 963, 879, 804, 776, 679. HRMS calcd for C22H31N2OSi (M+H)+ 367.2200, found (M+H)+ 367.2198.
Compound 14
A solution of high-vacuum-dried 2-pyridin-2-yl-1H-indole 13 (1.55 g, 4.23 mmol) in freshly distilled THF (11 mL) was cooled to −15 °C. Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (1 M solution in hexanes) (12.7 mL, 12.7 mmol) was added dropwise over 15 minutes and the resulting orange reaction mixture was stirred at −15 °C for an additional 45 minutes. A solution of vacuum dried 10 (1.64 g, 4.44 mmol) in freshly distilled THF (11 mL) cooled to 0 °C was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at −15 °C for 20 minutes and room temperature overnight. The resulting dark purple reaction mixture was carefully poured into stirring ice cold water (300 mL) and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (6:1 to 3:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide monobromide 14 (2.25 g, 82%) as an orange solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 10.22 (s, 1H), 8.58 (d, J = 4.2 Hz, 1H), 7.61 (ddd, J = 7.8, 7.8, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (ddd, J = 7.5, 4.9, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 6.99 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 1.34-1.23 (m, 3H), 1.12 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 18H), 1.00 (s, 9H), 0.49 (s, 6H). 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 173.4, 171.1, 151.1, 149.8, 149.4, 141.7, 137.2, 136.8, 131.5, 128.2, 125.6, 122.8, 122.7, 118.9, 112.5, 110.4, 101.7, 26.5, 19.1, 18.3, 12.9, −4.2. IR v (cm−1) 3337, 2947, 2865, 1703, 1635, 1473, 1313, 1269, 1213, 1186, 1086, 971, 892, 826, 735. HRMS calcd for C32H45BrN3O3Si2 (M+H)+ 654.2177, found (M+H)+ 654.2182.
Compound 7
An orange suspension of monobromide 14 (1.10 g, 1.68 mmol) in toluene (250 mL) was irradiated with a medium pressure Hg lamp using a uranium filter (50% transmission at 350 nm) for 6 hours with constant nitrogen flow through the reaction mixture. The resulting red solution was concentrated, and the reaction was repeated using an additional 1.10 g (1.68 mmol) of 14. Once combined, the red solution was concentrated to dryness in vacuo, adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (6:1 to 1:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide pyridocarbazole 7 (1.60 g, 83%) as a yellow solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 10.48 (s, 1H), 9.42 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 8.99 (dd, J = 4.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 8.69 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (dd, J = 8.5, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 7.41 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 1.46-1.34 (m, 3H), 1.18 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 18H), 1.07 (s, 9H), 0.63 (s, 6H). 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 175.7, 174.1, 151.5, 150.4, 140.8, 138.7, 134.9, 134.6, 131.0, 123.3, 122.9, 122.1, 121.5, 120.4, 115.4, 114.6, 111.9, 26.7, 19.3, 18.3, 12.9, −3.9. IR v (cm−1) 3456, 2946, 2866, 1751, 1695, 1527, 1473, 1338, 1314, 1281, 1216, 1182, 905, 827, 795. HRMS calcd for C32H44N3O3Si2 (M+H)+ 574.2916, found (M+H)+ 574.2926.
Compounds 15 and 16
A solution of pyridocarbazole 7 (510 mg, 0.890 mmol) in THF-EtOH (1:1) (51 mL) was cooled to 0 °C. Sodium borohydride (68 mg, 1.79 mmol) was added every hour for a total of 8 hours and the stirred reaction mixture was then allowed to naturally warm to room temperature overnight. The resulting yellow reaction mixture was again cooled to 0 °C, carefully quenched with addition of saturated aqueous NH4Cl and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (6:1 to 3:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to individually provide pure 15 (320 mg, 63%) and 16 (110 mg, 21%). The constitutions of 15 and 16 were assigned by ROESY analysis (see Figure 3).
Compound 15
1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 12.55 (s, 1H), 9.21 (d, J = 1.7 Hz, 1H), 9.07 (dd, J = 4.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 8.66 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 8.59 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (dd, J = 8.4, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.07 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.67 (d, J = 1.8 Hz, 1H), 1.39- 1.27 (m, 3H), 1.11 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 18H), 0.81 (s, 9H), 0.21 (s, 3H), −0.21 (s, 3H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 170.3, 150.1, 149.0, 138.6, 137.3, 135.6, 134.7, 133.2, 125.6, 122.4, 121.1, 120.9, 119.5, 114.0, 113.4, 112.4, 79.1, 25.6, 17.9, 17.6, 12.1, −4.0. IR v (cm−1) 3293, 3075, 2928, 2862, 1695, 1472, 1272, 1216, 1079, 1039, 981, 883, 832, 789, 668, 484. HRMS calcd for C32H45N3O3Si2Na (M+Na)+ 598.2892, found (M+Na)+ 598.2897.
Compound 16
1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 12.76 (s, 1H), 9.41 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 9.03 (dd, J = 4.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 9.00 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.72 (dd, J = 8.4, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.63 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 1.36- 1.26 (m, 3H), 1.10 (d, J = 6.7 Hz, 18H), 0.73 (s, 9H), 0.03 (s, 3H), −0.50 (s, 3H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 170.8, 149.4, 149.0, 143.6, 138.9, 137.2, 134.7, 131.9, 122.3, 122.1, 122.0, 119.0, 115.4, 114.6, 112.7, 111.9, 78.7, 25.6, 17.8, 17.6, 12.1, −3.4, −3.9. IR v (cm−1) 3156, 3071, 2945, 2927, 2865, 1686, 1670, 1530, 1471, 1280, 1251, 1213, 1094, 984, 957, 878, 831, 792, 780, 682, 665. HRMS calcd for C32H46N3O3Si2 (M+H)+ 576.3072, found (M+H)+ 576.3080.
