Abstract
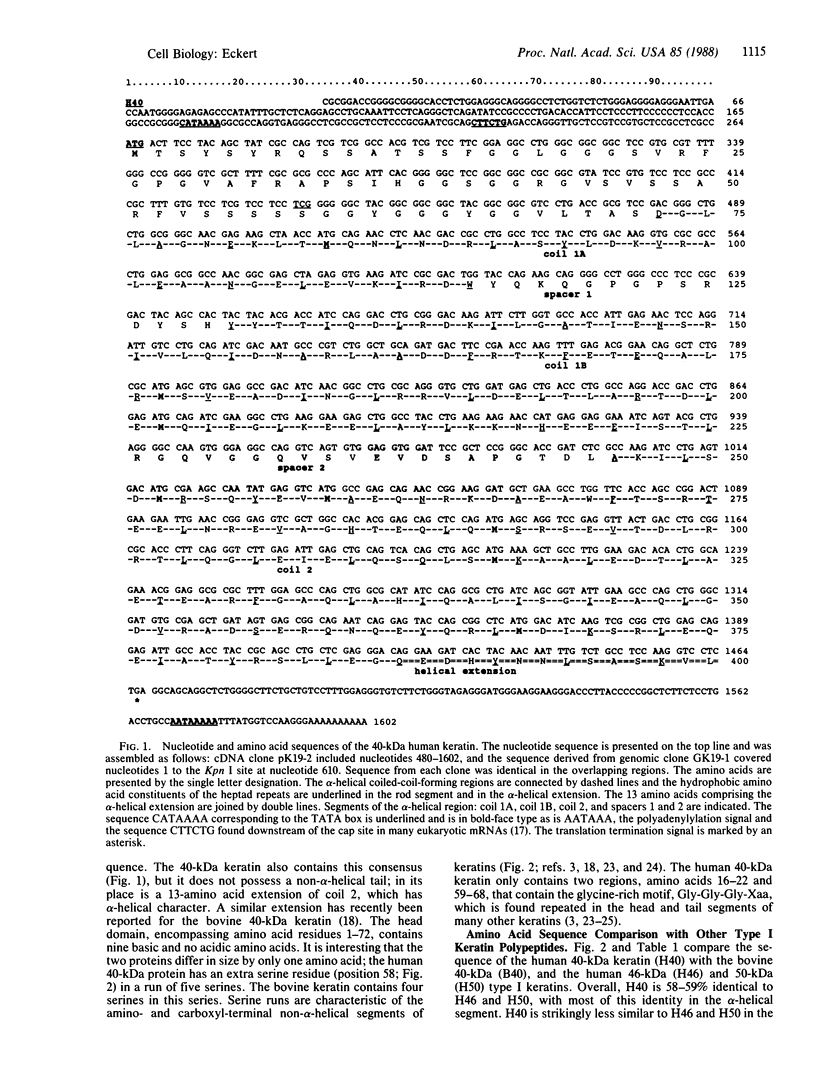
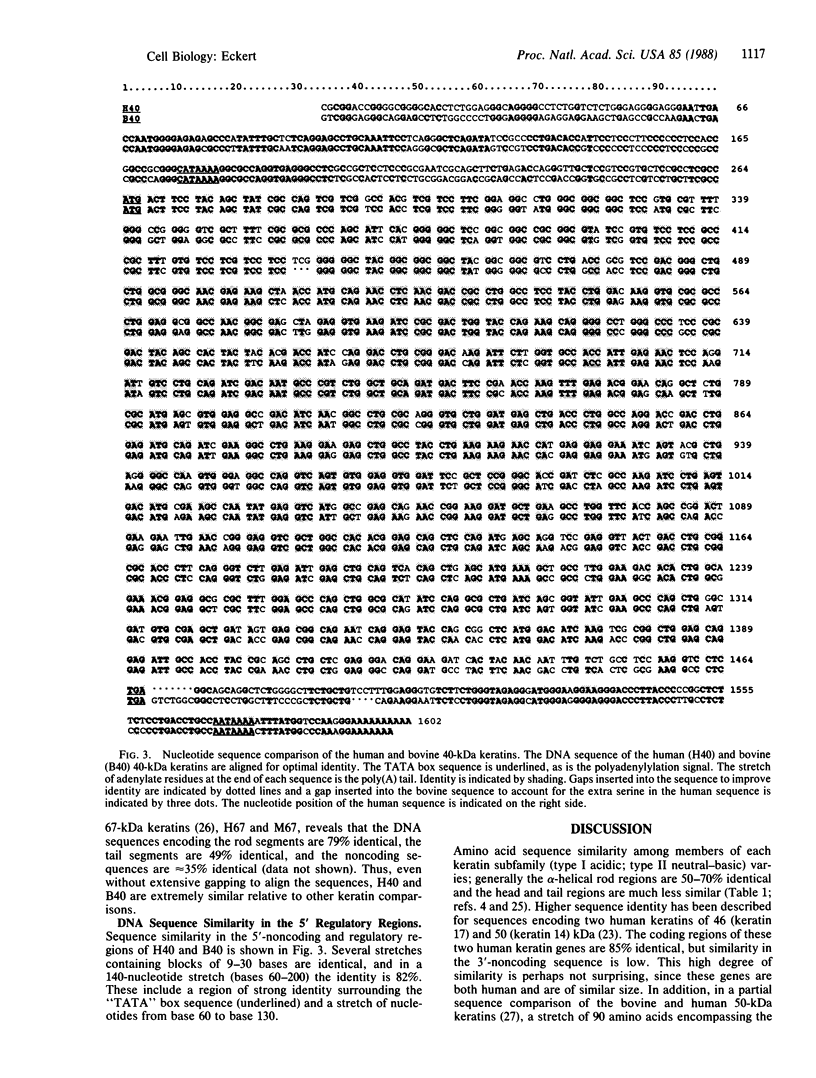
The complete amino acid and DNA sequences of the human 40-kDa keratin are reported. The DNA sequence encodes a protein of 44,098 Da, which is unique in that it lacks the terminal non-alpha-helical tail segment found in all other keratins. When the human 40-kDa keratin amino acid sequence is compared to the corresponding bovine keratin, the overall identity is 89%. The coil-forming regions are 89% identical and the head regions are 88% identical. This similarity is also evident in the DNA sequence of the coding region, the 5' upstream sequences, and the 3' noncoding sequences. The high degree of cross-species identity between bovine and human 40-kDa keratins suggests that there is strong evolutionary pressure to conserve the structure of this keratin. This in turn suggests an important and universal role for this intermediate filament subunit in all species.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader B. L., Magin T. M., Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Amino acid sequence and gene organization of cytokeratin no. 19, an exceptional tail-less intermediate filament protein. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1865–1875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baralle F. E., Brownlee G. G. AUG is the only recognisable signal sequence in the 5' non-coding regions of eukaryotic mRNA. Nature. 1978 Jul 6;274(5666):84–87. doi: 10.1038/274084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. L., Green H. Cloning of cDNAs specifying vitamin A-responsive human keratins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R. L. New vectors for rapid sequencing of DNA fragments by chemical degradation. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichner R., Sun T. T., Aebi U. The role of keratin subfamilies and keratin pairs in the formation of human epidermal intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1767–1777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Schiller D. L., Winter S., Jarasch E. D., Moll R., Denk H., Jackson B. W., Illmensee K. Differentiation-related patterns of expression of proteins of intermediate-size filaments in tissues and cultured cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):431–453. