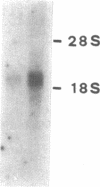
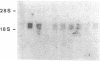
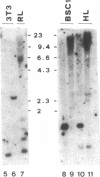
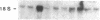Abstract
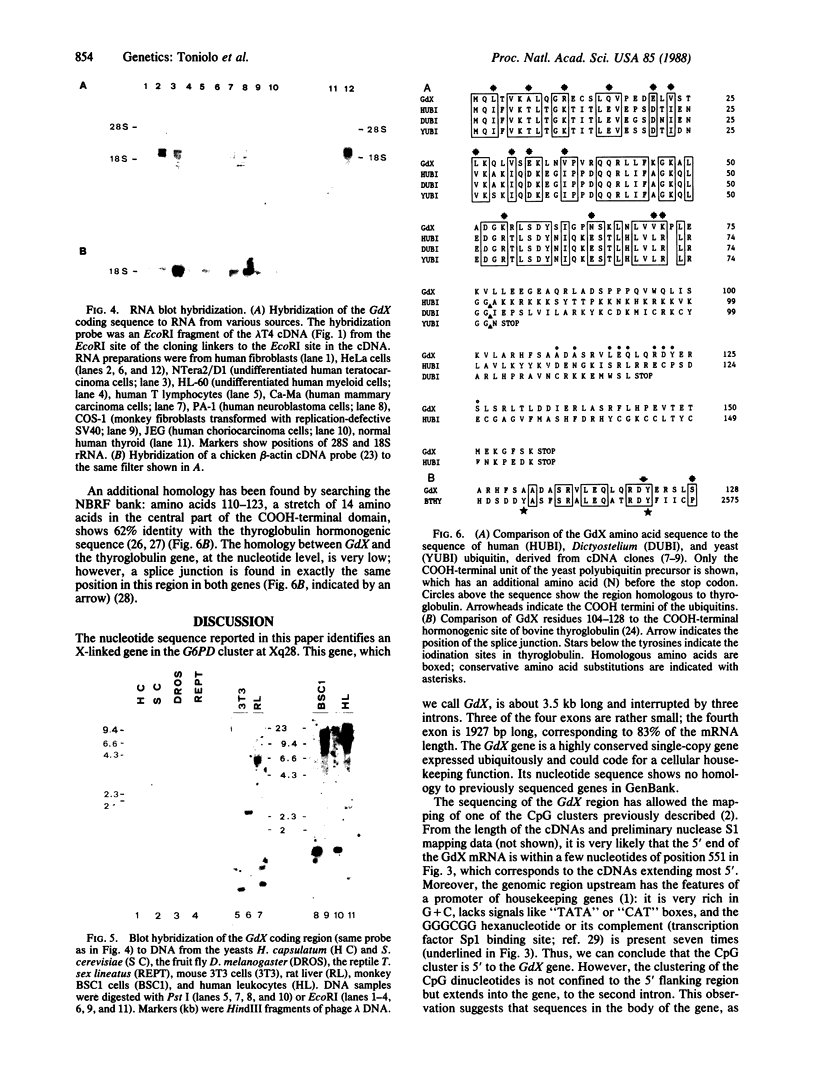
An X chromosome gene located 40 kilobases downstream from the G6PD gene, at Xq28, was isolated and sequenced. This gene, which we named GdX, spans about 3.5 kilobases of genomic DNA. GdX is a single-copy gene, is conserved in evolution, and has the features of a "housekeeping" gene. At its 5' end, a cluster of CpG dinucleotides is methylated on the inactive X chromosome and unmethylated on the active X chromosome. The GdX gene can code for a 157 amino acid protein, GdX. Residues 1-74 of GdX show 43% identity to ubiquitin, a highly conserved 76 amino acid protein. The COOH-terminal moiety of GdX is characterized in its central part (residues 110-128) by a sequence homologous to the COOH-terminal hormonogenic site of thyroglobulin. The structural organization of the GdX protein suggests the existence of a family of genes, in addition to the ubiquitin gene, that could play specific roles in key cellular processes, possibly through protein-protein recognition.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. W. Retinoic acid induces neuronal differentiation of a cloned human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. Ubiquitin is a heat shock protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):949–956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Lauro R., Obici S., Condliffe D., Ursini V. M., Musti A., Moscatelli C., Avvedimento V. E. The sequence of 967 amino acids at the carboxyl-end of rat thyroglobulin. Location and surroundings of two thyroxine-forming sites. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):7–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin-Rastl E., Shrutkowski A., Dworkin M. B. Multiple ubiquitin mRNAs during Xenopus laevis development contain tandem repeats of the 76 amino acid coding sequence. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Hidaka S., Sakaki Y. Sequence analysis of a KpnI family member near the 3' end of human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7813–7827. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A. Ubiquitin: roles in protein modification and breakdown. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):11–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. O., Bridson W. E. Isolation of hormone-producing clonal lines of human choriocarcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 May;32(5):683–687. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinger L., Varshavsky A. Selective arrangement of ubiquitinated and D1 protein-containing nucleosomes within the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Simmons J. G., Hoyt E., D'Ercole A. J., Martin F., Van Wyk J. J. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a cDNA encoding human ubiquitin reveals that ubiquitin is synthesized as a precursor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7609–7613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriq C., Rolland M., Lissitzky S. Structure-function relationship in thyroglobulin: amino acid sequence of two different thyroxine-containing peptides from porcine thyroglobulin. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):397–401. