Abstract
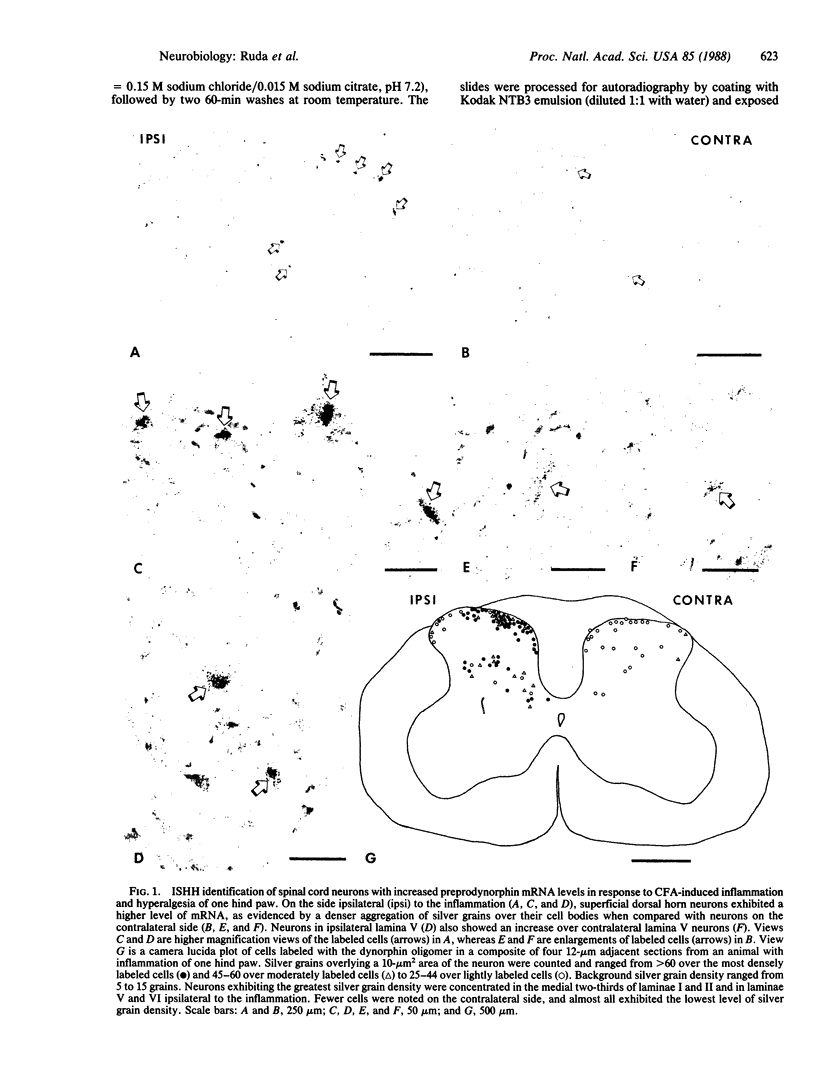
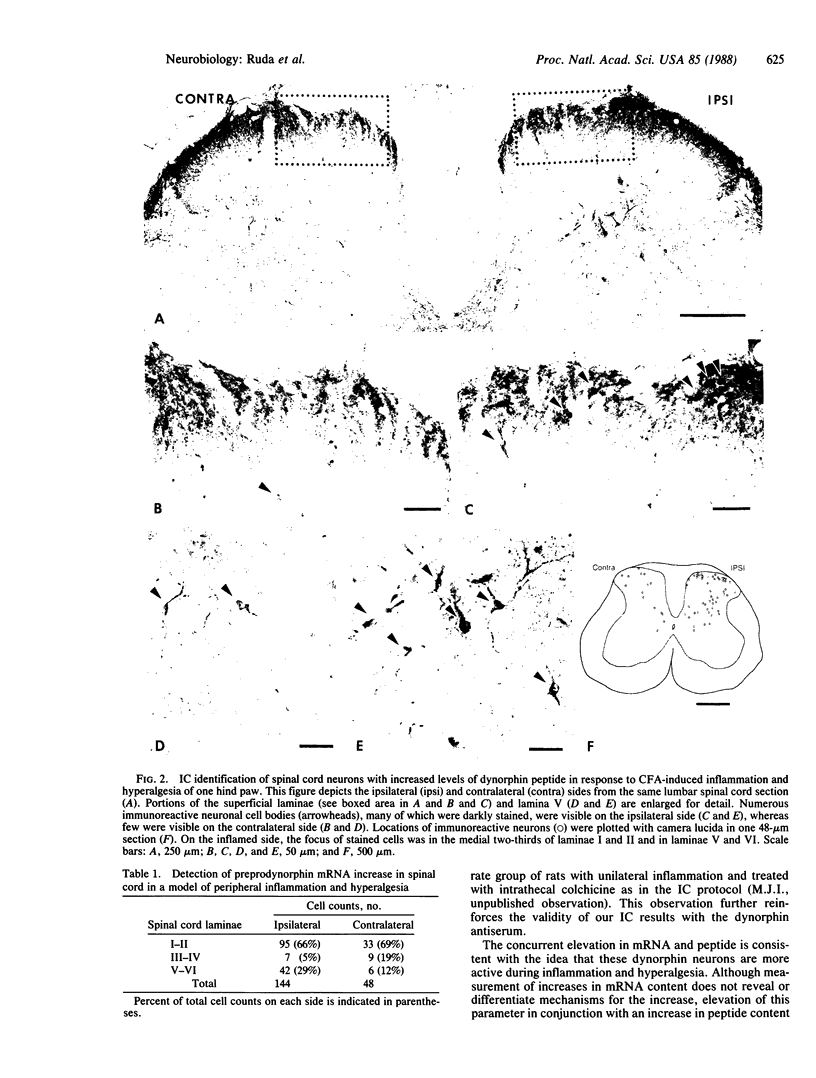
Dynorphin, an opioid peptide, is thought to play an important role in the modulation of nociceptive neural circuits at the level of the spinal cord. In a model of peripheral inflammation and hyperalgesia, an oligodeoxyribonucleotide probe complementary to a portion of preprodynorphin mRNA and antisera to dynorphin A-(1-8) were used to localize changes in dynorphin mRNA and peptide to individual spinal cord neurons. Intraplantar injection in rats of complete Freund's adjuvant resulted in edema and hyperalgesia to radiant heat stimulation of the injected hind paw that reached a peak at 4 days. At the same time, in situ hybridization histochemistry and immunocytochemistry identified an increase in transcription of preprodynorphin mRNA that was paralleled by an increase in dynorphin peptide. These changes were seen in spinal neurons in the medial two-thirds of laminae I and II and in laminae V and VI of lumbar segments receiving innervation from the inflamed paw. Since neurons demonstrating the increase in dynorphin biosynthesis are located in both the superficial and deep dorsal horn laminae, our data provide evidence for opioid modulation of nociceptive neural circuits in these two distinct spinal locations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Civelli O., Douglass J., Goldstein A., Herbert E. Sequence and expression of the rat prodynorphin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4291–4295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz L., Basbaum A. I. Multiple opioid peptides and the modulation of pain: immunohistochemical analysis of dynorphin and enkephalin in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis and spinal cord of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Oct 22;240(4):331–348. doi: 10.1002/cne.902400402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson A. H., Knox R. J. Antagonism of mu-opioid receptor-mediated inhibitions of nociceptive neurones by U50488H and dynorphin A1-13 in the rat dorsal horn. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Mar 31;75(2):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90302-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Tachibana S., Lowney L. I., Hunkapiller M., Hood L. Dynorphin-(1-13), an extraordinarily potent opioid peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6666–6670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman B. H., Goldstein A. Antinociception and paralysis induced by intrathecal dynorphin A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höllt V., Haarmann I., Millan M. J., Herz A. Prodynorphin gene expression is enhanced in the spinal cord of chronic arthritic rats. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 2;73(1):90–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iadarola M. J., Douglass J., Civelli O., Naranjo J. R. Increased spinal cord dynorphin mRNA during peripheral inflammation. NIDA Res Monogr. 1986;75:406–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iadarola M. J., Shin C., McNamara J. O., Yang H. Y. Changes in dynorphin, enkephalin and cholecystokinin content of hippocampus and substantia nigra after amygdala kindling. Brain Res. 1986 Feb 12;365(1):185–191. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90738-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J., Członkowski A., Pilcher C. W., Almeida O. F., Millan M. H., Colpaert F. C., Herz A. A model of chronic pain in the rat: functional correlates of alterations in the activity of opioid systems. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):77–87. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00077.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J., Millan M. H., Pilcher C. W., Członkowski A., Herz A., Colpaert F. C. Spinal cord dynorphin may modulate nociception via a kappa-opioid receptor in chronic arthritic rats. Brain Res. 1985 Aug 5;340(1):156–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90786-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. E., Seybold V. S. Comparison of met-enkephalin-, dynorphin A-, and neurotensin-immunoreactive neurons in the cat and rat spinal cords: I. Lumbar cord. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jan 8;255(2):293–304. doi: 10.1002/cne.902550212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piercey M. F., Varner K., Schroeder L. A. Analgesic activity of intraspinally administered dynorphin and ethylketocyclazocine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 May 21;80(2-3):283–284. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przewłocki R., Shearman G. T., Herz A. Mixed opioid/nonopioid effects of dynorphin and dynorphin related peptides after their intrathecal injection in rats. Neuropeptides. 1983 Jan;3(3):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(83)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren M. F., Lu C. H., Han J. S. Dynorphin-A-(1-13) antagonizes morphine analgesia in the brain and potentiates morphine analgesia in the spinal cord. Peptides. 1985 Nov-Dec;6(6):1015–1020. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90423-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruda M. A., Coffield J., Steinbusch H. W. Immunocytochemical analysis of serotonergic axons in laminae I and II of the lumbar spinal cord of the cat. J Neurosci. 1982 Nov;2(11):1660–1671. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-11-01660.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasek C. A., Seybold V. S., Elde R. P. The immunohistochemical localization of nine peptides in the sacral parasympathetic nucleus and the dorsal gray commissure in rat spinal cord. Neuroscience. 1984 Jul;12(3):855–873. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmauss C., Yaksh T. L. In vivo studies on spinal opiate receptor systems mediating antinociception. II. Pharmacological profiles suggesting a differential association of mu, delta and kappa receptors with visceral chemical and cutaneous thermal stimuli in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. P., Costa E. Hybridization approaches to the study of neuropeptides. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:277–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert D. G., Watson S. J., Houghten R. A., Saper C. B. Opioid peptide immunoreactivity in spinal and trigeminal dorsal horn neurons projecting to the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1220–1226. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01220.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Studies on the direct spinal action of narcotics in the production of analgesia in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):411–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9827–9831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]