Abstract
That the yolk proteins (YPs), or vitellins, stored in the oocytes of insects are a nutritional store for subsequent embryogenesis has long been assumed. Exhaustive data base searching programs revealed highly significant sequence similarity between the three YPs of Drosophila melanogaster and part of the triacylglycerol lipase of the domestic pig. Based upon time of degradation of YPs during embryogenesis, existence of maternally stored ecdysteroid conjugates in embryos, location of these conjugates in locust embryos, and the fact that free active ecdysteroid hormones are released at a specific time in embryogenesis to trigger cuticle deposition, we postulate that the similarity reflects a common property of Drosophila YPs--the ability to bind the fatty acid ecdysteroid conjugates. Our finding of conjugated ecdysteroids tightly bound to purified Drosophila YP supports this prediction.
Full text
PDF
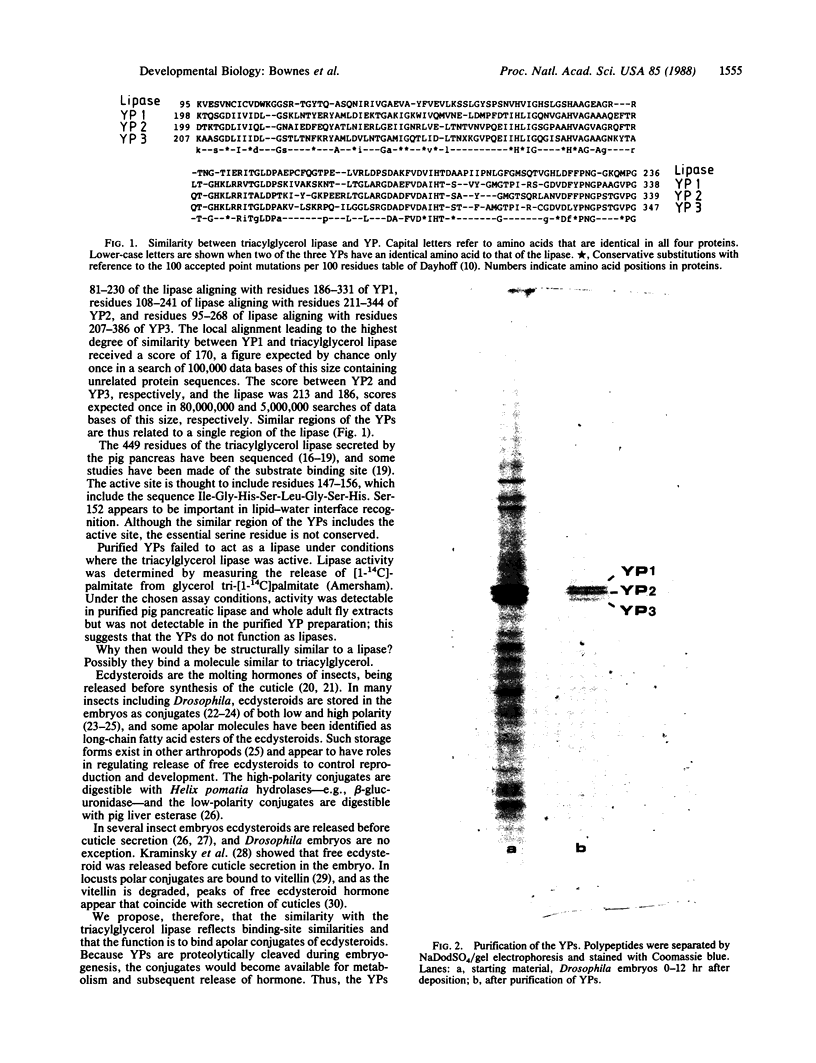
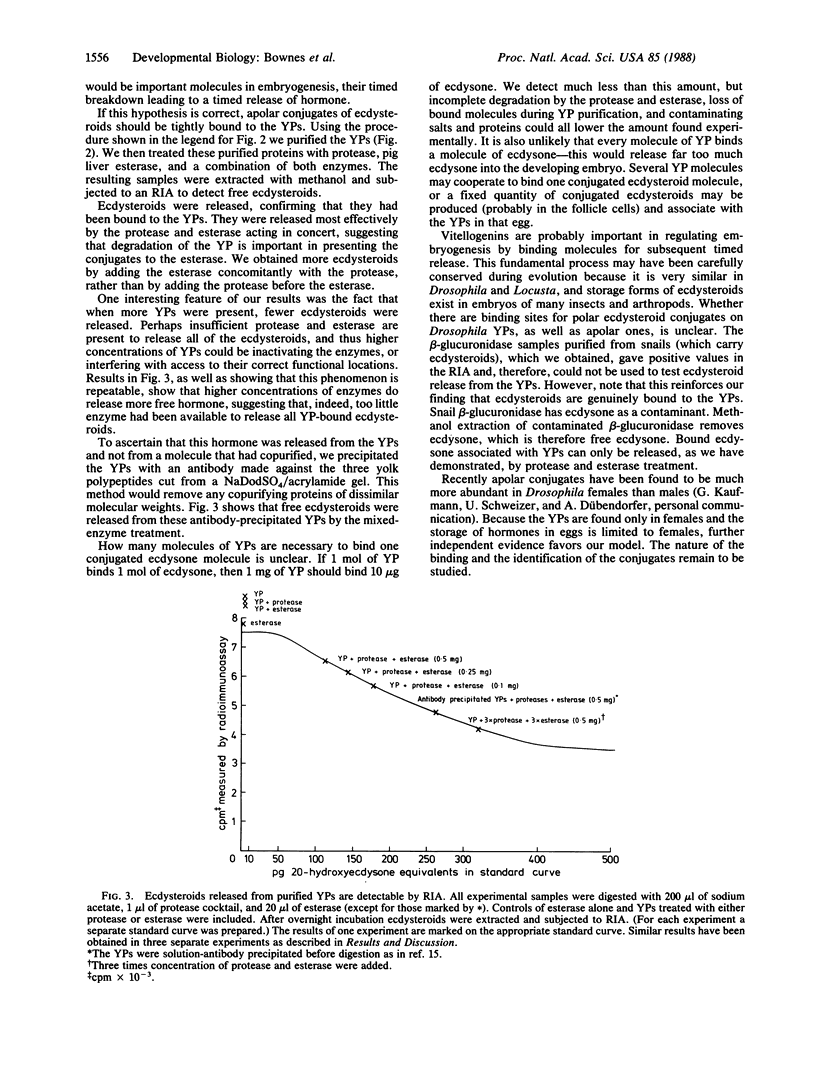

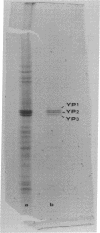
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amsterdam J. D., Case W. G., Csanalosi E., Singer M., Rickels K. A double-blind comparative trial of zimelidine, amitriptyline, and placebo in patients with mixed anxiety and depression. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1986 May;19(3):115–119. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1017167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett T., Pachl C., Gergen J. P., Wensink P. C. The isolation and characterization of Drosophila yolk protein genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):729–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90436-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchetta J. D., Bidaud J., Guidoni A. A., Bonicel J. J., Rovery M. Porcine pancreatic lipase. Sequence of the first 234 amino acids of the peptide chain. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):395–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13126.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownes M., Hames B. D. Accumulation and degradation of three major yolk proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. J Exp Zool. 1977 Apr;200(1):149–156. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402000118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownes M., Hames B. D. Analysis of the yolk proteins in Drosophila melanogaster. Translation in a cell free system and peptide analysis. FEBS Lett. 1978 Dec 15;96(2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan M. D., Weiner A. J., Goralski T. J., Mahowald A. P. The follicle cells are a major site of vitellogenin synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1982 Jan;89(1):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90309-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Shirras A. D., Bownes M., Wensink P. C. The nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for Drosophila melanogaster yolk protein 3. Gene. 1987;55(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90242-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidoni A., Benkouka F., De Caro J., Rovery M. Characterization of the serine reacting with diethyl p-nitrophenyl phosphate in porcine pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 24;660(1):148–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(81)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidoni A., Bonicel J., Bianchetta J., Rovery M. Porcine pancreatic lipase. Sequence between the 235th and 307th amino acids. Biochimie. 1979;61(7):841–845. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(79)80278-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovemann B., Galler R. Vitellogenin in Drosophila melanogaster: a comparison of the YPI and YPII genes and their transcription products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2261–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung M. C., Wensink P. C. Sequence and structure conservation in yolk proteins and their genes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 15;164(4):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaromy M. C., Schotz M. C. Cloning of rat hepatic lipase cDNA: evidence for a lipase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1526–1530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraminsky G. P., Clark W. C., Estelle M. A., Gietz R. D., Sage B. A., O'Connor J. D., Hodgetts R. B. Induction of translatable mRNA for dopa decarboxylase in Drosophila: an early response to ecdysterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4175–4179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagueux M., Harry P., Hoffmann J. A. Ecdysteroids are bound to vitellin in newly laid eggs of Locusta. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Dec;24(3):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwait J. H., Jowett T. Genetic analysis of the hormonally regulated yolk polypeptide genes in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):671–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Caro J., Boudouard M., Bonicel J., Guidoni A., Desnuelle P., Rovery M. Porcine pancreatic lipase. Completion of the primary structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 29;671(2):129–138. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]