Abstract
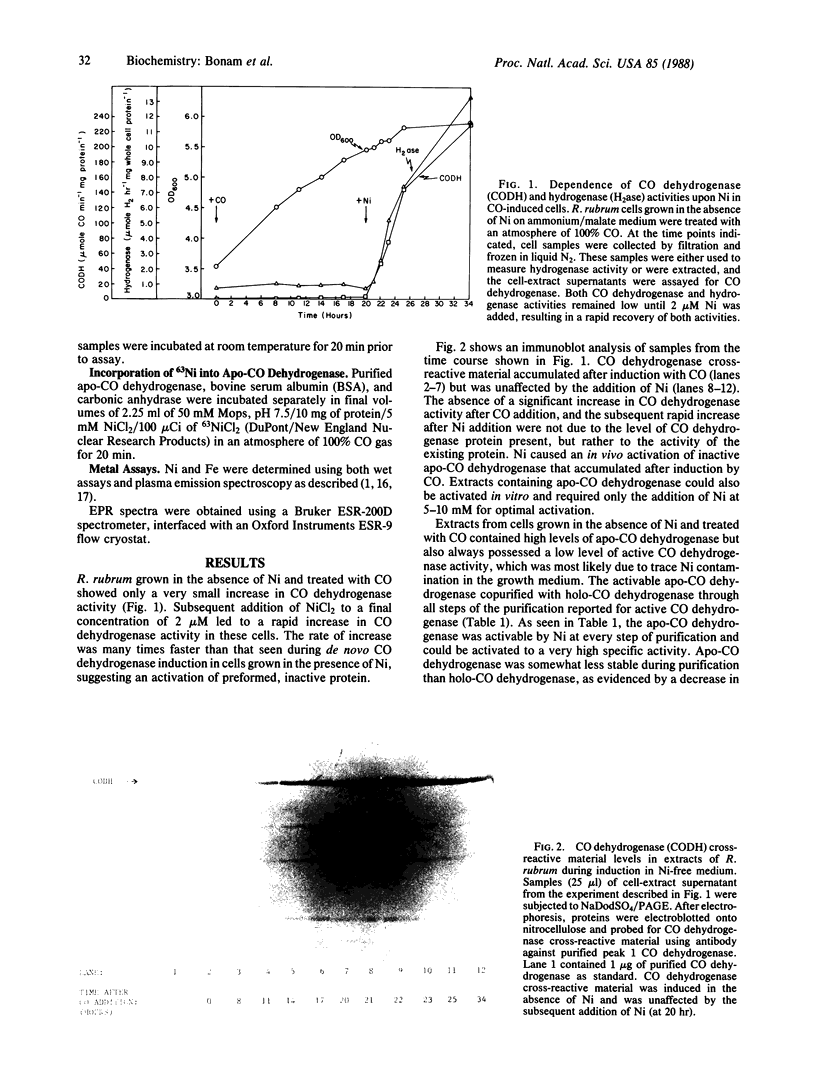
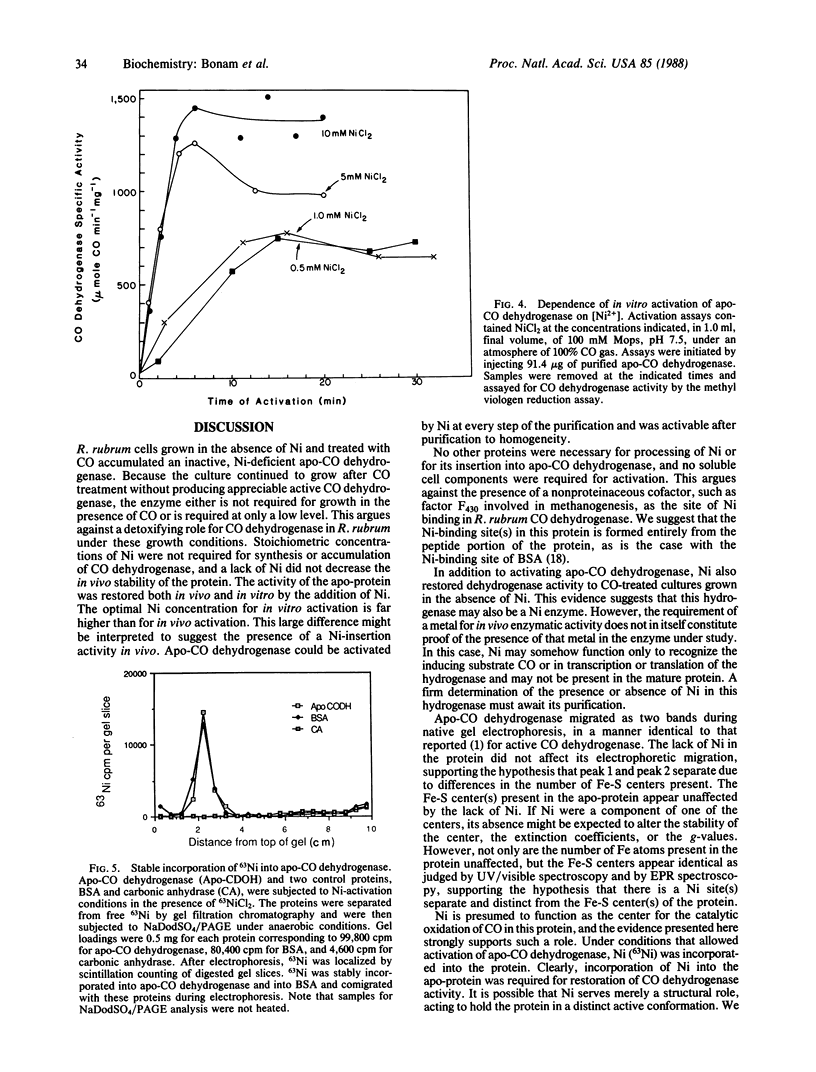
An inactive, Ni-deficient form of carbon monoxide (CO) dehydrogenase [carbon-monoxide:(acceptor) oxidoreductase; EC 1.2.99.2], designated apo-CO dehydrogenase, accumulated in Rhodospirillum rubrum when cells were grown in the absence of Ni and treated with CO. In vivo, both CO dehydrogenase activity and hydrogenase activity increased several hundred fold upon addition of 2 microM NiCl2. Apo-CO dehydrogenase was purified to homogeneity and differed from holo-CO dehydrogenase only in its activity and Ni content, containing less than 0.2 mol of Ni per mol of protein, and a specific activity of 35 mumol of CO per min per mg. Optimal in vitro activation of purified apo-CO dehydrogenase resulted in an enzyme with a specific activity of 2640 mumol of CO per min per mg. No additional enzymes or low molecular weight cofactors were required for activation. Apo-CO dehydrogenase was not activated by MgCl2, MnCl2, CuCl2, ZnCl2, CoCl2, or Na2MoO4. 63Ni was incorporated into apo-CO dehydrogenase during activation. The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra of dithionite-reduced apo- and holo-enzyme were identical, indicating that, in the reduced state, the Fe-S centers observed by EPR are unchanged in the apo-enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkin C. L., Thelander L., Reichard P., Lang G. Iron and free radical in ribonucleotide reductase. Exchange of iron and Mössbauer spectroscopy of the protein B2 subunit of the Escherichia coli enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 10;248(21):7464–7472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonam D., Ludden P. W. Purification and characterization of carbon monoxide dehydrogenase, a nickel, zinc, iron-sulfur protein, from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):2980–2987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonam D., Murrell S. A., Ludden P. W. Carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):693–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.693-699.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diekert G., Konheiser U., Piechulla K., Thauer R. K. Nickel requirement and factor F430 content of methanogenic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):459–464. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.459-464.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon J. D., Sarkar B. Nickel(II) transport in human blood serum. Studies of nickel(II) binding to human albumin and to native-sequence peptide, and ternary-complex formation with L-histidine. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):15–23. doi: 10.1042/bj2030015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell P. L., Wolfe R. S. Requirement of the nickel tetrapyrrole F430 for in vitro methanogenesis: reconstitution of methylreductase component C from its dissociated subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6726–6730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausinger R. P. Nickel utilization by microorganisms. