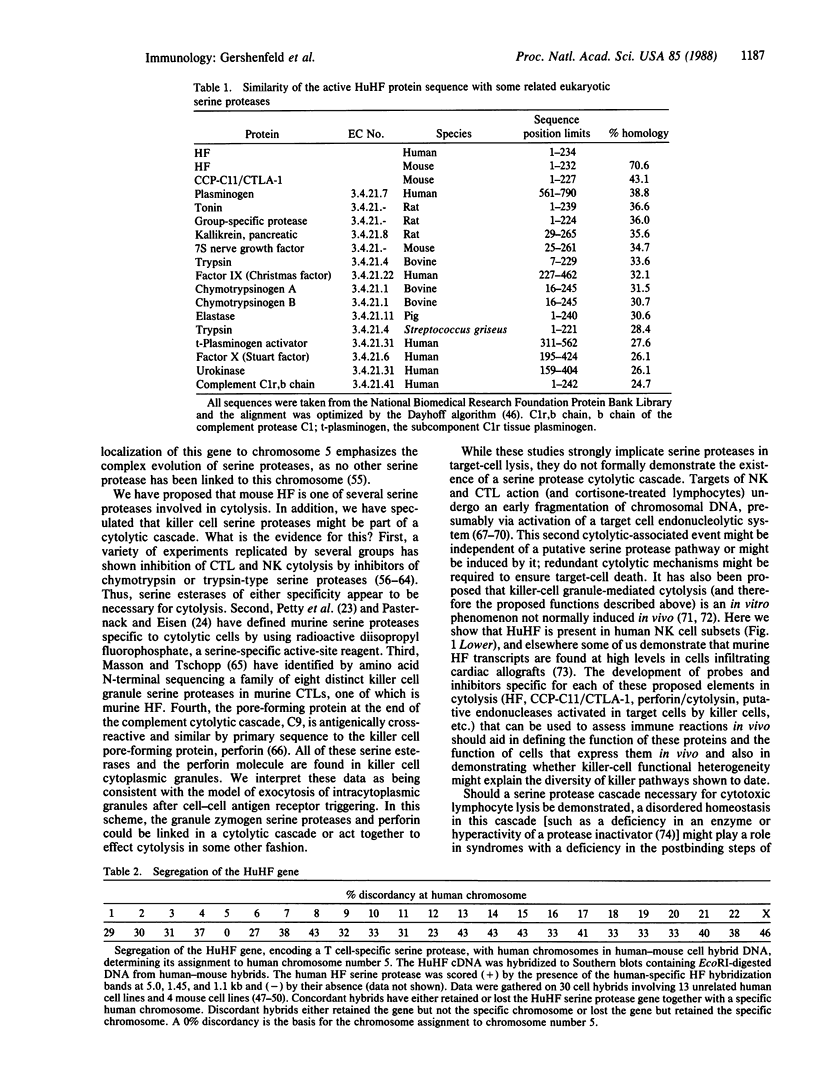
Abstract
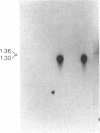
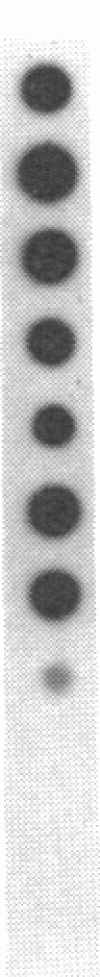
A cDNA clone encoding a human T cell- and natural killer cell-specific serine protease was obtained by screening a phage lambda gt10 cDNA library from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes with the mouse Hanukah factor cDNA clone. In an RNA blot-hybridization analysis, this human Hanukah factor cDNA hybridized with a 1.3-kilobase band in allogeneic-stimulated cytotoxic T cells and the Jurkat cell line, but this transcript was not detectable in normal muscle, liver, tonsil, or thymus. By dot-blot hybridization, this cDNA hybridized with RNA from three cytolytic T-cell clones and three noncytolytic T-cell clones grown in vitro as well as with purified CD16+ natural killer cells and CD3+, CD16- T-cell large granular lymphocytes from peripheral blood lymphocytes (CD = cluster designation). The nucleotide sequence of this cDNA clone encodes a predicted serine protease of 262 amino acids. The predicted protein has a 22-amino acid presegment, a 6-amino acid prosegment, and an active enzyme of 234 amino acids with a calculated unglycosylated molecular weight of 25,820. The active enzyme is 71% and 77% similar to the mouse sequence at the amino acid and DNA level, respectively. The human and mouse sequences conserve the active site residues of serine proteases--the trypsin-specific Asp-189 and all 10 cysteine residues. The gene for the human Hanukah factor serine protease is located on human chromosome 5. We propose that this trypsin-like serine protease may function as a common component necessary for lysis of target cells by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ades E. W., Hinson A., Chapuis-Cellier C., Arnaud P. Modulation of the immune response by plasma protease inhibitors. I. Alpha 2-macroglobulin and alpha 1-antitrypsin inhibit natural killing and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Jan;15(1):109–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G. An appraisal of some current thoughts on cytolytic T-lymphocyte killing mechanisms. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 Mar-Apr;138(2):304–308. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berke G., Rosen D. Are lytic granules and perforin 1 involved in lysis induced by in vivo-primed peritoneal exudate cytolytic T lymphocytes? Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 1):412–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunet J. F., Dosseto M., Denizot F., Mattei M. G., Clark W. R., Haqqi T. M., Ferrier P., Nabholz M., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Luciani M. F. The inducible cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated gene transcript CTLA-1 sequence and gene localization to mouse chromosome 14. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):268–271. doi: 10.1038/322268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Eisen H. N. Effects of N alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethylketone on the activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1028–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayberger C., Holmes N., Wang P. L., Koller T. D., Parham P., Krensky A. M. Determinants recognized by human cytotoxic T cells on a natural hybrid class I HLA molecule. J Exp Med. 1985 Nov 1;162(5):1709–1714. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.5.1709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Concannon P., Pickering L. A., Kung P., Hood L. Diversity and structure of human T-cell receptor beta-chain variable region genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Criado M., Lindstrom J. M., Anderson C. G., Dennert G. Cytotoxic granules from killer cells: specificity of granules and insertion of channels of defined size into target membranes. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4245–4251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke R. C., Chervenak R., Cohen J. J. Endogenous endonuclease-induced DNA fragmentation: an early event in cell-mediated cytolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6361–6365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganea D., Teodorescu M., Dray S. A low molecular weight proteinase inhibitor produced by T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):85–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershenfeld H. K., Weissman I. L. Cloning of a cDNA for a T cell-specific serine protease from a cytotoxic T lymphocyte. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):854–858. doi: 10.1126/science.2422755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley B. S. Homologies in serine proteinases. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Feb 12;257(813):77–87. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1970.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart M. P., Henkart P. A. Lymphocyte mediated cytolysis as a secretory phenomenon. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;146:227–247. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8959-0_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A., Yue C. C., Yang J., Rosenberg S. A. Cytolytic and biochemical properties of cytoplasmic granules of murine lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 15;137(8):2611–2617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P., Henkart M., Millard P., Frederikse P., Bluestone J., Blumenthal R., Yue C., Reynolds C. The role of cytoplasmic granules in cytotoxicity by large granular lymphocytes and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;184:121–138. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8326-0_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Reynolds C. W., Ortaldo J. R. Mechanism of cytotoxicity by natural killer (NK) cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:651–680. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudig D., Haverty T., Fulcher C., Redelman D., Mendelsohn J. Inhibition of human natural cytotoxicity by macromolecular antiproteases. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1569–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Zaytoun A. M., Lee J. H., Jr, Panush R. S., Longley S. Abnormal natural killer cell activity in systemic lupus erythematosus: an intrinsic defect in the lytic event. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1966–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Lederman M. M. Defective postbinding lysis underlies the impaired natural killer activity in factor VIII-treated, human T lymphotropic virus type III seropositive hemophiliacs. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1057–1062. doi: 10.1172/JCI112404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Protein transport. From organelle to organelle. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):14–15. doi: 10.1038/326014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel G. R., Herndon D. N., Fons M., Albrecht T., Asuncion M. T., Chin R., Stein M. D. Defective NK cell activity following thermal injury. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):384–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Binninger L., Schirrmacher V., Moll H., Prester M., Nerz G., Simon M. M. Characterization and isolation of a trypsin-like serine protease from a long-term culture cytolytic T cell line and its expression by functionally distinct T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4644–4651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krensky A. M., Reiss C. S., Mier J. W., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J. Long-term human cytolytic T-cell lines allospecific for HLA-DR6 antigen are OKT4+. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2365–2369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Siu G., Hood L. E., Shastri N. The molecular genetics of the T-cell antigen receptor and T-cell antigen recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:529–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Singer S. J., Dennert G. On the mechanism of unidirectional killing in mixtures of two cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Unidirectional polarization of cytoplasmic organelles and the membrane-associated cytoskeleton in the effector cell. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):489–498. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Phillips J. H., Hackett J., Jr, Tutt M., Kumar V. Natural killer cells: definition of a cell type rather than a function. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2735–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavie G., Leib Z., Servadio C. The mechanism of human NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Mode of action of surface-associated proteases in the early stages of the lytic reaction. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1470–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobe C. G., Finlay B. B., Paranchych W., Paetkau V. H., Bleackley R. C. Novel serine proteases encoded by two cytotoxic T lymphocyte-specific genes. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):858–861. doi: 10.1126/science.3518058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey D. M., Rupp F., Aebischer T., Grey P., Hengartner H., Podack E. R. Primary sequence homology between the effector molecules that mediate complement and T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 Mar-Apr;138(2):296–300. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Schmidt R. E., Caulfield J. P., Hein A., Bartley G. T., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Proteoglycans in cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Identification, localization, and exocytosis of a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan from human cloned natural killer cells during target cell lysis. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1771–1787. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Nabholz M., Estrade C., Tschopp J. Granules of cytolytic T-lymphocytes contain two serine esterases. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1595–1600. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. A family of serine esterases in lytic granules of cytolytic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):679–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90544-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Tschopp J. Isolation of a lytic, pore-forming protein (perforin) from cytolytic T-lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9069–9072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson D., Zamai M., Tschopp J. Identification of granzyme A isolated from cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-granules as one of the proteases encoded by CTL-specific genes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):84–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81537-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Eisen H. N. A novel serine esterase expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):743–745. doi: 10.1038/314743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Sitkovsky M. V., Eisen H. N. The site of action of N-alpha-tosyl-L-lysyl-chloromethyl-ketone (TLCK) on cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2477–2483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack M. S., Verret C. R., Liu M. A., Eisen H. N. Serine esterase in cytolytic T lymphocytes. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):740–743. doi: 10.1038/322740a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen B. K. Natural killer cells in relation to disease and treatment. Allergy. 1985 Nov;40(8):547–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb00881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty H. R., Hermann W., Dereski W., Frey T., McConnell H. M. Activatable esterase activity of murine natural killer cell--YAC tumour cell conjugates. J Cell Sci. 1984 Dec;72:1–13. doi: 10.1242/jcs.72.