Compound 17
A yellow suspension of 15 (260 mg, 0.452 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (23.4 mL) containing 0.1% ethanol, was cooled to 0 °C. Trifluoroacetic acid (2.6 mL) was then carefully added and the resulting orange solution was stirred at 0 °C for 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was then carefully quenched with addition of saturated aqueous NaHCO3 and extracted with CH2Cl2. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo to provide 17 (220 mg, 99%) as a light yellow solid. See Supporting Information for a ROESY analysis. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 12.57 (s, 1H), 9.28 (d, J = 1.3 Hz, 1H), 9.07 (dd, J = 4.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 8.65 (d, J = 2.6 Hz, 1H), 8.63 (dd, J = 8.3, 1.7 Hz, 1H), 7.73 (dd, J = 8.4, 4.3 Hz, 1H), 7.55 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.07 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.43 (d, J = 1.4 Hz, 1H), 3.67 (m, 1H), 3.39 (m, 1H), 1.40-1.27 (m, 3H), 1.15 (t, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H), 1.11 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 170.3, 150.1, 149.0, 138.3, 137.5, 134.7, 132.9, 132.7, 126.6, 122.4, 121.5, 121.1, 119.5, 114.1, 113.4, 112.4, 83.5, 60.7, 17.9, 15.3, 12.1. IR v (cm−1) 3284, 3172, 3072, 2942, 2864, 1689, 1471, 1338, 1280, 1260, 1214, 1069, 1049, 881, 814, 792, 726, 682, 667, 621, 483. HRMS calcd for C28H35N3O3SiNa (M+Na)+ 512.2340, found (M+Na)+ 512.2338.
Compound 5
A suspension of 17 (220 mg, 0.450 mmol) in CH2Cl2 was purged with nitrogen for approximately 15 minutes. Phenylselenol (191 μL, 1.80 mmol) followed by trifluoroacetic acid (52 μL, 0.675 mmol) were then added and the resulting dark orange solution was heated to reflux for 5 hours. The reaction mixture was then cooled to room temperature and carefully quenched with addition of saturated aqueous NaHCO3. The CH2Cl2 was then removed in vacuo and the resulting yellow precipitate was collected, washed with twice with water, followed by diethyl ether (2 ×) to provide lactam 5 (153 mg, 77%) as a light yellow solid. 1H-NMR (400 MHz, 100 °C, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 12.06 (s, 1H), 9.05 (dd, J = 4.0, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 8.77 (s, 1H), 8.53 (dd, J = 8.3, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 8.34 (s, 1H), 7.67 (dd, J = 8.1, 4.1 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 4.85 (s, 2H), 1.38 (m, 3H), 1.16 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, 100 °C, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 171.1, 149.3, 148.4, 138.1, 135.9, 134.3, 134.1, 131.8, 126.2, 122.4, 120.7, 120.5, 118.6, 114.5, 113.4, 111.6, 44.2, 17.4, 11.7. IR v (cm−1) 3283, 3163, 3060, 2940, 2865, 1680, 1661, 1469, 1261, 1214, 1171, 1058, 978, 914, 879, 671, 658, 623, 553, 457. HRMS calcd for C26H32N3O2Si (M+H)+ 446.2258, found (M+H)+ 446.2258.
Compound 6
A suspension of 16 (45 mg, 0.078 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (3.6 mL) containing 0.1% ethanol, was cooled to 0 °C. Trifluoroacetic acid (0.9 mL) was then carefully added and the resulting orange solution was allowed to naturally warm to room temperature, stirring for a total of 3 hours. Following thin layer chromatography analysis, the reaction mixture was purged with nitrogen for approximately 15 minutes. Phenylselenol (34 μL, 0.312 mmol) was then added and the reaction was heated to reflux overnight. The reaction mixture was then cooled to room temperature and carefully quenched with addition of saturated aqueous NaHCO3. The CH2Cl2 was then removed in vacuo and the resulting yellow precipitate was collected, washed twice with water, followed by diethyl ether (2 ×) to provide lactam 6 (32 mg, 94% over 2 steps) as a white solid. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, 100 °C, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 12.35 (s, 1H), 9.53 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.99 (dd, J = 4.2, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 8.13 (s, 1H), 7.69-7.64 (m, 2H), 7.46 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.10 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.2 Hz, 1H), 4.89 (s, 2H), 1.35 (septet, J = 7.4, 3H), 1.15 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 18H). IR v (cm−1) 3156, 3063, 2943, 2865, 1678, 1652, 1533, 1463, 1279, 1244, 1209, 1174, 964, 868, 809, 787, 672, 568, 434. HRMS calcd for C26H31N3O2SiNa (M+Na)+ 468.2078, found (M+Na)+ 468.2083.
