Abstract
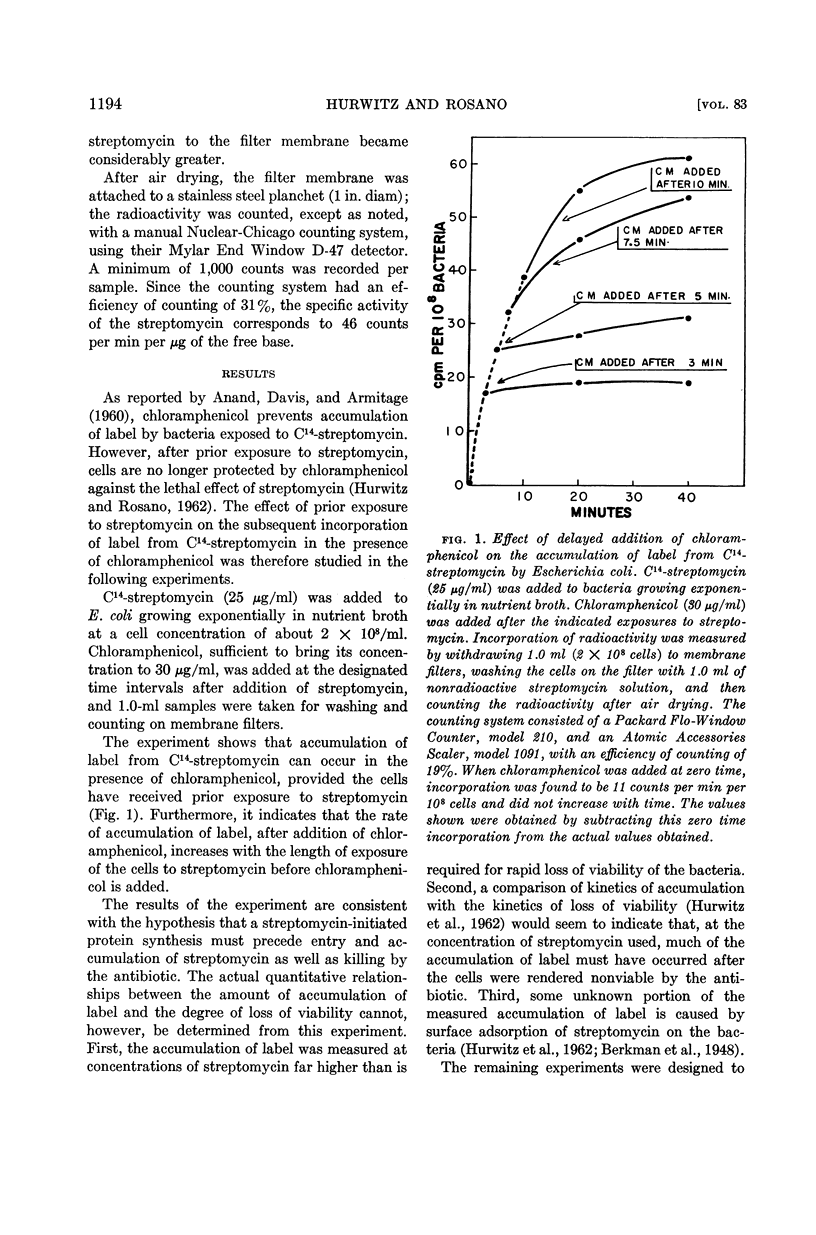
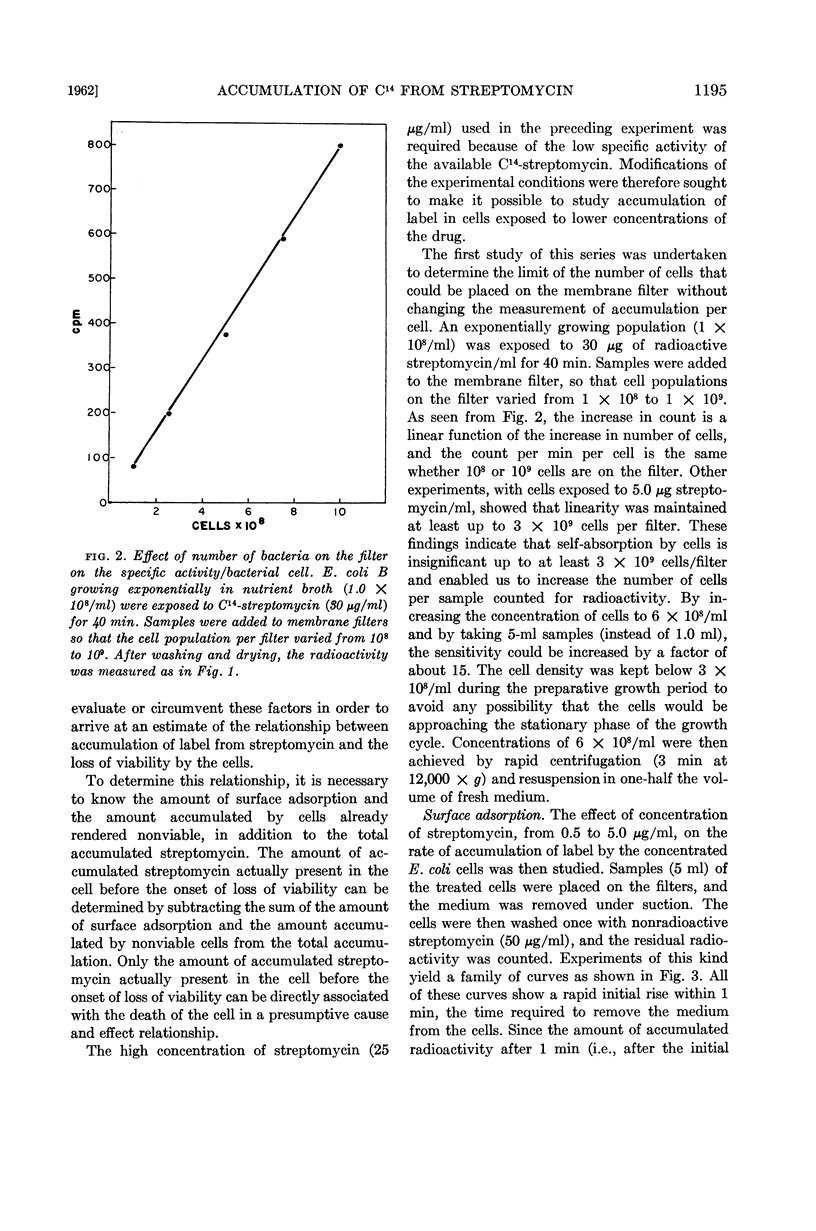
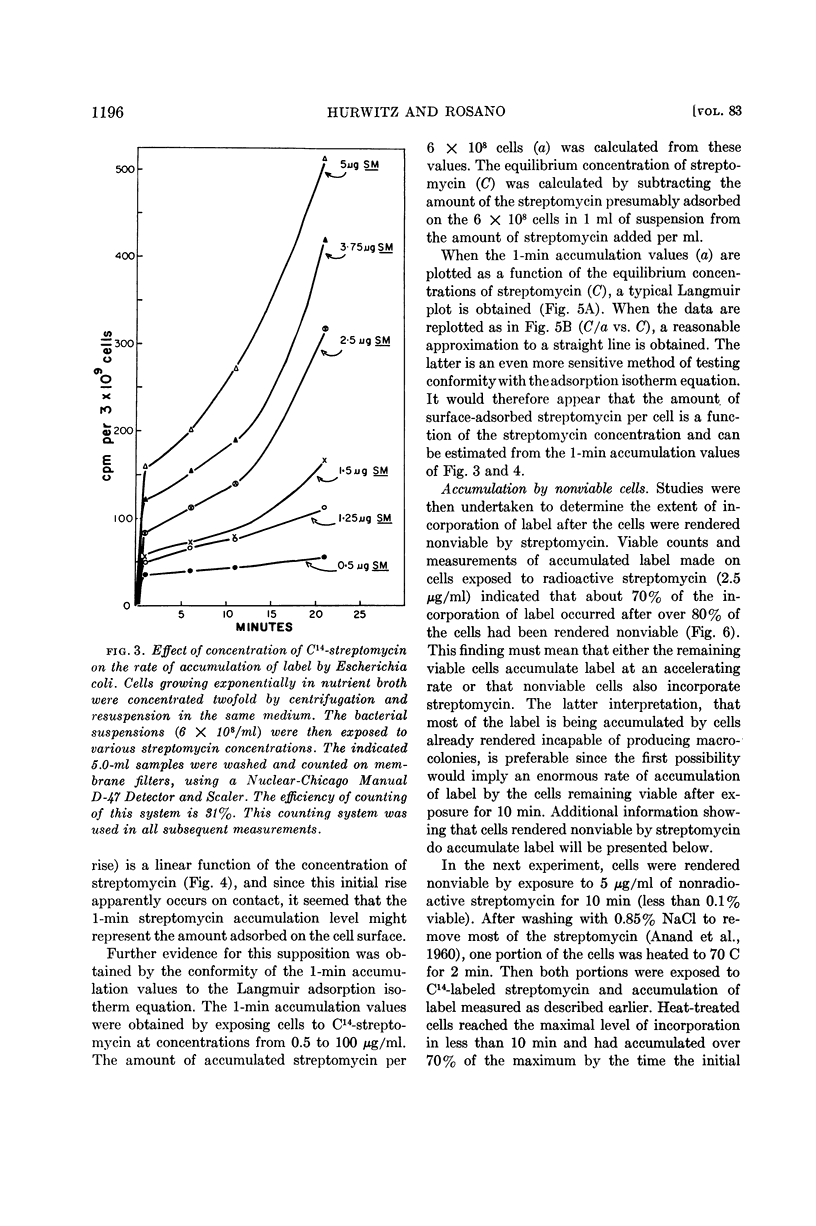
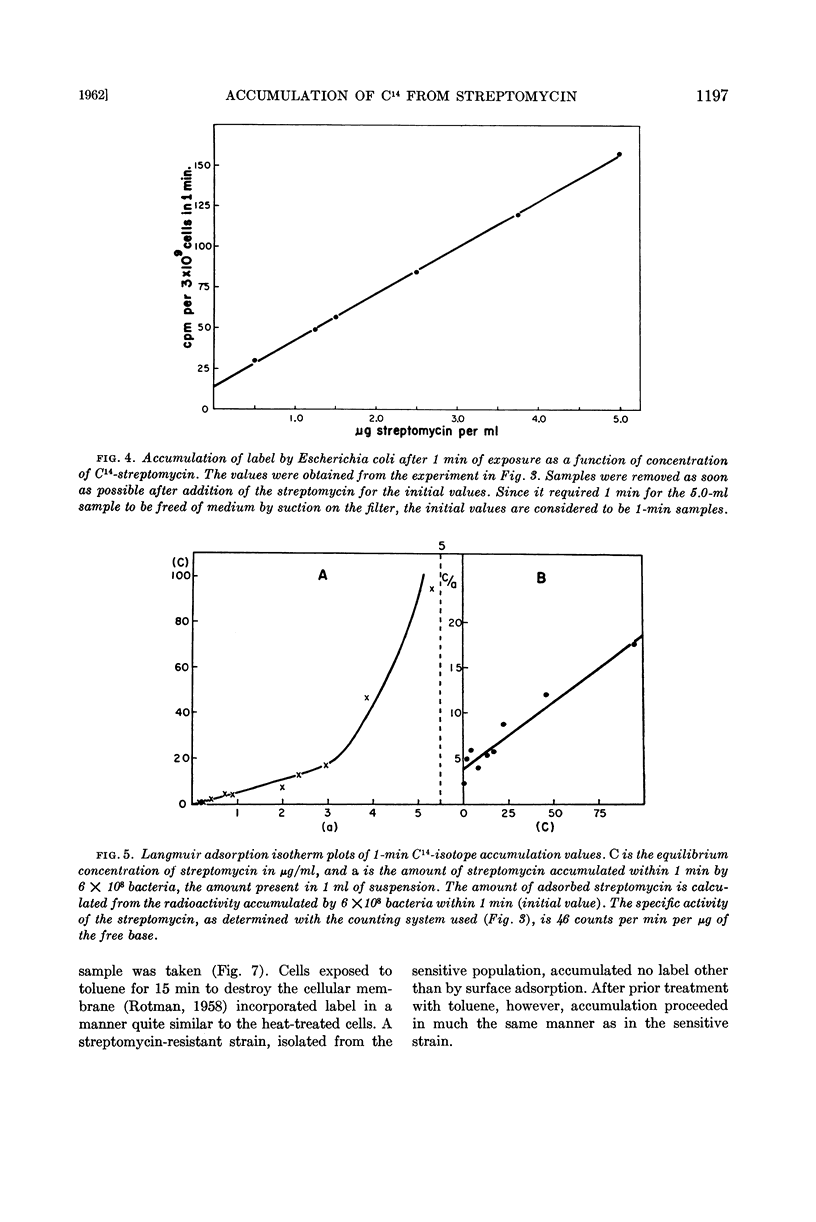
Hurwitz, Charles (Veterans Administration Hospital, Albany, N.Y.) and Carmen L. Rosano. Accumulation of label from C14-streptomycin by Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 83:1193–1201. 1962.—Accumulation of label from C14-streptomycin by sensitive Escherichia coli occurs in the presence of chloramphenicol, provided the cells receive a prior exposure to streptomycin. The rate of accumulation increases with the concentration and length of exposure to streptomycin during the initiation phase. Accumulation of label from streptomycin in the presence of chloramphenicol is also a function of the streptomycin concentration during the killing phase. Evidence is presented for the presence of a barrier to the entry and exit of streptomycin. It is further shown that total accumulation of streptomycin can be divided into three portions: surface-adsorbed streptomycin, streptomycin present at the time of onset of loss of viability, and streptomycin accumulated by killed cells. Only about 10% of the total accumulated streptomycin is present at the onset of loss of viability and can therefore be presumed to play a role in the lethal action of the antibiotic.
