Abstract
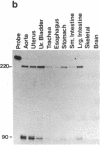
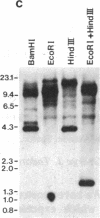
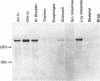
A cDNA clone, SMHC-29, encoding the light meromyosin of smooth muscle myosin heavy chain (MHC), was isolated from a rabbit uterus cDNA library constructed in phage lambda gt11. This smooth muscle MHC cDNA demonstrates significant nucleotide and amino acid sequence homologies with known sarcomeric MHC genes from rabbit, rat skeletal, and nematode body wall myosin, and even with nonmuscle MHC gene from a slime mold (Dictyostelium discoideum), suggesting that smooth muscle, striated muscle, and nonmuscle MHC genes diverged from a common ancestor. The deduced amino acid sequences of the smooth muscle light meromyosin show very similar periodic distributions of hydrophobic and charged residues as found for the light meromyosin of striated muscle MHCs together with a high potential for alpha-helical formation, indicating an alpha-helical coiled-coil structure for the smooth muscle light meromyosin sequences. Furthermore, S1 nuclease mapping has revealed that this smooth muscle MHC gene for SMHC-29 is specifically expressed in smooth muscles of vascular and nonvascular types but not in the striated muscles or nonmuscle cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton F. T., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. The contractile apparatus of vascular smooth muscle: intermediate high voltage stereo electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 15;98(1):17–29. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers-Bleukx G., Maréchal G. Detection and distribution of myosin isozymes in vertebrate smooth muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):207–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. I., Hansen C. J., Becker K. D., Wassenberg D. R., 2nd, Roche E. S., Donady J. J., Emerson C. P., Jr Alternative RNA splicing generates transcripts encoding a thorax-specific isoform of Drosophila melanogaster myosin heavy chain. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2511–2519. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P., Jr, Bernstein S. I. Molecular genetics of myosin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER R. D., MACRAE T. P., MILLER A. THE COILED-COIL MODEL OF ALPHA-KERATIN STRUCTURE. J Mol Biol. 1964 Oct;10:147–156. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gröschel-Stewart U. Comparative studies of human smooth and striated muscle myosins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 16;229(2):322–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90191-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. All members of the MHC multigene family respond to thyroid hormone in a highly tissue-specific manner. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):597–600. doi: 10.1126/science.3945800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. Protein structural domains in the Caenorhabditis elegans unc-54 myosin heavy chain gene are not separated by introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavinsky C. J., Umeda P. K., Sinha A. M., Elzinga M., Tong S. W., Zak R., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M. Cloned mRNA sequences for two types of embryonic myosin heavy chains from chick skeletal muscle. I. DNA and derived amino acid sequence of light meromyosin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5196–5205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D. M., Fujiwara K., Alexander R. W., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Myosin in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells: immunofluorescence and immunochemical studies of alterations in antigenic expression. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1582–1589. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Molecular characterization of two myosin heavy chain genes expressed in the adult heart. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):659–664. doi: 10.1038/297659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Karn J. Periodic charge distributions in the myosin rod amino acid sequence match cross-bridge spacings in muscle. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):226–231. doi: 10.1038/299226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen H. T., Gubits R. M., Wydro R. M., Nadal-Ginard B. Sarcomeric myosin heavy chain is coded by a highly conserved multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5230–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H., Wakabayashi T. Electron microscopic studies of myosin molecules from chicken gizzard muscle I: the formation of the intramolecular loop in the myosin tail. J Biochem. 1982 Sep;92(3):871–879. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A. Analysis of the primary sequence of alpha-tropomyosin from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):519–535. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A. Structure of rabbit skeletal myosin. Analysis of the amino acid sequences of two fragments from the rod region. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):459–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Wieczorek D. F., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of a developmentally regulated perinatal myosin heavy-chain gene expressed in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13573–13578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Wydro R. M., Strehler-Page M. A., Strehler E. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of cDNA and genomic sequences corresponding to an embryonic myosin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15856–15862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovner A. S., Thompson M. M., Murphy R. A. Two different heavy chains are found in smooth muscle myosin. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):C861–C870. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.6.C861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Differential processing of RNA transcribed from the single-copy Drosophila myosin heavy chain gene produces four mRNAs that encode two polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2128–2132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V. Studies on isolated smooth muscle cells: The contractile apparatus. J Cell Sci. 1977 Apr;24:327–349. doi: 10.1242/jcs.24.1.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Birnboim H. C., Darnell J. E. Rapidly labeled HeLa cell nuclear RNA. II. Base composition and cellular localization of a heterogeneous RNA fraction. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):362–372. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehler E. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Perriard J. C., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Complete nucleotide and encoded amino acid sequence of a mammalian myosin heavy chain gene. Evidence against intron-dependent evolution of the rod. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):291–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trybus K. M., Huiatt T. W., Lowey S. A bent monomeric conformation of myosin from smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6151–6155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., De Lozanne A., Leinwand L. A., Spudich J. A. Conserved protein domains in a myosin heavy chain gene from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9433–9437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]