Abstract
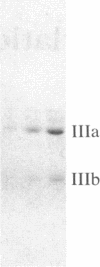
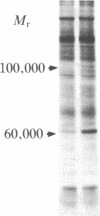
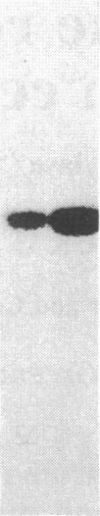
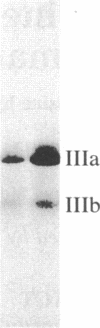
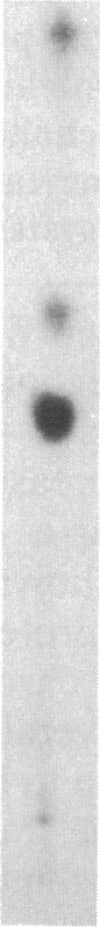
Chromaffin cells were isolated from bovine adrenal medullae and maintained in primary culture. After prelabeling with 32PO4, exposure of the chromaffin cells to acetylcholine increased the phosphorylation of a Mr approximately equal to 100,000 protein and a Mr approximately equal to 60,000 protein (tyrosine hydroxylase), visualized after separation of total cellular proteins in naDodSO4/polyacrylamide gels. Immunoprecipitation with antibodies to three known phosphoproteins ("100-kDa," "87-kDa," and protein III) revealed an acetylcholine-dependent phosphorylation of these proteins. These three proteins were also shown to be present in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by immunolabeling techniques. "100-kDa" is a Mr approximately equal to 100,000 protein selectively phosphorylated by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III, "87-kDa" is a Mr approximately equal to 87,000 protein selectively phosphorylated by protein kinase C, and protein III is a phosphoprotein doublet of Mr approximately equal to 74,000 (IIIa) and Mr approximately equal to 55,000 (IIIb) phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I. Furthermore, 100-kDa was shown to be identical to the Mr approximately equal to 100,000 protein whose phosphorylation was increased by acetylcholine treatment. The acetylcholine-dependent increase in phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase, 100-kDa, 87-kDa, and protein III required extracellular calcium and was mimicked by nicotine, veratridine, elevated K+, and calcium ionophore A23187, but not by muscarine. In addition, forskolin increased the phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase, 100-kDa, and protein III, but not that of 87-kDa. Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate increased the phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase, 87-kDa, and protein III, but not that of 100-kDa. The data demonstrate that cholinergic activation of chromaffin cells increases the phosphorylation of several proteins and that several protein kinase systems may be involved in these effects.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert K. A., Wu W. C., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Inhibition by calmodulin of calcium/phospholipid-dependent protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3622–3625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amy C. M., Kirshner N. Phosphorylation of adrenal medulla cell proteins in conjunction with stimulation of catecholamine secretion. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):847–854. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning M. D., Huang C. K., Greengard P. Similarities between protein IIIa and protein IIIb, two prominent synaptic vesicle-associated phosphoproteins. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):847–853. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00847.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. V., Furness P. N., Helle K. B. Adrenal medullary responses to stimulation of the splanchnic nerve in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:15–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick E. M., Fajdiga P. B., Howe N. B., Livett B. G. Functional and morphological characterization of isolated bovine adrenal medullary cells. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jan;76(1):12–30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarizing agents and cyclic nucleotides regulate the phosphorylation of specific neuronal proteins in rat cerebral cortex slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W., Bennett W. F., George R. J., Waymire J. C. Multiple site phosphorylation of tyrosine hydroxylase. Differential regulation in situ by a 8-bromo-cAMP and acetylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13699–13703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock J. W., Meligeni J. A., Bennett W. F., Waymire J. C. Phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine hydroxylase mediate the acetylcholine-induced increase in catecholamine biosynthesis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12641–12648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Browning M. D., Greengard P. Purification and characterization of protein IIIb, a mammalian brain phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6524–6528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imada M., Sueoka N. A two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis system for the analysis of mammalian cell surface proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Oct 21;625(2):179–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90282-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karagueuzian H. S., Katzung B. G. Voltage-clamp studies of transient inward current and mechanical oscillations induced by ouabain in ferret papillary muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Jun;327:255–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarization-induced phosphorylation of specific proteins, mediated by calcium ion influx, in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2764–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meligeni J. A., Haycock J. W., Bennett W. F., Waymire J. C. Phosphorylation and activation of tyrosine hydroxylase mediate the cAMP-induced increase in catecholamine biosynthesis in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12632–12640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Bhagat B., Palfrey H. C. Identification of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III and its major Mr 100,000 substrate in mammalian tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7939–7943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Purification and characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7273–7281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Palfrey H. C. Identification of the major Mr 100,000 substrate for calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III in mammalian cells as elongation factor-2. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17299–17303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C., Nairn A. C., Muldoon L. L., Villereal M. L. Rapid activation of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III in mitogen-stimulated human fibroblasts. Correlation with intracellular Ca2+ transients. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9785–9792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey H. C. Presence in many mammalian tissues of an identical major cytosolic substrate (Mr 100 000) for calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jun 27;157(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsou K., Greengard P. Regulation of phosphorylation of proteins I, IIIa, and IIIb in rat neurohypophysis in vitro by electrical stimulation and by neuroactive agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6075–6079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viveros O. H., Arqueros L., Kirshner N. Quantal secretion from adrenal medulla: all-or-none release of storage vesicle content. Science. 1969 Aug 29;165(3896):911–913. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3896.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waymire J. C., Bennett W. F., Boehme R., Hankins L., Gilmer-Waymire K., Haycock J. W. Bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: high-yield purification and viability in suspension culture. J Neurosci Methods. 1983 Apr;7(4):329–351. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/phospholipid regulates phosphorylation of a Mr "87k" substrate protein in brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5249–5253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]