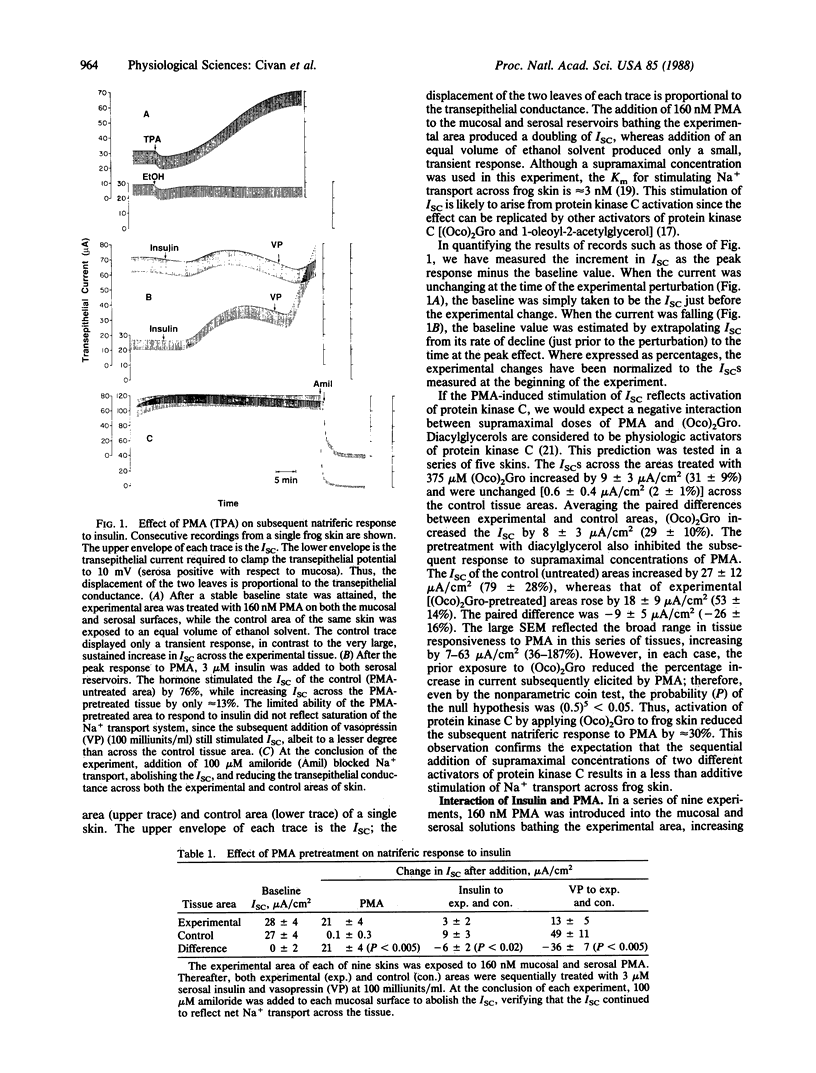
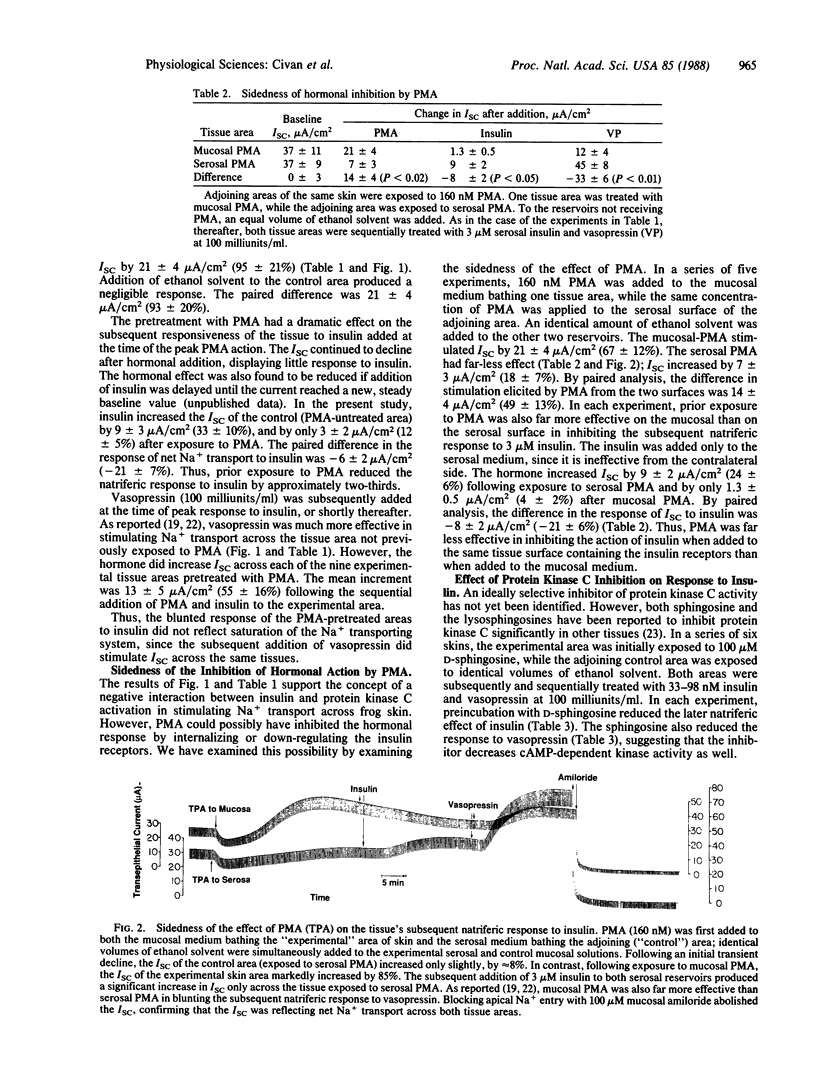
Abstract
Insulin stimulates Na+ transport across frog skin, toad urinary bladder, and the distal renal nephron. This stimulation reflects an increase in apical membrane Na+ permeability and a stimulation of the basolateral membrane Na,K-exchange pump. Considerable indirect evidence has suggested that the apical natriferic effect of insulin is mediated by activation of protein kinase C. However, no direct information has been available documenting that insulin and protein kinase C indeed share a common pathway in stimulating Na+ transport across frog skin. In the present work, we have studied the interaction of insulin and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), a documented activator of protein kinase C. Preincubation of skins with 1,2-dioctanoylglycerol, another activator of protein kinase C, increases baseline Na+ transport and reduces the subsequent natriferic response to PMA. Preincubation with PMA markedly reduces the subsequent natriferic action of insulin. This effect does not appear to primarily reflect PMA-induced internalization of insulin receptors. The insulin receptors are localized on the basolateral surface of frog skin, but the application of PMA to this surface is much less effective than mucosal treatment in reducing the response to insulin. Preincubation with D-sphingosine, an inhibitor of protein kinase C, also reduces the natriferic action of insulin. The current results provide documentation that insulin and protein kinase C share a common pathway in stimulating Na+ transport across frog skin. The data are consistent with the concept that the natriferic effect of insulin on frog skin is, at least in part, mediated by activation of protein kinase C.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt S. J., Niedel J. E., Bell R. M., Young W. S., 3rd Distinct patterns of expression of different protein kinase C mRNAs in rat tissues. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):57–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90755-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Lin L. E., Peterson-Yantorno K., Taylor J., Deutsch C. Intracellular pH of perfused single frog skin: combined 19F- and 31P-NMR analysis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):C506–C510. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.247.5.C506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Peterson-Yantorno K., O'Brien T. G. Diacylglycerols stimulate short-circuit current across frog skin by increasing apical Na+ permeability. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(3):193–204. doi: 10.1007/BF01869222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Rubenstein D., Mauro T., O'Brien T. G. Effects of tumor promoters on sodium ion transport across frog skin. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C457–C465. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Yang C. P., Brown J. A., Jr, Scott W. N. Insulin-stimulated sodium transport in toad urinary bladder. