Abstract
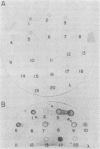
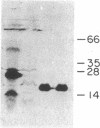
A major allergen of white-face hornet (Dolichovespula maculata) venom is antigen 5 (also designated Dol m V). We have determined the primary structures of two forms of this protein by cDNA and protein sequencings. These two forms with 204 and 205 amino acid residues differ in 23% of their sequences but they are antigenically similar. Both forms have sequence similarity with a pathogenesis-related protein of tobacco leaf. In a 130-residue overlap of these proteins, 35-39 residues were identical. Hornet antigen 5 cDNAs were isolated from an expression library in lambda gt11 phage using antibody probes. Several of the cDNAs were not full length, but the fusion fragments expressed were immunoreactive. These results suggest that antigenic determinants of the sequential type are distributed throughout the entire molecule of antigen 5. After subcloning, antigen 5 was also expressed in pKK233-2 plasmid.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Kawai N., Niwa A. Purification and properties of a presynaptically acting neurotoxin, mandaratoxin, from hornet (Vespa mandarinia). Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1693–1697. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen B. J., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Van Loon L. C., Bol J. F. Molecular characterization of messenger RNAs for 'pathogenesis related' proteins la, lb and lc, induced by TMV infection of tobacco. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):37–40. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04174.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. R. Allergens in Hymenoptera venom XV: The immunologic basis of vespid venom cross-reactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 May;75(5):611–613. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F. Sequencing of large double-stranded DNA using the dideoxy sequencing technique. Biosci Rep. 1982 Nov;2(11):907–912. doi: 10.1007/BF01114897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Joslyn A., Kochoumian L. Antigenic cross-reactivity of venom proteins from hornets, wasps, and yellow jackets. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 May;75(5):621–628. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Kochoumian L., Joslyn A. Wasp venom proteins: phospholipase A1 and B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Apr;230(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Kochoumian L., Lam T. Immunochemical observations of antigen 5, a major venom allergen of hornets, yellowjackets and wasps. Mol Immunol. 1987 Aug;24(8):857–864. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King T. P., Sobotka A. K., Alagon A., Kochoumian L., Lichtenstein L. M. Protein allergens of white-faced hornet, yellow hornet, and yellow jacket venoms. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5165–5174. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Valentine M. D., Sobotka A. K. Insect allergy: the state of the art. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1979 Jul;64(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(79)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D. G., Goodfriend L., King T. P., Lowenstein H., Platts-Mills T. A. Allergen nomenclature. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(5):767–774. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pure E., Luster A. D., Unkeless J. C. Cell surface expression of murine, rat, and human Fc receptors by Xenopus oocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):606–611. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman R. E. Stinging insect allergy: progress and problems. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 May;75(5):553–555. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchanek G., Kreil G., Hermodson M. A. Amino acid sequence of honeybee prepromelittin synthesized in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):701–704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. F., Alianell G. A., Bencen G. H., Gray H. B., Jr Isolation and comparison of two molecular species of the BAL 31 nuclease from Alteromonas espejiana with distinct kinetic properties. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13506–13512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]