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):22–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.22-42.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin R., Rabinowitz J. C. The reconstitution of clostridial ferredoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 21;23(6):822–827. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90561-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani H. H., Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Activation of inactive nitrogenase by acid-treated component I. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):697–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.697-701.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nason A., Lee K. Y., Pan S. S., Ketchum P. A., Lamberti A., DeVries J. Invitro formation of assimilatory reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate: nitrate reductase from a Neurospora mutant and a component of molybdenum-enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3242–3246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino T., Usami C., Tsushima K. Reversible interconversion between sulfo and desulfo xanthine oxidase in a system containing rhodanese, thiosulfate, and sulfhydryl reagent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1826–1829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polson A., von Wechmar M. B., van Regenmortel M. H. Isolation of viral IgY antibodies from yolks of immunized hens. Immunol Commun. 1980;9(5):475–493. doi: 10.3109/08820138009066010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale S. W., Ljungdahl L. G., DerVartanian D. V. EPR evidence for nickel-substrate interaction in carbon monoxide dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 30;108(2):658–663. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90880-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadoss C. S., Shen T. C., Vennesland B. Molybdenum insertion in vitro in demolybdo nitrate reductase of Chlorella vulgaris. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11532–11537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saari L. L., Triplett E. W., Ludden P. W. Purification and properties of the activating enzyme for iron protein of nitrogenase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15502–15508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider K., Schlegel H. G., Jochim K. Effect of nickel on activity and subunit composition of purified hydrogenase from Nocardia opaca 1 b. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 1;138(3):533–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah V. K., Brill W. J. Isolation of an iron-molybdenum cofactor from nitrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3249–3253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Bogart M., Beinert H. Micro methods for the quantitative determination of iron and copper in biological material. Anal Biochem. 1967 Aug;20(2):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90038-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]