Abstract
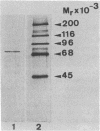
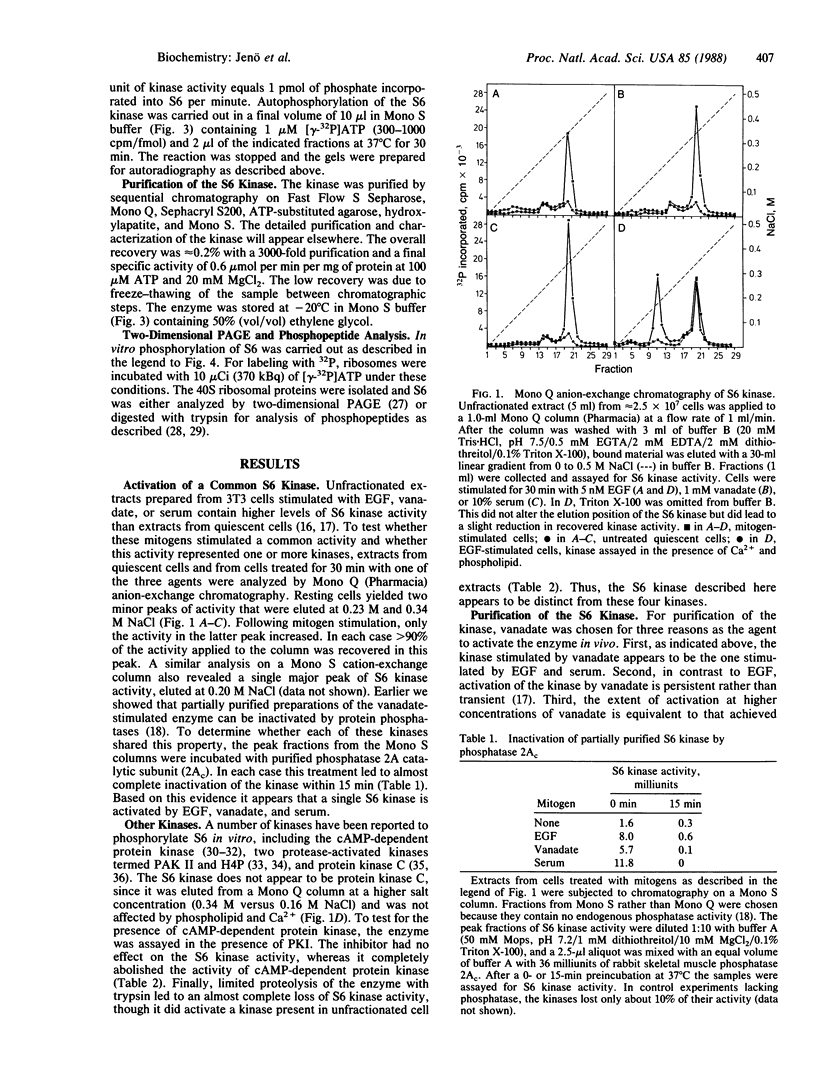
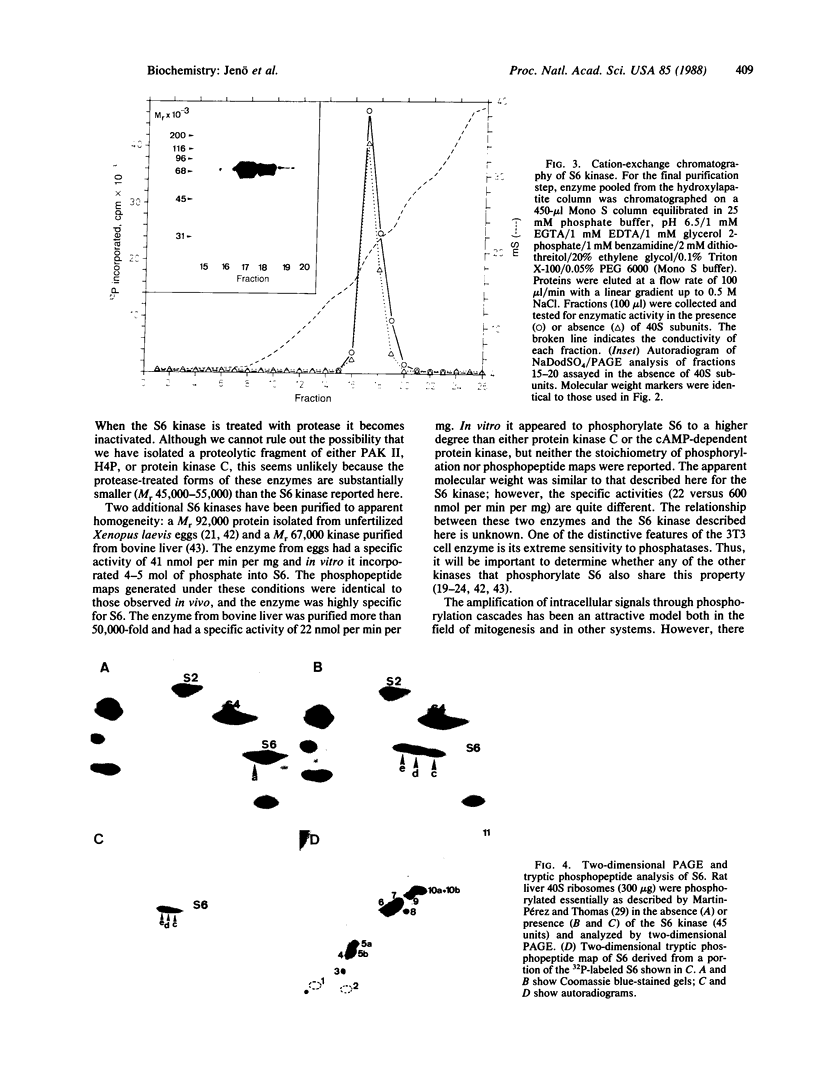
Treatment of Swiss mouse 3T3 cells with epidermal growth factor, orthovanadate, or serum results in the activation of a kinase that phosphorylates protein S6 of the 40S ribosomal subunit in vitro. This kinase is eluted as a single peak of activity from either a Mono Q anion-exchange column at 0.34 M NaCl or a Mono S cation-exchange column at 0.20 M NaCl. Treatment of the peak fraction from the Mono S column with phosphatase 2A completely abolishes the activity of the enzyme. The kinase appears to be distinct from protein kinase C, cAMP-dependent protein kinase, and two protease-activated kinases, PAK II and H4P. The kinase has been purified to apparent homogeneity and migrates as a single band at Mr 70,000 in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels. The kinase exhibits the ability to autophosphorylate, and this activity directly parallels S6 phosphorylation activity on the final step of purification. In vitro, the kinase incorporates up to 5 mol of phosphate into S6, and the tryptic phosphopeptide maps obtained are equivalent to those from S6 phosphorylated in vivo. Most important, treatment of the purified kinase with phosphatase 2A results in complete inactivation of the enzyme, arguing that the activity of the kinase is directly controlled by phosphorylation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballinger D. G., Hunt T. Fertilization of sea urchin eggs is accompanied by 40 S ribosomal subunit phosphorylation. Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 30;87(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Stimulation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by pp60v-src or by serum: dissociation from phorbol ester-stimulated activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1733–1737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bommer U. A., Noll F., Lutsch G., Bielka H. Immunochemical detection of proteins in the small subunit of rat liver ribosomes involved in binding of the ternary initiation complex. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 25;111(1):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80785-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhard S. J., Traugh J. A. Changes in ribosome function by cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14003–14008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue M. J., Masaracchia R. A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 at multiple sites by a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase from lymphoid cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):435–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., McConkey E. H. Preferential utilization of phosphorylated 40-S ribosomal subunits during initiation complex formation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):535–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Two interferon-induced proteins are involved in the protein kinase complex dependent on double-stranded RNA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):685–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gressner A. M., Wool I. G. The phosphorylation of liver ribosomal proteins in vivo. Evidence that only a single small subunit protein (S6) is phosphorylated. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6917–6925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Humbel R. E., Thomas G. Insulin-like growth factor: insulin or serum increase phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of stationary chick embryo fibroblasts into early G1 phase of the cell cycle. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 1;100(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa T., Perkins J. P., Krebs E. G. Studies of the subunit structure of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):574–580. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Peuch C. J., Ballester R., Rosen O. M. Purified rat brain calcium- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6858–6862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubben T. H., Traugh J. A. Cyclic nucleotide-independent protein kinases from rabbit reticulocytes. Purification and characterization of protease-activated kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13992–13997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macphee C. H., Drummond A. H., Otto A. M., Jimenez de Asua L. Prostaglandin F2 alpha stimulates phosphatidylinositol turnover and increases the cellular content of 1,2-diacylglycerol in confluent resting Swiss 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Apr;119(1):35–40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041190107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Thomas G. EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin induce the phosphorylation of identical S6 peptides in swiss mouse 3T3 cells: effect of cAMP on early sites of phosphorylation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Thomas G. Ordered phosphorylation of 40S ribosomal protein S6 after serum stimulation of quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):926–930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Thomas G. Phosphopeptide analysis of 40 S ribosomal protein S6. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:369–375. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Guroff G. Purification and mechanism of activation of a nerve growth factor-sensitive S6 kinase from PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2832–2844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemenoff R. A., Gunsalus J. R., Avruch J. An insulin-stimulated (ribosomal S6) protein kinase from soluble extracts of H4 hepatoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 15;245(1):196–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90205-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Manchester K. L., Towbin H., Gordon J., Thomas G. The phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in rat tissues following cycloheximide injection, in diabetes, and after denervation of diaphragm. A simple immunological determination of the extent of S6 phosphorylation on protein blots. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12316–12321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Thomas G., Maller J. L. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of an S6 kinase in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palen E., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase differentially alters translation of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3518–3523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Katan M., Waterfield M. D., Leader D. P. The phosphorylation of eukaryotic ribosomal protein S6 by protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Olwin B. B., Krebs E. G. Fibroblast growth factor treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells activates a subunit S6 kinase that phosphorylates a synthetic peptide substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Rodriguez-Pena M., Smith K. A. Phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and growth factors rapidly stimulate the phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 protein in intact quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7244–7248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegmann M., Thomas G. Separation of multiple phosphorylated forms of 40 S ribosomal protein S6 by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;146:362–369. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(87)46037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Garcia de Herreros A., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Purification of a bovine liver S6 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):891–899. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao K., Ogata K. Proteins of small subunits of rat liver ribosomes that interact with poly(U). I. Effects of preincubation of poly(U) with 40 S subunits on the interactions of 40 S subunit proteins with aurintricarboxylic acid and with N,N'-p-phenylenedimaleimide. J Biochem. 1979 Sep;86(3):597–603. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Gordon J., Rogg H. N4-Acetylcytidine. A previously unidentified labile component of the small subunit of eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1101–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Gordon J. Multiple phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of quiescent 3T3 cells into early G1, and cellular compartmentalization of the phosphate donor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Kubler A. M., Gordon J., Jimenez de Asua L. Regulation of 40S ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1015–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolan D. R., Traut R. R. Protein topography of the 40 S ribosomal subunit from rabbit reticulocytes shown by cross-linking with 2-iminothiolane. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10129–10136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Cohen P. Isolation and characterisation of cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation sites from rat liver ribosomal protein S6. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80910-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Grande R. W., Traugh J. A. Phosphorylation of 40-S ribosomal subunits by cAMP-dependent, cGMP-dependent and protease-activated protein kinases. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):421–428. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]