Abstract
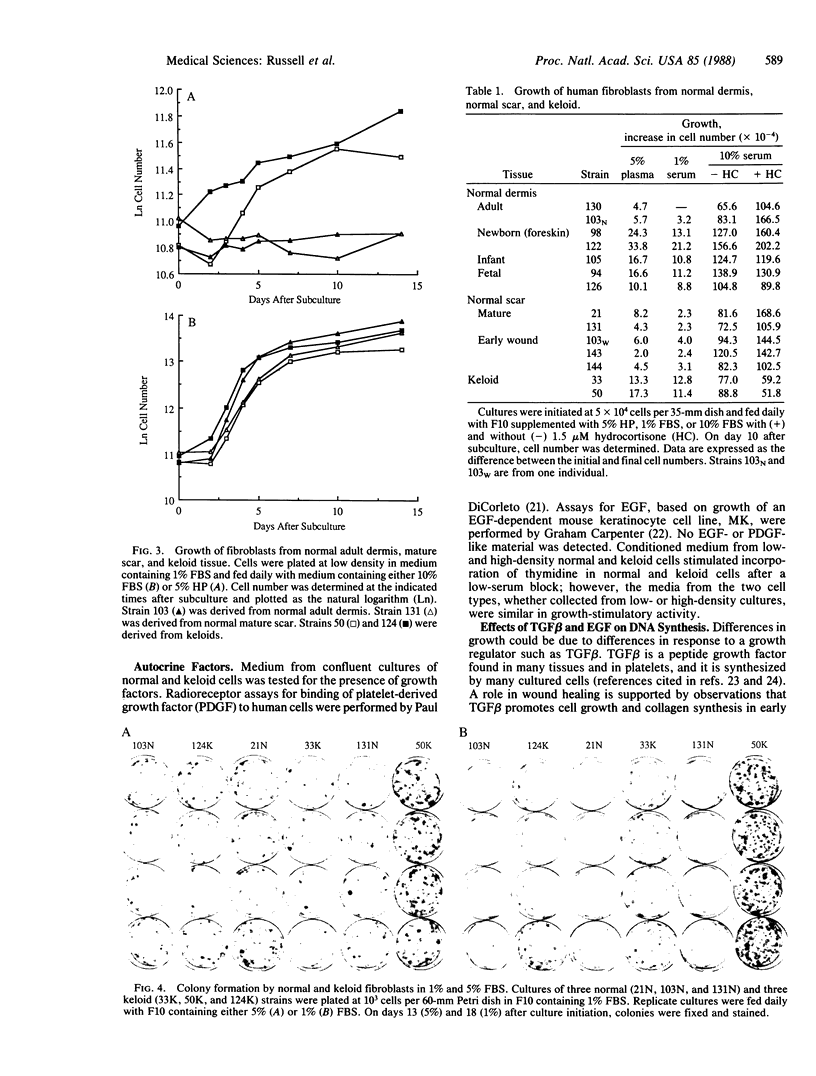
Keloids are benign dermal tumors that form during an abnormal wound-healing process in genetically susceptible individuals. Although growth of normal and keloid cells did not differ in medium containing 10% (vol/vol) fetal bovine serum, keloid cultures grew to significantly higher densities than normal cells in medium containing 5% (vol/vol) plasma or 1% fetal bovine serum. Conditioned medium from keloid cultures did not stimulate growth of normal cells in plasma nor did it contain detectable platelet-derived growth factor or epidermal growth factor. Keloid fibroblasts responded differently than normal adult fibroblasts to transforming growth factor beta. Whereas transforming growth factor beta reduced growth stimulation by epidermal growth factor in cells from normal adult skin or scars, it enhanced the activity of epidermal growth factor in cells from keloids. Normal and keloid fibroblasts also responded differently to hydrocortisone: growth was stimulated in normal adult cells and unaffected or inhibited in keloid cells. Fetal fibroblasts resembled keloid cells in their ability to grow in plasma and in their response to hydrocortisone. The ability of keloid fibroblasts to grow to higher cell densities in low-serum medium than cells from normal adult skin or from normal early or mature scars suggests that a reduced dependence on serum growth factors may account for their prolonged growth in vivo. Similarities between keloid and fetal cells suggest that keloids may result from the untimely expression of a growth-control mechanism that is developmentally regulated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. B., Barsh G. S., Carney D. H., Cunningham D. D. Dexamethasone modulates binding and action of epidermal growth factor in serum-free cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1882–1886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Lind P., Urdea M. S., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Philpott K., Mellor A. L. cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization of human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and its expression in tumour cell lines. Nature. 1986 Apr 24;320(6064):695–699. doi: 10.1038/320695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Westermark B., Ek B., Heldin C. H. Coexpression of a PDGF-like growth factor and PDGF receptors in a human osteosarcoma cell line: implications for autocrine receptor activation. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betsholtz C., Westermark B. Growth factor-induced proliferation of human fibroblasts in serum-free culture depends on cell density and extracellular calcium concentration. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Feb;118(2):203–210. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Zendegui J. A biological assay for epidermal growth factor/urogastrone and related polypeptides. Anal Biochem. 1986 Mar;153(2):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R. Age dependent production of a competence factor by human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jan;114(1):61–67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Dollar L. A., Hintz R. L., Rosenfeld R. G. Insulin-like growth factor I/somatomedin-C (IGF-I/SM-C) and glucocorticoids synergistically regulate mitosis in competent human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Aug;116(2):191–197. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Hormonal control of the replication of human fetal fibroblasts: role of somatomedin C/insulin-like growth factor I. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Jul;128(1):47–54. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diegelmann R. F., Cohen I. K., McCoy B. J. Growth kinetics and collagen synthesis of normal skin, normal scar and keloid fibroblasts in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Feb;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040980210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine A., Goldstein R. H. The effect of transforming growth factor-beta on cell proliferation and collagen formation by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3897–3902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox P. L., DiCorleto P. E. Regulation of production of a platelet-derived growth factor-like protein by cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Nov;121(2):298–308. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J. S. Stimulation of division of sparse and confluent 3T3 cell populations by a fibroblast growth factor, dexamethasone, and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4584–4588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbacher G. K., Irminger J. C., Zapf J., Ziegler W. H., Humbel R. E. Insulin-like growth factor II in human adrenal pheochromocytomas and Wilms tumors: expression at the mRNA and protein level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1104–1106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Mar;39(3):169–187. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Strain A. J., Elstow S. F., Swenne I., Milner R. D. Bi-functional action of transforming growth factor-beta on DNA synthesis in early passage human fetal fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1986 Aug;128(2):322–328. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041280226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates the expression of fibronectin and collagen and their incorporation into the extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4337–4345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurobe M., Furukawa S., Hayashi K. Synthesis and secretion of an epidermal growth factor (EGF) by human fibroblast cells in culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 30;131(3):1080–1085. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Pircher R., Krycève-Martinerie C., Jullien P. Normal embryo fibroblasts release transforming growth factors in a latent form. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):184–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Guyre P. M., Holbrook N. J. Physiological functions of glucocorticoids in stress and their relation to pharmacological actions. Endocr Rev. 1984 Winter;5(1):25–44. doi: 10.1210/edrv-5-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Pollack S. V., Pinnell S. R. Keloids: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Apr;4(4):461–470. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)70048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoletis C., Bazin S., Lous M. L. Clinical and biochemical features of normal, defective, and pathologic scars. Clin Plast Surg. 1977 Jul;4(3):347–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L., Kang A. H. Transforming growth factor-beta increases steady state levels of type I procollagen and fibronectin messenger RNAs posttranscriptionally in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1285–1288. doi: 10.1172/JCI112950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeve A. E., Eccles M. R., Wilkins R. J., Bell G. I., Millow L. J. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II transcripts in Wilms' tumour. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):258–260. doi: 10.1038/317258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Wakefield L. M., Roche N. S., Stern D. F., Sporn M. B. Type beta transforming growth factor: a bifunctional regulator of cellular growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):119–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. W., Starman B. J., Fujimoto W. Y., Williams R. H. Differences in growth response to hydrocortisone and ascorbic acid by human diploid fibroblasts. In Vitro. 1977;13(12):824–830. doi: 10.1007/BF02615130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. D., Russell S. B., Trupin K. M. Differential effects of hydrocortisone on both growth and collagen metabolism of human fibroblasts from normal and keloid tissue. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Nov;97(2):221–229. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. D., Russell S. B., Trupin K. M. Fibroblast heterogeneity in glucocorticoid regulation of collagen metabolism: genetic or epigenetic? In Vitro. 1982 Jun;18(6):557–564. doi: 10.1007/BF02810079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. D., Witt W. S. Cell size and growth characteristics of cultured fibroblasts isolated from normal and keloid tissue. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1976 Feb;57(2):207–212. doi: 10.1097/00006534-197602000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. B., Russell J. D., Trupin J. S. Alteration of amino acid transport by hydrocortisone. Different effects in human fibroblasts derived from normal skin and keloid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9525–9531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Pledger W. J., Martin P., Antoniades H., Stiles C. D. Transforming viruses directly reduce the cellular growth requirement for a platelet derived growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1978 Dec;97(3 Pt 1):371–380. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040970312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Cowell J., Robertson M. E., Priestley L. M., Wadey R., Hopkins B., Pritchard J., Bell G. I., Rall L. B., Graham C. F. Insulin-like growth factor-II gene expression in Wilms' tumour and embryonic tissues. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):260–262. doi: 10.1038/317260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley G. D., Tucker R. F., Moses H. L. Type beta transforming growth factor/growth inhibitor stimulates entry of monolayer cultures of AKR-2B cells into S phase after a prolonged prereplicative interval. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4147–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slayback J. R., Cheung L. W., Geyer R. P. Comparative effects of human platelet growth factor on the growth and morphology of human fetal and adult diploid fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Dec;110(2):462–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90313-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Shull J. H., Smith J. M., Ward J. M., Sodek J. Polypeptide transforming growth factors isolated from bovine sources and used for wound healing in vivo. Science. 1983 Mar 18;219(4590):1329–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.6572416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., Assoian R. K. Transforming growth factor-beta: biological function and chemical structure. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):532–534. doi: 10.1126/science.3487831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles C. D. Autocrine control of growth? Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):604–605. doi: 10.1038/311604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syms A. J., Norris J. S., Smith R. G. Autocrine regulation of growth: I. Glucocorticoid inhibition is overcome by exogenous platelet derived growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90440-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trupin J. S., Russell S. B., Russell J. D. Variation in prolyl hydroxylase activity of keloid-derived and normal human fibroblasts in response to hydrocortisone and ascorbic acid. Coll Relat Res. 1983;3(1):13–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W. Newborn human skin fibroblasts senesce in vitro without acquiring adult growth factor requirements. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Sep;154(1):310–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90691-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]