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini G., Toniolo D., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., Dono R., Viglietto G., Paonessa G., D'Urso M., Persico M. G. Structural analysis of the X-linked gene encoding human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1849–1855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken L., Simons M. J., Swillens S., Massaer M., Vassart G. Primary structure of bovine thyroglobulin deduced from the sequence of its 8,431-base complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):647–651. doi: 10.1038/316647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musti A. M., Avvedimento E. V., Polistina C., Ursini V. M., Obici S., Nitsch L., Cocozza S., Di Lauro R. The complete structure of the rat thyroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin genes: a family of natural gene fusions. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1429–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin gene: head-to-tail repeats encoding a polyubiquitin precursor protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):663–666. doi: 10.1038/312663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parag H. A., Raboy B., Kulka R. G. Effect of heat shock on protein degradation in mammalian cells: involvement of the ubiquitin system. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):55–61. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Toniolo D., Nobile C., D'Urso M., Luzzatto L. cDNA sequences of human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase cloned in pBR322. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):778–780. doi: 10.1038/294778a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persico M. G., Viglietto G., Martini G., Toniolo D., Paonessa G., Moscatelli C., Dono R., Vulliamy T., Luzzatto L., D'Urso M. Isolation of human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) cDNA clones: primary structure of the protein and unusual 5' non-coding region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 25;14(6):2511–2522. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawitch A. B., Chernoff S. B., Litwer M. R., Rouse J. B., Hamilton J. W. Thyroglobulin structure-function. The amino acid sequence surrounding thyroxine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2079–2082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M., Bond M. W., Gallatin W. M., St John T., Smith H. T., Fried V. A., Weissman I. L. Cell surface molecule associated with lymphocyte homing is a ubiquitinated branched-chain glycoprotein. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):823–829. doi: 10.1126/science.3003913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Expression of a cytoplasmic LINE-1 transcript is regulated in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6050–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., D'Urso M., Martini G., Persico M., Tufano V., Battistuzzi G., Luzzatto L. Specific methylation pattern at the 3' end of the human housekeeping gene for glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):1987–1995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02080.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Persico M. G., Battistuzzi G., Luzzatto L. Partial purification and characterization of the messenger RNA for human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Apr;2(2):89–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijay-Kumar S., Bugg C. E., Wilkinson K. D., Cook W. J. Three-dimensional structure of ubiquitin at 2.8 A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3582–3585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiborg O., Pedersen M. S., Wind A., Berglund L. E., Marcker K. A., Vuust J. The human ubiquitin multigene family: some genes contain multiple directly repeated ubiquitin coding sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):755–759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]