Abstract
At present, the dilute (dv) coat-color mutation of DBA mice provides the only simple means for measuring the relative somatic and germ-line reverse mutation rates of retrovirus-induced mutations in mammals. The dv mutation was generated by the spontaneous integration of an ecotropic murine leukemia virus into noncoding sequences of the dilute locus. Reversion of the dv mutation occurs by provirus excision and is mediated by homologous recombination events involving the viral long terminal repeat sequences. Although numerous independent germ-line d+ revertants have been identified, somatic d+ revertants have not been reported previously. During the past 5 years, we have screened more than one million mice homozygous for the dv mutation to determine whether we could identify somatic d+ revertants. This survey has resulted in the identification of a somatic d+ revertant and has provided a data base from which we can estimate the relative somatic and germ-line excision frequencies of retroviruses in mice and speculate about the nature of homologous recombination events producing d+ revertant alleles.
Full text
PDF
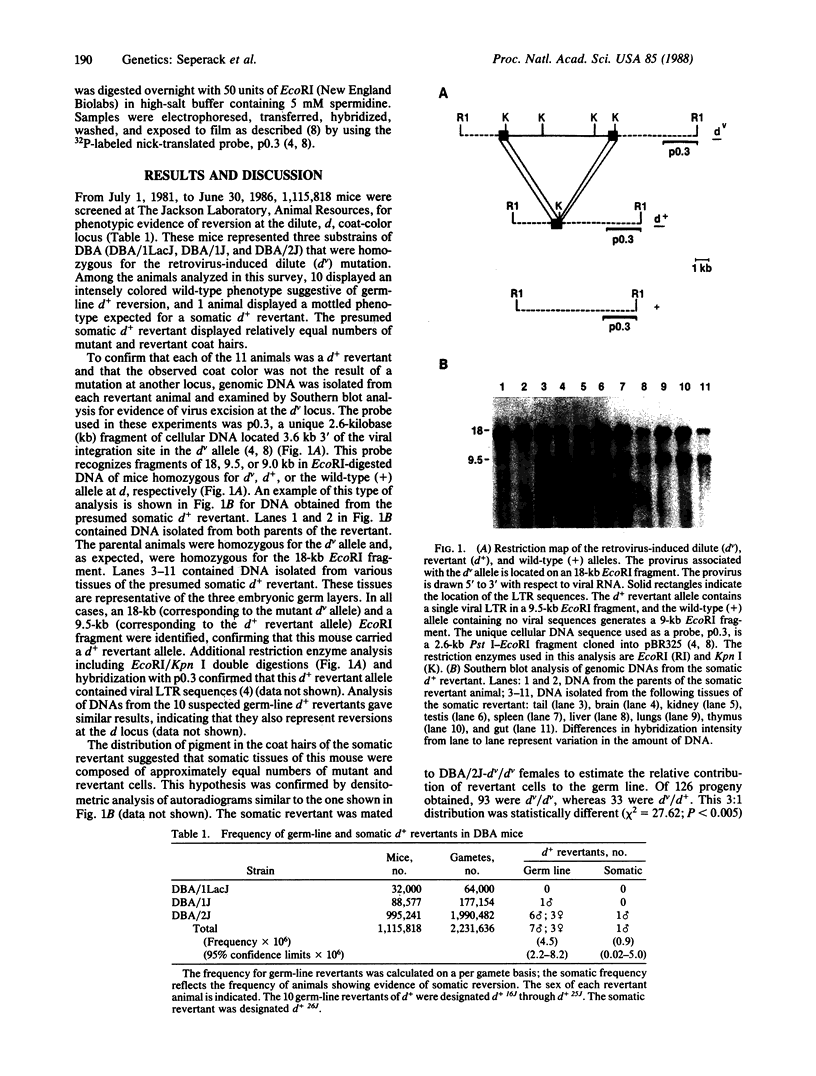
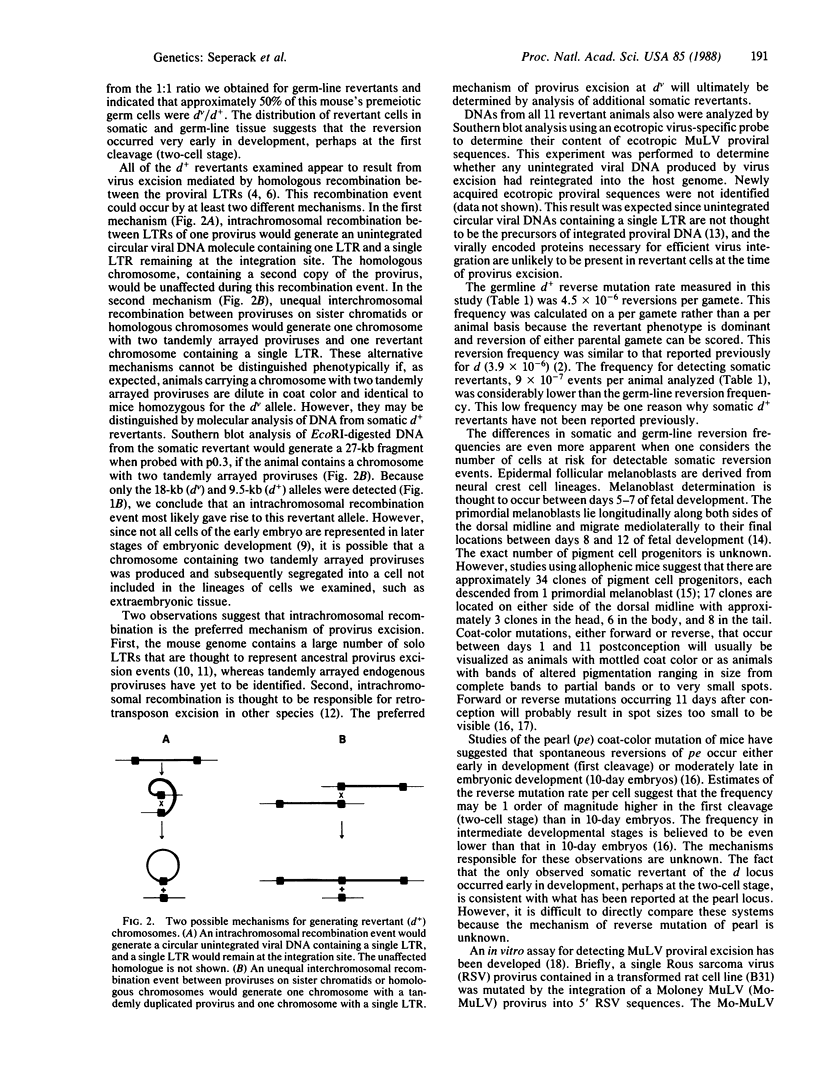

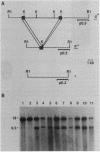
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carbonare B. D., Gehring W. J. Excision of copia element in a revertant of the white-apricot mutation of Drosophila melanogaster leaves behind one long-terminal repeat. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;199(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00327501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Hutchison K. W., Jenkins N. A. Excision of the DBA ecotropic provirus in dilute coat-color revertants of mice occurs by homologous recombination involving the viral LTRs. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döring H. P., Starlinger P. Barbara McClintock's controlling elements: now at the DNA level. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. L. The relationship between cell lineage and differentiation in the early mouse embryo. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1978;9:205–241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-35803-9_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. W., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Dilute-coat-color locus of mice: nucleotide sequence analysis of the d+2J and d+Ha revertant alleles. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2899–2904. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. W., Medhora M. M., Hartl D. L. Molecular structure of a somatically unstable transposable element in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8684–8688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Dilute (d) coat colour mutation of DBA/2J mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):370–374. doi: 10.1038/293370a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melvold R. W. Spontaneous somatic reversion in mice. Effects of parental genotype on stability at the p-locus. Mutat Res. 1971 Jun;12(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz B. Gene control of mammalian differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:411–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.002211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panganiban A. T., Temin H. M. Circles with two tandem LTRs are precursors to integrated retrovirus DNA. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinchik E. M., Russell L. B., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Molecular genetic analysis of the dilute-short ear (d-se) region of the mouse. Genetics. 1986 Feb;112(2):321–342. doi: 10.1093/genetics/112.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig B., Liao L. W., Hirsh D. Sequence of the C. elegans transposable element Tc1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):4201–4209. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell L. B. Definition of functional units in a small chromosomal segment of the mouse and its use in interpreting the nature of radiation-induced mutations. Mutat Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):107–123. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager G., Dickie M. M. Natural mutation rates in the house mouse. Estimates for five specific loci and dominant mutations. Mutat Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(71)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Ortiz S. Retroviruses as mutagens: insertion and excision of a nontransforming provirus alter expression of a resident transforming provirus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Chaleff D. T., Valent B., Fink G. R. Mutations affecting Ty-mediated expression of the HIS4 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1984 Jun;107(2):179–197. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Glöggler K., Baumruker T., Schmidt M., Horak I. Family of middle repetitive DNA sequences in the mouse genome with structural features of solitary retroviral long terminal repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3327–3330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Schmidt M., Baumruker T., Horak I. Evidence for mobility of a new family of mouse middle repetitive DNA elements (LTR-IS). Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3603–3610. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Davison D., Garza D., Bingham P. M. A detailed developmental and structural study of the transcriptional effects of insertion of the Copia transposon into the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1985 Nov;111(3):495–515. doi: 10.1093/genetics/111.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]