Full text
PDF
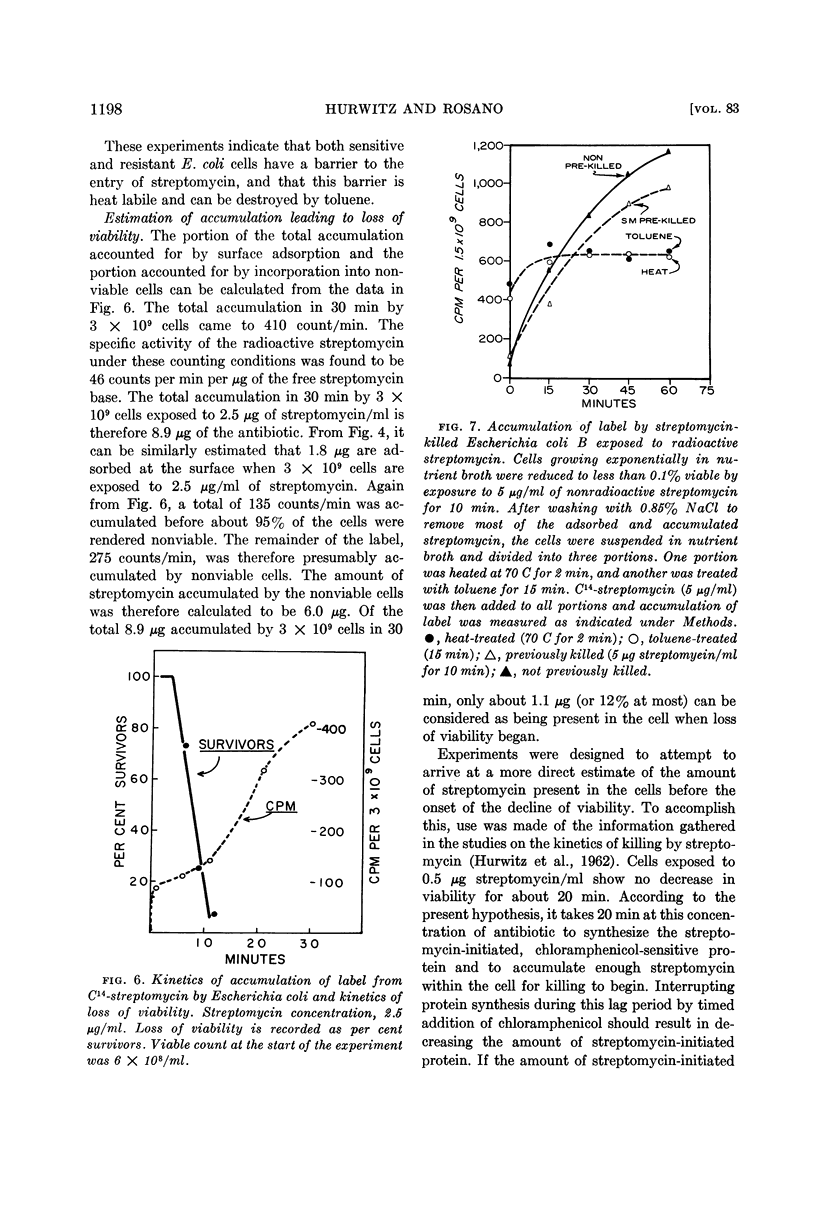
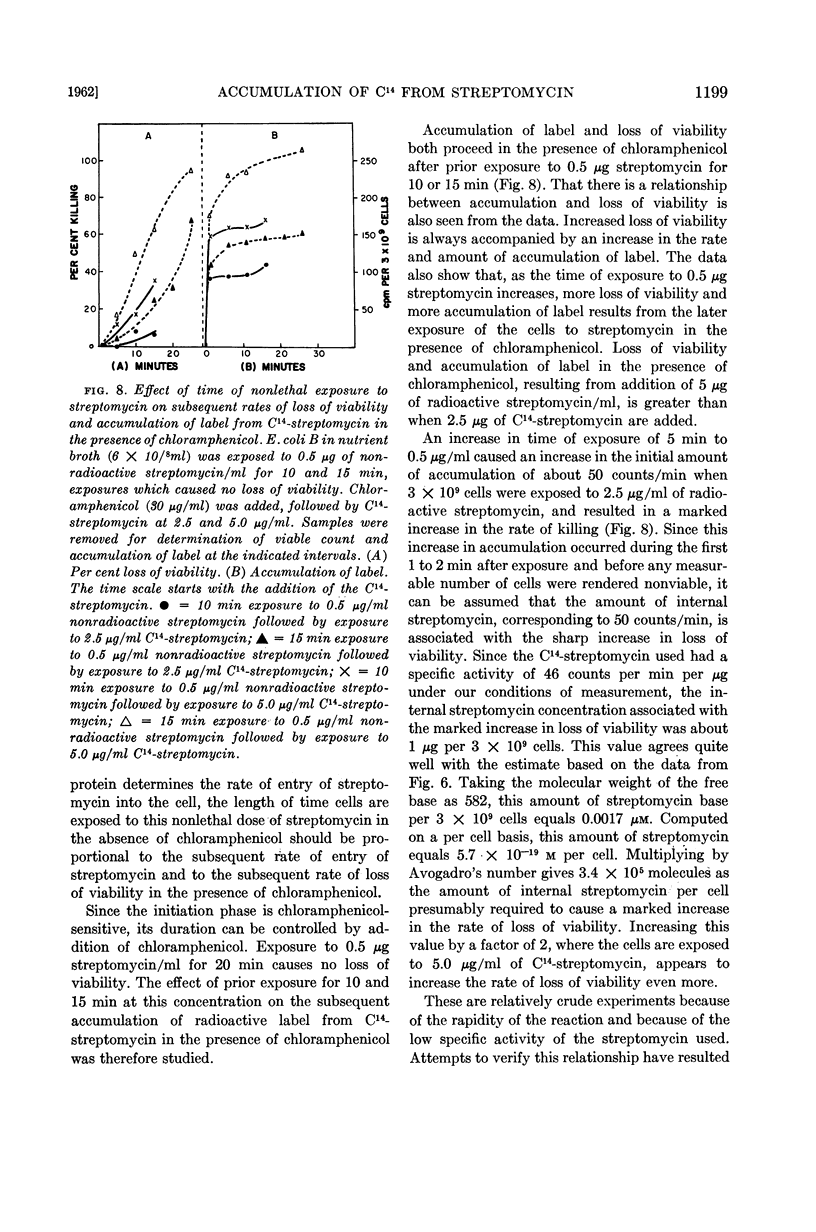


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D., ARMITAGE A. K. Uptake of streptomycin by Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:23–24. doi: 10.1038/185023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. S., LICHTENSTEIN J. The isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from bacterial extracts by precipitation with streptomycin. J Biol Chem. 1960 Nov;235:PC55–PC56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Chloramphenicol-sensitive and-insensitive phases of the lethal action of streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1202–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1202-1209.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L., LANDAU J. V. Kinetics of loss of vibility of Escherichia coli exposed to streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1210–1216. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1210-1216.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne R. E., Jr, Pollard A. L. The Identification of Streptomycin on Paper Strip Chromatograms. J Bacteriol. 1948 Feb;55(2):231–234. doi: 10.1128/jb.55.2.231-234.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTMAN B. Regulation of enzymatic activity in the intact cell: the beta-D-galactosidase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):1–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.1-14.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


