Abstract
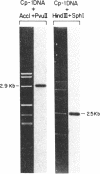
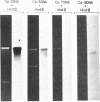
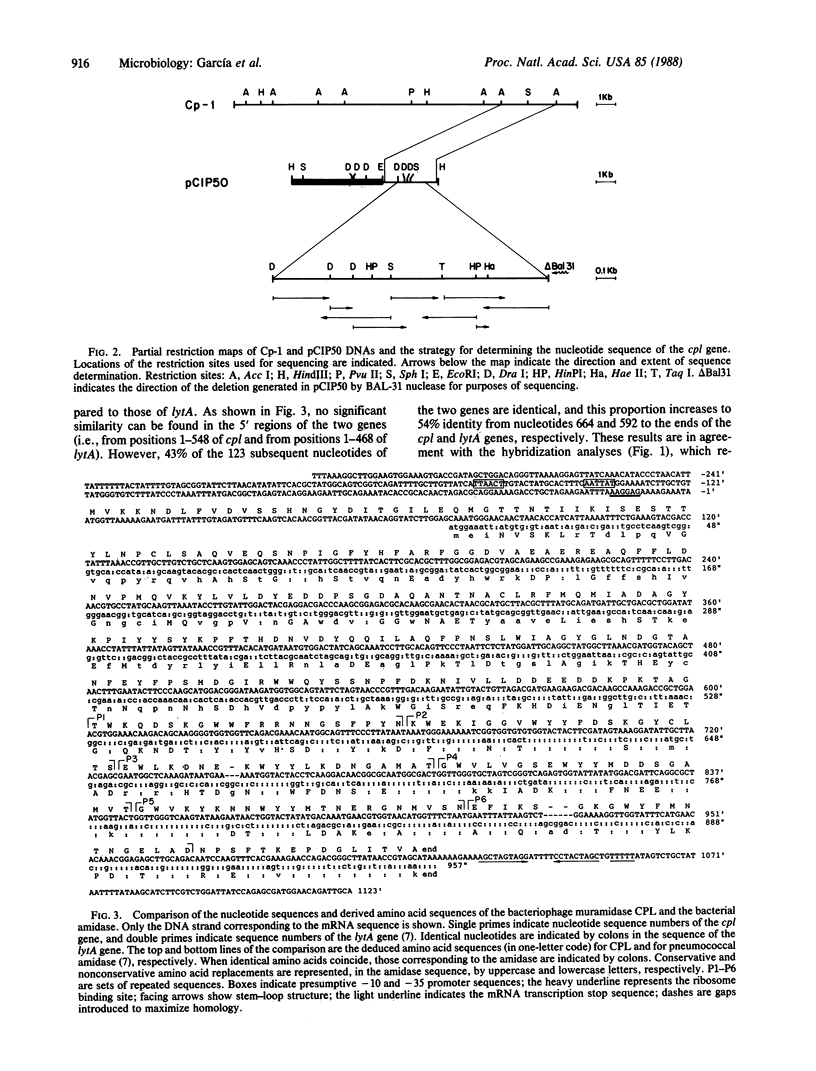
A 2.9-kilobase Acc I fragment of the DNA of the pneumococcal bacteriophage Cp-1, containing the cpl gene, hybridizes with the lytA gene encoding the pneumococcal amidase. The nucleotide sequence of the cpl gene of Cp-1, encoding a muramidase (CPL), has been determined. The 3' regions of the cpl and lytA coding sequences show considerable nucleotide sequence homology and the carboxyl-terminal domains of the deduced amino acid sequences of these lysins are quite similar: 73 of the carboxyl-terminal 142 amino acid residues are identical, and of the 69 substitutions, 55 are conservative. Comparisons between CPL, the pneumococcal amidase, and the muramidase of the fungus Chalaropsis sp. (an enzyme that also degrades the pneumococcal cell wall) strongly suggest that the carboxyl-terminal domains of CPL and of the amidase might be responsible for the specific recognition of choline-containing cell walls, as well as for the noncompetitive inhibition of the catalytic activity of these enzymes by the pneumococcal lipoteichoic acid or by high concentrations of choline. In addition, the active center of these enzymes should be located in their amino-terminal domains. Our results suggest an evolutionary relationship between phage and host lysins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D. A theory of modular evolution for bacteriophages. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:484–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27987.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briese T., Hakenbeck R. Interaction of the pneumococcal amidase with lipoteichoic acid and choline. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jan 15;146(2):417–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANFIELD R. E. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF EGG WHITE LYSOZYME. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2698–2707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouche P. B., Hash J. H. The N,O-diacetylmuramidase of Chalaropsis species. Identificaiton of aspartyl and glutamyl residues in the active site. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6787–6793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia P., Garcia E., Ronda C., Lopez R., Tomasz A. A phage-associated murein hydrolase in Streptococcus pneumoniae infected with bacteriophage Dp-1. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):489–497. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García J. L., Sánchez-Puelles J. M., García P., López R., Ronda C., García E. Molecular characterization of an autolysin-defective mutant of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):614–619. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García P., García J. L., García E., López R. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the pneumococcal autolysin gene from its own promoter in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1986;43(3):265–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudicelli S., Tomasz A. Attachment of pneumococcal autolysin to wall teichoic acids, an essential step in enzymatic wall degradation. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1188–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1188-1190.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V., Gooder H. Specificity of the autolysin of Streptococcus (Diplococcus) pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.796-804.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Lipoteichoic acid: a specific inhibitor of autolysin activity in Pneumococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1690–1694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp H. H., Wirtz W. A., Baer P. R., Slotboom A. J., Rosenthal A. F., Paltauf F., van Deenem L. L. Specificity of the phosphatidylcholine exchange protein from bovine liver. Biochemistry. 1977 Apr 5;16(7):1310–1316. doi: 10.1021/bi00626a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López R., Sánchez-Puelles J. M., García E., García J. L., Ronda C., García P. Isolation, characterization and physiological properties of an autolytic-deficient mutant of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Aug;204(2):237–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00425504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronda-Lain C., Lopez R., Tapia A., Tomasz A. Role of the pneumococcal autolysin (murein hydrolase) in the release of progeny bacteriophage and in the bacteriophage-induced lysis of the host cells. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.366-374.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronda C., García J. L., García E., Sánchez-Puelles J. M., López R. Biological role of the pneumococcal amidase. Cloning of the lytA gene in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 4;164(3):621–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Puelles J. M., Ronda C., Garcia J. L., Garcia P., Lopez R., Garcia E. Searching for autolysin functions. Characterization of a pneumococcal mutant deleted in the lytA gene. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jul 15;158(2):289–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09749.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susskind M. M., Botstein D. Molecular genetics of bacteriophage P22. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):385–413. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.385-413.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Biological consequences of the replacement of choline by ethanolamine in the cell wall of Pneumococcus: chanin formation, loss of transformability, and loss of autolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):86–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Choline in the cell wall of a bacterium: novel type of polymer-linked choline in Pneumococcus. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Geus P., Verheij H. M., Riegman N. H., Hoekstra W. P., de Haas G. H. The pro- and mature forms of the E. coli K-12 outer membrane phospholipase A are identical. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1799–1802. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]