Abstract
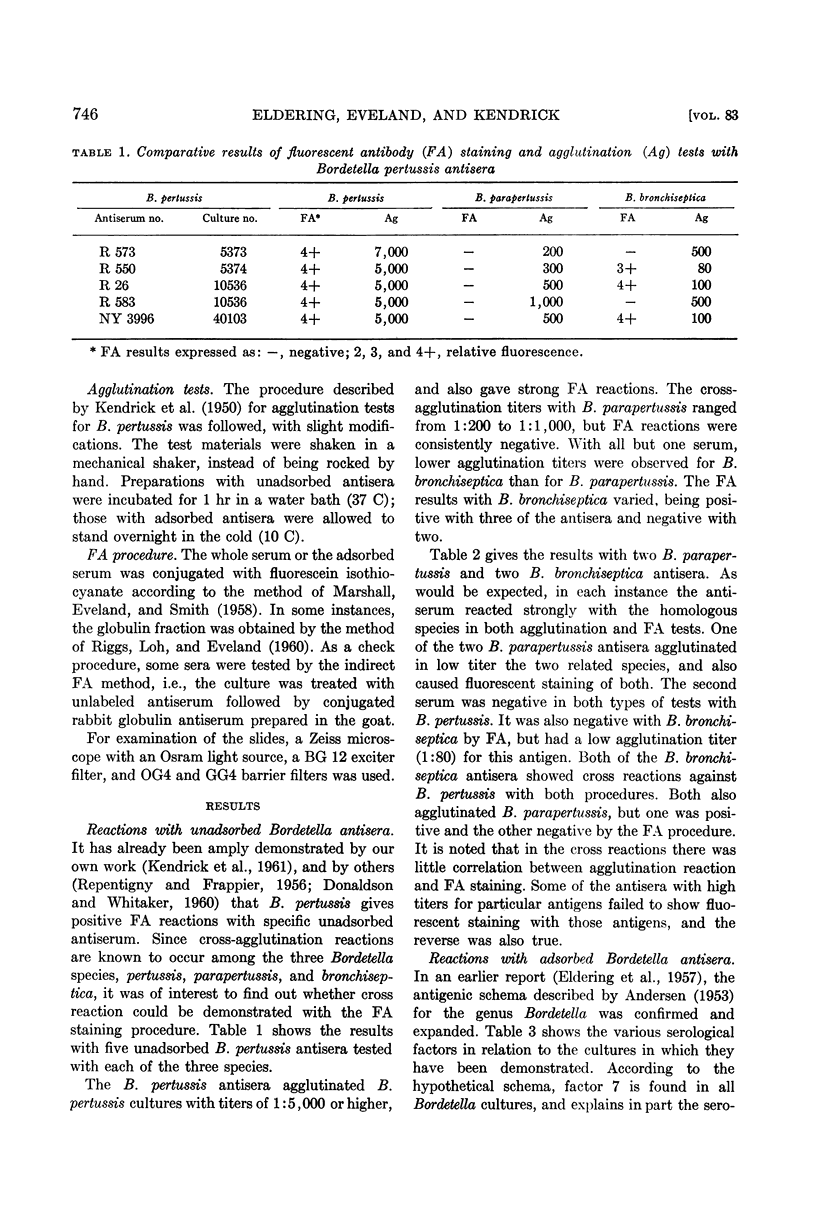
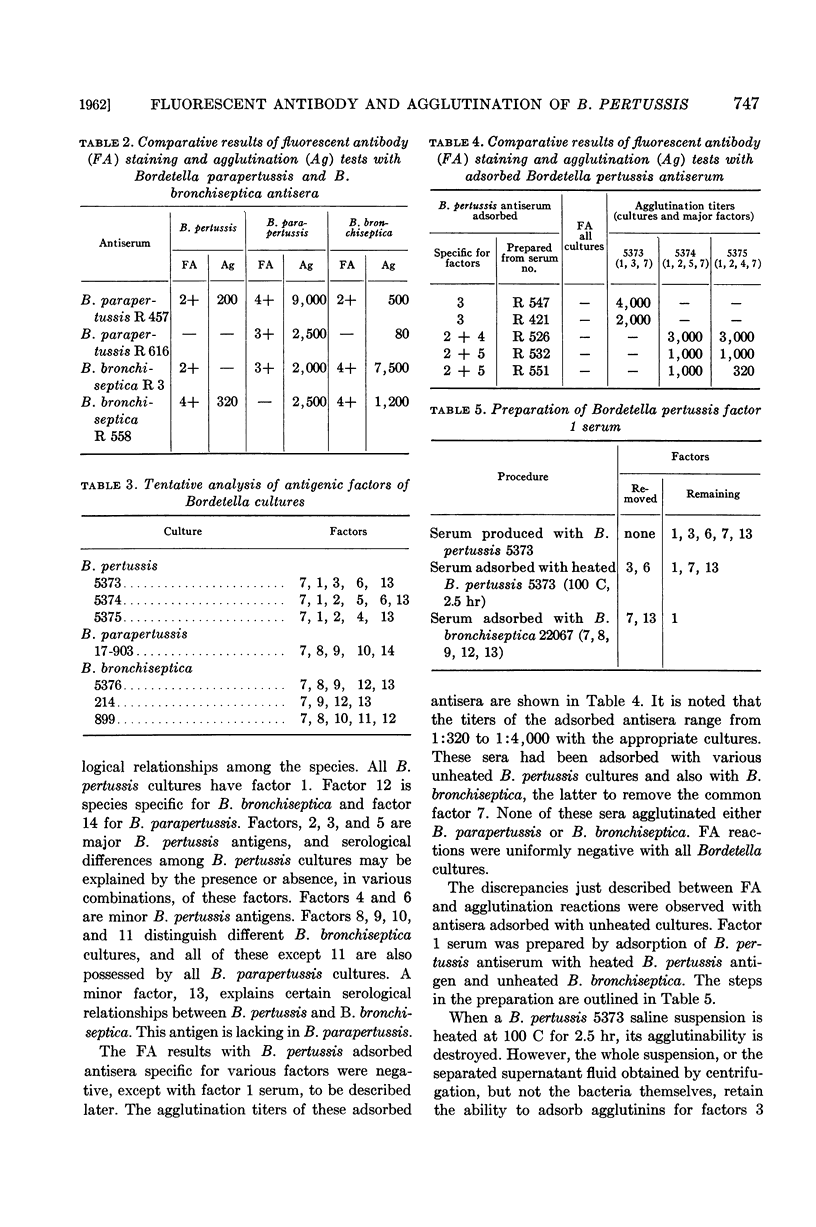
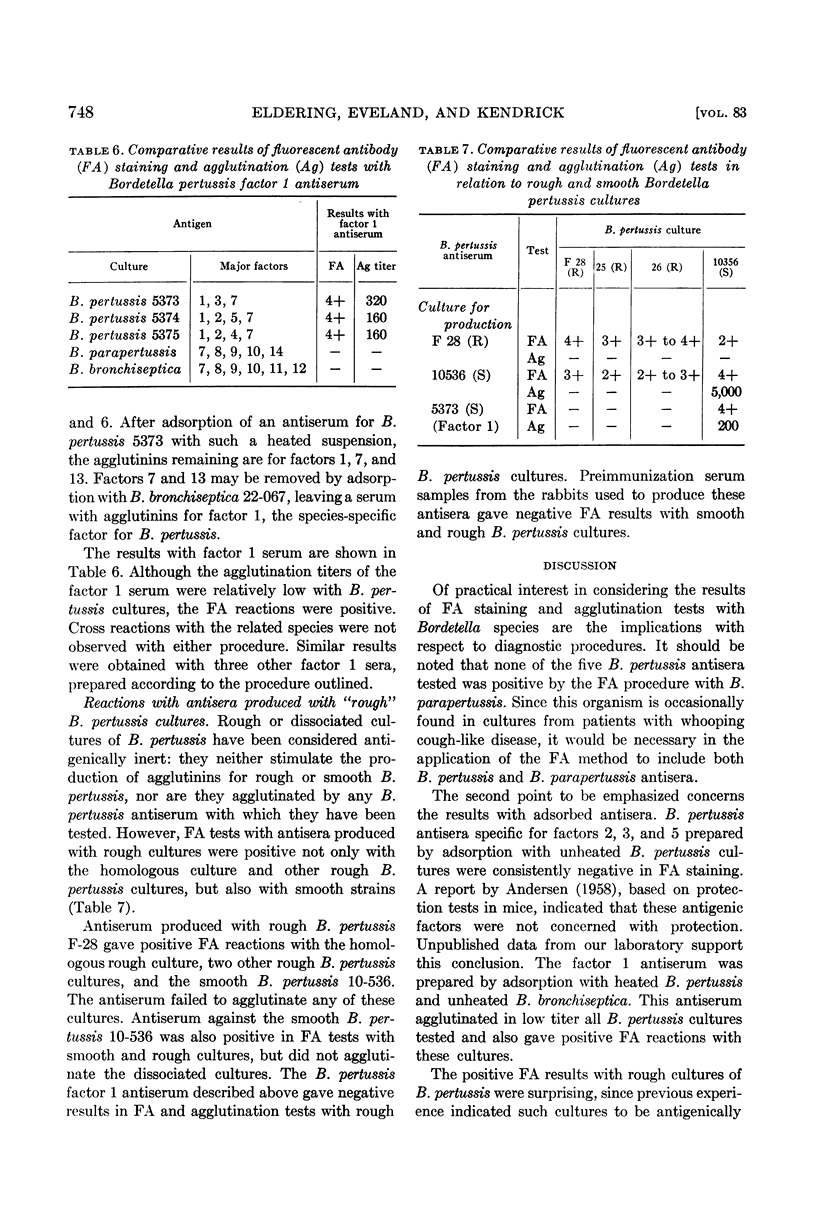
Eldering, Grace (Michigan Department of Health, Grand Rapids), Warren C. Eveland, and Pearl L. Kendrick. Fluorescent antibody staining and agglutination reactions in Bordetella pertussis cultures. J. Bacteriol. 83:745–749. 1962—Bordetella pertussis antisera produced with smooth cultures gave positive results in agglutination and fluorescent antibody (FA) tests with smooth B. pertussis cultures. Similar results were obtained with antisera produced with the related species B. parapertussis and B. bronchiseptica when each was tested with the respective homologous antigen. Cross reactions occurred with some of the antisera and heterologous antigens but a positive agglutination test was not always correlated with a positive FA reaction, and the reverse was also observed. Adsorbed B. pertussis antisera specific for factors 2, 3, 4, and 5 agglutinated appropriate B. pertussis cultures, but gave negative FA reactions. Factor 1 antiserum prepared by adsorption with heated (100 C) antigen gave positive results in both FA and agglutination tests. Rough B. pertussis cultures were inagglutinable, but were FA positive when tested with unadsorbed