Abstract
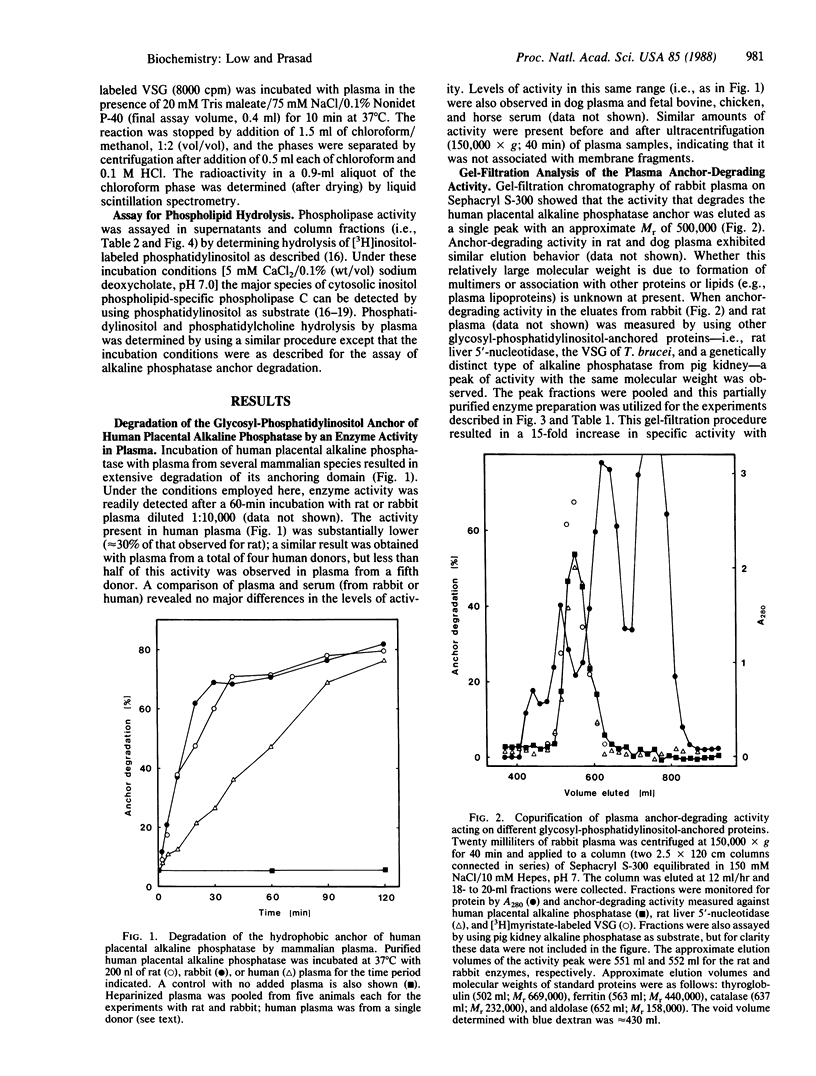
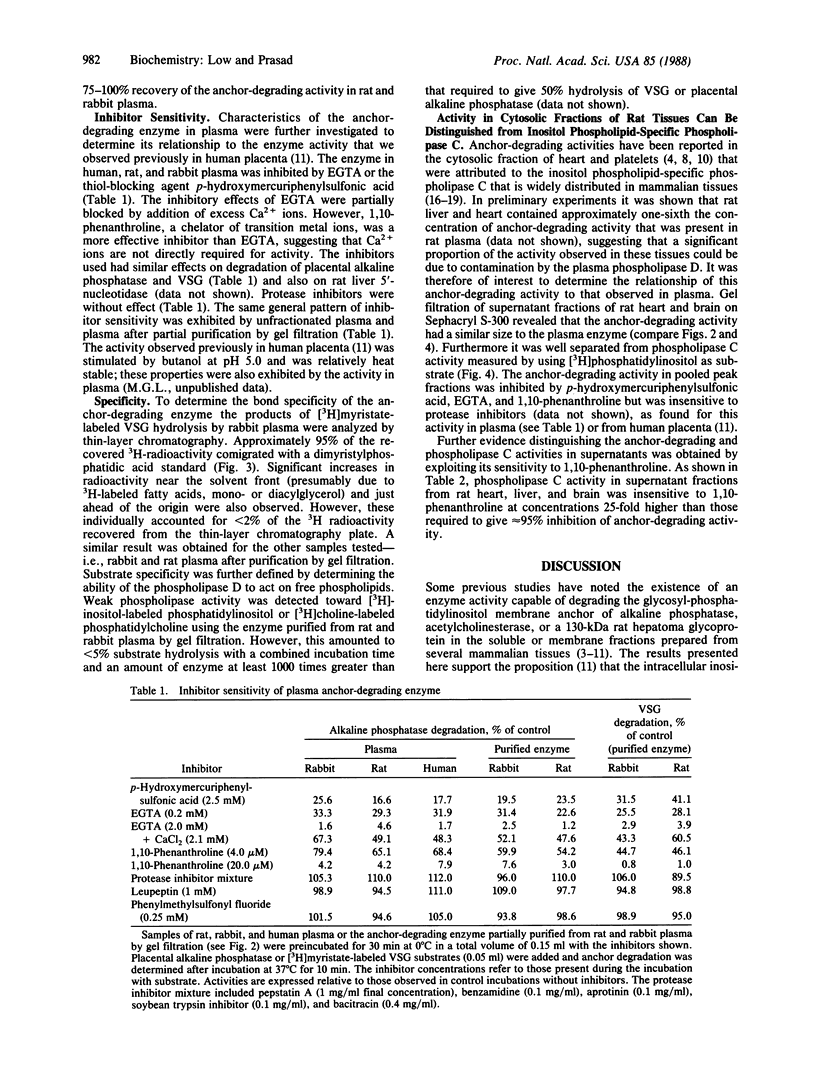
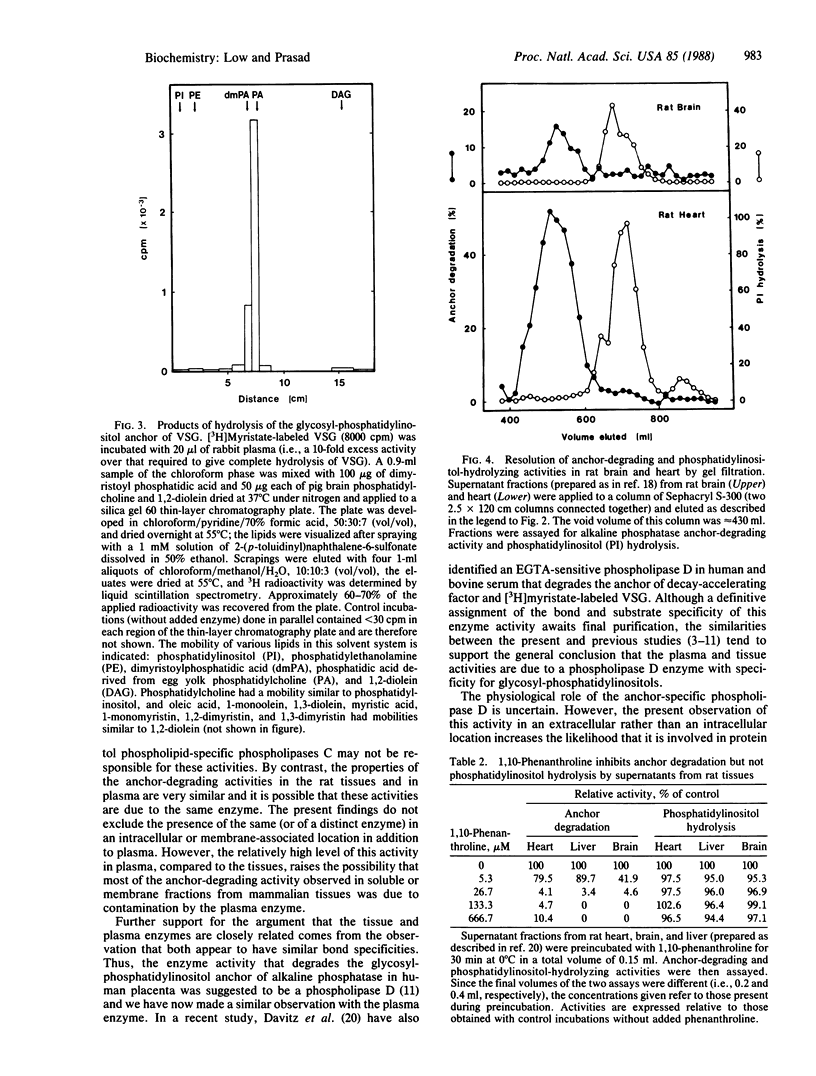
An enzyme activity capable of degrading the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of cell-surface proteins has previously been reported in a number of mammalian tissues. The experiments reported here demonstrate that this anchor-degrading activity is also abundant in mammalian plasma. The activity was inhibited by EGTA or 1,10-phenanthroline. It was capable of removing the anchor from alkaline phosphatase, 5'-nucleotidase, and variant surface glycoprotein but had little or not activity toward phosphatidylinositol or phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidic acid was the only 3H-labeled product when this enzyme hydrolyzed [3H]myristate-labeled variant surface glycoprotein. It could be distinguished from the Ca2+-dependent inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C activity in several rat tissues on the basis of its molecular size and its sensitivity to 1,10-phenanthroline. The data therefore suggest that this activity is due to a phospholipase D with specificity for glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Although the precise physiological function of this anchor-specific phospholipase D remains to be determined, these findings indicate that it could play an important role in regulating the expression and release of cell-surface proteins in vivo.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bülow R., Overath P. Purification and characterization of the membrane-form variant surface glycoprotein hydrolase of Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11918–11923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Hereld D., Shak S., Krakow J., Englund P. T., Nussenzweig V. A glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase D in human serum. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):81–84. doi: 10.1126/science.2443973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Duszenko M., Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Purification and characterization of a novel glycan-phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15767–15771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. A., Soliz