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Mar 27;856(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. R., Konda T. S., Standaert M. L., Davis J. S., Pollet R. J., Farese R. V. Insulin increases membrane and cytosolic protein kinase C activity in BC3H-1 myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3633–3639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Parker P. J., Rhee L., Yang-Feng T. L., Chen E., Waterfield M. D., Francke U., Ullrich A. Multiple, distinct forms of bovine and human protein kinase C suggest diversity in cellular signaling pathways. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):859–866. doi: 10.1126/science.3755548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Cooke C. R., Andres R., Faloona G. R., Davis P. J. The effect of insulin on renal handling of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):845–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI107996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Goldberg M., Agus Z. S. The effects of glucose and insulin on renal electrolyte transport. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jul;58(1):83–90. doi: 10.1172/JCI108463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. Tumor promoters and cell transformation. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;26(1):89–145. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlij D., Schoen H. F. Effects of insulin on alkali-cation movements across muscle and epithelial cell membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1981;372:272–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb15481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Konda T. S., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Cooper D. R. Insulin rapidly increases diacylglycerol by activating de novo phosphatidic acid synthesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):586–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3107122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Soliz N. M., Saltiel A. R. Purification of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase C from liver plasma membranes: a possible target of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelehrter T. D., Shreve P. D., Dilworth V. M. Insulin regulation of Na/K pump activity in rat hepatoma cells. Diabetes. 1984 May;33(5):428–434. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.5.428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRERA F. C., WHITTEMBURY G., PLANCHART A. Effect of insulin on short-circuit current across isolated frog skin in the presence of calcium and magnesium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 15;66:170–172. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Lysosphingolipids inhibit protein kinase C: implications for the sphingolipidoses. Science. 1987 Feb 6;235(4789):670–674. doi: 10.1126/science.3101176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera F. C. Effect of insulin on short-circuit current and sodium transport across toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1965 Oct;209(4):819–824. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.4.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hougen T. J., Hopkins B. E., Smith T. W. Insulin effects on monovalent cation transport and Na-K-ATPase activity. Am J Physiol. 1978 Mar;234(3):C59–C63. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1978.234.3.C59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarett L., Wong E. H., Macaulay S. L., Smith J. A. Insulin mediators from rat skeletal muscle have differential effects on insulin-sensitive pathways of intact adipocytes. Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):533–535. doi: 10.1126/science.3917578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Cooperative roles of various membrane phospholipids in the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7146–7149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf J. L., Lee M. H., Sultzman L. A., Kriz R. W., Loomis C. R., Hewick R. M., Bell R. M. Cloning and expression of multiple protein kinase C cDNAs. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Kelly K. L., Abler A., Jarett L. Identification of a novel insulin-sensitive glycophospholipid from H35 hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2131–2137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauro T., O'Brien T. G., Civan M. M. Effects of TPA on short-circuit current across frog skin. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 1):C173–C178. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.2.C173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D. Effects of insulin upon ion transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):1–49. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano R. E., Longmuir K. J. Phosphorylation, transbilayer movement, and facilitated intracellular transport of diacylglycerol are involved in the uptake of a fluorescent analog of phosphatidic acid by cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1909–1916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorsman P., Arkhammar P., Berggren P. O. Voltage-activated Na+ currents and their suppression by phorbol ester in clonal insulin-producing RINm5F cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):C912–C919. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.6.C912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlondorff D., Levine S. D. Inhibition of vasopressin-stimulated water flow in toad bladder by phorbol myristate acetate, dioctanoylglycerol, and RHC-80267. Evidence for modulation of action of vasopressin by protein kinase C. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1071–1078. doi: 10.1172/JCI112060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoen H. F., Erlij D. Basolateral membrane responses to transport modifiers in the frog skin epithelium. Pflugers Arch. 1985;405 (Suppl 1):S33–S38. doi: 10.1007/BF00581777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel B., Civan M. M. Aldosterone and insulin effects on driving force of Na+ pump in toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jun;230(6):1603–1608. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.6.1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanase M., Handler J. S. Activators of protein kinase C inhibit sodium transport in A6 epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C517–C522. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Effect of insulin on potassium efflux from rat muscle in the presence and absence of glucose. Am J Physiol. 1960 May;198:1066–1070. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.5.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Hyperpolarization of muscle by insulin in a glucose-free environment. Am J Physiol. 1959 Sep;197:524–526. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]