Abstract
Marcus, Leon (University of California, Davis), and Allen G. Marr. Polyol dehydrogenases of Azotobacter agilis. J. Bacteriol. 82:224–232. 1961.—Two soluble diphosphopyridine-linked polyol dehydrogenases are formed by Azotobacter agilis (A. vinelandii). The first, d-mannitol dehydrogenase is induced by d-mannitol and all of the pentitols except l-arabitol. Ribitol is an excellent inducer of mannitol dehydrogenase although it is not metabolized, nor does the enzyme act upon it. This allows study of the gratuitous induction of mannitol dehydrogenase.
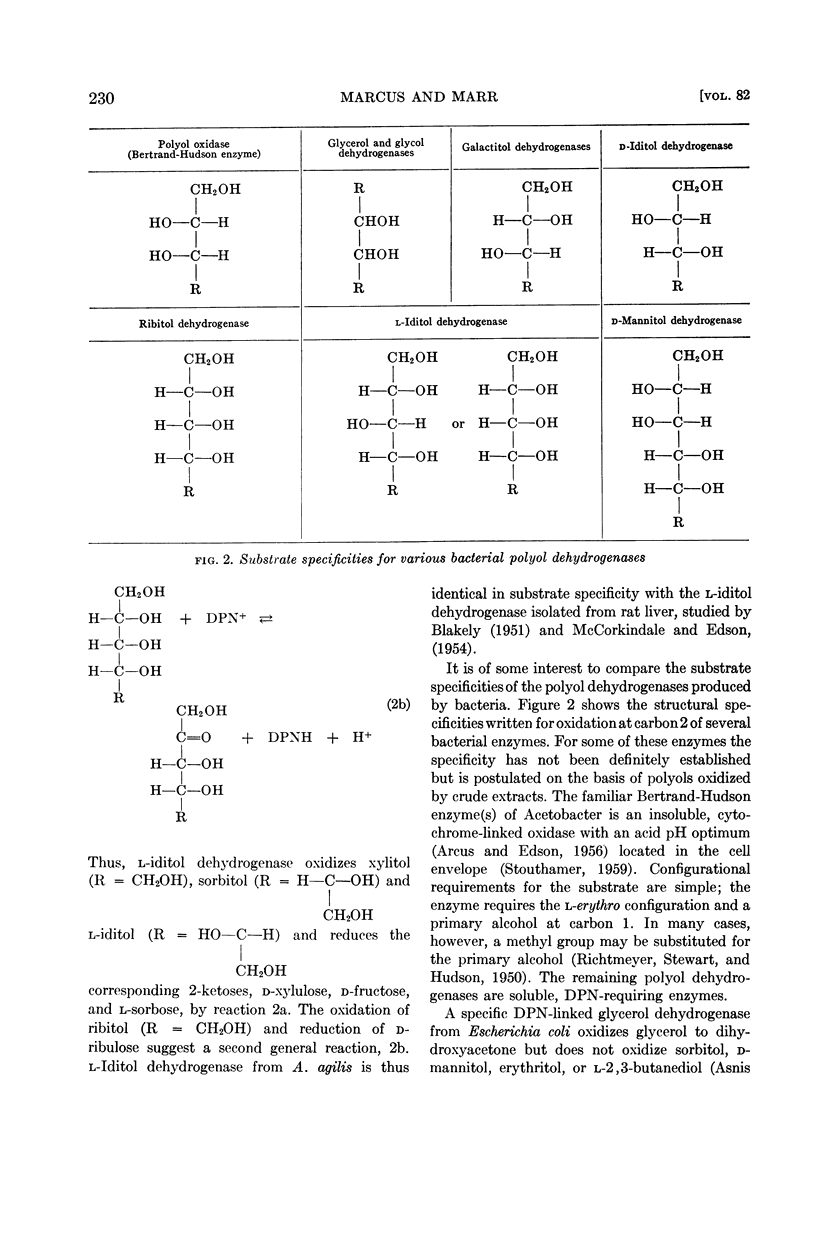
Of the polyols tested, mannitol dehydrogenase oxidizes d-mannitol, d-arabitol, d-rhamnitol, and perseitol, demonstrating its requirement for substrates bearing the d-manno configuration. The corresponding 2-ketoses, d-fructose, d-xylulose, and presumably d-rhamnulose, and perseulose are reduced.
