Abstract
In contrast with speciation in terrestrial organisms, marine plankton frequently display gradual morphological change without lineage division (e.g., phyletic gradualism or gradual evolution), which has raised the possibility that a different mode of evolution dominates within pelagic environments. Here, we reexamine a classic case of putative gradual evolution within the Globorotalia plesiotumida–G. tumida lineage of planktonic foraminifera, and find both compelling evidence for the existence of a third cryptic species during the speciation event and the abrupt evolution of the descendant G. tumida. The third morphotype, not recognized in previous analyses, differs in shape and coiling direction from its ancestor, G. plesiotumida. This species dominates the globorotaliid population for 414,000 years just before the appearance of G. tumida. The first population of the descendant, G. tumida, evolves abruptly within a 44,000-year interval. A combination of morphological data and biostratigraphic evidence suggests that G. tumida evolved by cladogenesis. Our findings provide an unexpected twist on one of the best-documented cases of within-lineage phyletic gradualism and, in doing so, revisit the limitations and promise of the study of speciation in the fossil record.
Keywords: cladogenesis, evolutionary dynamics, foraminifera, fossil record, plankton
The fossil record in marine plankton is characterized by gradual morphological change both with and without apparent cladogenesis (1–10). Phyletic gradualism has been attributed to a lack of barriers to gene flow in species that are both cosmopolitan and phenotypically plastic (11–13). However, a growing number of phylogenetic studies have revealed the presence of multiple cryptic species within named marine morphospecies (14–16). In some cases, within-species morphological clines have subsequently been found to consist of numerous genetically, biogeographically, and ecologically distinct species (17, 18). The presence of cryptic species complexes in the modern ocean suggests a fossil record laden with hidden cladogenetic events (19) potentially affecting the perception and interpretation of evolutionary patterns.
The existence of cryptic species complexes, and the consequent discrepancy between morphological and genetic species, is of general concern because open ocean microfossils provide one of the best records (temporally and spatially) of the last 130 million years of life (20–22). For instance, planktonic foraminifera have been used in global studies of the determinants of species richness (23), body size (24, 25), and speciation (26). For all the utility of open ocean microfossils, there have been relatively few coordinated studies of both the morphologic and genetic similarity of individuals in the modern ocean (although see refs. 17, 18, 27, and 28). There is also evidence that open ocean microfossils may not actually conform to the morphological species concept. A high-resolution study of the Globorotalia lineage of planktonic foraminifera in the Early to Middle Miocene failed to find evidence of discrete, nonoverlapping morphological clouds as is expected in the typical morphological species concept (29).
The morphological similarity of foraminiferal species has implications for the detection of cladogenesis. Most past studies have either assumed a priori that cladogenesis occurred (7–9, 30) or, if not, have interpreted evolutionary trends as cases of within-lineage evolution after considering trait distributions (1, 5). Trait variation within a given species is typically normally distributed and, in theory, deviations from normality should occur when two or more species coexist. In practice, this normality test for cladogenesis has little statistical power when two morphologically similar species with high trait variability coexist (as described in ref. 29) and are sampled at the sample sizes typical of past studies (31). Sample variance can also be used to detect the presence of multiple taxa with some of the same statistical limitations (4). The lack of clear correspondences between named morphospecies and discrete morphological clusters increases the difficulty of detecting cladogenesis in fossil planktonic foraminifera. In one instance, reproductive isolation and, putatively, speciation was found to be uncoupled from morphological evolution in the Fohsella lineage of globorotaliid foraminifera (32).
Here we test for speciation in the fossil record within a lineage of planktonic foraminifera. In this study, we use the term speciation to refer to cladogenetic events (e.g., phyletic splitting), and not within-lineage evolution. We reexamine a classic case of putative gradual evolution in which the ancestor Globorotalia plesiotumida is thought to have evolved over ≈500,000 years into the descendant G. tumida (1, 33). Both before and after the morphological transition there are several million years of morphological stasis suggesting that this case represents a hybrid of phyletic gradualism and morphological stasis dubbed “punctuated gradualism” (33). The G. tumida lineage has often been reexamined in studies of evolutionary mode (34–40), due to the compelling results and data availability of Malmgren et al.'s original study (33). In readdressing this widely cited case of within-lineage gradual evolution, we consider the effect of methodology on our perception of evolutionary trends, test for the possibility of phyletic splitting and within-lineage change, and reconsider the morphological species concept in planktonic foraminifera.