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and biochemical and functional characterization of perforin 1 from cytolytic T-cell granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8629–8633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan P. C., Ishizaka T., Bloom B. R. Studies on the mechanism of NK cell lysis. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1786–1791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redelman D., Hudig D. The mechanism of cell-mediated cytotoxicity. I. Killing by murine cytotoxic T lymphocytes requires cell surface thiols and activated proteases. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):870–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L. T-cell receptors. Who needs more? Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):660–663. doi: 10.1038/325660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristow S. S., Starkey J. R., Hass G. M. In vitro effects of protease inhibitors on murine natural killer cell activity. Immunology. 1983 Jan;48(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. Exon shuffling and intron insertion in serine protease genes. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):458–459. doi: 10.1038/315458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Masakowski V. R., Dobos C. B. Mechanisms of immune lysis. I. Physiological distinction between target cell death mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and antibody plus complement. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1100–1105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi A. Y., Shows T. B. Coronavirus 229E susceptibility in man-mouse hybrids is located on human chromosome 15. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Jan;8(1):83–94. doi: 10.1007/BF01538652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Sakaguchi A. Y., Naylor S. L. Mapping the human genome, cloned genes, DNA polymorphisms, and inherited disease. Adv Hum Genet. 1982;12:341–452. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8315-8_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T., Eddy R., Haley L., Byers M., Henry M., Fujita T., Matsui H., Taniguchi T. Interleukin 2 (IL2) is assigned to human chromosome 4. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 May;10(3):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF01535253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D. A specific serine proteinase is inducible in Lyt-2+,L3T4- and Lyt-2-,L3T4+ T cells in vitro but is mainly associated with Lyt-2+,L3T4- effector cells in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Dec;16(12):1559–1568. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830161215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. M., Fruth U., Simon H. G., Kramer M. D. Evidence for the involvement of a T-cell-associated serine protease (TSP-1) in cell killing. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 Mar-Apr;138(2):309–314. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80085-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Morgan R., Link M. P., McFall P., Hecht F. Cytogenetic and immunophenotypic analysis of cell lines established from patients with T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 1986 Mar;67(3):650–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Byron K. S., Brewster F. E., Purtilo D. T. Deficient natural killer cell activity in x-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):543–545. doi: 10.1126/science.6158759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama H., Trenn G., Humphrey W., Jr, Bluestone J. A., Henkart P. A., Sitkovsky M. V. Antigen receptor-triggered secretion of a trypsin-type esterase from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):566–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and glucocorticoids activate an endogenous suicide process in target cells. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):62–64. doi: 10.1038/327062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Wiskocil R. L., Stobo J. D. The role of T3 surface molecules in the activation of human T cells: a two-stimulus requirement for IL 2 production reflects events occurring at a pre-translational level. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M. Regulation of virus infections by natural killer cells. A review. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1986;5(4):169–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yannelli J. R., Sullivan J. A., Mandell G. L., Engelhard V. H. Reorientation and fusion of cytotoxic T lymphocyte granules after interaction with target cells as determined by high resolution cinemicrography. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):377–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Role of granule proteins in lymphocyte-mediated killing. J Cell Biochem. 1986;32(2):151–167. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240320207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Leong L. G., Liu C. C., Damiano A., Wall D. A., Cohn Z. A. Isolation and characterization of a serine esterase from cytolytic T cell granules. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):183–194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Podack E. R., Cohn Z. A. Properties of a purified pore-forming protein (perforin 1) isolated from H-2-restricted cytotoxic T cell granules. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):144–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagury D. Direct analysis of individual killer T cells: susceptibility of target cells to lysis and secretion of hydrolytic enzymes by CTL. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;146:149–169. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8959-0_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]