Abstract
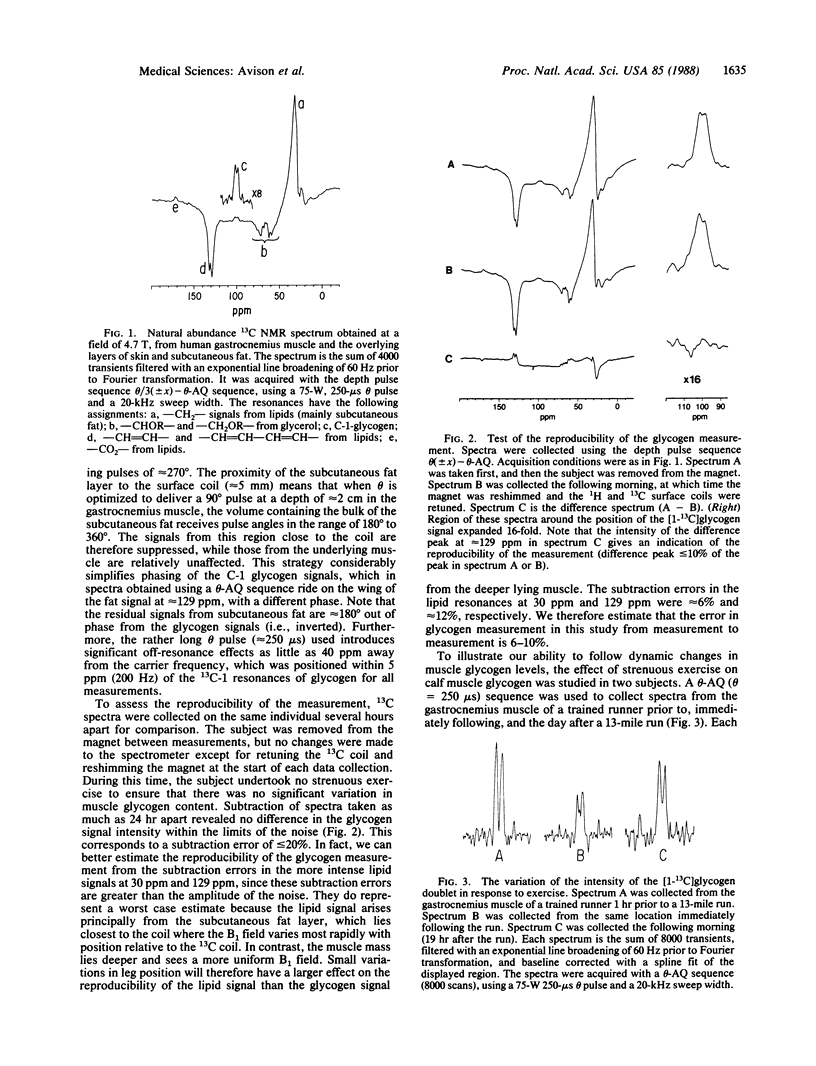
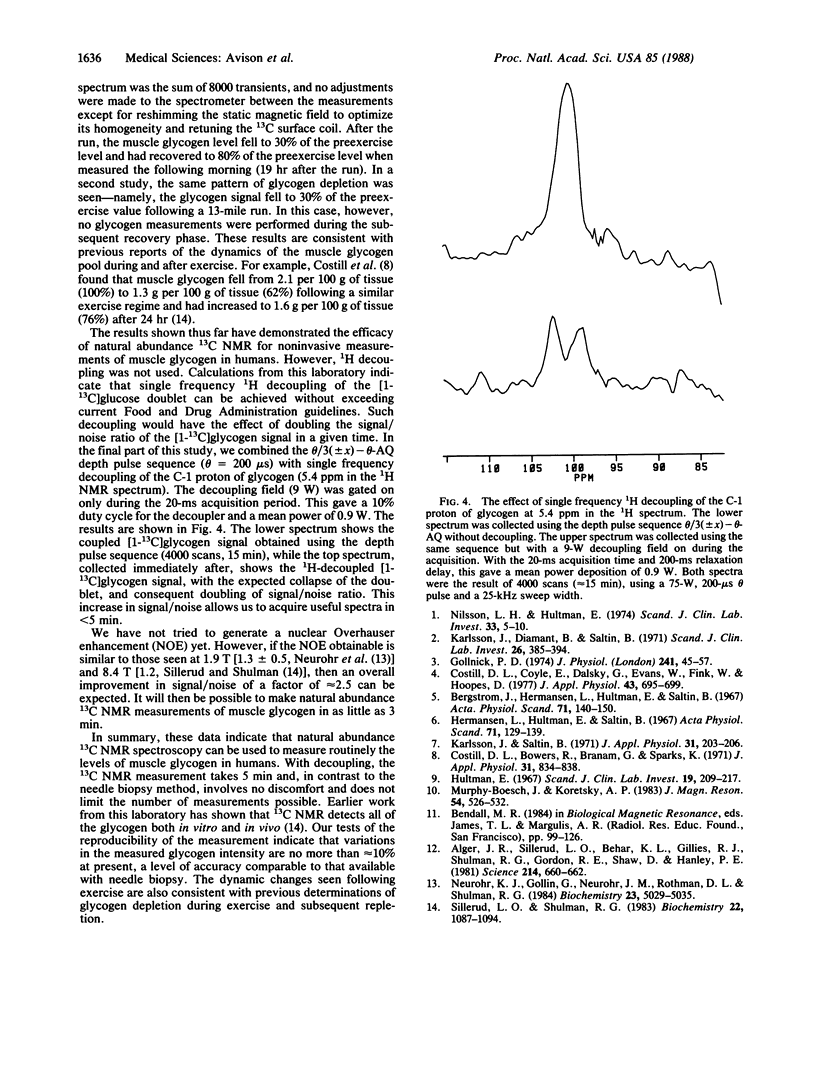
Natural abundance 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy was used to detect signals from glycogen in the human gastrocnemius muscle. The reproducibility of the measurement was demonstrated, and the ability to detect dynamic changes was confirmed by measuring a decrease in muscle glycogen levels after exercise and its subsequent repletion. Single frequency gated 1H decoupling was used to obtain decoupled natural abundance 13C NMR spectra of the C-1 position of muscle glycogen.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alger J. R., Sillerud L. O., Behar K. L., Gillies R. J., Shulman R. G., Gordon R. E., Shae D., Hanley P. E. In vivo carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of mammals. Science. 1981 Nov 6;214(4521):660–662. doi: 10.1126/science.7292005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström J., Hermansen L., Hultman E., Saltin B. Diet, muscle glycogen and physical performance. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Oct-Nov;71(2):140–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costill D. L., Bowers R., Branam G., Sparks K. Muscle glycogen utilization during prolonged exercise on successive days. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Dec;31(6):834–838. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.6.834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costill D. L., Coyle E., Dalsky G., Evans W., Fink W., Hoopes D. Effects of elevated plasma FFA and insulin on muscle glycogen usage during exercise. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Oct;43(4):695–699. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.4.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollnick P. D., Piehl K., Saltin B. Selective glycogen depletion pattern in human muscle fibres after exercise of varying intensity and at varying pedalling rates. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):45–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen L., Hultman E., Saltin B. Muscle glycogen during prolonged severe exercise. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Oct-Nov;71(2):129–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman E. Muscle glycogen in man determined in needle biopsy specimens: method and normal values. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1967;19(3):209–217. doi: 10.3109/00365516709090628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J., Diamant B., Saltin B. Muscle metabolites during submaximal and maximal exercise in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;26(4):385–394. doi: 10.3109/00365517009046250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson J., Saltin B. Diet, muscle glycogen, and endurance performance. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Aug;31(2):203–206. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.2.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurohr K. J., Gollin G., Neurohr J. M., Rothman D. L., Shulman R. G. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of myocardial glycogen metabolism in live guinea pigs. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5029–5035. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L. H., Hultman E. Liver and muscle glycogen in man after glucose and fructose infusion. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1974 Feb;33(1):5–10. doi: 10.3109/00365517409114190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillerud L. O., Shulman R. G. Structure and metabolism of mammalian liver glycogen monitored by carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1087–1094. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