Results and Discussion
We analyze morphological change in the Globorotalia plesiotumida–G. tumida evolutionary series in a deep-sea sediment core record from the western tropical Pacific [Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) site 806B, Ontong Java Plateau, 0°19.11′N, 159°21.69′E, 2,520 m water depth]. Using eigenshape analysis (a morphometric technique for comparing outlines) (41, 42) and an updated time scale (supporting information (SI) Fig. S1), we obtained a similar pattern of morphological evolution in the western tropical Pacific as was found in an earlier study in the central Indian Ocean (Fig. 1A and Fig. S2). The similarity of both results, despite using materials from widely separated sites, suggests that the evolutionary transition is synchronous across a large stretch of the ocean. Indeed, G. tumida displays a near-simultaneous first appearance throughout the tropical Indo-Pacific with a geographic range overlapping that of G. plesiotumida at the Miocene/Pliocene boundary (refs. 43–45; see also SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S3). Our study design was therefore predicated on the hypothesis that the morphological evolution of G. tumida in the western tropical Pacific occurred in situ.
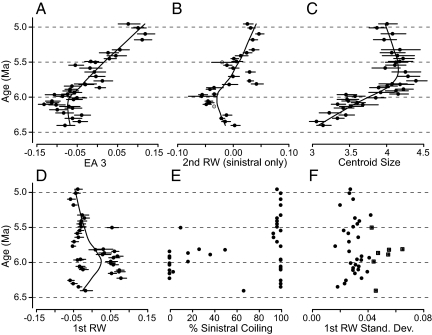
Fig. 1.
Morphological trends over time in the Globorotalia plesiotumida–G. tumida lineage in the western equatorial Pacific. Mean morphology as a function of time expressed as (A) an eigenshape amplitude (EA 3) from eigenshape analysis (all individuals), (B) a relative warp score (RW 2) from semilandmark TPS analysis (all individuals analyzed, sinistrally coiled individuals plotted), (C) centroid size (all individuals), and (D) a relative warp score (RW 1) from semilandmark TPS analysis (all individuals). Error bars in (A–D) are parametric 95% CI and mean values are fit with a loess curve. (E) Percent sinistral coiling individuals and (F) the standard deviation of RW 1 as a function of time. Boxed values in (F) indicate samples with 20% or greater overlap in sinistral and dextral coiled individuals. Gray points in (B) indicate samples containing three or fewer individuals.
Our analysis departs from previous analyses by controlling for the effects of shell size on morphology, and by using a different morphometric method. In Malmgren et al.'s study (33), a 3-fold increase in mean size accompanies the morphological transition in the G. tumida–G. plesiotumida lineage and is strongly correlated with mean morphology along eigenaxis 2 (EA 2, Pearson's r = 0.89 and P < 0.001). Here we explicitly control for the effect of size on the perceived evolutionary trend by sampling individuals in a narrower size range (250–500 μm in contrast to the ∼150-500 μm originally used). Given this greater control for size, the correlation between size and EA 3 is weak (Pearson's r = 0.23 and P < 0.001). However, we still note a ≈1.4-fold increase in mean centroid size in the equatorial Pacific (Fig. 1C).
In an additional departure, we use a second morphometric technique for analyzing outlines, semilandmark thin-plate spline analysis (semilandmark TPS) (46). Methodological aspects of semilandmark TPS techniques suggest advantages of this approach over eigenshape analysis (SI Materials and Methods). The second relative warp (RW 2, a morphological eigenaxis capturing 20% of morphological variance) is correlated to EA 3 from eigenshape analysis (Pearson's r = 0.70 and P < 0.001 for sinistrally coiled individuals; see also Fig. S4) and reveals a comparable shift in mean morphology (Fig. 1B). However, our findings also show critical differences between the two methods.