antiserum produced with either smooth or rough cultures. Rough cultures were FA negative with factor 1 serum. The results suggest that for B. pertussis different serum components may be responsible for agglutination and FA staining. The implications with respect to the protection-inducing antigen are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN E. K., BENTZON M. W. The failure to show correlation between type-specificity and protection in experimental pertussis in mice. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;43(1):106–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1958.tb04877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSEN E. K. Serological studies on H. pertussis H. parapertussis and H. bronchisepticus. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1953;33(2):202–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1953.tb01512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALDSON P., WHITAKER J. A. Diagnosis of pertussis by fluorescent antibody staining of nasopharyngeal smears. AMA J Dis Child. 1960 Apr;99:423–427. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1960.02070030425004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDERING G., HORNBECK C., BAKER J. Serological study of Bordetella pertussis and related species. J Bacteriol. 1957 Aug;74(2):133–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.2.133-136.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDRICK P. L., ELDERING G., EVELAND W. C. Fluorescent antibody techniques. Methods for identification of Bordetella pertussis. Am J Dis Child. 1961 Feb;101:149–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL J. D., EVELAND W. C., SMITH C. W. Superiority of fluorescein isothiocyanate (Riggs) for fluorescent-antibody technic with a modification of its application. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):898–900. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS J. L., LOH P. C., EVELAND W. C. A simple fractionation method for preparation of fluorescein-labeled gamma globulin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Dec;105:655–658. doi: 10.3181/00379727-105-26207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITAKER J., PAGE R. H., STULBERG C. S., ZUELZER W. W. Rapid identification of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O127:B8 by the fluorescent antibody technique. AMA J Dis Child. 1958 Jan;95(1 Pt 1):1–8. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1958.02060050003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