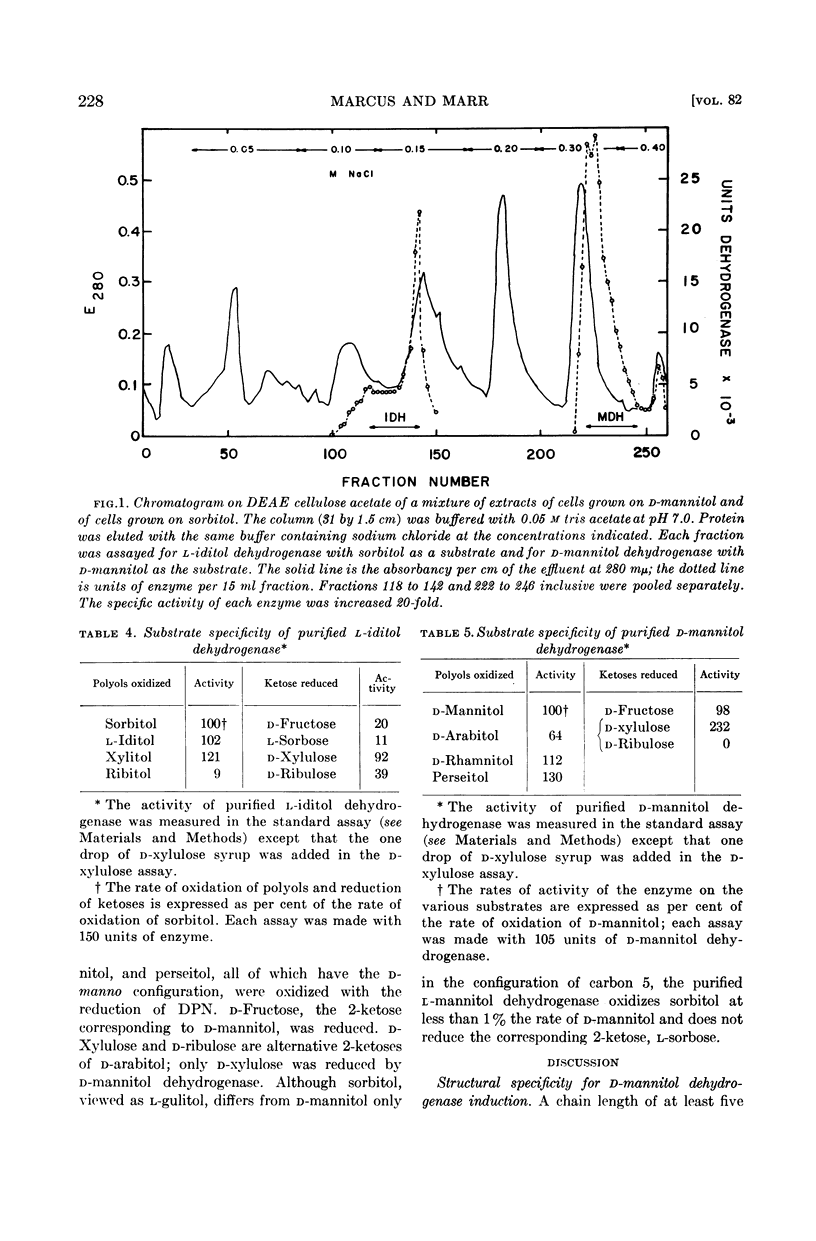
The second enzyme, l-iditol dehydrogenase is induced only by polyols containing the d-xylo configuration, i.e., sorbitol and xylitol. l-Iditol dehydrogenase oxidizes d-xylo polyols seven times faster than it does d-ribo polyols. Substrates oxidized include l-iditol, sorbitol, xylitol, and ribitol. The corresponding 2-ketoses, l-sorbose, d-fructose, d-xylulose, and d-ribulose, are reduced.
The two polyol dehydrogenases have been separated and purified by chromatography on a modified cellulose ion exchanger.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCUS A. C., EDSON N. L. Polyol dehydrogenases. 2. The polyol dehydrogenases of Acetobacter suboxydans and Candida utilis. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):385–394. doi: 10.1042/bj0640385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASNIS R. E., BRODIE A. F. A glycerol dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jul;203(1):153–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAXTER R. M., GIBBONS N. E. The glycerol dehydrogenases of Pseudomonas salinaria, Vibrio costicolus, and Escherichia coli in relation to bacterial halophilism. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1954 May;32(3):206–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAKLEY R. L. The metabolism and antiketogenic effects of sorbitol; sorbitol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1951 Aug;49(3):257–271. doi: 10.1042/bj0490257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMM H. J. Ribitol dehydrogenase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1958 Nov;233(5):1049–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMBORG M., KAPLAN N. O. A comparison of some vicglycol dehydrogenase systems found in Aerobacter aerogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Feb 26;38:272–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCORKINDALE J., EDSON N. L. Polyol dehydrogenases. I. The specificity of rat-liver polyol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1954 Jul;57(3):518–523. doi: 10.1042/bj0570518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAW D. R. Polyol dehydrogenases. 3. Galactitol dehydrogenase and D-iditol dehydrogenase. Biochem J. 1956 Nov;64(3):394–405. doi: 10.1042/bj0640394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRECKER H. J., HARARY I. Bacterial butylene glycol dehydrogenase and diacetyl reductase. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):263–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF J. B., KAPLAN N. O. D-Mannitol 1-phosphate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):849–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