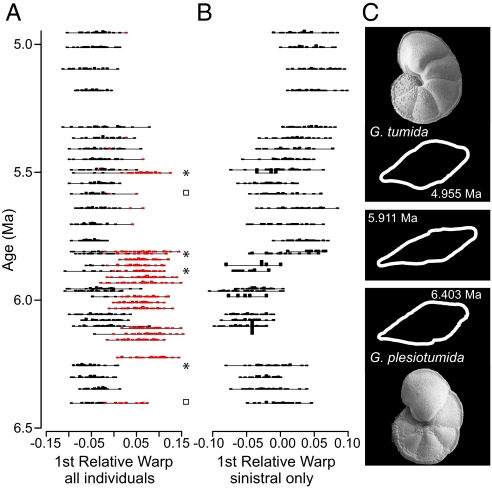
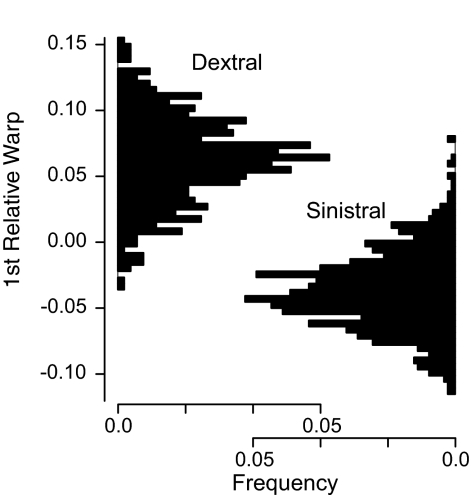
Surprisingly, the first relative warp (RW 1) of the semilandmark TPS analysis indicates that some individuals present during the transition are morphologically more distinct than Globorotalia plesiotumida and G. tumida are from each other (Fig. 1D; RW 1 captures 53% of morphological variance). These divergent individuals are distinctly flattened (see Fig. 3C Middle and Movie S1) and are easily differentiated by eye. Furthermore, the flattened morphotype is almost exclusively dextrally coiled (clockwise chamber addition from the spiral perspective) and rarely coexists with sinistral G. plesiotumida (Figs. 2 and 3A). Grouping individuals by coiling direction reveals a significant difference in the RW 1 scores of sinistral and dextral coiled individuals (Fig. 2; t test, P < 0.001). A few dextral individuals occur in our oldest sample at 6.403 Ma, but these are more G. plesiotumida-like in their outline morphology than any subsequent dextral population. Dextral morphotypes display the typical elongated final chamber often used as a defining characteristic of G. plesiotumida. Where dextral and sinistral individuals do co-occur (20% or greater overlap), the populations exhibit higher morphological variance along RW 1 (Fig. 1F) than is the case for populations dominated by one coiling morphology. Additionally, we find significant differences in RW 1 scores between coiling groups in each of the seven time periods containing at least three individuals per coiling direction (t test, P < 0.001). A maximum likelihood analysis of mixture models provides statistical support for the interpretation of two coexisting morphotypes rather than a single morphotype in six time periods (Fig. 3A; stars indicate significance at 0.05 and squares at 0.06 significance level; details in Materials and Methods and ref. 47).
Fig. 3.
Morphological change in the Globorotalia plesiotumida–G. tumida lineage. (A) Morphology viewed as histograms along relative warp 1, with sinistrally coiled individuals in black and dextrally coiled individuals in red, and (B) along relative warp 1 as calculated for sinistrally coiled individuals. Stars indicate two overlapping populations supported at a 0.05 significance level and squares at a 0.06 significance level. (C) Scanning electron microscopy (umbilical view) and digitized outlines (edge view) of sinistrally coiled Globorotalia plesiotumida and G. tumida (top two and bottom two panels) and the dextral morphospecies (Middle). Individuals panels of morphology with time along RW 1 and RW 2 are shown in Movie S2.
Fig. 2.
Distribution of relative warp 1 scores for dextrally and sinistrally coiled individuals. Each histogram is scaled to a unit area. Sinistral and dextral distributions are significantly different (t test, P < 0.001).
The correspondence between coiling direction and morphology suggests that the flattened, dextral morphotype represents a species fully differentiated from the sinistral G. plesiotumida. Our evidence for a cryptic species in the G. plesiotumida complex is consistent with evidence in other groups of foraminifera that coiling direction is a heritable trait (48, 49). In two modern planktonic foraminiferal species, Neogloboquadrina pachyderma and Globorotalia truncatulinoides, coiling direction was found to be indicative of cryptic species (17, 28).
The dextral, flattened morphotype becomes abruptly dominant in our record at 6.225 Ma, and persists for 414,000 years until 5.819 Ma. During this period, which overlaps the start of the gradual evolution of G. tumida in eigenshape analyses, the dextrally coiled morphogroup oscillates in dominance with the sinistrally coiled morphogroup. In many oscillations, the abundance of the rare morphotype (sinistral or dextral) is zero. These recorded absences may coincide with time periods during which a given morphotype is globally rare and therefore unsampled. Alternatively, the absences may indicate periods of changing biogeographic distributions, with rare morphotypes found in abundance in other locations. Based on our sampling scheme, we cannot determine which of these two alternatives is more likely.
