Abstract
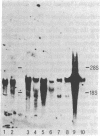
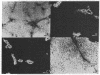
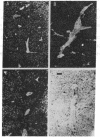
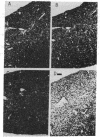
Mitochondrial glutamine synthetase (EC 6.3.1.2) is the primary ammonia-detoxifying enzyme in avian liver and is therefore analogous in function to carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I (ammonia) (EC 6.3.4.16) in mammalian liver. In mammalian liver, glutamine synthetase is cytosolic and its distribution is restricted to a few hepatocytes around the terminal venules. These cells do not express carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I. Using immunocytochemistry, we show here that there is little or no zonation of glutamine synthetase in avian liver. Rather, it is broadly distributed to most hepatocytes, much like carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I in mammalian liver. In situ hybridization with a cloned glutamine synthetase cDNA probe showed the distribution of glutamine synthetase mRNA in both mammalian and avian liver to correspond to the distribution of immunoreactive protein. Neither glutamine synthetase nor carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I and ornithine transcarbamoylase (EC 2.1.3.3) are strictly zoned in liver of the Texas tortoise or of an Argentine tree frog, both of which possess a complete urea cycle but which may also rely on glutamine synthetase for ammonia detoxication. These latter results suggest that the mutually exclusive expression of either carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase I or glutamine synthetase may be unique to mammalian liver.
Full text
PDF
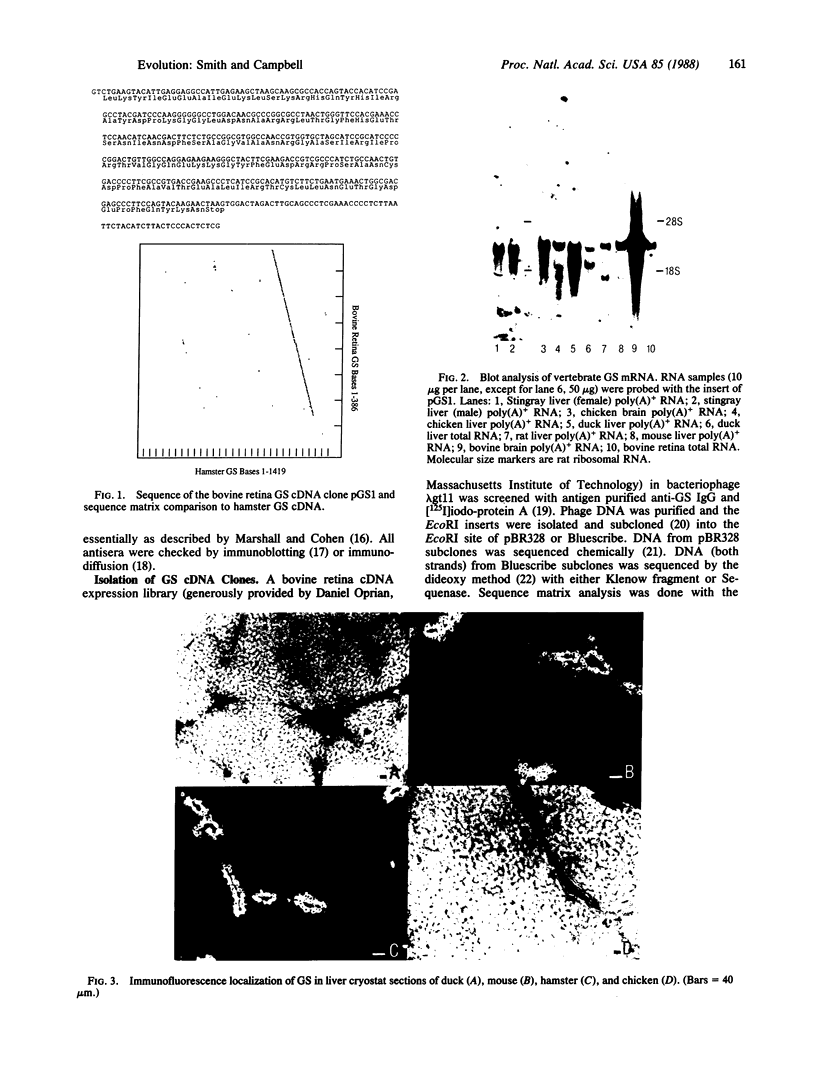
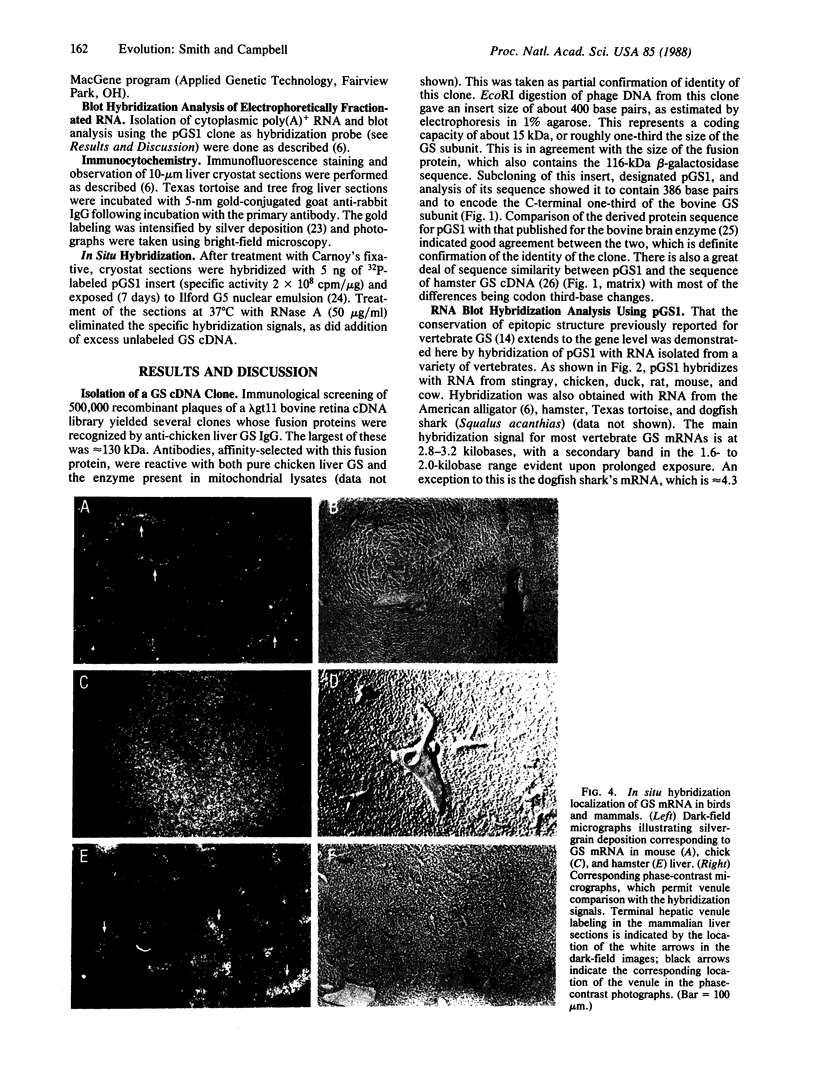
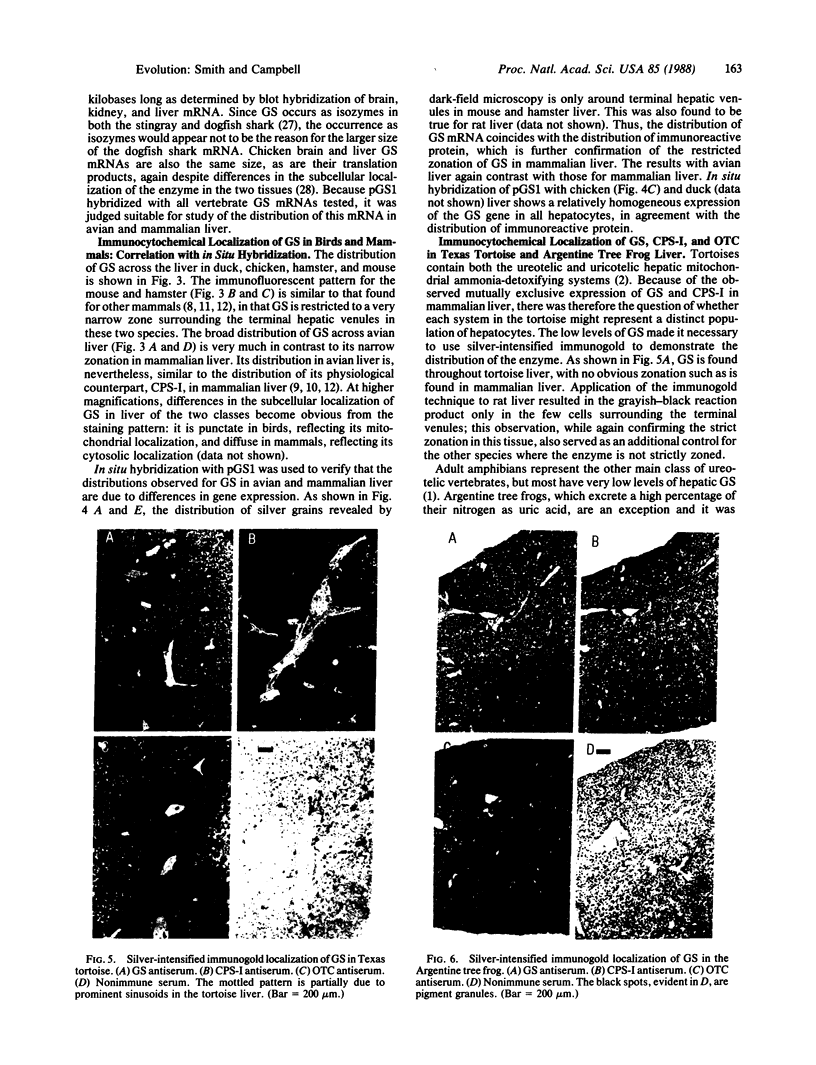

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloch B., Popovici T., Levin M. J., Tuil D., Kahn A. Transferrin gene expression visualized in oligodendrocytes of the rat brain by using in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. W., Smith D. D., Jr, Vorhaben J. E. Avian and Mammalian mitochondrial ammonia-detoxifying systems in tortoise liver. Science. 1985 Apr 19;228(4697):349–351. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4697.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. W., Vorhaben J. E., Smith D. D., Jr Hepatic ammonia metabolism in a uricotelic treefrog Phyllomedusa sauvagei. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):R805–R810. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.5.R805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. W., Vorhaben J. E., Smith D. D., Jr Uricoteley:its nature and origin during the evolution of tetrapod vertebrates. J Exp Zool. 1987 Sep;243(3):349–363. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402430302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaasbeek Janzen J. W., Gebhardt R., ten Voorde G. H., Lamers W. H., Charles R., Moorman A. F. Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase during rat liver development. J Histochem Cytochem. 1987 Jan;35(1):49–54. doi: 10.1177/35.1.2878950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaasbeek Janzen J. W., Lamers W. H., Moorman A. F., de Graaf A., Los J. A., Charles R. Immunohistochemical localization of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (ammonia) in adult rat liver; evidence for a heterogeneous distribution. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Jun;32(6):557–564. doi: 10.1177/32.6.6373912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaasbeek Janzen J. W., Moorman A. F., Lamers W. H., Charles R. Development of the heterogeneous distribution of carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase (ammonia) in rat-liver parenchyma during postnatal development. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Dec;33(12):1205–1211. doi: 10.1177/33.12.4067274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Heterogeneous distribution of glutamine synthetase among rat liver parenchymal cells in situ and in primary culture. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):567–570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward B. E., Hussain A., Wilson R. H., Lyons A., Woodcock V., McIntosh B., Harris T. J. The cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA for an amplified glutamine synthetase gene from the Chinese hamster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):999–1008. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. J., Piskiewicz D. Primary structure of peptides from bovine brain glutamine synthetase. Comparison with sequences of glutamine synthetases from other organisms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 1;827(3):439–446. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(85)90230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manigley C., Roth J. Applications of immunocolloids in light microscopy. IV. Use of photochemical silver staining in a simple and efficient double-staining technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Dec;33(12):1247–1251. doi: 10.1177/33.12.2415576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M., Cohen P. P. Ornithine transcarbamylase from Streptococcus faecalis and bovine liver. I. Isolation and subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1641–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. D., Jr, Campbell J. W. Glutamine synthetase in liver of the American alligator, Alligator mississippiensis. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1987;86(4):755–762. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(87)90223-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. D., Jr, Campbell J. W. Subcellular location of chicken brain glutamine synthetase and comparison with chicken liver mitochondrial glutamine synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12265–12268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. D., Jr, Ritter N. M., Campbell J. W. Glutamine synthetase isozymes in elasmobranch brain and liver tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):198–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. D., Jr, Vorhaben J. E., Campbell J. W. Preparation and cross-reactivity of anti-avian glutamine synthetase antibody. J Exp Zool. 1983 Apr;226(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402260105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorhaben J. E., Campbell J. W. Glutamine synthetase. A mitochondrial enzyme in uricotelic species. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2763–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorhaben J. E., Campbell J. W. Submitochondrial localization and function of enzymes of glutamine metabolism in avian liver. J Cell Biol. 1977 May;73(2):300–310. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot C. J., ten Voorde G. H., van Andel R. E., te Kortschot A., Gaasbeek Janzen J. W., Wilson R. H., Moorman A. F., Charles R., Lamers W. H. Reciprocal regulation of glutamine synthetase and carbamoylphosphate synthetase levels in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 29;908(3):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90103-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]