Abstract
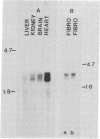
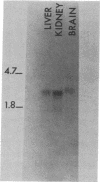
cDNA clones comprising the entire coding region for human dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (dihydrolipoamide:NAD+ oxidoreductase, EC 1.8.1.4) have been isolated from a human liver cDNA library. The cDNA sequence of the largest clone consisted of 2082 base pairs and contained a 1527-base open reading frame that encodes a precursor dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase of 509 amino acid residues. The first 35-amino acid residues of the open reading frame probably correspond to a typical mitochondrial import leader sequence. The predicted amino acid sequence of the mature protein, starting at the residue number 36 of the open reading frame, is almost identical (greater than 98% homology) with the known partial amino acid sequence of the pig heart dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase. The cDNA clone also contains a 3' untranslated region of 505 bases with an unusual polyadenylylation signal (TATAAA) and a short poly(A) track. By blot-hybridization analysis with the cDNA as probe, two mRNAs, 2.2 and 2.4 kilobases in size, have been detected in human tissues and fibroblasts, whereas only one mRNA (2.4 kilobases) was detected in rat tissues.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carothers D. J., Raefsky-Estrin C., Pons G., Patel M. S. Rat liver mitochondria contain two immunologically distinct dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Aug 1;256(2):597–605. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90617-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A., Robinson C. Protein import into organelles: hierarchical targeting signals. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):321–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90650-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook K. G., Bradford A. P., Yeaman S. J. Resolution and reconstitution of bovine kidney branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase complex. Biochem J. 1985 Feb 1;225(3):731–735. doi: 10.1042/bj2250731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marcucci O. L., Hunter A., Lindsay J. G. Low immunogenicity of the common lipoamide dehydrogenase subunit (E3) of mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj2260509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffelfinger S. C., Sewell E. T., Danner D. J. Antibodies to bovine liver branched-chain 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase cross-react with this enzyme complex from other tissues and species. Biochem J. 1983 Aug 1;213(2):339–344. doi: 10.1042/bj2130339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho L., Hu C. W., Packman S., Patel M. S. Deficiency of the pyruvate dehydrogenase component in pyruvate dehydrogenase complex-deficient human fibroblasts. Immunological identification. J Clin Invest. 1986 Sep;78(3):844–847. doi: 10.1172/JCI112651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y., Morris S. M., Hanson R. W. Induction by cAMP of the mRNA encoding the cytosolic form of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) from the chicken. Identification and characterization of a cDNA clone for the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15603–15608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Schatz G. A cytosolic protein contains a cryptic mitochondrial targeting signal. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):499–503. doi: 10.1038/325499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Cowman A. F. Direct immunoassay for detecting Escherichia coli colonies that contain polypeptides encoded by cloned DNA segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4520–4524. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi G., Hiraga K., Yoshida T. Role of the glycine-cleavage system in glycine and serine metabolism in various organs. Biochem Soc Trans. 1980 Oct;8(5):504–506. doi: 10.1042/bst0080504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike M., Koike K. Structure, assembly and function of mammalian alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. Adv Biophys. 1976:187–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuda S., Saheki T. Intracellular distribution and biosynthesis of lipoamide dehydrogenase in rat liver. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):553–561. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matuda S., Shirahama T., Saheki T., Miura S., Mori M. Purification and immunochemical studies of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from rat heart, and cell-free synthesis of lipoamide dehydrogenase, a component of the complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 13;741(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packman L. C., Perham R. N. An amino acid sequence in the active site of lipoamide dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. FEBS Lett. 1982 Mar 22;139(2):155–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80839-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Reed L. J. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex from bovine kidney and heart. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):376–386. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Yeaman S. J., Reed L. J. Purification and characterization of branched chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex of bovine kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4881–4885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D. W., Schulz G. E., Guest J. R. Structural relationship between glutathione reductase and lipoamide dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 15;174(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90332-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai Y., Fekuyoshi Y., Hamada M., Hayakawa T., Koike M. Mammalian alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes. VI. Nature of the multiple forms of pig heart lipoamide dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4453–4462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens P. E., Lewis H. M., Darlison M. G., Guest J. R. Nucleotide sequence of the lipoamide dehydrogenase gene of Escherichia coli K12. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):519–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaitukaitis J. L. Production of antisera with small doses of immunogen: multiple intradermal injections. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. H., Jr, Arscott L. D., Schulz G. E. Amino acid sequence homology between pig heart lipoamide dehydrogenase and human erythrocyte glutathione reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2199–2201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]