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured human keratinocytes by vitamin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfix B. M., Eckert R. L. Coordinate control by vitamin A of keratin gene expression in human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14026–14029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Pair formation and promiscuity of cytokeratins: formation in vitro of heterotypic complexes and intermediate-sized filaments by homologous and heterologous recombinations of purified polypeptides. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1826–1841. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. D., Idler W. W., Zhou X. M., Roop D. R., Steinert P. M. Structure of a gene for the human epidermal 67-kDa keratin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1896–1900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcano J. L., Rieger M., Franz J. K., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Franke W. W. Identification of two types of keratin polypeptides within the acidic cytokeratin subfamily I. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 25;179(2):257–281. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments: a chemically heterogeneous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Complete sequence of a gene encoding a human type I keratin: sequences homologous to enhancer elements in the regulatory region of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RayChaudhury A., Marchuk D., Lindhurst M., Fuchs E. Three tightly linked genes encoding human type I keratins: conservation of sequence in the 5'-untranslated leader and 5'-upstream regions of coexpressed keratin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Parry D. A., Idler W. W., Johnson L. D., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. Amino acid sequences of mouse and human epidermal type II keratins of Mr 67,000 provide a systematic basis for the structural and functional diversity of the end domains of keratin intermediate filament subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):7142–7149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Rheinwald J. G. A new small (40 kd) keratin filament protein made by some cultured human squamous cell carcinomas. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]