Abstract
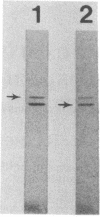
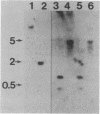
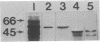
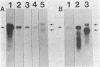
Ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase activase is a recently discovered enzyme that catalyzes the activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase ["rubisco"; ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase; 3-phospho-D-glycerate carboxy-lyase (dimerizing), EC 4.1.1.39] in vivo. Clones of rubisco activase cDNA were isolated immunologically from spinach (Spinacea oleracea L.) and Arabidopsis thaliana libraries. Sequence analysis of the spinach and Arabidopsis cDNAs identified consensus nucleotide binding sites, consistent with an ATP requirement for rubisco activase activity. A derived amino acid sequence common to chloroplast transit peptides was also identified. After synthesis of rubisco activase in vitro, the transit peptide was cleaved and the protein was transported into isolated chloroplasts. Analysis of spinach and Arabidopsis nuclear DNA by hybridization indicated a single rubisco activase gene in each species. Leaves of spinach and Arabidopsis wild type contained a single 1.9-kilobase rubisco activase mRNA. In an Arabidopsis mutant lacking rubisco activase protein, mRNA species of 1.7 and 2.1 kilobases were observed under conditions of high-stringency hybridization with a wild-type cDNA probe. This observation indicates that the lesion in the mutant arises from an error in mRNA processing.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan T. M., Parsonage D., Senior A. E. Structure of the nucleotide-binding domain in the beta-subunit of Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA in a wheat germ system. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:38–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hiles I. D., Salmond G. P., Gill D. R., Downie J. A., Evans I. J., Holland I. B., Gray L., Buckel S. D., Bell A. W. A family of related ATP-binding subunits coupled to many distinct biological processes in bacteria. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):448–450. doi: 10.1038/323448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan D. B., Chollet R. Inhibition of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase by substrate ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13752–13758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin-Neumann G. A., Tobin E. M. Transit peptides of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins share a common amino acid framework. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):9–13. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy M. J., Voss E. W., Jr A modified method to induce immune polyclonal ascites fluid in BALB/c mice using Sp2/0-Ag14 cells. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Mar 13;87(2):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90527-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lizardi P. M., Williamson R., Brown D. D. The size of fibroin messenger RNA and its polyadenylic acid content. Cell. 1975 Mar;4(3):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorimer G. H., Badger M. R., Andrews T. J. The activation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by carbon dioxide and magnesium ions. Equilibria, kinetics, a suggested mechanism, and physiological implications. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):529–536. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain D., Blobel G. Protein import into chloroplasts requires a chloroplast ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3288–3292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perchorowicz J. T., Raynes D. A., Jensen R. G. Light limitation of photosynthesis and activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in wheat seedlings. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2985–2989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis A. R., Salvucci M. E., Ogren W. L. Activation of Ribulosebisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase at Physiological CO(2) and Ribulosebisphosphate Concentrations by Rubisco Activase. Plant Physiol. 1986 Dec;82(4):967–971. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.4.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Portis A. R., Jr, Ogren W. L. Purification of ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase with high specific activity by fast protein liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 15;153(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvucci M. E., Werneke J. M., Ogren W. L., Portis A. R. Purification and species distribution of rubisco activase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jul;84(3):930–936. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Mishkind M. L. The transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:879–912. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. R., Portis A. R., Ogren W. L. A Mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana Which Lacks Activation of RuBP Carboxylase In Vivo. Plant Physiol. 1982 Aug;70(2):381–387. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streusand V. J., Portis A. R. Rubisco Activase Mediates ATP-Dependent Activation of Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):152–154. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]