N. M., Saltiel A. R. Purification of a phosphatidylinositol-glycan-specific phospholipase C from liver plasma membranes: a possible target of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2663–2667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Bangs J. D., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. A phospholipase C from Trypanosoma brucei which selectively cleaves the glycolipid on the variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13813–13819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikehara Y., Hayashi Y., Ogata S., Miki A., Kominami T. Purification and characterization of a major glycoprotein in rat hepatoma plasma membranes. One of the membrane proteins released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):63–70. doi: 10.1042/bj2410063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominami T., Miki A., Ikehara Y. Electrophoretic characterization of hepatic alkaline phosphatase released by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. A comparison with liver membrane and serum-soluble forms. Biochem J. 1985 Apr 1;227(1):183–189. doi: 10.1042/bj2270183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. Biochemistry of the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol membrane protein anchors. Biochem J. 1987 May 15;244(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2440001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Carroll R. C., Cox A. C. Characterization of multiple forms of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C purified from human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj2370139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Carroll R. C., Weglicki W. B. Multiple forms of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C of different relative molecular masses in animal tissues. Evidence for modification of the platelet enzyme by Ca2+-dependent proteinase. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):813–820. doi: 10.1042/bj2210813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Weglicki W. B. Resolution of myocardial phospholipase C into several forms with distinct properties. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):325–334. doi: 10.1042/bj2150325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Zilversmit D. B. Role of phosphatidylinositol in attachment of alkaline phosphatase to membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):3913–3918. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majerus P. W., Connolly T. M., Deckmyn H., Ross T. S., Bross T. E., Ishii H., Bansal V. S., Wilson D. B. The metabolism of phosphoinositide-derived messenger molecules. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1519–1526. doi: 10.1126/science.3024320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar R., Balasubramanian A. S. Essential and non-essential phosphatidylinositol residues in acetylcholinesterase and arylacylamidase of sheep basal ganglia. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 20;146(2):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80947-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar R., Balasubramanian A. S. The solubilization of platelet membrane-bound acetylcholinesterase and aryl acylamidase by exogenous or endogenous phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Dec 1;34(23):4109–4115. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. S., Low M. G. Conversion of human placental alkaline phosphatase from a high Mr form to a low Mr form during butanol extraction. An investigation of the role of endogenous phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2400519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki A., Kominami T., Ikehara Y. pH-dependent conversion of liver-membranous alkaline phosphatase to a serum-soluble form by n-butanol extraction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Kruijer W., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Bierman A. J., de Laat S. W. Growth factor-like action of phosphatidic acid. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):171–173. doi: 10.1038/323171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Phosphatidic acid may stimulate membrane receptors mediating adenylate cyclase inhibition and phospholipid breakdown in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5522–5529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



