Abstract
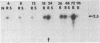
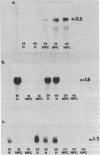
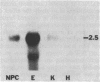
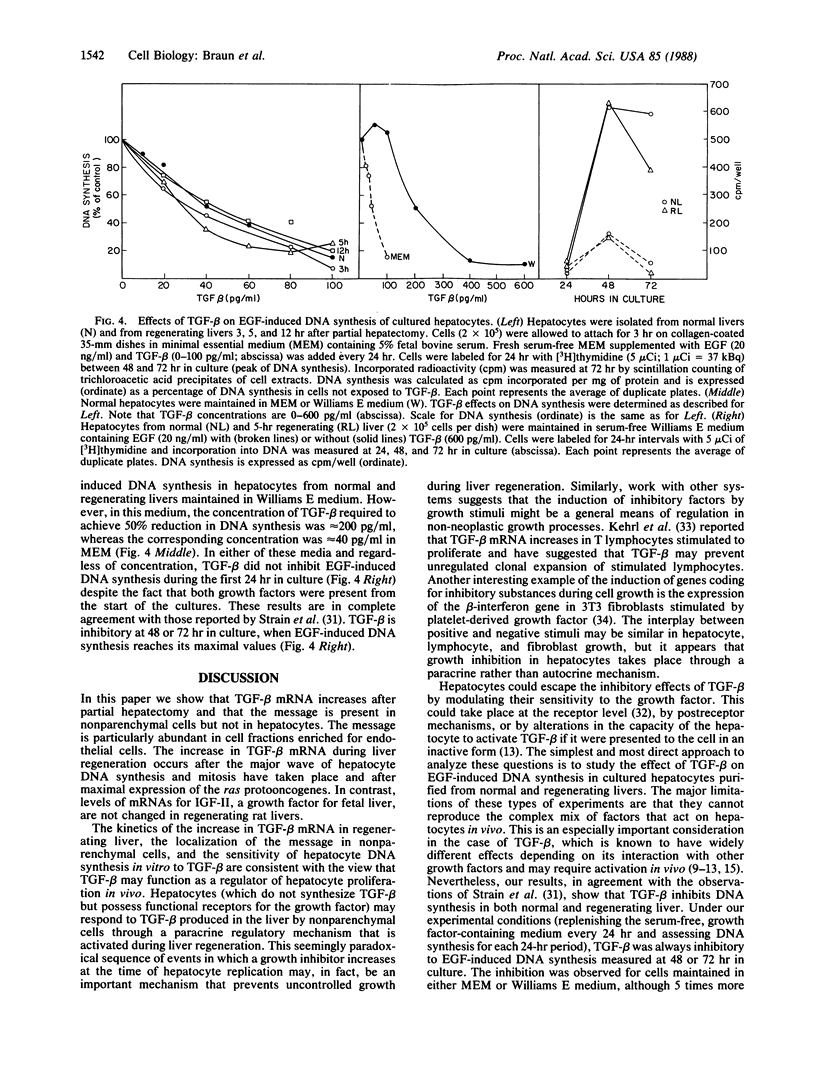
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) is a growth factor with multiple biological properties including stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation. To determine whether TGF-beta is involved in hepatocyte growth responses in vivo, we measured the levels of TGF-beta mRNA in normal liver and during liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. TGF-beta mRNA increases in the regenerating liver and reaches a peak (about 8 times higher than basal levels) after the major wave of hepatocyte cell division and mitosis have taken place and after the peak expression of the ras protooncogenes. Although hepatocytes from normal and regenerating liver respond to TGF-beta, they do not synthesize TGF-beta mRNA. Instead, the message is present in liver nonparenchymal cells and is particularly abundant in cell fractions enriched for endothelial cells. TGF-beta inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in vitro in hepatocytes from normal or regenerating liver, although the dose-response curves vary according to the culture medium used. We conclude that TGF-beta may function as the effector of an inhibitory paracrine loop that is activated during liver regeneration, perhaps to prevent uncontrolled hepatocyte proliferation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carr B. I., Hayashi I., Branum E. L., Moses H. L. Inhibition of DNA synthesis in rat hepatocytes by platelet-derived type beta transforming growth factor. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2330–2334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fausto N., Mead J. E., Braun L., Thompson N. L., Panzica M., Goyette M., Bell G. I., Shank P. R. Proto-oncogene expression and growth factors during liver regeneration. Symp Fundam Cancer Res. 1986;39:69–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRISHAM J. W. A morphologic study of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and cell proliferation in regenerating rat liver; autoradiography with thymidine-H3. Cancer Res. 1962 Aug;22:842–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Leof E. B., Shipley G. D., Moses H. L. Growth factors and cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Mar;46(3):1015–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Petropoulos C. J., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Expression of a cellular oncogene during liver regeneration. Science. 1983 Feb 4;219(4584):510–512. doi: 10.1126/science.6297003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M., Petropoulos C. J., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Regulated transcription of c-Ki-ras and c-myc during compensatory growth of rat liver. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1493–1498. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. E., Rechler M. M., Brown A. L., Frunzio R., Romanus J. A., Bruni C. B., Whitfield H. J., Nissley S. P., Seelig S., Berry S. Coordinate developmental regulation of high and low molecular weight mRNAs for rat insulin-like growth factor II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., D'Ercole A. J., Lund P. K. Cellular localization of somatomedin (insulin-like growth factor) messenger RNA in the human fetus. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):193–197. doi: 10.1126/science.3563497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han V. K., Hill D. J., Strain A. J., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Underwood L. E., D'Ercole A. J. Identification of somatomedin/insulin-like growth factor immunoreactive cells in the human fetus. Pediatr Res. 1987 Sep;22(3):245–249. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198709000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Endo T., Massagué J. Regulation of fibronectin and type I collagen mRNA levels by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6443–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehrl J. H., Wakefield L. M., Roberts A. B., Jakowlew S., Alvarez-Mon M., Derynck R., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S. Production of transforming growth factor beta by human T lymphocytes and its potential role in the regulation of T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1037–1050. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knook D. L., Sleyster E. C. Separation of Kupffer and endothelial cells of the rat liver by centrifugal elutriation. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):444–449. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90605-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Type beta transforming growth factor is an inhibitor of myogenic differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8206–8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon J. B., Richards W. L., del Campo A. A., Song M. K., Thorgeirsson S. S. Differential effects of transforming growth factor-beta on proliferation of normal and malignant rat liver epithelial cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1986 Sep;46(9):4665–4671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Tomita Y., Hirai R., Yamaoka K., Kaji K., Ichihara A. Inhibitory effect of transforming growth factor-beta on DNA synthesis of adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 31;133(3):1042–1050. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos C. J., Yaswen P., Panzica M., Fausto N. Cell lineages in liver carcinogenesis: possible clues from studies of the distribution of alpha-fetoprotein RNA sequences in cell populations isolated from normal, regenerating, and preneoplastic rat livers. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5762–5768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. New class of transforming growth factors potentiated by epidermal growth factor: isolation from non-neoplastic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5339–5343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Wakefield L. M., Roche N. S., Stern D. F., Sporn M. B. Type beta transforming growth factor: a bifunctional regulator of cellular growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):119–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factors. Cancer Surv. 1985;4(4):683–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Ishii D. N., Efstratiadis A. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of a family of transcripts related to rat insulin-like growth factor II mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1119–1134. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stempien M. M., Fong N. M., Rall L. B., Bell G. I. Sequence of a placental cDNA encoding the mouse insulin-like growth factor II precursor. DNA. 1986 Oct;5(5):357–361. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain A. J., Frazer A., Hill D. J., Milner R. D. Transforming growth factor beta inhibits DNA synthesis in hepatocytes isolated from normal and regenerating rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):436–442. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. L., Mead J. E., Braun L., Goyette M., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Sequential protooncogene expression during rat liver regeneration. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):3111–3117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Masui T., Harris C. C., Sporn M. B. Distribution and modulation of the cellular receptor for transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):965–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Brune J. L., Naylor S. L., Cupples R. L., Naberhaus K. H., Bowman B. H. Human group-specific component (Gc) is a member of the albumin family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7994–7998. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaswen P., Goyette M., Shank P. R., Fausto N. Expression of c-Ki-ras, c-Ha-ras, and c-myc in specific cell types during hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):780–786. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaswen P., Hayner N. T., Fausto N. Isolation of oval cells by centrifugal elutriation and comparison with other cell types purified from normal and preneoplastic livers. Cancer Res. 1984 Jan;44(1):324–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Cochran B. H., Huang A. S., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and double-stranded ribonucleic acids stimulate expression of the same genes in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]