After the period of oscillating dominance, rare dextrally coiled individuals are present for an additional 444,000 years with a second peak in dextral abundance at 5.503 Ma. Together, these data suggest that the flattened, dextral taxon evolved by cladogenesis and coexisted with its ancestor for at least 850,000 years. If the global first appearance of the dextral species is recorded in our sample set at 6.256 Ma, then its evolution was very rapid, occurring within a 26,000-year window. However, we caution that it is possible that the first appearance of the flattened dextral taxon could reflect immigration or have occurred at or before 6.403 Ma in the equatorial Pacific. Dextral individuals are recorded in the Indian Ocean before 6.4 Ma (33), but whether these have the flattened morphology of the cryptic taxon described here is yet to be determined.
A second cladogenetic event may accompany the first appearance of fully differentiated Globorotalia tumida between 5.865 and 5.819 Ma. In this case, both the ancestor, G. plesiotumida, and the descendant, G. tumida, are sinistrally coiled and therefore differentiated entirely upon a change in outline morphology (Fig. 3B). Cladogenesis is indicated by several factors, including (i) the abrupt shift in mean morphology toward G. tumida within a 44,000-year span (mean shift >1.5 SD), (ii) the co-occurrence of pre- and postshift morphologies at 5.819 Ma, a period of elevated population variance (one of the three highest observed), (iii) the observation of several reversals in the population morphology toward the G. plesiotumida type, and (iv) periods of elevated variance between 5.819 and ≈5.5 Ma. Finally, a short interval of co-occurrence (several 100 kya) between G. plesiotumida and G. tumida is indicated in Indian Ocean records (50). In the Atlantic, G. plesiotumida persists well into the middle Pliocene (51, 52).
Throughout the entire time series, maximum likelihood analysis of mixture models provides support for only one sinistral population per time interval (Fig. 3B; RW 1sinistral results shown, approximately equivalent to RW 2all as explained in Materials and Methods and see Fig. S5), in possible agreement with Malmgren et al.'s (33) interpretation of gradual, within-lineage evolution. However, the high variance in morphology within some samples (particularly between 5.5 and 6.0 Ma) suggests that there could be two coexisting species at several points in the time series. Unfortunately, our maximum likelihood analysis has very low power (0.01–0.48) to detect overlapping populations if they exist, due in part to our small sample size. We conclude that we cannot unambiguously determine whether G. plesiotumida co-occurs in the same samples with G. tumida during the transition period from approximately 6–5.5 Ma. Both larger sample sizes and more informative traits could help resolve this ambiguity in future studies.
Our conclusions differ from those of Malmgren et al. (1, 33) in two critical ways. First, our methods clearly identify the ecological dominance of a flattened, dextral cryptic species just before the appearance of G. tumida, which is inferred to have arisen cladogenetically from a G. plesiotumida ancestor. Malmgren et al. (33) noted the presence of dextral, biconvex forms during the transitional period like the compressed, dextrally coiled individuals we see in the western equatorial Pacific. However, they did not find morphometric evidence that would distinguish these dextral forms as species in their own right. Second, previous work has not detected as rapid an appearance of fully formed G. tumida as we observe here at 5.81 Ma. Malmgren et al. (33) did observe a step in both shell size and morphology about this time, but they attributed these morphological shifts to oscillations within a longer evolutionary trend.
Our findings show that morphometric techniques and measurement strategy are key to the interpretation of evolution in the fossil record. It is disturbing that eigenshape analysis (used by previous authors) fails to detect differences in compression of individuals in the equatorial Pacific, where both semilandmark TPS analysis and visual inspection confirm the distinct morphology of dextrally coiled individuals. We hypothesize that eigenshape analysis cannot detect differences in shell compression that are not accompanied by major changes in the angles between many points (see SI Materials and Methods). Malmgren et al. (33) also ruled out the possibility of cladogenesis due to the apparent lack of bimodality within populations. This test is less powerful than the mixture models used here, because distributions never appear bimodal along RW 1 even when multiple morphospecies coexist (Fig. 3A). Finally, both our outline data and those collected by Malmgren et al. (33) fail to capture essential aspects of shell morphology, such as the shape of the final chamber, that are used by taxonomists to differentiate Globorotalia plesiotumida and G. tumida. Without examining a larger subset of informative characters, it is difficult to assess whether the perceived mode of evolution and the applicability of the morphological species concept is an artifact of the morphological traits under consideration. Consequently, this and other morphometric studies may lack adequate information to clearly differentiate speciation from within lineage evolution.