Compound 19
To a vacuum dried solid mixture of lactam 5 (20 mg, 0.045 mmol), ruthenium precursor 426 (21 mg, 0.050 mmol) and K2CO3 (7.0 mg, 0.050 mmol) was added freshly distilled DMF (2.0 mL) and the resulting suspension was purged with nitrogen for approximately 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was then heated to 80 °C for 10 minutes in a microwave reactor (CEM Discover). The resulting dark red solution was concentrated using high vacuum and co-evaporated once with EtOAc. The crude material was subjected to silica gel chromatography with toluene:acetone (3:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide complex 19 (23 mg, 79%) as an orange film. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 8.86 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 8.56 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.17 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 7.32-7.28 (m, 2H), 7.15 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.92 (s, 1H), 5.20 (s, 5H), 4.76 (s, 2H), 1.48-1.38 (m, 3H), 1.21 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 200.6, 173.0, 154.1, 151.1, 148.7, 147.9, 146.1, 131.7, 129.3, 128.0, 124.5, 121.0, 119.6, 119.4, 115.8, 114.7, 114.0, 80.9, 45.1, 18.4, 13.0. IR v (cm−1) 3183, 3077, 2942, 2925, 2865, 1951, 1731, 1686, 1607, 1544, 1462, 1405, 1267, 1244, 1210, 1189, 1127, 1056, 997, 977, 922, 896, 884, 835, 805, 791, 688. HRMS calcd for C32H36N3O3RuSi (M+H)+ 640.1564, found (M+H)+ 640.1561.
Compound 20
To a vacuum dried solid mixture of lactam 6 (10 mg, 0.023 mmol), ruthenium precursor 4 (11 mg, 0.025 mmol) and K2CO3 (3.5 mg, 0.025 mmol) was added freshly distilled DMF (1.0 mL) and the resulting suspension was purged with nitrogen for approximately 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was then heated to 80 °C for 10 minutes in a microwave reactor (CEM Discover). The resulting yellow-orange solution was concentrated using high vacuum and co-evaporated once with EtOAc. The crude material was subjected to silica gel chromatography with toluene:acetone (3:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide complex 20 (13 mg, 87%) as an yellow solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 9.41 (dd, J = 8.3, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.81 (dd, J = 5.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (dd, J = 8.3, 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.13 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.26 (s, 1H), 5.19 (s, 5H), 4.95 (s, 2H), 1.40-1.28 (m, 3H), 1.17 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 200.4, 173.7, 153.2, 153.1, 149.6, 147.8, 145.2, 145.0, 133.2, 124.6, 123.3, 121.0, 118.6, 115.7, 115.2, 111.9, 110.7, 80.8, 45.1, 18.3, 13.0. IR v (cm−1) 2943, 2865, 1951, 1676, 1608, 1583, 1520, 1456, 1432, 1421, 1397, 1334, 1275, 1247, 1207, 1189, 923, 882, 685. HRMS calcd for C32H36N3O3RuSi (M+H)+ 640.1564, found (M+H)+ 640.1537.
Compound 1
To a vacuum dried sample of complex 19 (23 mg, 0.036 mmol) was added freshly distilled THF (2.3 mL) and the resulting solution was purged with nitrogen while cooling to 0 °C. Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (1 M solution in THF, dried over 4 Å molecular sieves) (47 μL, 0.047 mmol) was then added and the reaction mixture immediately became a dark red suspension. Within 1 minute, the reaction was quenched with excess saturated aqueous NH4Cl (orange color returns) and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was then subjected to silica gel chromatography with CH2Cl2:MeOH (20:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide complex 1 (13 mg, 76%) as a light red solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 9.19 (dd, J = 5.1, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 8.79 (s, 1H), 8.72 (s, 1H), 8.56 (dd, J = 8.2, 1.1 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (d, J = 2.2 Hz, 1H), 7.57 (dd, J = 8.3, 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.31 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 6.93 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 5.48 (s, 5H), 4.80 (s, 2H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 201.7, 171.6, 155.3, 150.0, 149.4, 146.2, 144.9, 132.7, 128.9, 128.7, 124.0, 120.6, 120.2, 115.0, 114.9, 114.2, 108.4, 81.6, 44.6. IR v (cm−1) 3263, 3108, 2930, 2856, 1940, 1680, 1608, 1473, 1406, 1223, 1186, 1048, 1024, 1004, 808, 793, 698. HRMS calcd for C23H15N3O3RuNa (M+Na)+ 506.0049, found (M+Na)+ 506.0055.
Compound 2
To a vacuum dried sample of complex 20 (11 mg, 0.017 mmol) was added freshly distilled THF (1.1 mL) and the resulting solution was purged with nitrogen while cooling to −40 °C. Ice cold nitrogen-purged tetrabutylammonium fluoride (1 M solution in THF, dried over 4 Å molecular sieves) (19 μL, 0.019 mmol) was then added and the reaction mixture immediately became a dark suspension. Within 1 minute, the reaction was quenched with excess glacial acetic acid and the resulting yellow solution was concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was then subjected to silica gel chromatography with CH2Cl2:MeOH (20:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide complex 2 (5.8 mg, 71%) as a yellow orange solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 9.25 (dd, J = 8.3, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 9.11 (dd, J = 5.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.95 (s, 1H), 8.31 (s, 1H), 7.57 (dd, J = 8.3, 5.2 Hz, 1H), 7.39-7.36 (m, 2H), 6.99 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 5.46 (s, 5H), 4.84 (s, 2H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 201.6, 172.0, 154.0, 151.5, 150.5, 146.1, 144.7, 143.8, 131.7, 124.3, 122.1, 121.1, 115.8, 114.6, 114.2, 111.7, 105.6, 81.6, 44.3. IR v (cm−1) 3232, 3108, 2928, 2854, 1938, 1651, 1606, 1583, 1520, 1452, 1401, 1334, 1216, 1184, 1024, 1004, 814, 789, 715, 693, 559. HRMS calcd for C23H16N3O3Ru (M+H)+ 484.0230, found (M+H)+ 484.0233.
