Abstract
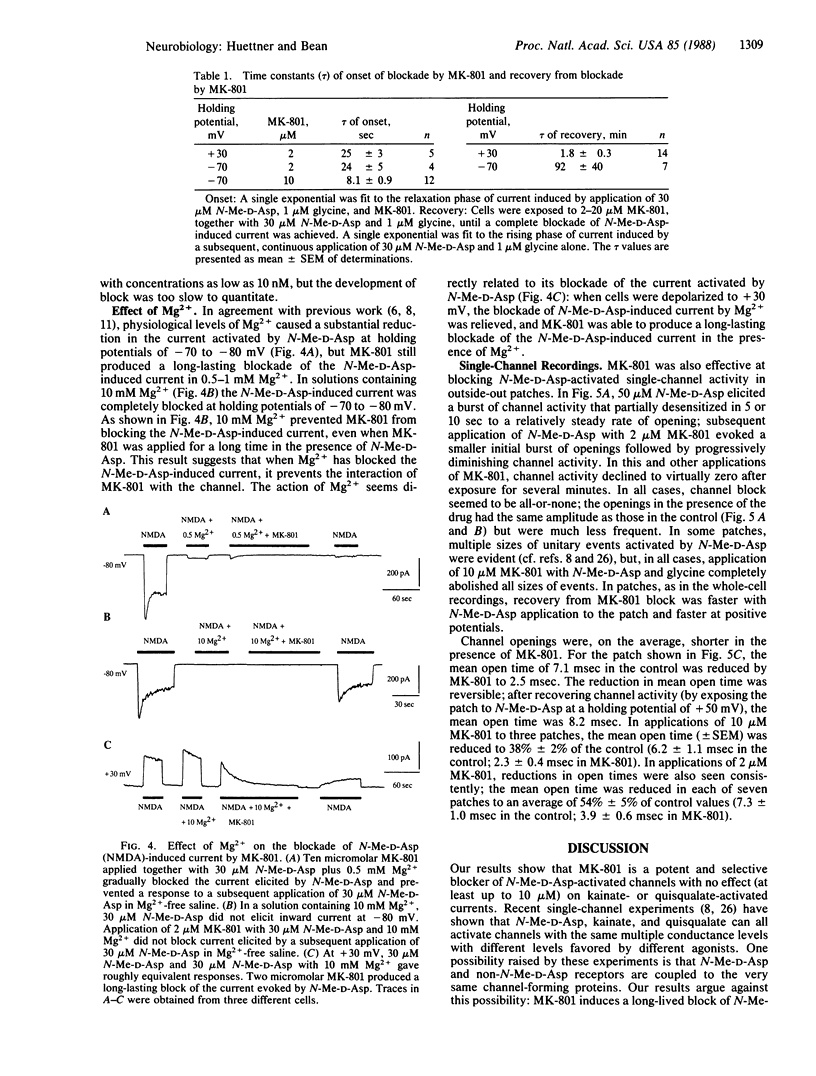
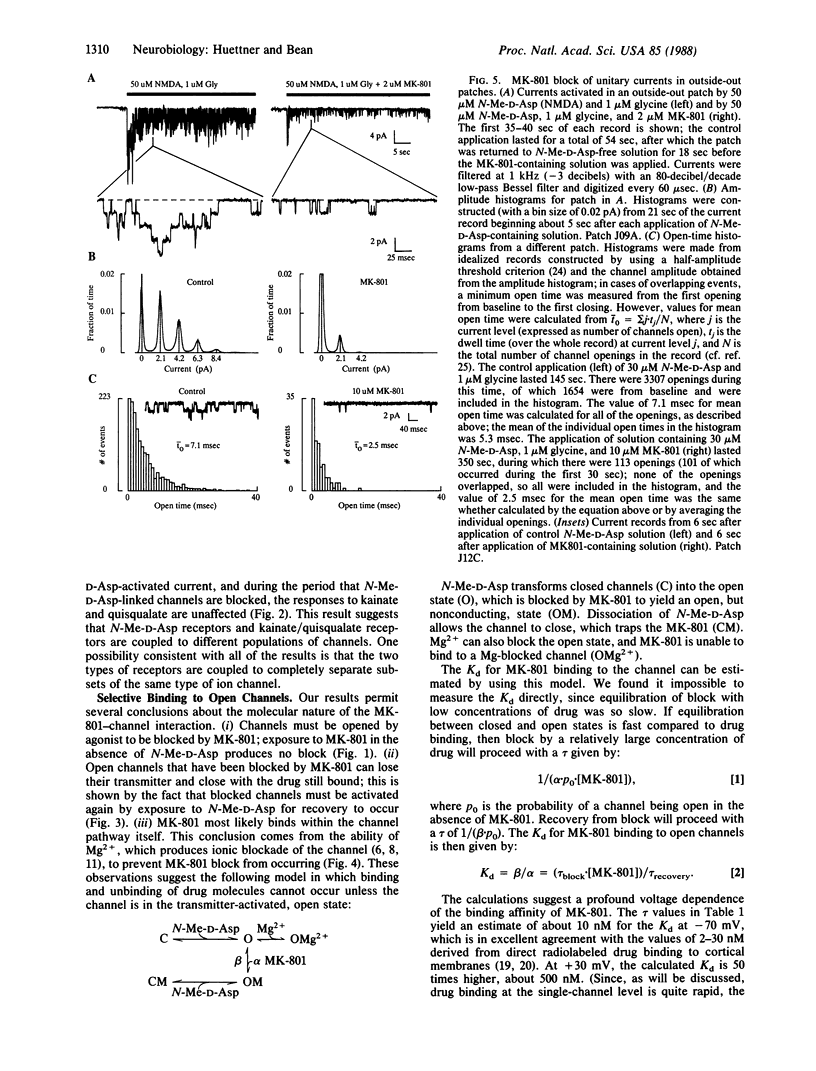
Whole-cell and single-channel recording techniques were used to study the action of the anticonvulsant drug MK-801 [(+)-5-methyl-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[a,d]- cyclohepten-5,10-imine maleate) on responses to excitatory amino acids in rat neocortical neurons in cell culture. MK-801 caused a progressive, long-lasting blockade of current induced by N-methyl-D-aspartate (N-Me-D-Asp). However, during the time that N-Me-D-Asp responses were inhibited, there was no effect on responses to quisqualate or kainate, suggesting that N-Me-D-Asp receptors and kainate/quisqualate receptors open separate populations of ion channels. Binding and unbinding of MK-801 seems to be possible only if the N-Me-D-Asp-operated channel is in the transmitter-activated state: MK-801 was effective only when applied simultaneously with N-Me-D-Asp, and recovery from MK-801 blockade was speeded by continuous exposure to N-Me-D-Asp [time constant (tau) approximately equal to 90 min at -70 to -80 mV]. Recovery from block during continuous application of N-Me-D-Asp was strongly voltage dependent, being faster at positive potentials (tau approximately equal to 2 min at +30 mV). Mg2+, which is thought to block the N-Me-D-Asp-activated ion channel, inhibited blockade by MK-801 at negative membrane potentials. In single-channel recordings from outside-out patches. MK-801 greatly reduced the channel activity elicited by application of N-Me-D-Asp but did not significantly alter the predominant unitary conductance. Consistent with an open-channel blocking mechanism, the mean channel open time was reduced by MK-801 in a dose-dependent manner.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry S. C., Dawkins S. L., Lodge D. Comparison of sigma- and kappa-opiate receptor ligands as excitatory amino acid antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;83(1):179–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W. Ionic dependence of glutamate neurotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):369–379. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00369.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Kehl S. J., McLennan H. Excitatory amino acids in synaptic transmission in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1983 Jan;334:33–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crunelli V., Forda S., Kelly J. S. The reversal potential of excitatory amino acid action on granule cells of the rat dentate gyrus. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:327–342. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cull-Candy S. G., Usowicz M. M. Multiple-conductance channels activated by excitatory amino acids in cerebellar neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):525–528. doi: 10.1038/325525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Marty A., Neher E. Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:599–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Wong E. H. The novel anticonvulsant MK-801 binds to the activated state of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun;91(2):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb10295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hablitz J. J., Langmoen I. A. Excitation of hippocampal pyramidal cells by glutamate in the guinea-pig and rat. J Physiol. 1982 Apr;325:317–331. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honey C. R., Miljkovic Z., MacDonald J. F. Ketamine and phencyclidine cause a voltage-dependent block of responses to L-aspartic acid. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Oct 24;61(1-2):135–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E., Baughman R. W. Primary culture of identified neurons from the visual cortex of postnatal rats. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):3044–3060. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-03044.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E., Baughman R. W. The pharmacology of synapses formed by identified corticocollicular neurons in primary cultures of rat visual cortex. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):160–175. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00160.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahr C. E., Stevens C. F. Glutamate activates multiple single channel conductances in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):522–525. doi: 10.1038/325522a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. Glycine potentiates the NMDA response in cultured mouse brain neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):529–531. doi: 10.1038/325529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M. G., Henderson G. Actions of phencyclidine on rat locus coeruleus neurones in vitro. Neuroscience. 1986 Feb;17(2):485–494. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Smith S. J., Barker J. L. NMDA-receptor activation increases cytoplasmic calcium concentration in cultured spinal cord neurones. 1986 May 29-Jun 4Nature. 321(6069):519–522. doi: 10.1038/321519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald J. F., Miljkovic Z., Pennefather P. Use-dependent block of excitatory amino acid currents in cultured neurons by ketamine. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Aug;58(2):251–266. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.58.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The action of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid on mouse spinal neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:65–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. The physiology of excitatory amino acids in the vertebrate central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1987;28(3):197–276. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(87)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Steinbach J. H. Local anaesthetics transiently block currents through single acetylcholine-receptor channels. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:153–176. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. J., Fischbach G. D. Characterization of excitatory amino acid receptors expressed by embryonic chick motoneurons in vitro. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3275–3283. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03275.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S., Koh J., Choi D. W. Zinc selectively blocks the action of N-methyl-D-aspartate on cortical neurons. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):589–593. doi: 10.1126/science.2883728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman S. M. The neurotoxicity of excitatory amino acids is produced by passive chloride influx. J Neurosci. 1985 Jun;5(6):1483–1489. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-06-01483.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. P., Swan J. H., Griffiths T., Meldrum B. S. Blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors may protect against ischemic damage in the brain. Science. 1984 Nov 16;226(4676):850–852. doi: 10.1126/science.6093256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westbrook G. L., Mayer M. L. Micromolar concentrations of Zn2+ antagonize NMDA and GABA responses of hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):640–643. doi: 10.1038/328640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieloch T. Hypoglycemia-induced neuronal damage prevented by an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):681–683. doi: 10.1126/science.2996146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E. H., Kemp J. A., Priestley T., Knight A. R., Woodruff G. N., Iversen L. L. The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