A synthesis of past studies of cladogenesis has documented a common pattern of sympatric speciation in open ocean taxa (6), with the gradual divergence of the mean daughter morphotype from a stable ancestral morphotype for ≈500,000 years following speciation in foraminifera (8, 9), radiolarians (30, 53), and diatoms (7). In contrast to instances of sympatric speciation, morphological change associated with allopatric speciation in marine microfossils can be rapid (10 kya) (54).
Our findings add to these observations by showing that, at least in this classic case, the evolution of G. tumida from G. plesiotumida was not a simple affair. Evolution involved both the cryptic evolution of a dextral, compressed morphotype and the rapid evolution of G. tumida, in both cases likely by cladogenesis. The dramatic decrease in abundance of the flattened dextral forms coincides with the abrupt appearance of G. tumida. It is clear that the first G. tumida appeared very rapidly, in less than 45,000 years, rather than the hundreds of thousands of years inferred from previous work. Furthermore, stratigraphic analysis from other sites has shown that G. plesiotumida persists after the evolution of G. tumida. Changes in the dominance of coexisting ancestral and descendant morphotypes occur several times and may be due to an oscillation in the environment. Our work underscores the inherent difficulty of inferring evolutionary mechanisms from fossils. At the same time, our study highlights observations unique to the fossil record, including the measurement of evolutionary patterns, species coexistence, and changing population variance through time.
Materials and Methods
Sample Preparation.
Within each time interval, we sampled the first 30 individuals encountered from the Globorotalia plesiotumida–tumida lineage in the >250-μm size fraction from ODP site 806B on the Ontong Java Plateau (1,140 individuals from 38 depth intervals; Dataset S1). An age model was calculated for the Ontong Java Plateau using 10 biostragraphic markers (55) and assuming constant sedimentation rates between markers (Fig. S1; age model for Atlantic site 959C also shown). The two exceptions to the sampling protocol of 30 individuals occurred in samples at 163.27- and 194.77-meter composite depth (mcd) where 31 and 29 individuals were analyzed, respectively. Individuals were cleaned, taped to glass coverslips, and mounted on a universal stage for the digitization of the edge view using a video capture system. A digitized 2D outline of each individual (100 coordinate points, approximately evenly spaced around the foraminiferal edge view) was initialized at the proloculous for morphometric analyses (41, 42) (Dataset S1).
Morphometric Methods.
Semilandmark thin-plate spline analysis is a landmark morphometric technique adapted to assessing similarity among outlines by ignoring differences that arise from the location of coordinates along an outline (46). After an initial consensus form (or mean shape) is calculated, points are allowed to slide along individual outlines to minimize the difference between individual shapes and the consensus form (56, 57). If the semilandmark analysis is recursive, then the postsliding location of points for each outline is used in the next iteration. If the semilandmark analysis is not recursive, then the consensus form is updated for each iteration, but individual outline points always start in same initial location. Eigenshape analysis (41, 42) was also used to compare results between the Pacific and Indian Ocean (see SI Materials and Methods for details on this method). Note, the signs of eigenaxes and relative warps can vary between analyses. Signs were reversed along eigenaxes and relative warps when necessary to conform to the orientation of Malmgren et al. (33). For instance, signs were reversed for RW 1all and RW 2all in Figs. 1–3 and related statistics.
Although theoretically preferable, recursive semilandmark TPS was computationally prohibitive given the large number of outlines (1,140) and sliding points (100 per outline) in this study. We assessed the effect of using recursive versus nonrecursive TPS by analyzing a representative subset of individuals with both techniques (304 total outlines, including eight randomly chosen individuals per time interval). Recursive and nonrecursive semilandmark results were highly correlated along the first three relative warps (Pearson's r > 0.91, P < 0.001), accounting altogether for 73% and 82% of morphological variance, respectively (Table S1). Judging from this subset of outlines, and specifically comparing the relative assignments of dextral and sinistral individuals, the effect of using nonrecursive semilandmark analysis on our interpretation of the large-scale RW 1 displacements is minimal. This was potentially not the case for the subtle trends in sinistrally coiled individuals along relative warp 2. Therefore, sinistral individuals (719 total) were separately analyzed using a recursive semilandmark analysis (three iterations). The first relative warp from sinistral semilandmark TPS analysis was strongly correlated with the second relative warp from the full analysis (r2 = 0.94, P < 0.001), and was used in Fig. 3 and in all statistical considerations of the evolution of G. tumida from G. plesiotumida.