Resolution of (RRu)-1 and (SRu)-1
Baseline separation of the enantiomers of half sandwich complex 19 was achieved using the Chiral Pak 1B analytical HPLC column (Daicel/Chiral Technologies). First, 19 was dissolved in a minimal amount of methylene chloride and carefully filtered. Then, each injection was run using an ethanol gradient of 20% to 80% over 20 minutes in hexanes. A flow rate of 0.7 mL/min was used and injection volumes of approximately 50 μL could be reached without compromising baseline separation. Each enantiomer was then treated separately with TBAF to provide both (RRu)-1 and (SRu)-1. Retention of enantiomeric purity was confirmed using the same Chiral Pak 1B analytical HPLC column. For this, 10 mM stock solutions (RRu)-1 and (SRu)-1 in DMSO were diluted with an equal volume of ethanol and carefully filtered. Then, analytical injections (5 μL) were run using an ethanol gradient of 50% to 95% over 20 minutes in hexanes with a flow rate of 0.7 mL/min. (RRu)-1 and (SRu)-1 were determined to be 99% and 98% enantiopure, respectively. Absolute configurations were assigned by CD-spectroscopy (see Supporting Information).
Resolution of (RRu)-2 and (SRu)-2
Baseline separation of the enantiomers of half sandwich complex 20 was achieved using the Chiral Pak 1B analytical HPLC column (Daicel/Chiral Technologies). First, 20 was dissolved in a minimal amount of methylene chloride and carefully filtered. Then, each injection was run using an acetone gradient of 25% to 75% over 20 minutes in hexanes. A flow rate of 0.7 mL/min was used and injection volumes of approximately 50 μL could be reached without compromising baseline separation. Additionally, a detection wavelength of 470 nm was used to avoid acetone absorption. Each enantiomer was then treated separately with TBAF to provide both (RRu)-2 and (SRu)-2. Retention of enantiomeric purity was confirmed using the same Chiral Pak 1B analytical HPLC column. First, 10 mM stock solutions (RRu)-2 and (SRu)-2 in DMSO were diluted with an equal volume of ethanol and carefully filtered. Then, analytical injections (5 μL) were run using an acetone gradient of 40% to 75% over 2 hours in hexanes with a flow rate of 0.7 mL/min and a detection wavelength of 470 nm. (RRu)-2 and (SRu)-2 were determined to be 99% and 98% enantiopure, respectively. Absolute configurations were assigned by CD-spectroscopy (see Supporting Information).
5-(Triisopropylsilyloxy)indole (22)27
A solution of 5-benzyloxyindole (2.50 g, 11.2 mmol) in EtOAc (100 mL) was purged with nitrogen for 15 minutes. Following thorough nitrogen purge, palladium (10 wt% on activated carbon, dry) (2.50 g) was added and the reaction mixture was carefully purged with hydrogen gas for approximately 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was then stirred at room temperature under an atmosphere of hydrogen, monitoring by thin layer chromatography. After 45 minutes, the resulting dark reaction mixture was filtered through celite with EtOAc and the filtrate concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The resulting light yellow solid was then redissolved in DMF (40 mL) and purged with nitrogen while cooling to 0 °C. Then, N,N-diisopropylethylamine (9.70 mL, 56.0 mmol) was added dropwise. After stirring for 10 minutes at 0 °C, triisopropylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate (3.0 mL, 11.2 mmol) was added dropwise over 15 minutes and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for an additional hour. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and excess 1 M NH4OAc was carefully added. The mixture was then further diluted with water and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was subjected to a short flash column using only CH2Cl2. The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide indole 22 (2.85 g, 87% over 2 steps) as a clear oil. 1H-NMR consistent with literature reported spectrum.27
1-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-5-(triisopropylsilyloxy)indole (23)
A solution of indole 22 (2.85 g, 9.86 mmol) in THF (7.3 mL) was purged with nitrogen while cooling to 0 °C. To the solution was added di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (2.39 mL, 10.4 mmol) followed by the careful addition of solid (dimethylamino)pyridine (1.44 g, 10.4 mmol). The resulting yellow suspension was stirred overnight, naturally warming to room temperature. The reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and 1 M HCl (7 mL) was carefully added. After stirring at room temperature for 5 minutes, the organic layer was separated and the aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (20:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide 23 (3.76 g, 98%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 7.95 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (d, J = 3.6 Hz, 1H), 7.02 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (dd, J = 8.9, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.45 (d, J = 3.7 Hz, 1H), 1.66 (s, 9H), 1.33-1.21 (m, 3H), 1.11 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 18H). 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 152.0, 150.0, 131.7, 130.4, 126.6, 117.7, 115.7, 110.8, 107.3, 83.6, 28.4, 18.2, 12.9. IR ν (cm−1) 2941, 2866, 1723, 1458, 1376, 1327, 1280, 1257, 1217, 1183, 1150, 1122, 1078, 962, 877, 857, 811, 764, 725, 685, 637, 500, 478. HRMS calcd for C22H36NO3Si (M+H)+ 390.2459, found (M+H)+ 390.2458.
