Abstract
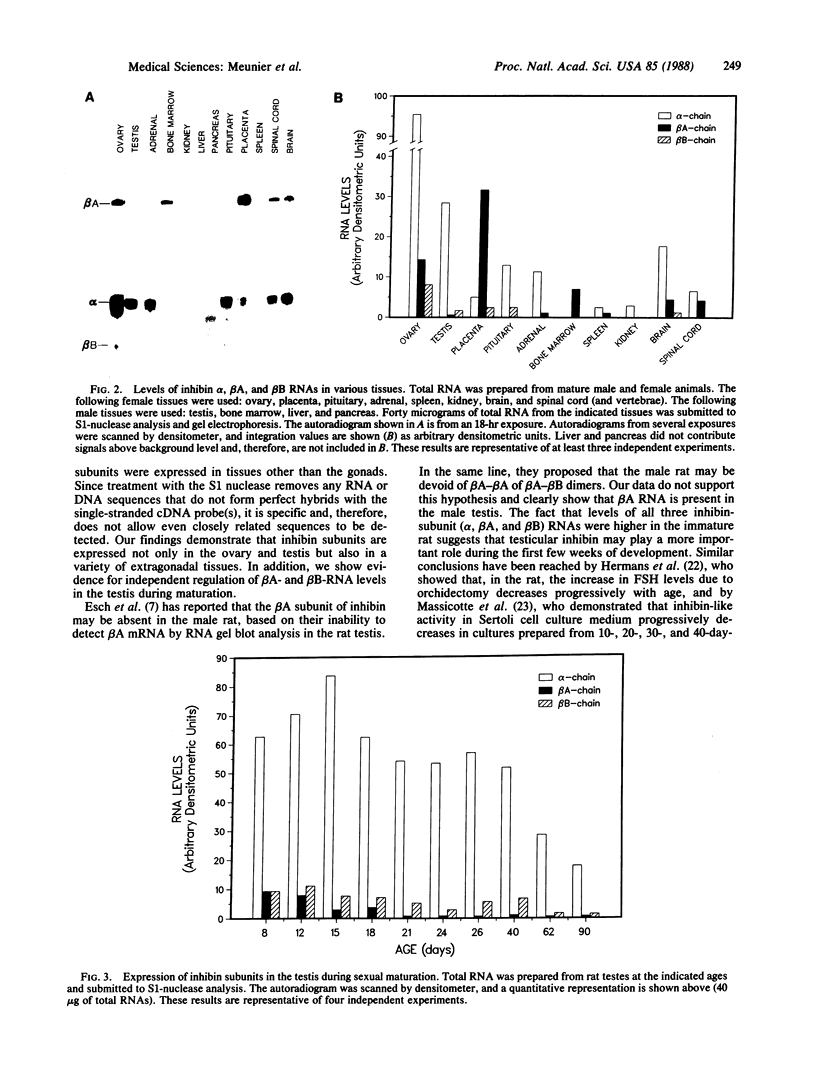
The S1-nuclease analysis was used to investigate the pattern of inhibin expression in the rat. In a first series of experiments, expression of the alpha, beta A, and beta B subunits of inhibin were monitored in various tissues from male and female rats. Two observations emerge from these studies. First, expression of inhibin subunits was found in gonadal and extragonadal tissues. In addition to the ovary and testis, inhibin alpha, beta A, and beta B RNAs were detected in the placenta, pituitary, adrenal, bone marrow, kidney, spinal cord, and brain. Detection of inhibin RNAs in the brain and spinal cord suggested that these subunits may exert neuroregulatory functions in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Furthermore, the presence of inhibin alpha and beta subunits in the placenta and the pituitary gland, two cell types that have clearly been shown to be regulated by exogenous inhibin, may reflect existing paracrine and/or autocrine processes active in these tissues. The second observation is that expression of inhibin subunit RNAs may vary by severalfold in a tissue-specific fashion. for example, alpha-subunit RNA levels are abundant in the gonads, whereas beta A-subunit RNA is predominant in the placenta and bone marrow. Finally, it is noted that expression of testicular inhibin RNA subunits decreases during sexual maturation. We conclude that the dimers comprised of inhibin subunits possess diverse functions and may act as growth/differentiation factors as well as a hormone.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicsak T. A., Vale W., Vaughan J., Tucker E. M., Cappel S., Hsueh A. J. Hormonal regulation of inhibin production by cultured Sertoli cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Feb;49(2-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90215-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate R. L., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Tizard R., Farber N. M., Cheung A., Ninfa E. G., Frey A. Z., Gash D. J., Chow E. P. Isolation of the bovine and human genes for Müllerian inhibiting substance and expression of the human gene in animal cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):685–698. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90783-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. R., Dench F., Nikolaidis I., Clements J. A., Forage R. G., Krozowski Z., Burger H. G. Inhibin A-subunit gene expression in the ovaries of immature female rats is stimulated by pregnant mare serum gonadotrophin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1191–1195. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80408-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellingsworth L. R., Brennan J. E., Fok K., Rosen D. M., Bentz H., Piez K. A., Seyedin S. M. Antibodies to the N-terminal portion of cartilage-inducing factor A and transforming growth factor beta. Immunohistochemical localization and association with differentiating cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12362–12367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Shimasaki S., Cooksey K., Mercado M., Mason A. J., Ying S. Y., Ueno N., Ling N. Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) cloning and DNA sequence analysis of rat ovarian inhibins. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 May;1(5):388–396. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-5-388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eto Y., Tsuji T., Takezawa M., Takano S., Yokogawa Y., Shibai H. Purification and characterization of erythroid differentiation factor (EDF) isolated from human leukemia cell line THP-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):1095–1103. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forage R. G., Ring J. M., Brown R. W., McInerney B. V., Cobon G. S., Gregson R. P., Robertson D. M., Morgan F. J., Hearn M. T., Findlay J. K. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA species coding for the two subunits of inhibin from bovine follicular fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3091–3095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans W. P., van Leeuwen E. C., Debets M. H., de Jong F. H. Involvement of inhibin in the regulation of follicle-stimulating hormone concentrations in prepubertal and adult, male and female rats. J Endocrinol. 1980 Jul;86(1):79–92. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0860079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg Z., Weiss J., Richman R. A. Inhibin-like activity in extracts of rabbit placentae. Placenta. 1981 Jul-Sep;2(3):259–264. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4004(81)80009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsueh A. J., Dahl K. D., Vaughan J., Tucker E., Rivier J., Bardin C. W., Vale W. Heterodimers and homodimers of inhibin subunits have different paracrine action in the modulation of luteinizing hormone-stimulated androgen biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5082–5086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knabbe C., Lippman M. E., Wakefield L. M., Flanders K. C., Kasid A., Derynck R., Dickson R. B. Evidence that transforming growth factor-beta is a hormonally regulated negative growth factor in human breast cancer cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):417–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Ying S. Y., Ueno N., Shimasaki S., Esch F., Hotta M., Guillemin R. Pituitary FSH is released by a heterodimer of the beta-subunits from the two forms of inhibin. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):779–782. doi: 10.1038/321779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Hayflick J. S., Ling N., Esch F., Ueno N., Ying S. Y., Guillemin R., Niall H., Seeburg P. H. Complementary DNA sequences of ovarian follicular fluid inhibin show precursor structure and homology with transforming growth factor-beta. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):659–663. doi: 10.1038/318659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Niall H. D., Seeburg P. H. Structure of two human ovarian inhibins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 28;135(3):957–964. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Type beta transforming growth factor is an inhibitor of myogenic differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8206–8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. E., Cerelli G. M., Spiess J., Rivier J., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M., Vale W. Inhibin A-subunit cDNAs from porcine ovary and human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5849–5853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullagh D. R. DUAL ENDOCRINE ACTIVITY OF THE TESTES. Science. 1932 Jul 1;76(1957):19–20. doi: 10.1126/science.76.1957.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan R. I., Healy D. L., Robertson D. M., Burger H. G., de Kretser D. M. The human placenta: a novel source of inhibin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):485–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90758-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. W., St Johnston R. D., Gelbart W. M. A transcript from a Drosophila pattern gene predicts a protein homologous to the transforming growth factor-beta family. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):81–84. doi: 10.1038/325081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan V., Convey E. M., Roche J. F., Ireland J. J. Changes in inhibin-like bioactivity in ovulatory and atretic follicles and utero-ovarian venous blood after prostaglandin-induced luteolysis in heifers. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1332–1340. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petraglia F., Sawchenko P., Lim A. T., Rivier J., Vale W. Localization, secretion, and action of inhibin in human placenta. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):187–189. doi: 10.1126/science.3299703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier C., Rivier J., Vale W. Inhibin-mediated feedback control of follicle-stimulating hormone secretion in the female rat. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):205–208. doi: 10.1126/science.3092356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier C., Vale W. Inhibin: measurement and role in the immature female rat. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1688–1690. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander H. J., van Leeuwen E. C., de Jong F. H. Inhibin-like activity in media from cultured rat granulosa cells collected throughout the oestrous cycle. J Endocrinol. 1984 Oct;103(1):77–84. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1030077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., Assoian R. K. Transforming growth factor-beta: biological function and chemical structure. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):532–534. doi: 10.1126/science.3487831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Rivier J., Vaughan J., McClintock R., Corrigan A., Woo W., Karr D., Spiess J. Purification and characterization of an FSH releasing protein from porcine ovarian follicular fluid. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):776–779. doi: 10.1038/321776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff T. K., Meunier H., Jones P. B., Hsueh A. J., Mayo K. E. Rat inhibin: molecular cloning of alpha- and beta-subunit complementary deoxyribonucleic acids and expression in the ovary. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Aug;1(8):561–568. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-8-561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]