Abstract
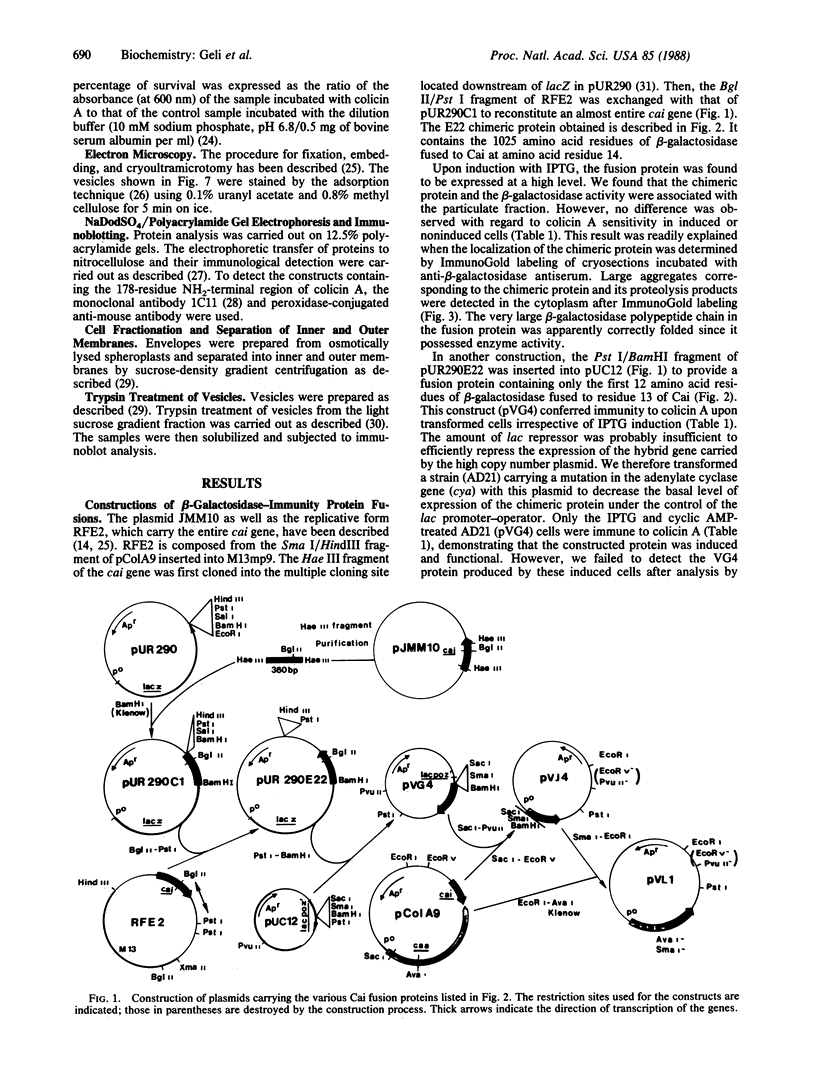
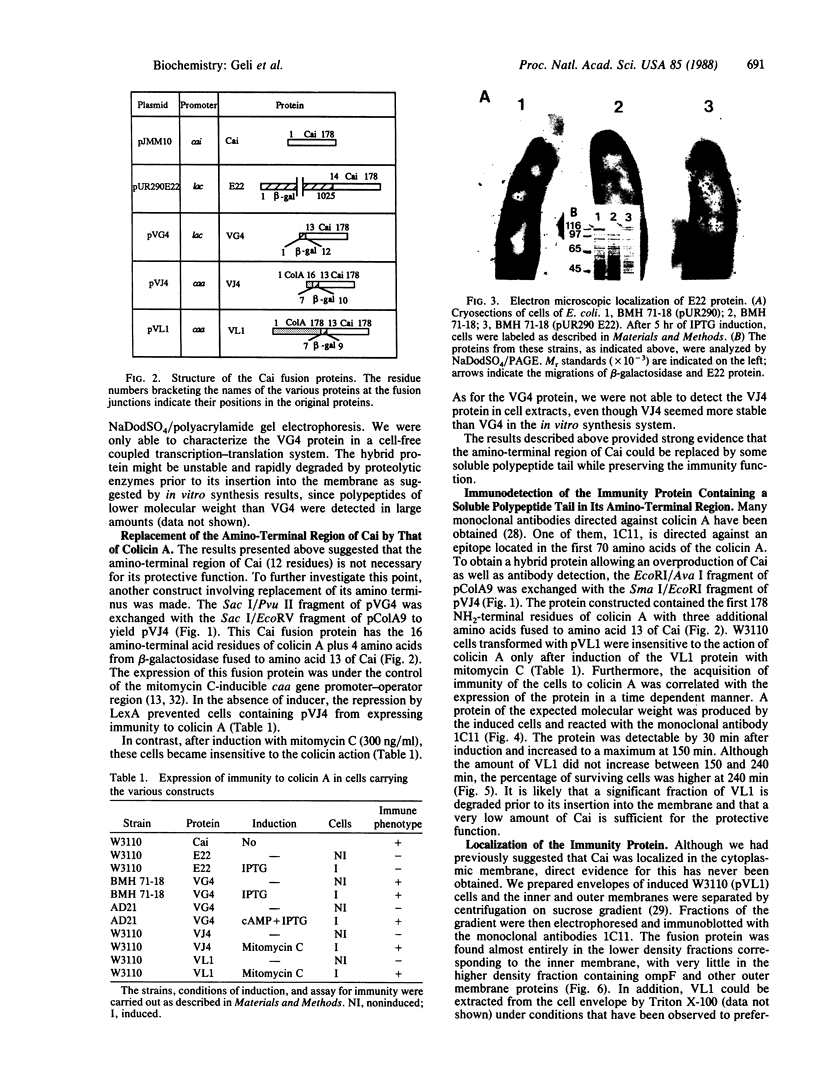
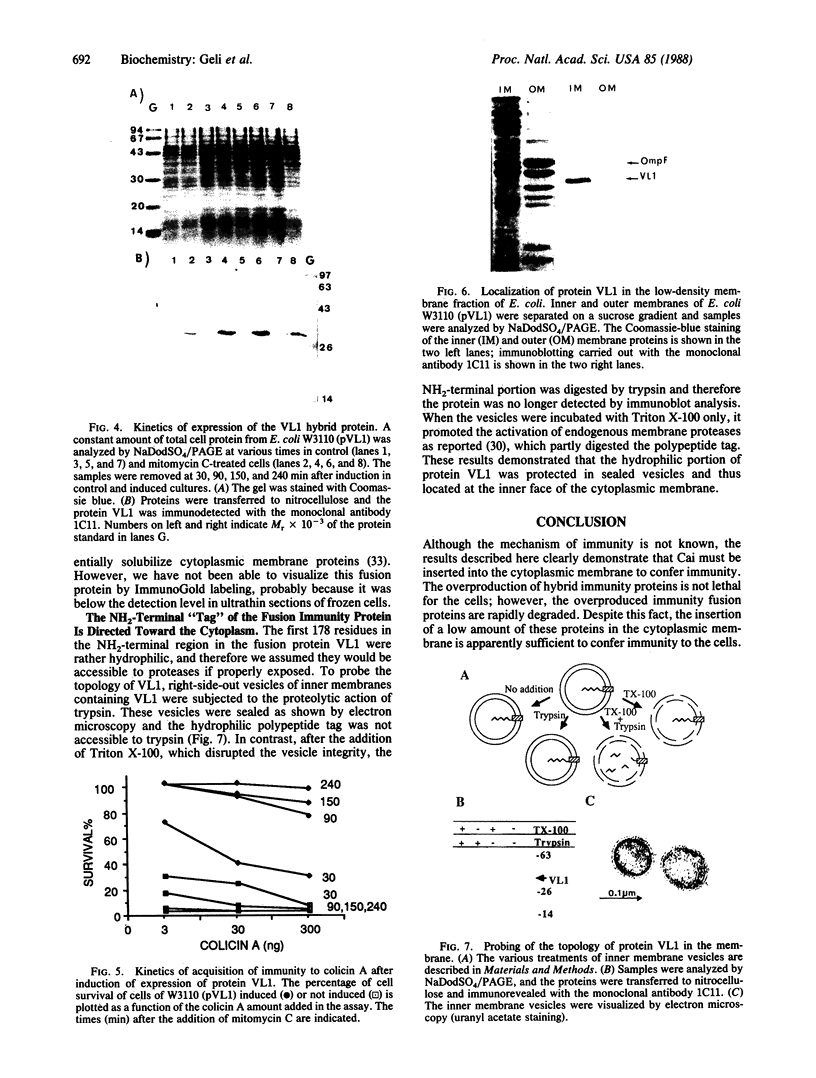
The immunity protein to colicin A (Cai), which is constitutively expressed at a very low level in Escherichia coli strains, has been studied in recombinant plasmid constructs allowing expression of various immunity fusion proteins under the control of inducible promoters. The 13-amino acid NH2-terminal region of Cai was substituted by polypeptides from beta-galactosidase or from colicin A. Upon induction of the chimeric proteins, the rate of expression of the immunity protein could be correlated to the level of resistance to colicin A. The immunity protein has been "tagged" with an epitope from the colicin A protein for which a monoclonal antibody is available. Using this technique, we have directly demonstrated that the immunity protein is located in the cytoplasmic membrane. The results indicate that the NH2-terminal region of Cai is directed toward the cytoplasm and is probably not required for Cai insertion into the membrane or for its function.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Ito K. The SecY membrane component of the bacterial protein export machinery: analysis by new electrophoretic methods for integral membrane proteins. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3351–3356. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baty D., Knibiehler M., Verheij H., Pattus F., Shire D., Bernadac A., Lazdunski C. Site-directed mutagenesis of the COOH-terminal region of colicin A: effect on secretion and voltage-dependent channel activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1152–1156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop L. J., Bjes E. S., Davidson V. L., Cramer W. A. Localization of the immunity protein-reactive domain in unmodified and chemically modified COOH-terminal peptides of colicin E1. J Bacteriol. 1985 Oct;164(1):237–244. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.1.237-244.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Crozel V., Gorvel J. P., Pattus F., Baty D., Lazdunski C. A molecular, genetic and immunological approach to the functioning of colicin A, a pore-forming protein. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Lazdunski C. J. Purification and molecular properties of a new colicin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland M. V., Slatin S., Finkelstein A., Levinthal C. Structure-function relationships for a voltage-dependent ion channel: properties of COOH-terminal fragments of colicin E1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3706–3710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collarini M., Amblard G., Lazdunski C., Pattus F. Gating processes of channels induced by colicin A, its C-terminal fragment and colicin E1 in planar lipid bilayers. Eur Biophys J. 1987;14(3):147–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00253839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramer W. A., Dankert J. R., Uratani Y. The membrane channel-forming bacteriocidal protein, colicin El. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):173–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson V. L., Brunden K. R., Cramer W. A., Cohen F. S. Studies on the mechanism of action of channel-forming colicins using artificial membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;79(2):105–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01872115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Steitz T. A. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geli V., Baty D., Crozel V., Morlon J., Lloubes R., Pattus F., Lazdunski C. A molecular genetic approach to the functioning of the immunity protein to colicin A. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Mar;202(3):455–460. doi: 10.1007/BF00333276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman K., Suit J. L., Kayalar C. Identification of the plasmid-encoded immunity protein for colicin E1 in the inner membrane of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 14;190(2):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konisky J., Cowell B. S. Interaction of colicin Ia with bacterial cells. Direct measurement of Ia-receptor interaction. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6524–6529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn R., Konisky J., Nomura M. Interaction of colicins with bacterial cells. IV. Immunity breakdown studied with colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):811–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.811-821.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloubes R. P., Chartier M. J., Journet A. M., Varenne S. G., Lazdunski C. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the immunity protein to colicin A. Analysis of codon usage of immunity proteins as compared to colicins. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloubes R., Baty D., Lazdunski C. The promoters of the genes for colicin production, release and immunity in the ColA plasmid: effects of convergent transcription and Lex A protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2621–2636. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankovich J. A., Hsu C. H., Konisky J. DNA and amino acid sequence analysis of structural and immunity genes of colicins Ia and Ib. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):228–236. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.228-236.