Potassium-1-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-5-(triisopropylsilyloxy)indol-2-yl-trifluoroborate (24)
Indole 23 (3.04 g, 7.81 mmol) was dried under high-vacuum and dissolved in freshly distilled THF (10.2 mL). Following the addition of triisopropyl borate (2.73 mL, 11.8 mmol), the reaction mixture was cooled to 0 °C and lithium diisopropylamide (2.0 M solution in heptane/tetrahydrofuran/ethylbenzene) (5.9 mL, 11.8 mmol) was added dropwise over 1 hour. After stirring for an additional 30 minutes at 0 °C, 2 M HCl (20 mL) was carefully added and allowed to stir at room temperature for 10 minutes. The resulting layers were separated and the aqueous layer was extracted using EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo to provide 1-(tert- butoxycarbonyl)-5-(triisopropylsilyloxy)indol-2-yl-boronic acid as an orange foam, which due to instability was converted to the trifluoroborate 24 by reacting with KHF2 (5.7 mL, 4.5 M in water) in MeOH. After 30 minutes, the solution was evaporated to dryness and the crude solid was dissolved in acetone, sonicated, and then separated from the remaining insoluble material by filtration. The combined filtrates were concentrated in vacuo and the crude product was redissolved in a minimal amount of hot acetone and the subsequent addition of hexane led to the precipitation of the product, which was filtered, collected, and dried in vacuo to provide compound 24 as a white solid (2.11 g, 55%). 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 7.85 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.83 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.64 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.30 (s, 1H), 1.55 (s, 9H), 1.27-1.19 (m, 3H), 1.06 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (75 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 151.2, 150.1, 132.6, 131.7, 114.9, 114.4, 111.6, 108.8, 81.1, 27.7, 17.8, 12.0 (C-B not observed). IR v (cm−1), 2968, 2943, 2867, 1699, 1458, 1366, 1303, 1256, 1188, 1127, 984, 969, 884, 873, 851, 689, 626, 478. HRMS calcd for C22H34BF3NO3Si (M-K)− 456.2359, found (M-K)− 456.2348.
Compound 26
To a vacuum dried solid mixture of trifluoroborate 24 (2.23 g, 4.51 mmol), triflate 25 (1.00 g, 3.61 mmol), tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0) (416 mg, 0.36 mmol), and Na2CO3 (1.05 g, 9.93 mmol), was added freshly distilled anhydrous THF (20 mL). After purging with nitrogen for 15 minutes, the reaction mixture was heated to reflux overnight. The resulting orange reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with water and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and purified by chromatography using hexanes:EtOAc (10:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide compound 26 (1.17 g, 78%) as a white solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): 9.71 (s, 1H), 9.22 (s, 1H), 8.10 (s, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.68 (ddd, J = 8.2, 6.9, 1.3 Hz, 1H), 7.54 (ddd, J = 8.1, 6.9, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.14 (d, J = 2.3 Hz, 1H), 7.00 (dd, J = 2.1, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 6.84 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.3 Hz, 1H), 1.37-1.25 (m, 3H), 1.15 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 152.3, 150.3, 144.7, 138.0, 136.8, 132.3, 131.0, 130.3, 128.0, 128.0, 127.1, 126.9, 117.4, 115.5, 111.8, 109.9, 99.3, 18.3, 13.0. IR v (cm−1) 3409, 2944, 2866, 1621, 1575, 1470, 1447, 1407, 1258, 1211, 1182, 1143, 1123, 991, 960, 880, 853, 789, 752, 684, 641, 623, 575, 548, 502, 471. HRMS calcd for C26H33N2OSi (M+H)+ 417.2357, found (M+H)+ 417.2355.
Compound 27
A solution of isoquinolinyl-indole 26 (750 mg, 1.80 mmol) in freshly distilled THF (4.7 mL) was prepared after drying 26 under high vacuum. After cooling the solution to −15 °C, lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (1 M solution in hexanes) (5.4 mL, 5.4 mmol) was added dropwise over 15 minutes and the resulting orange solution was stirred at −15 °C for an additional 45 minutes. A solution of vacuum-dried maleimide 10 (697 mg, 1.89 mmol) in freshly distilled THF (4.7 mL) cooled to 0 °C was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at −15 °C for 20 minutes and room temperature overnight. The resulting dark purple reaction mixture was carefully poured into stirring ice cold water (200 mL) and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (10:1 to 8:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide the unstable monobromide 27 (1.0 g, 79%) as an orange solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 10.00 (s, 1H), 9.21 (s, 1H), 7.94 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.71-7.66 (m, 2H), 7.61-7.57 (m, 2H), 7.26 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 7.00 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.86 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 1H), 1.30 (septet, J = 7.4 Hz, 3H), 1.14 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 18H), 0.98 (s, 9H), 0.47 (s, 6H). IR v (cm−1) 3335, 2942, 2892, 2863, 1697, 1648, 1625, 1580, 1466, 1431, 1312, 1266, 1217, 1182, 1076, 977, 897, 879, 844, 824, 795, 742, 709, 680, 619, 582, 556, 467, 405. HRMS calcd for C36H47BrN3O3Si2 (M+H)+ 706.2313, found (M+H)+ 706.2313.
