Abstract
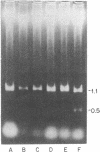
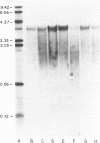
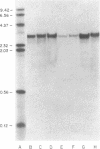
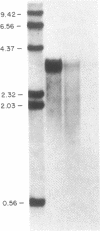
To gain insight into factors associated with the excessive accumulation of beta-amyloid in the Alzheimer disease (AD) brain, the present studies were initiated to distinguish between a unique primary structure of the AD-specific amyloid precursor mRNA vis a vis other determinants that may affect amyloid levels. Previous molecular cloning experiments focused on amyloid derived from sources other than AD cases. In the present work, we cloned and characterized amyloid cDNA derived directly from AD brain mRNA. Poly(A)+ RNA from AD cortices was used for the preparation of lambda gt11 recombinant cDNA libraries. An insert of 1564 nucleotides was isolated that included the beta-amyloid domain and corresponded to 75% of the coding region and approximately equal to 70% of the 3'-noncoding region of the fetal precursor amyloid cDNA reported by others. On RNA blots, the AD amyloid mRNA consisted of a doublet of 3.2 and 3.4 kilobases. In control and AD cases, the amyloid mRNA levels were nonuniform and were independent of glial-specific mRNA levels. Based on the sequence analysis data, we conclude that a segment of the amyloid gene is expressed in the AD cortex as a high molecular weight precursor mRNA with major coding and 3'-noncoding regions that are identical to the fetal brain gene product.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blessed G., Tomlinson B. E., Roth M. The association between quantitative measures of dementia and of senile change in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Br J Psychiatry. 1968 Jul;114(512):797–811. doi: 10.1192/bjp.114.512.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breimer L. H., Denny P. Alzheimer amyloid aspects. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):749–750. doi: 10.1038/326749c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Goldgaber D., Lamour Y., Nicole A., Huret J. L., de Grouchy J., Brown P., Gajdusek D. C., Sinet P. M. Beta amyloid gene duplication in Alzheimer's disease and karyotypically normal Down syndrome. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1390–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2950593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis: the beta-fibrilloses (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 12;302(24):1333–1343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006123022403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Neary D., Yates P. O., Lincoln J., Snowden J. S., Stanworth P. Alterations in protein synthetic capability of nerve cells in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1981 Feb;44(2):97–102. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.44.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Neary D., Yates P. O., Lincoln J., Snowden J. S., Stanworth P. Neurofibrillary pathology and protein synthetic capability in nerve cells in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 Jan-Feb;7(1):37–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Sinclair K. G. The quantitative assessment of lipofuscin pigment, cytoplasmic RNA and nucleolar volume in senile dementia. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1978 Mar-Apr;4(2):129–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1978.tb00553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotta C. A., Brown B. A., Strocchi P., Bird E. D., Gilbert J. M. In vitro synthesis of human brain proteins including tubulin and actin by purified postmortem polysomes. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):966–975. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotta C. A., Majocha R. E., Coughlin J. F., Manz H. J., Davies P., Ventosa-Michelman M., Chou W. G., Zain S. B., Sajdel-Sulkowska E. M. Transcriptional and translational regulatory mechanisms during normal aging of the mammalian brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Brain Res. 1986;70:303–320. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Bobin S. A., Masters C. L., Iqbal K. Ultrastructural morphology of amyloid fibrils from neuritic and amyloid plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;60(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00685355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. R., Pardue S., Maschoff K., Griffin W. S., White C. L., 3rd, Gilbert J., Roses A. Brain messenger RNA levels and ribonuclease activity in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):133–134. doi: 10.1042/bst0150133a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary D., Snowden J. S., Mann D. M., Bowen D. M., Sims N. R., Northen B., Yates P. O., Davison A. N. Alzheimer's disease: a correlative study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986 Mar;49(3):229–237. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.49.3.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Wisniewski H. M., Jenkins E. C., Devine-Gage E. A., Houck G. E., Yao X. L., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Silverman W. P., Brown W. T. Chromosome 21q21 sublocalisation of gene encoding beta-amyloid peptide in cerebral vessels and neuritic (senile) plaques of people with Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):384–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91754-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G. Correlation between scores for dementia and counts of 'senile plaques' in cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Nature. 1966 Jan 1;209(5018):109–110. doi: 10.1038/209109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel-Sulkowska E. M., Marotta C. A. Alzheimer's disease brain: alterations in RNA levels and in a ribonuclease-inhibitor complex. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):947–949. doi: 10.1126/science.6206567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel-Sulkowska E., Coughlin J. F., Marotta C. A. In vitro synthesis of polypeptides of moderately large size by poly(A)-containing messenger RNA from postmortem human brain and mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1983 Mar;40(3):670–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08032.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A new computer method for the storage and manipulation of DNA gel reading data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 25;8(16):3673–3694. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.16.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. R., Carter G. I., Crow T. J., Johnson J. A., Fairbairn A. F., Perry E. K., Perry R. H. Recovery and measurement of RNA in Alzheimer's disease by molecular hybridisation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987 Mar;50(3):356–356. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.50.3.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura E., Hartmann H. A. Quantitative studies of neuronal RNA on the subiculum of demented old individuals. Brain Res Bull. 1979 May-Jun;4(3):301–305. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(79)80005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]