Abstract
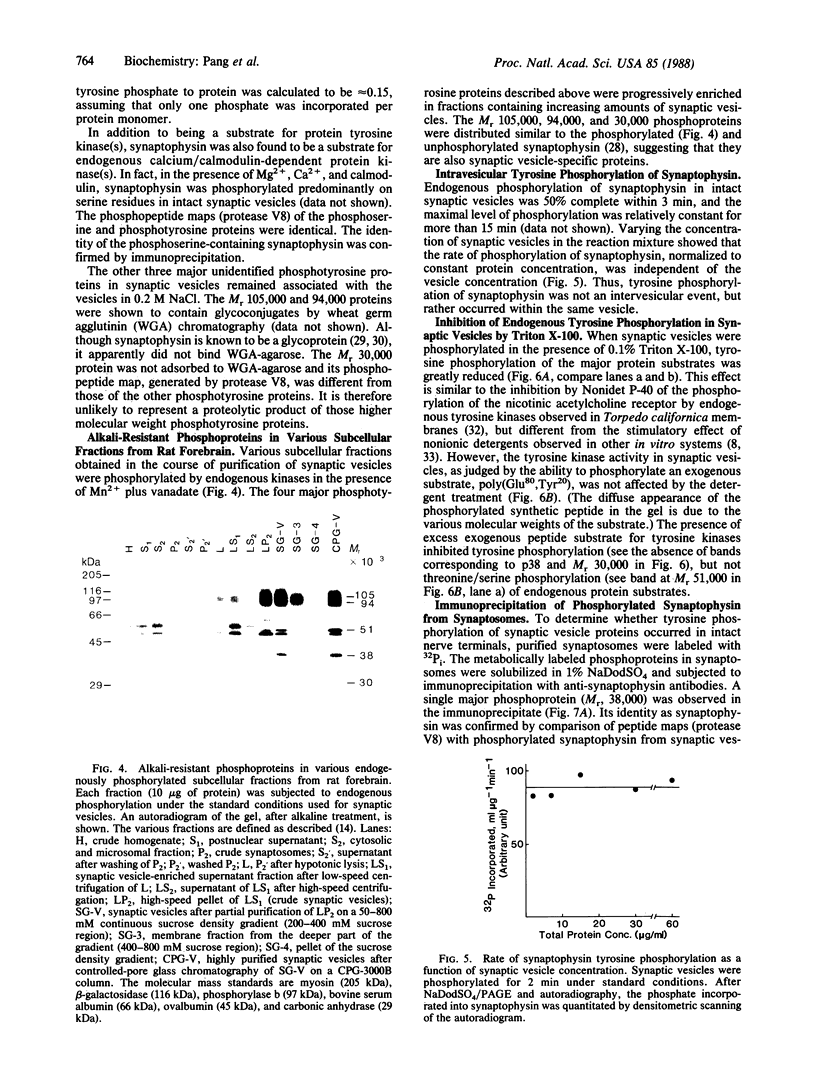
Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in purified synaptic vesicles from rat forebrain has been studied in the presence of Mn2+ and orthovanadate. High levels of endogenous protein tyrosine phosphorylation were observed. Four major phosphoproteins, with apparent molecular masses of 105, 94, 38, and 30 kDa, were shown to contain phosphotyrosine. The 38-kDa phosphoprotein was identified as synaptophysin (p38), a well-characterized integral membrane protein of synaptic vesicles. The three other phosphotyrosine-containing proteins distributed in the same manner as synaptophysin in all subcellular fractions. Like synaptophysin, the two high molecular weight phosphotyrosine proteins (105 and 94 kDa) were found to be glycoproteins by lectin chromatography. Tyrosine phosphorylation of synaptophysin was an intravesicular reaction and reached 50% of maximal level within 3 min. Triton X-100, a nonionic detergent, inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of endogenous protein substrates but not the phosphorylation of an exogenous substrate, poly(Glu80,-Tyr20). Tyrosine phosphorylation of synaptophysin was also demonstrated in synaptosomes, indicating that tyrosine phosphorylation of synaptic vesicle proteins occurs in intact nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bollag G. E., Roth R. A., Beaudoin J., Mochly-Rosen D., Koshland D. E., Jr Protein kinase C directly phosphorylates the insulin receptor in vitro and reduces its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5822–5824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Rapid enhancement of protein phosphorylation in A-431 cell membrane preparations by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4884–4891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Pike L. J., Hellström K. E., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of synthetic peptides by a tyrosine protein kinase from the particulate fraction of a lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton P. C., Brugge J. S. Neural tissues express high levels of the cellular src gene product pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1157–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Jarvie P. E., Heath J. W., Kidd G. J., Rostas J. A. A rapid method for isolation of synaptosomes on Percoll gradients. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 30;372(1):115–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earp H. S., Austin K. S., Buessow S. C., Dy R., Gillespie G. Y. Membranes from T and B lymphocytes have different patterns of tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2347–2351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D. W., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Maness P. F. pp60c-src in the developing cerebellum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelz S. E., Nestler E. J., Chehrazi B., Greengard P. Distribution of protein I in mammalian brain as determined by a detergent-based radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greengard P. Neuronal phosphoproteins. Mediators of signal transduction. Mol Neurobiol. 1987 Spring-Summer;1(1-2):81–119. doi: 10.1007/BF02935265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Miles K., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by an endogenous tyrosine-specific protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6968–6972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada M., Sueoka N. A two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis system for the analysis of mammalian cell surface proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 21;625(2):179–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., McGuinness T. L., Leonard C. S., Sugimori M., Greengard P. Intraterminal injection of synapsin I or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II alters neurotransmitter release at the squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3035–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliaccio A., Rotondi A., Auricchio F. Calmodulin-stimulated phosphorylation of 17 beta-estradiol receptor on tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5921–5925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Purification and characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7273–7281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang D. T., Lewis S. D., Sharma B. R., Shafer J. A. Relationship between the subunit structure of insulin receptor and its competence to bind insulin and undergo phosphorylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):629–638. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90313-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., Creutz C. E. p60c-src activity detected in the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):736–742. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. A mutation at the ATP-binding site of pp60v-src abolishes kinase activity, transformation, and tumorigenicity. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1772–1779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudol M., Hanafusa H. Cellular proteins homologous to the viral yes gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2839–2846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Cohen S., Garbers D. L. Inhibition of membrane phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase activity by vanadate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1104–1109. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90635-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Dasgupta J. D., Garbers D. L. Tyrosine protein kinase activity of rat spleen and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10341–10347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Brown T. A., Whipple J. H., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Dubler R. E., Cheng K., Larner J. A novel mechanism for the insulin-like effect of vanadate on glycogen synthase in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6650–6658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuy F. P., Henry J., Rosenfeld C., Kahn A. High tyrosine kinase activity in normal nonproliferating cells. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):435–438. doi: 10.1038/305435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Walaas S. I., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation in nerve terminals: comparison of calcium/calmodulin-dependent and calcium/diacylglycerol-dependent systems. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):281–288. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00281.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Haring H. U., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Kinetic properties and sites of autophosphorylation of the partially purified insulin receptor from hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]