Compound 28
An orange suspension of monobromide 27 (800 mg, 1.14 mmol) in toluene (250 mL) was irradiated with a medium pressure Hg lamp using an uranium filter (50% transmission at 350 nm) for 4 hours with constant nitrogen flow through the reaction mixture. The resulting bright orange suspension was concentrated to dryness in vacuo, adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (6:1 to 3:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide heterocycle 28 (610 mg, 86%) as a yellow solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 10.23 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 1H), 9.95 (s, 1H), 9.31 (s, 1H), 8.87 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 8.09 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 8.00 (ddd, J = 8.6, 7.1, 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (ddd, J = 8.0, 7.0, 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.46 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.21 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 1.49-1.39 (m, 3H), 1.20 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 18H), 1.09 (s, 9H), 0.68 (s, 6H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 175.4, 173.9, 154.3, 151.2, 142.6, 135.5, 135.2, 132.2, 131.7, 129.9, 128.8, 128.5, 127.8, 123.1, 121.6, 120.4, 116.1, 115.6, 111.6, 26.8, 19.5, 18.3, 12.9, −3.5 (two hidden carbons). IR v (cm−1) 2939, 2862, 1686, 1482, 1463, 1362, 1333, 1301, 1276, 1248, 1212, 1178, 1156, 1080, 976, 884, 866, 846, 821, 787, 753, 682, 665, 607, 583, 478, 407. HRMS calcd for C36H46N3O3Si2 (M+H)+ 624.3072, found (M+H)+ 624.3072.
Compound 29
A solution of imide 28 (135 mg, 0.217 mmol) in THF-MeOH (1:1) (14 mL) was cooled to 0 °C. Sodium borohydride (16 mg, 0.421 mmol) was added every hour for a total of 5 hours and the stirred reaction mixture was then allowed to naturally warm to room temperature overnight. The reaction mixture was again cooled to 0 °C, carefully quenched with addition of saturated aqueous NH4Cl, and further diluted with water and extracted with CH2Cl2. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography with hexanes:EtOAc (6:1 to 3:1) to provide a yellow solid. A yellow suspension of this solid (100 mg) in CH2Cl2 (9.0 mL) containing 0.1% ethanol was cooled to 0 °C, and trifluoroacetic acid (1.0 mL) was then carefully added and the resulting orange solution stirred at 0 °C for 15 minutes. The reaction mixture was then carefully quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3 and extracted with CH2Cl2. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. A suspension of the crude material in CH2Cl2 (10 mL) was purged with nitrogen for 15 minutes. Phenylselenol (68 μL, 0.640 mmol), followed by trifluoroacetic acid (18.4 μL, 0.240 mmol) were added and the resulting dark orange solution was heated to reflux for 5 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, carefully quenched with saturated aqueous NaHCO3, and extracted with CH2Cl2. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was adsorbed onto silica gel and subjected to silica gel chromatography first with hexanes:EtOAc (3.5:1) and followed using CH2Cl2:MeOH (80:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide lactam 29 (51 mg, 47% over 3 steps) as a light yellow solid. The constitution of 29 was confirmed by ROESY analysis. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 12.27 (s, 1H), 9.60 (s, 1H), 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.90 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 8.53 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 1H), 8.42 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 8.09 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.09 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 5.25 (s, 2H), 1.40-1.34 (m, 3H), 1.14 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (125 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 171.0, 168.3, 153.5, 148.5, 137.9, 135.3, 132.6, 132.2, 132.1, 129.6, 127.3, 127.0, 126.7, 124.9, 122.3, 119.5, 116.5, 115.8, 114.5, 111.9, 48.6, 17.9, 12.1. IR v (cm−1) 3187, 3069, 2941, 2893, 2863, 1686, 1665, 1623, 1572, 1461, 1369, 1258, 1209, 1185, 1159, 1077, 1040, 1015, 998, 974, 881, 801, 745, 710, 679, 627, 600, 559, 503, 449. HRMS calcd for C30H34N3O2Si (M+H)+ 496.2415, found (M+H)+ 496.2427.
Ruthenium complex 31
To a vacuum dried solid mixture of lactam 29 (10 mg, 0.020 mmol), ruthenium precursor 305 (11 mg, 0.022 mmol), and K2CO3 (3.0 mg, 0.022 mmol) was added freshly distilled DMF (1.0 mL) and the resulting suspension was purged with nitrogen for approximately 10 minutes. The reaction mixture was then heated to 80 °C for 10 minutes in a microwave reactor (CEM Discover). The resulting dark red solution was concentrated using high vacuum and co-evaporated once with EtOAc. The crude material was subjected to silica gel chromatography with toluene:acetone (3:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide ruthenium complex 31 (8.3 mg, 54%) as a red film. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 9.34 (s, 1H), 8.72 (d, J = 2.5 Hz, 1H), 8.31 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.96 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.76 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H), 7.30 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 6.77 (s, 1H), 6.02 (m, 1H), 5.89 (m, 1H), 5.46 (m, 1H), 5.34 (m, 1H), 5.19 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 2H), 3.75 (s, 3H), 1.48-1.38 (m, 3H), 1.22 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 18H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ (ppm) 199.1, 172.7, 167.2, 157.9, 151.7, 148.3, 147.8, 140.3, 133.3, 132.9, 129.4, 128.5, 127.3, 127.0, 126.6, 124.3, 124.1, 119.7, 117.3, 116.2, 114.6, 113.7, 93.8, 86.0, 85.3, 77.7, 75.3, 52.2, 48.5, 18.2, 12.8. IR v (cm−1) 2923, 2854, 1962, 1714, 1684, 1601, 1457, 1440, 1380, 1289, 1271, 1251, 1209, 1144, 884, 755. HRMS calcd for C37H40N3O4RuSi (M−CO+H)+ 720.1826, found (M−CO+H)+ 720.1823.