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez M. C., Lazdunski C., Pattus F. Isolation, molecular and functional properties of the C-terminal domain of colicin A. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1501–1507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morlon J., Lloubès R., Varenne S., Chartier M., Lazdunski C. Complete nucleotide sequence of the structural gene for colicin A, a gene translated at non-uniform rate. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 25;170(2):271–285. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. Escherichia coli K12 strains for use in the identification and characterization of colicins. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Feb;131(2):369–376. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-2-369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Josefsson L. G., Hardy S. J. Processing in vitro of precursor periplasmic proteins from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Dec;92(2):411–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12761.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Koenen M., Sippel A. E., Müller-Hill B. Exon cloning: immunoenzymatic identification of exons of the chicken lysozyme gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6852–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein S. J., Kagan B. L., Finkelstein A. Colicin K acts by forming voltage-dependent channels in phospholipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):159–163. doi: 10.1038/276159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silhavy T. J., Benson S. A., Emr S. D. Mechanisms of protein localization. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):313–344. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.313-344.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suit J. L., Fan M. L., Sabik J. F., Labarre R., Luria S. E. Alternative forms of lethality in mitomycin C-induced bacteria carrying ColE1 plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):579–583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda H., Konisky J. Effect of colicins Ia and E1 on ion permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6167–6171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. A study of positive staining of ultrathin frozen sections. J Ultrastruct Res. 1978 Jun;63(3):287–307. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(78)80053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver C. A., Redborg A. H., Konisky J. Plasmid-determined immunity of Escherichia coli K-12 to colicin Ia Is mediated by a plasmid-encoded membrane protein. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):817–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.817-828.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]