Abstract
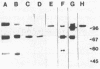
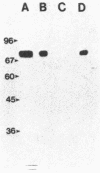
We have purified completely the principal asymmetric ("heavy") form of acetylcholinesterase (Ac-ChoEase; EC 3.1.1.7) from chick muscle (i.e., the synaptic form in the twitch muscle fibers) by using a monoclonal antibody that recognizes AcChoEase but not pseudocholinesterase (ChoEase; cholinesterase, EC 3.1.1.8). The purified protein exhibits catalytic and inhibition properties characteristic of AcChoEase and ChoEase and contains three distinct subunits of apparent sizes 110 kDa, 72 kDa, and 58 kDa in the ratio 2:2:1. The discovery of an AcChoEase/ChoEase hybrid asymmetric form has been further supported by (i) the identification of active site properties of AcChoEase in the 110-kDa subunit and of ChoEase in the 72-kDa subunit, (ii) the purification or precipitation of both activities together by, also, a ChoEase-specific monoclonal antibody, and (iii) evidence that all subunits are bound in the asymmetric forms by disulfide bonds. The 58-kDa subunit is the only one that is sensitive to digestion with purified collagenase; it carries the collagenous "tail" of the asymmetric form. A model is proposed for this form of AcChoEase.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allemand P., Bon S., Massoulié J., Vigny M. The quaternary structure of chicken acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase; effect of collagenase and trypsin. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):860–867. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman H. A., Decker M. M., Jo S. Reciprocal regulation of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in mammalian skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1987 Mar;120(1):154–161. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Huet M., Lemonnier M., Rieger F., Massoulié J. Molecular forms of Electrophorus acetylcholinesterase. Molecular weight and composition. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):523–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10840.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Massoulié J. Collagen-tailed and hydrophobic components of acetylcholinesterase in Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Massoulié J. Collagenase sensitivity and aggregation properties of Electrophorus acetylcholinesterase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Vigny M., Massoulié J. Asymmetric and globular forms of acetylcholinesterase in mammals and birds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandan E., Inestrosa N. C. Binding of the asymmetric forms of acetylcholinesterase to heparin. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 15;221(2):415–422. doi: 10.1042/bj2210415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimijoin S., Mintz K. P., Alley M. C. Production and characterization of separate monoclonal antibodies to human acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;24(3):513–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimijoin S., Rakonczay Z., Mintz K. Immunochemistry of mammalian cholinesterases. Fed Proc. 1986 Dec;45(13):2960–2964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doctor B. P., Camp S., Gentry M. K., Taylor S. S., Taylor P. Antigenic and structural differences in the catalytic subunits of the molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5767–5771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Engel A. G., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase of human erythrocytes and neuromuscular junctions: homologies revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1078–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. L. Properties of 16S acetylcholinesterase from rat motor nerve skeletal muscle. Neurochem Res. 1981 Sep;6(9):1005–1017. doi: 10.1007/BF00965031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall Z. W. Multiple forms of acetylcholinesterase and their distribution in endplate and non-endplate regions of rat diaphragm muscle. J Neurobiol. 1973;4(4):343–361. doi: 10.1002/neu.480040404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedrzejczyk J., Silman I., Lyles J. M., Barnard E. A. Molecular forms of the cholinesterases inside and outside muscle endplates. Biosci Rep. 1981 Jan;1(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF01115148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koelle G. B., Rickard K. K., Ruch G. A. Interrelationships between ganglionic acetylcholinesterase and nonspecific cholinesterase of the cat and rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J., Jedrzejczyk J., Pizzey J. A., Green D., Barnard E. A. Neural control of the forms of acetylcholinesterase in slow mammalian muscles. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):72–74. doi: 10.1038/321072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. L., Heinemann S., Taylor P. Structural characterization of the asymmetric (17 + 13) S forms of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo. I. Analysis of subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12282–12291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockridge O., Bartels C. F., Vaughan T. A., Wong C. K., Norton S. E., Johnson L. L. Complete amino acid sequence of human serum cholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):549–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles J. M., Silman I., Barnard E. A. Developmental changes in levels and forms of cholinesterases in muscles of normal and dystrophic chickens. J Neurochem. 1979 Sep;33(3):727–738. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles J. M., Silman I., Di Giamberardino L., Couraud J. Y., Barnard E. A. Comparison of the molecular forms of the cholinesterases in tissues of normal and dystrophic chickens. J Neurochem. 1982 Apr;38(4):1007–1021. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb05342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh D., Grassi J., Vigny M., Massoulié J. An immunological study of rat acetylcholinesterase: comparison with acetylcholinesterases from other vertebrates. J Neurochem. 1984 Jul;43(1):204–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays C., Rosenberry T. L. Characterization of pepsin-resistant collagen-like tail subunit fragments of 18S and 14S acetylcholinesterase from Electrophorus electricus. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2810–2817. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall W. R., Tsim K. W., Lai J., Barnard E. A. Monoclonal antibodies against chicken brain acetylcholinesterase. Their use in immunopurification and immunochemistry to demonstrate allelic variants of the enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 1;164(1):95–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L. Purification and properties of the membrane-bound form of acetylcholinesterase from chicken brain. Evidence for two distinct polypeptide chains. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13186–13194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Camp S., Maulet Y., Newton M., MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor S. S., Friedmann T., Taylor P. Primary structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase deduced from its cDNA sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):407–409. doi: 10.1038/319407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Krejci E., Massoulié J. cDNA sequences of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase: primary structure of the precursor of a catalytic subunit; existence of multiple 5'-untranslated regions. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1865–1873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Vallette F., Grassi J., Massoulié J. Isolation of a cDNA clone for a catalytic subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant J. P., Massoulié J., Bon S. Polymorphism of pseudocholinesterase in Torpedo marmorata tissues: comparative study of the catalytic and molecular properties of this enzyme with acetylcholinesterase. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):580–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Bon S., Massoulié J., Leterrier F. Active-site catalytic efficiency of acetylcholinesterase molecular forms in Electrophorus, torpedo, rat and chicken. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):317–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Gisiger V., Massoulié J. "Nonspecific" cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in rat tissues: molecular forms, structural and catalytic properties, and significance of the two enzyme systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2588–2592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigny M., Koenig J., Rieger F. The motor end-plate specific form of acetylcholinesterase: appearance during embryogenesis and re-innervation of rat muscle. J Neurochem. 1976 Dec;27(6):1347–1353. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb02614.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younkin S. G., Rosenstein C., Collins P. L., Rosenberry T. L. Cellular localization of the molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase in rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13630–13637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]