Ruthenium complex 21
To a vacuum dried sample of complex 31 (14.8 mg, 0.020 mmol) was added freshly distilled THF (2.1 mL) and the resulting solution was purged with nitrogen while cooling to 0 °C. Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (1 M solution in THF, dried over 4 Å molecular sieve) (25 μL, 0.025 mmol) was then added and the reaction mixture immediately became a dark red-brown suspension. Within 1 minute, the reaction was quenched with excess saturated aqueous NH4Cl and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried using Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated to dryness in vacuo. The crude material was then subjected to silica gel chromatography first with CH2Cl2:hexanes (5:1) and followed by using CH2Cl2:MeOH (30:1). The combined product eluents were dried in vacuo to provide ruthenium complex 21 (7.8 mg, 66%) as a dark red solid. 1H-NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 9.80 (s, 1H), 9.00 (s, 1H), 8.79 (s, 1H), 8.51 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.39-8.36 (m, 2H), 8.13 (ddd, J = 8.4, 7.2, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.92 (t, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 1H), 6.99 (dd, J = 8.7, 2.6 Hz, 1H), 6.20 (m, 2H), 5.67 (m, 2H), 5.20 (m, 2H), 3.48 (s, 3H). 13C-NMR (100 MHz, DMSO-d6): δ (ppm) 200.8, 171.0, 166.0, 159.5, 150.9, 149.3, 146.4, 139.2, 133.4, 132.2, 129.7, 128.8, 127.8, 127.1, 126.8, 124.8, 123.7, 115.8, 115.7, 115.4, 114.2, 109.4, 89.9, 89.6, 81.4, 81.0, 79.2, 51.8, 47.9. IR v (cm−1) 2918, 2850, 2957, 1953, 1668, 1601, 1464, 1440, 1379, 1286, 1259, 1160, 1022, 798, 755, 718, 680, 559, 438, 402. HRMS calcd for C28H20N3O4Ru (M−CO+H)+ 564.0492, found (M−CO+H)+ 564.0491.
Resolution of (RRu)-21 and (SRu)-21
Baseline separation of the enantiomers of racemic half sandwich complex 21 was achieved using a Chiral Pak 1B analytical HPLC column (Daicel/Chiral Technologies). First, 21 was dissolved in a minimal amount of CH2Cl2 and carefully filtered. Then, each injection was run using an EtOH gradient of 50% to 90% over 20 minutes in hexanes. A flow rate of 0.7 mL/min was used and injection volumes of approximately 25 μL could be reached without compromising baseline separation. Amounts of 2.8 mg of both (RRu)-21 and (SRu)-21 were isolated and the absolute configuration assigned by CD-spectroscopy (see Supporting Information).
Protein Kinase Assays Using [γ-32P]ATP
Protein kinases (human) and substrates were purchased from Upstate Biotechnology USA, Millipore. Various concentrations of (RRu)-1, (SRu)-1, (RRu)-2, and (SRu)-2 were incubated at room temperature in 20 mM MOPS, 30 mM MgCl2, 0.8 μg/μL BSA, 5% DMSO (resulting from the inhibitor stock solution), pH 7.0, in the presence of substrate (GSK3β and CLK2: 20 μM and 100 μM phosphoglycogen synthase peptide-2, respectively; Pim1: 100 μM S6 kinase/Rsk2 substrate peptide 2; TrkA: 250 μM Trk peptide KKKSPGEYVNIEFG) and kinase (2.4 nM GSK3β, 0.8 nM Pim1, 8.0 nM TrkA, 0.6 nM CLK2). After 15 minutes, the reaction was initiated by adding ATP to a final concentration of 100 μM, including approximately 0.2 μCi/μL [γ-32P]ATP. Reactions were performed in a total volume of 25 μL and incubated at 30 °C. After 30 minutes (Pim1) or 45 minutes (GSK3β, TrkA, and CLK2), the reaction was terminated by spotting 17.5 μL on a circular P81 phosphocellulose paper (2.1 cm diameter, Whatman), followed by washing four times (5 minutes each wash) with 0.75% phosphoric acid and once with acetone. The dried P81 papers were transferred to a scintillation vial, and 5 mL of scintillation cocktail was added, and the counts per minute (CPM) were determined with a Beckmann 6000 scintillation counter. IC50 values were defined to be the concentration of inhibitor at which the CPM was 50% of the control sample, corrected by the background.
