Abstract
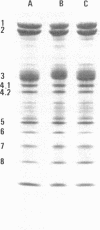
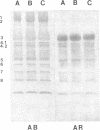
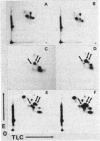
Band 3 is the major anion transport polypeptide of erythrocytes. It appears to be the binding site of several glycolytic enzymes. Structurally, band 3 is the major protein spanning the erythrocyte membrane and connects the plasma membrane to band 2.1, which binds to the cytoskeleton. In the present study, we report an alteration of band 3 molecule that is associated with the following changes: erythrocyte shape change from discoid to "thorny cells" (acanthocytes), restriction of rotational diffusion of band 3 in the membrane, increase in anion transport, and decrease in the number of high-affinity ankyrin-binding sites. Changes in erythrocyte IgG binding, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, fluorescence polarization (indicative of membrane fluidity), and other membrane proteins as determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis were not detected. Cells containing the altered band 3 polypeptide were obtained from individuals with abnormal erythrocyte morphology. Two-dimensional peptide maps revealed differences in the Mr 17,000 anion transport segment of band 3 consistent with additions of tyrosines or tyrosine-containing peptides. The data suggest that (i) this alteration of band 3 does not result in accelerated aging as does cleavage and (ii) structural changes in the anion transport region result in alterations in anion transport.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appell K. C., Low P. S. Partial structural characterization of the cytoplasmic domain of the erythrocyte membrane protein, band 3. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11104–11111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. D., Kay M. M. Homeostatic removal of senescent murine erythrocytes by splenic macrophages. Exp Hematol. 1981 Mar;9(3):297–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Association between ankyrin and the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 isolated from the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. The membrane attachment protein for spectrin is associated with band 3 in human erythrocyte membranes. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):468–473. doi: 10.1038/280468a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beth A. H., Conturo T. E., Venkataramu S. D., Staros J. V. Dynamics and interactions of the anion channel in intact human erythrocytes: an electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopic study employing a new membrane-impermeant bifunctional spin-label. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3824–3832. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. A., Feinstein M. B., Sha'afi R. I. Membrane proteins related to water transport in human erythrocytes. Nature. 1975 Apr 10;254(5500):523–525. doi: 10.1038/254523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Rothstein A. Membrane proteins related to anion permeability of human red blood cells. I. Localization of disulfonic stilbene binding sites in proteins involved in permeation. J Membr Biol. 1974;15(3):207–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01870088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox J. V., Moon R. T., Lazarides E. Anion transporter: highly cell-type-specific expression of distinct polypeptides and transcripts in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1548–1557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenckhahn D., Schlüter K., Allen D. P., Bennett V. Colocalization of band 3 with ankyrin and spectrin at the basal membrane of intercalated cells in the rat kidney. Science. 1985 Dec 13;230(4731):1287–1289. doi: 10.1126/science.2933809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenckhahn D., Zinke K., Schauer U., Appell K. C., Low P. S. Identification of immunoreactive forms of human erythrocyte band 3 in nonerythroid cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1984 May;34(1):144–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Shiffer K. A., Casoria L. A., Eyster M. E. Identification of the molecular defect in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton of some kindreds with hereditary spherocytosis. Blood. 1982 Sep;60(3):772–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves W. R., Giedd K. N., Verkleij A., Branton D. Reassociation of ankyrin with band 3 in erythrocyte membranes and in lipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11965–11972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karadsheh N. S., Uyeda K., Oliver R. M. Studies on structure of human erythrocyte phosphofructokinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 25;252(10):3515–3524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Bosman G. J., Shapiro S. S., Bendich A., Bassel P. S. Oxidation as a possible mechanism of cellular aging: vitamin E deficiency causes premature aging and IgG binding to erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2463–2467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Goodman S. R., Sorensen K., Whitfield C. F., Wong P., Zaki L., Rudloff V. Senescent cell antigen is immunologically related to band 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1631–1635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M. Localization of senescent cell antigen on band 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5753–5757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M. Mechanism of removal of senescent cells by human macrophages in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3521–3525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M. Role of physiologic autoantibody in the removal of senescent human red cells. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(4):555–567. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Sorensen K., Wong P., Bolton P. Antigenicity, storage, and aging: physiologic autoantibodies to cell membrane and serum proteins and the senescent cell antigen. Mol Cell Biochem. 1982 Nov 26;49(2):65–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00242486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. M., Tracey C. M., Goodman J. R., Cone J. C., Bassel P. S. Polypeptides immunologically related to band 3 are present in nucleated somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6882–6886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman H. J., Steck T. L. Association of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase with the human red cell membrane. A kinetic analysis. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6314–6321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopito R. R., Lodish H. F. Primary structure and transmembrane orientation of the murine anion exchange protein. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):234–238. doi: 10.1038/316234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepke S., Fasold H., Pring M., Passow H. A study of the relationship between inhibition of anion exchange and binding to the red blood cell membrane of 4,4'-diisothiocyano stilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid (DIDS) and its dihydro derivative (H2DIDS). J Membr Biol. 1976 Oct 20;29(1-2):147–177. doi: 10.1007/BF01868957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Marchesi V. T. The carboxyl-terminal domain of human erythrocyte band 3. Description, isolation, and location in the bilayer. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 25;256(12):6463–6468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Cherry R. J. Anchorage of a band 3 population at the erythrocyte cytoplasmic membrane surface: protein rotational diffusion measurements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4702–4706. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramjeesingh M., Rothstein A. The location of a chymotrypsin cleavage site and of other sites in the primary structure of the 17,000-dalton transmembrane segment of band 3, the anion transport protein of red cell. Membr Biochem. 1982;4(4):259–269. doi: 10.3109/09687688209065435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Shaklai N. Functional properties of human hemoglobin bound to the erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):893–899. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell K. F., Gerhardt S., Schöppe-Fredenburg A. Kinetic characteristics of the sulfate self-exchange in human red blood cells and red blood cell ghosts. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jan 28;30(4):319–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01869675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier S. L. Organization of enzymes in human erythrocyte membranes. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jan;210(1):139–145. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Koziarz J. J., Singh M. K., Reddy G., Köhler H. Preparation and analysis of seven major, topographically defined fragments of band 3, the predominant transmembrane polypeptide of human erythrocyte membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1216–1222. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Ramos B., Strapazon E. Proteolytic dissection of band 3, the predominant transmembrane polypeptide of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):1153–1161. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The band 3 protein of the human red cell membrane: a review. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(3):311–324. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strapazon E., Steck T. L. Interaction of the aldolase and the membrane of human erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1977 Jun 28;16(13):2966–2971. doi: 10.1021/bi00632a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam P., Petz L. D., Spath P. Detection of IgG sensitization of red cells with 125I staphylococcal protein A. Am J Hematol. 1982 Jun;12(4):337–346. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830120405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]