As a preprocessing step to semilandmark TPS analysis, we first performed a Generalized Procrustes alignment (involving translation, rotation, and scaling) to minimize the sum-squared distance between outline points and a consensus shape using the function procGPA in the package “shapes” (version 1.0–8) in R (version 2.2.1) (58). This particular function allows shapes to be mirrored, an option that we used to minimize the apparent shape differences between left- and right-coiled individuals (shape outlines and mirroring results visualized in Movie S1).
Here we use relative warps (RWs) to described main patterns of shape change in the G. plesiotumida–G. tumida lineage. We used the program tpsRelw (version 1.46, created by F. James Rohlf) for all semilandmark analyses, including the calculation of relative warps. In tpsRelw, we used orthogonal projections and scaling by the cos (rho) for Procrustes alignments; results were unaffected by scaling by a unit centroid size (r2 > 0.9999 for the first 10 relative warps in TPS analysis). Uniform weighting of all partial warps (α = 0) was used to include uniform components in the partial warp scores matrix. Uniform components of shape change were estimated as the complement to the nonuniform shape variation (59). Finally, due to computational limitations and the similarity of TPS and semilandmark TPS results (Table S1), semilandmark TPS analysis was run for a maximum of three sliding iterations.
Maximum Likelihood Analysis of Mixture Models.
A maximum likelihood analysis of mixture models was used to assess the number of distinct populations along RW 1all and RW 1sinstral. The maximum likelihood framework allowed us to test the relative support for one or more overlapping populations within a single time period and morphological distribution (specifically, the histograms in Fig. 3). All analyses were performed using the program Mixture Model Analysis (version 1.32, created by G. Hunt) and a previously described approach (47).
In brief, we calculated the likelihood of one to two populations for each time interval along RW 1all and RW 1sinistral (roughly equivalent to RW 2all) using 200 random initiations, and assuming equal population variance and a normal distribution. A bootstrap approach was used to determine the relative support for one or more distributions, as increasing parameters generally improves model fit (e.g., the log-likelihood ratio will favor the model with more populations). To compare the relative support for one versus two overlapping populations, we generated 1,000 sample distributions based on the mean and variance calculated for a single population and compared these maximum likelihood estimates with that determined empirically for two overlapping populations. If the two-population log-likelihood ratio was greater than 95% of those generated from a single population (α = 0.05), then we considered two overlapping populations more likely than a single population in a given time period. In interpreting negative results (e.g., the failure to reject a single population), we assessed the power of the maximum likelihood test using a second bootstrapped approach (log-likelihood ratio obtained from alpha in the first bootstrap test and assumed population parameters for two populations to generate distributions; see details in ref. 47).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
We thank L. Saul and S. Belongie for morphometric advice; M. D. Ohman and P. J. S. Franks for comments on the manuscript; G. Hunt, two anonymous reviewers, and the editor for thorough and insightful suggestions that greatly improved the manuscript; J. M. Lewis for making key contributions to an earlier iteration of this study; and the Ocean Drilling Program for providing samples. This work was supported by a National Science Foundation Division of Earth Sciences (EAR) grant (to R.D.N.) and a National Science Foundation graduate research fellowship (to P.M.H.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission. M.K. is a guest editor invited by the Editorial Board.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/0902887106/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Malmgren BA, Berggren WA, Lohmann GP. Species formation through punctuated gradualism in planktonic foraminifera. Science. 1984;225:317–319. doi: 10.1126/science.225.4659.317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Malmgren BA, Kennett JP. Phyletic gradualism in a Late Cenozoic planktonic foraminiferal lineage: DSDP site 284, southwest Pacific. Paleobiology. 1981;7:230–240. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Malmgren BA, Kucera M, Ekman G. Evolutionary changes in supplementary apertural characteristics of the late Neogene Sphaeroidinella dehiscens lineage (planktonic foraminifera) Palaios. 1996;11:192–206. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arnold AJ. Phyletic evolution in the Globorotalia crassaformis (Galloway and Wissler) lineage: A preliminary report. Paleobiology. 1983;9:390–397. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kucera M, Malmgren BA. Differences between evolution of mean form and evolution of new morphotypes: An example from Late Cretaceous planktonic foraminifera. Paleobiology. 1998;24:49–63. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Benton MJ, Pearson PN. Speciation in the fossil record. Trends Ecol Evol. 2001;16:405–411. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5347(01)02149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sorhannus U, Fenster EJ, Burckle LH, Hoffman A. Cladogenetic and anagenetic changes in the morphology of Rhizosolenia praebergonii Mukhina. Hist Biol. 1988;1:185–205. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lazarus D, Hilbrecht H, Spencercervato C, Thierstein H. Sympatric speciation and phyletic change in Globorotalia truncatulinoides. Paleobiology. 1995;21:28–51. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wei KY. Stratophenetic tracing of phylogeny using SIMCA pattern recognition technique: A case study of the late Neogene planktic Foraminifera Globoconella clade. Paleobiology. 1994;20:52–65. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hunt G. The relative importance of directional change, random walks, and stasis in the evolution of fossil lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104:18404–18408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704088104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lohmann GP, Malmgren BA. Equatorward migration of Globorotalia truncatulinoides ecophenotypes through the Late Pleistocene: Gradual evolution or ocean change? Paleobiology. 1983;9:414–421. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kucera M, Malmgren BA. Latitudinal variation in the planktic foraminifer Contusotruncana contusa in the terminal Cretaceous ocean. Mar Micropaleontol. 1996;28:31–52. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Boltovskoy D, Vrba A. Latitude-related shell patterns in Radiolaria: Botryostrobus auritus/australis morphotypes in the equatorial to Antarctic Pacific. Mar Micropaleontol. 1989;13:309–323. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Knowlton N. Sibling species in the sea. Annu Rev Ecol Syst. 1993;24:189–216. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Goetze E. Cryptic speciation on the high seas; global phylogenetics of the copepod family Eucalanidae. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B. 2003;270:2321–2331. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2003.2505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Saez AG, et al. Pseudo-cryptic speciation in coccolithophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:7163–7168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1132069100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.de Vargas C, Renaud S, Hilbrecht H, Pawlowski J. Pleistocene adaptive radiation in Globorotalia truncatulinoides: Genetic, morphologic, and environmental evidence. Paleobiology. 2001;27:104–125. [Google Scholar]
- 18.de Vargas C, et al. Molecular evidence of cryptic speciation in planktonic foraminifers and their relation to oceanic provinces. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:2864–2868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.2864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Alizon S, Kucera M, Jansen VAA. Competition between cryptic species explains variations in rates of lineage evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:12382–12386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805039105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Phleger FB. Foraminifera and deep-sea research. Deep Sea Res. 1954;2:1–23. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vincent E, Berger WH. In: The Oceanic Lithosphere. Emiliani C, editor. Vol 7. New York: Wiley; 1981. pp. 1025–1119. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Norris RD, de Vargas C. Evolution all at sea. Nature. 2000;405:23–24. doi: 10.1038/35011162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rutherford S, D'Hondt S, Prell W. Environmental controls on the geographic distribution of zooplankton diversity. Nature. 1999;400:749–753. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schmidt DN, Thierstein HR, Bollmann J, Schiebel R. Abiotic forcing of plankton evolution in the Cenozoic. Science. 2004;303:207–210. doi: 10.1126/science.1090592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schmidt DN, et al. Size distribution of Holocene planktic foraminifer assemblages: Biogeography, ecology and adaptation. Mar Micropaleontol. 2004;50:319–338. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Allen AP, Gillooly JF, Savages VM, Brown JH. Kinetic effects of temperature on rates of genetic divergence and speciation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:9130–9135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603587103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Huber BT, Bijma J, Darling K. Cryptic speciation in the living planktonic foraminifer Globigerinella siphonifera (d'Orbigny) Paleobiology. 1997;23:33–62. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Darling KF, Kucera M, Kroon D, Wade CM. A resolution for the coiling direction paradox in Neogloboquadrina pachyderma. Paleoceanography. 2006;21:PA2011. doi: 10.1029/2005PA001189. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tabachnick RE, Bookstein FL. The structure of individual variation in Miocene Globorotalia. Evolution. 1990;44:416–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1990.tb05209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kellogg DE, Hays JD. Microevolutionary patterns in Late Cenozoic Radiolaria. Paleobiology. 1975;1:150–160. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Norris RD, Corfield RM, Cartlidge J. What is gradualism? Cryptic speciation in globorotaliid foraminifera. Paleobiology. 1996;22:386–405. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Malmgren BA, Berggren WA, Lohmann GP. Evidence for punctuated gradualism in the Late Neogene Globorotalia tumida lineage of planktonic foraminifera. Paleobiology. 1983;9:377–389. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bookstein FL. Random walk and the existence of evolutionary rates. Paleobiology. 1987;13:446–464. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Charlesworth B. Some quantitative methods for studying evolutionary patterns in single characters. Paleobiology. 1984;10:308–318. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Roopnarine PD. The description and classification of evolutionary mode: A computational approach. Paleobiology. 2001;27:446–465. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kitchell JA, Estabrook G, Macleod N. Testing for equality of rates of evolution. Paleobiology. 1987;13:272–285. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hunt G. Gradual or pulsed evolution: When should punctuational explanations be preferred? Paleobiology. 2008;34:360–377. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jackson JBC, Cheetham AH. Tempo and mode of speciation in the sea. Trends Ecol Evol. 1999;14:72–77. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5347(98)01504-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Macleod N. Punctuated anagenesis and the importance of stratigraphy to paleobiology. Paleobiology. 1991;17:167–188. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lohmann GP. Eigenshape analysis of microfossils: A general morphometric procedure for describing changes in shape. J Int Assoc Math Geol. 1983;15:659–672. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lohmann GP, Schweitzer PN. In: Rohlf FJ, Bookstein FL, editors. Proceedings of the Michigan Morphometrics Workshop; Ann Arbor, MI: Univ of Michigan Museum of Zoology; 1990. pp. 147–166. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Banner FT, Blow WH. Two new taxa of Globorotaliinae (Globigerinacea Foraminifera) assisting determination of Late Miocene/Middle Miocene boundary. Nature. 1965;207:1351–1354. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Banner FT, Blow WH. Progress in planktonic foraminiferal biostratigraphy of Neogene. Nature. 1965;208:1164–1166. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kennett JP, Srinivasan MS. Neogene Planktonic Foraminifera: A Phylogenetic Atlas. Stroudsburg, PA: Hutchinson Ross; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bookstein FL. Landmark methods for forms without landmarks: Morphometrics of group differences in outline shape. Med Image Anal. 1997;1:225–243. doi: 10.1016/s1361-8415(97)85012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hunt G, Chapman RE. Evaluating hypotheses of instar-grouping in arthropods: A maximum likelihood approach. Paleobiology. 2001;27:466–484. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Norris RD, Nishi H. Evolutionary trends in coiling of tropical Paleogene planktic foraminifera. Paleobiology. 2001;27:327–347. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Brummer GJA, Kroon D. In: Planktonic Foraminifers as Tracers of Ocean-Climate History. Brummer GJA, Kroon D, editors. Amsterdam: Free Univ Press; 1988. pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Srinivasan MS, Chaturvedi SN. In: Centenary of Japanese Micropaleontology. Ishizaki K, Saito T, editors. Tokyo: Terra Scientific; 1992. pp. 175–188. [Google Scholar]
- 51.Norris RD. In: Mascle J, Lohmann GP, Moullade M, editors. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results; College Station, TX: Ocean Drilling Program; 1998. pp. 445–479. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Chaisson WP, Pearson PN. In: Shackleton NJ, Curry WB, Richter C, Brawlower TJ, editors. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results; College Station, TX: Ocean Drilling Program; 1997. pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lazarus D, Scherer RP, Prothero DR. Evolution of the radiolarian species-complex Pterocanium: A preliminary survey. J Paleontol. 1985;59:183–220. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wei KY, Kennett JP. Phyletic gradualism and punctuated equilibrium in the late Neogene planktonic foraminiferal clade Globoconella. Paleobiology. 1988;14:345–363. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Berggren WA, Kent DV, Swisher CC, Aubry M-P. Geochronology, Time Scales and Global Stratigraphic Correlation. Tulsa, OK: Society for Sedimentary Geology; 1995. SEPM Special Publication 54. [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bookstein FL. Morphometric Tools for Landmark Data: Geometry and Biology. Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge Univ Press; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zelditch M. Geometric Morphometrics for Biologists: A Primer. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Dryden IL, Mardia KV. Statistical Shape Analysis. Chichester, U.K.: Wiley; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rohlf FJ, Bookstein FL. Computing the uniform component of shape variation. Systematic Biol. 2003;52:66–69. doi: 10.1080/10635150390132759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.