Protein Kinase Assays Using [γ-33P]ATP
Protein kinases (human) and substrates were purchased from Upstate Biotechnology USA, Millipore. Various concentrations of (RRu)-3, (SRu)-3, or (RRu)-21 were incubated at room temperature in 20 mM MOPS, 30 mM Mg(OAc)2, 0.8 μg/μL BSA, 5% DMSO (resulting from the inhibitor stock solution), pH 7.0, in the presence of substrate (GSK3β: 20 μM phosphoglycogen synthase peptide-2; Pim1: 50 μM S6 kinase/Rsk2 substrate peptide 2; TrkA: 150 μM Trk peptide KKKSPGEYVNIEFG) and kinase (0.4–2.0 nM GSK3β, 0.3–1.6 nM Pim1, 4.9–9.8 nM TrkA). After 15 minutes, the reaction was initiated by adding ATP to a final concentration of 100 μM, including approximately 0.05 μCi/μL [γ-33P]ATP (GSK3β and Pim1) or 0.1 μCi/μL [γ-33P]ATP (TrkA). Reactions were performed in a total volume of 25 μL. After 30 minutes (GSK3β and Pim1) or 2 hours (TrkA), the reaction was terminated by spotting 15 μL (TrkA) or 17.5 μL (GSK3β, Pim1) on a circular P81 phosphocellulose paper (2.1 cm diameter, Whatman), followed by washing four times (5 minutes each wash) with 0.75% phosphoric acid and once with acetone. The dried P81 papers were transferred to a scintillation vial, and 5 mL of scintillation cocktail was added, and the counts per minute (CPM) were determined with a Beckmann 6000 scintillation counter. IC50 values were defined to be the concentration of inhibitor at which the CPM was 50% of the control sample, corrected by the background.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank the US National Institutes of Health for financial support (GM071695 and U54-HG003915).
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available: Screening results of compounds 1–3 and (RRu)-21 against a panel of human kinases, assignment of the absolute configurations of (RRu)-1, (SRu)-1, (RRu)-2, (SRu)-2, (RRu)-21, 1H-1H-ROESY analysis of compound 17, and NMR spectra for all new compounds. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Meggers E, Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Bregman H, Maksimoska J, Mulcahy SP, Pagano N, Williams DS. Synlett. 2007;8:1177–1189. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bregman H, Williams DS, Atilla GE, Carroll PJ, Meggers E. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:13594–13595. doi: 10.1021/ja046049c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Williams DS, Atilla GE, Bregman H, Arzoumanian A, Klein PS, Meggers E. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44:1984–1987. doi: 10.1002/anie.200462501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bregman H, Carroll PJ, Meggers E. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:877–884. doi: 10.1021/ja055523r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Williams DS, Bregman H, Pagano N, Meggers E. ChemBioChem. 2006;7:1443–1450. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200600117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bregman H, Meggers E. Org Lett. 2006;8:5465–5468. doi: 10.1021/ol0620646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Pagano N, Streu C, Maksimoska J, Filippakopoulos P, Knapp S, Meggers E. ChemBioChem. 2008;9:2933–2936. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200800489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Debreczeni JÉ, Bullock AN, Atilla GE, Williams DS, Bregman H, Knapp S, Meggers E. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2006;45:1580–1585. doi: 10.1002/anie.200503468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Maksimoska J, Feng L, Harms K, Yi C, Kissil J, Marmorstein R, Meggers E. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:15764–15765. doi: 10.1021/ja805555a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Xie P, Williams DS, Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Milk L, Xiao M, Smalley KSM, Herlyn M, Meggers E, Marmorstein R. ACS Chem Biol. 2008;3:305–316. doi: 10.1021/cb800039y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Maksimoska J, Williams DS, Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Smalley KSM, Carroll PJ, Webster RD, Filippakopoulos P, Knapp S, Herlyn M, Meggers E. Chem Eur J. 2008;14:4816–4822. doi: 10.1002/chem.200800294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sánchez C, Méndez C, Salas JA. Nat Prod Rep. 2006;23:1007–1045. doi: 10.1039/b601930g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Pagano N, Maksimoska J, Bregman H, Williams DS, Webster RD, Xue F, Meggers E. Org Biomol Chem. 2007;5:1218–1227. doi: 10.1039/b700433h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bregman H, Williams DS, Meggers E. Synthesis. 2005:1521–1527. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Molander GA, Canturk B, Kennedy LE. J Org Chem. 2009;74:973–980. doi: 10.1021/jo802590b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Molander GA, Ellis N. Acc Chem Res. 2007;40:275–286. doi: 10.1021/ar050199q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Link JT, Danishefsky SJ. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994;49:9135–9138. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Issa F, Fischer J, Turner P, Coster MJ. J Org Chem. 2006;71:4703–4705. doi: 10.1021/jo0605750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mase N, Nishi T, Takamori Y, Yoda H, Takabe K. Tetrahedron Asymm. 1999;10:4469–4471. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mase N, Nishi T, Hiyoshi M, Ichihara K, Bessho J, Yoda H, Takabe K. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1. 2002:707–709. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mangaleswaran S, Argade NP. Synthesis. 2004;10:1560–1562. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Link JT, Raghavan S, Danishefsky SJ. J Am Chem Soc. 1999;117:552–553. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Link JT, Raghavan S, Gallant M, Danishefsky SJ, Chou TC, Ballas LM. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:2825–2842. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. doi: 10.1126/science.1075762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.For the binding modes of small molecules to the ATP binding sites of protein kinases, see for example: Ghose AK, Herbertz T, Pippin DA, Salvino JM, Mallamo JP. J Med Chem. 2008;51:5149–5171. doi: 10.1021/jm800475y.
- 26.Gill TP, Mann KR. Organometallics. 1982;1:485–488. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kondo Y, Kojima S, Sakamoto T. J Org Chem. 1997;62:6507–6511. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.